Introduction
The insurance sector is navigating rapid disruption—shifting customer expectations, complex risk profiles, rising fraud, and regulatory pressure. Traditional models can no longer keep pace with these challenges. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now at the forefront of driving intelligent automation, predictive decision-making, and hyper-personalized service across the insurance value chain.
This guide explores how AI is revolutionizing the insurance sector through real-world use cases—from underwriting and claims to fraud detection and customer engagement.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in the Insurance Sector?
 Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence—such as learning from data, recognizing patterns, and making decisions. Key technologies include machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision source.
In insurance, AI is applied to automate claims processing, enhance risk assessment, prevent fraud, and deliver personalized customer interactions. It augments human expertise, increases operational efficiency, and unlocks new models of value creation.
Want to explore how AI can transform your sector? Discover real-world strategies for deploying smart technologies in airline systems. Visit How to Integrate AI into Your Business in 2025 to get started today and unlock the full potential of AI for your business!
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming Insurance
AI is reshaping how insurers assess and underwrite risks. Machine learning models now analyze thousands of data points—from satellite imagery to IoT data—to assess risk in real time. This leads to more accurate pricing, faster decisions, and lower loss ratios.
In claims management, AI expedites triage, estimation, and fraud detection. Insurers like Lemonade and Progressive use AI-powered chatbots and damage assessment tools to settle simple claims in minutes rather than days or weeks.
AI is also elevating the customer experience. NLP-enabled virtual assistants handle queries 24/7, while personalized policy recommendations and proactive alerts are helping insurers move from reactive to relationship-driven engagement models.
Key Statistics or Trends in AI Adoption
AI adoption in insurance is accelerating. According to McKinsey, AI and advanced analytics could generate up to $1.1 trillion annually in value across the global insurance industry by 2030 source.
Fraud detection is a key use case. The Coalition Against Insurance Fraud reports that insurers using AI-based detection systems have seen fraud identification accuracy increase by 40%, saving billions annually source.
InsurTech growth reflects AI’s potential. The global InsurTech market—much of it driven by AI—was valued at $10.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32.7% through 2030 source.
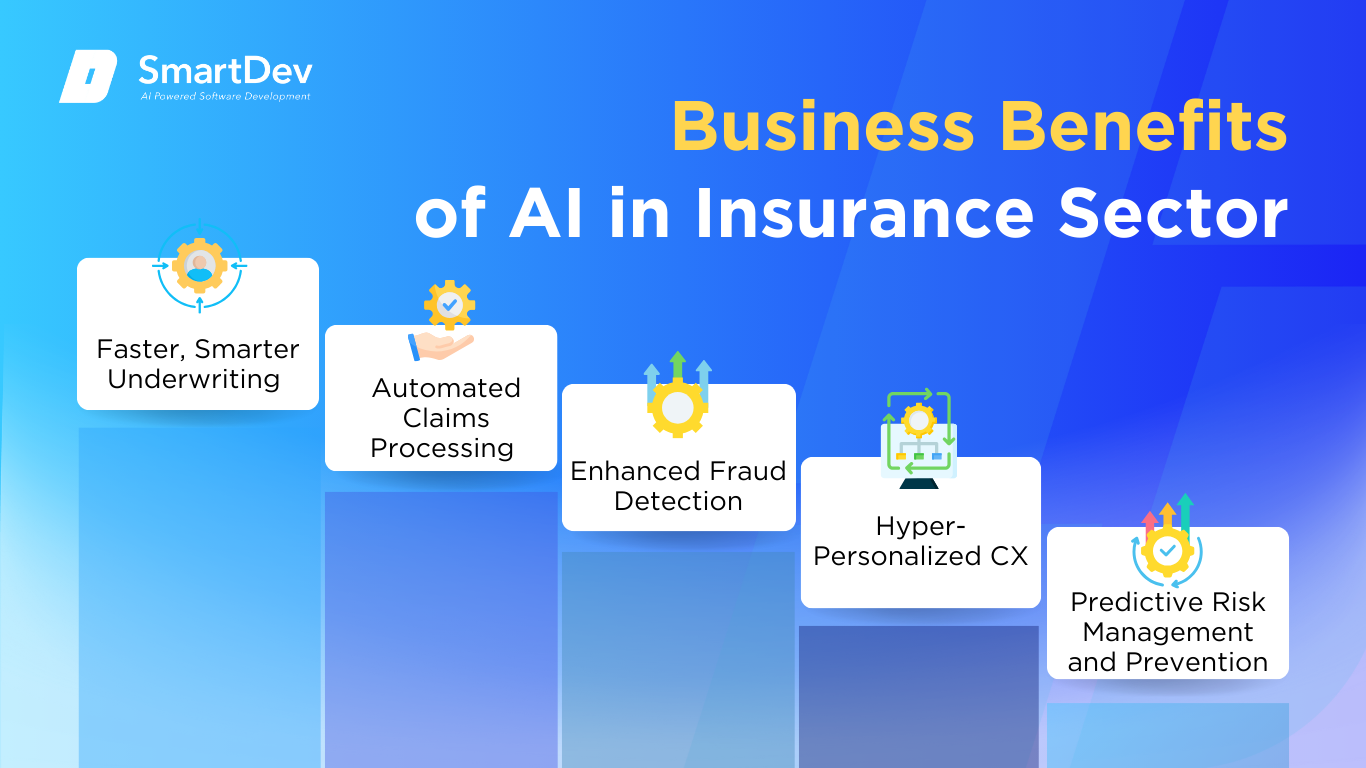
Business Benefits of AI in Insurance Sector
AI is more than a technology upgrade—it’s a strategic enabler. Below are five business-critical benefits driving adoption across insurers.
 1. Faster, Smarter Underwriting
1. Faster, Smarter Underwriting
Traditional underwriting relies heavily on manual data input and static risk models. AI changes the game by processing real-time data—from wearables, social media, or connected homes—to build dynamic risk profiles.
For example, life insurers now use AI to assess applicants’ health risks based on wearable data and behavioral patterns. This not only shortens underwriting time but enables more personalized policies.
Advanced models also improve risk segmentation and loss prediction, giving underwriters deeper insights and enabling product innovation for underserved segments.
2. Automated Claims Processing
Claims processing is historically slow, paper-heavy, and prone to errors. AI automates the entire workflow—from FNOL (First Notice of Loss) to settlement—enhancing speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Computer vision tools assess vehicle or property damage from uploaded images, generating repair estimates within seconds. NLP engines parse handwritten documents or voice notes to extract structured claim data.
Insurers like Zurich have reported reducing claims processing time by 40% using AI-powered automation, resulting in faster payouts and improved customer loyalty.
3. Enhanced Fraud Detection
Insurance fraud costs billions each year. AI excels at identifying suspicious behavior by analyzing vast datasets—claims history, social connections, geolocation data, and more—in real time.
Machine learning algorithms flag anomalies and learn from investigator feedback, becoming smarter over time. NLP models also analyze sentiment or inconsistencies in claim narratives or recorded calls.
This proactive approach allows insurers to prevent false claims before payout, rather than chasing recovery afterward. According to Accenture, AI can reduce false claims payout by up to 25%.
4. Hyper-Personalized Customer Experience
AI enables a shift from policy-centric to customer-centric engagement. By analyzing user behavior, preferences, and life events, insurers can offer relevant products, alerts, and services at the right moment.
Virtual assistants powered by NLP handle routine inquiries instantly—policy details, billing questions, renewal alerts—improving convenience. AI also powers robo-advisors for insurance planning, especially in digital-first channels.
The result? Higher NPS (Net Promoter Score), better retention rates, and lower service costs. As personalization becomes a baseline expectation, AI ensures insurers stay competitive.
5. Predictive Risk Management and Prevention
Modern insurers aim to predict and prevent risk—not just react to it. AI-powered analytics allow for dynamic monitoring of risk across individuals, fleets, properties, and supply chains.
For example, commercial insurers monitor telematics data to proactively alert fleet managers about risky driving behavior. Similarly, health insurers use AI to trigger early intervention for chronic conditions based on patient patterns.
This not only reduces claims but strengthens the insurer-client relationship, positioning insurers as partners in risk prevention rather than just payout providers.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Insurance Sector
Despite the upside, implementing AI in insurance comes with real challenges. Below are five critical obstacles insurers must address to scale responsibly.
1. Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
Insurance deals with sensitive personal and financial data. As AI models process and infer insights from this data, compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and local data laws becomes more complex.
Using AI in underwriting or claims decisions also raises transparency concerns. Black-box models must be explainable to meet regulatory scrutiny—and to maintain customer trust.
Siloed systems and scattered data can cripple decision-making and slow growth. Discover how AI is helping organizations unify, clean, and unlock value from their data faster and smarter. Explore the full article to see how AI transforms data chaos into clarity.
2. Legacy Infrastructure and Fragmented Systems
Many insurers still rely on outdated policy admin systems, paper-based processes, and siloed data warehouses. These environments lack the agility and data readiness needed for effective AI deployment.
Modernizing IT infrastructure—through cloud migration, data lakes, and API integrations—is essential but costly and time-consuming, especially for large incumbents with decades-old systems.
3.Model Bias and Fairness Risks
If trained on biased or incomplete data, AI models can perpetuate discrimination in pricing, claims approvals, or fraud detection. This can lead to regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
Establishing strong AI governance—including bias testing, diverse training datasets, and ethical review boards—is key to deploying AI responsibly in insurance.
For those navigating these complex waters, a business-oriented guide to responsible AI and ethics offers practical insights on deploying AI responsibly and transparently, especially when public trust is at stake.
4. Talent and Cultural Readiness
AI success depends not just on tools but on people. Many insurers lack in-house AI talent or experience integrating AI into actuarial, claims, or operations teams.
There’s also cultural resistance to changing long-standing workflows. Upskilling staff, hiring hybrid AI-business experts, and championing a data-driven mindset are essential for AI adoption to stick.
5. Return on Investment (ROI) Clarity
AI initiatives can be costly, especially in early stages. Without a clear ROI narrative—linked to KPIs like claims cycle time, loss ratio, or customer retention—executive buy-in can stall.
Starting with high-impact, low-complexity pilots (e.g., claims triage or chatbot deployment) helps insurers demonstrate value, gain momentum, and scale AI use cases with confidence.
Specific Applications of AI in Insurance Sector
 Use case 1. Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment and Pricing
Use case 1. Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment and Pricing
Insurers are under pressure to accurately assess risk and price policies competitively. Predictive analytics powered by AI enables companies to analyze historical data and customer behavior to forecast claims likelihood and tailor premiums. This supports more precise underwriting and reduces loss ratios.
Machine learning algorithms analyze structured and unstructured data, including driving habits, credit scores, weather data, and claim histories. These models identify high-risk profiles, evaluate exposures, and support dynamic pricing models. Integration is typically with core insurance platforms and underwriting tools.
Strategically, this application improves profitability, pricing fairness, and underwriting speed. Ethical concerns include data privacy and avoiding discrimination based on sensitive variables, requiring strong governance and transparency.
Real-World Example:
Progressive Insurance uses AI-driven predictive modeling to refine pricing strategies. Leveraging telematics data and machine learning tools, they deliver usage-based insurance plans. The approach improved underwriting accuracy and increased customer retention by 15%.
Use case 2. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) for Claims and Policies
Insurance companies manage large volumes of forms, contracts, and policy documents daily. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) automates document intake, classification, and data extraction, enhancing claims processing and customer onboarding. It solves inefficiencies and errors from manual handling.
IDP solutions use OCR, NLP, and machine learning to process PDFs, emails, and scanned images. Trained on domain-specific templates, they extract key fields and validate data against internal records. These systems integrate with claims management and document storage platforms.
The benefits include faster processing times, improved accuracy, and better compliance. Security and auditability are essential when handling sensitive policyholder information.
Real-World Example:
AXA implemented IDP to digitize and automate claims intake across multiple business lines. Using UiPath and ABBYY, they accelerated document processing by 60%. This led to a 20% increase in claims handling efficiency and improved customer satisfaction.
Use case 3. AI-Powered Fraud Detection
Fraudulent claims cost the insurance industry billions annually. AI-powered fraud detection tools analyze behavior patterns, detect anomalies, and flag suspicious claims for investigation. This strengthens fraud prevention and reduces financial losses.
AI models are trained on past fraud cases, transaction histories, and social network analysis to uncover hidden patterns. Techniques include anomaly detection, link analysis, and behavioral profiling. Integration occurs with claims systems, investigation platforms, and external databases.
The strategic value lies in cost savings, faster detection, and more focused investigations. However, transparency and fairness in AI decisions are critical to prevent false positives and ensure regulatory compliance.
Real-World Example:
Zurich Insurance Group uses AI to detect fraudulent motor and health claims. Their system, powered by SAS and in-house models, helped identify over $100 million in fraud annually. It cut investigation time by 40% and improved fraud detection rates by 30%.
Use case 4. AI Chatbots and Virtual Assistants for Policyholder Support
Insurers receive high volumes of customer inquiries about coverage, claims, and policy updates. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants automate routine interactions, offering 24/7 support and faster resolution. This improves service delivery and operational efficiency.
Chatbots use NLP and conversational AI trained on insurance FAQs, policy terms, and historical chats. These assistants can be deployed on websites, mobile apps, and messaging platforms. They escalate complex issues to human agents with context preservation.
Benefits include reduced call center load, enhanced user satisfaction, and lower support costs. Regulatory compliance and ensuring clear communication are essential for customer trust.
Real-World Example:
Allianz launched a virtual assistant called Allie to handle basic customer queries and policy information. Built on IBM Watson, it resolved 70% of questions without human intervention. This boosted customer engagement and reduced support costs by 25%.
Use case 5. AI in Claims Automation and Decision-Making
Manual claims processing is time-consuming and error-prone. AI streamlines claims intake, triage, and settlement decisions, reducing turnaround times and improving accuracy. This is essential for both customer experience and operational efficiency.
Computer vision models analyze damage photos, NLP parses claim descriptions, and ML predicts liability or payout values. These tools interface with CRM and claims systems to provide real-time recommendations or approvals. AI can also automate FNOL (First Notice of Loss) intake from mobile apps.
Strategic advantages include cost savings, customer satisfaction, and workforce efficiency. Insurers must ensure models are interpretable and decisions are auditable to meet regulatory standards.
Real-World Example:
Lemonade uses AI to automate the entire claims journey for renters and home insurance. Its AI Jim bot reviews claims, checks policy terms, and processes simple payouts in seconds. Over 30% of claims are handled instantly, increasing operational scalability and user delight.
Use case 6. AI for Personalized Product Recommendations
The modern policyholder expects tailored insurance options. AI enables insurers to analyze customer behavior and preferences to deliver personalized product suggestions and cross-sell offers. This enhances marketing effectiveness and customer lifetime value.
AI engines use behavioral segmentation, historical purchases, and life events to predict customer needs. These systems integrate with CRM platforms, marketing automation tools, and recommendation engines. Real-time personalization enhances both direct and agent-assisted channels.
This leads to higher conversion rates, stronger retention, and improved user engagement. Ethical use of personal data and compliance with GDPR/CCPA are critical in these implementations.
Real-World Example:
MetLife implemented AI to provide personalized product recommendations based on life stage and risk profile. Using Salesforce Einstein and proprietary models, they increased upsell conversion rates by 22%. The initiative also improved customer loyalty and cross-sell revenue.
Need Expert Help Turning Ideas Into Scalable Products?
Partner with SmartDev to accelerate your software development journey — from MVPs to enterprise systems.
Book a free consultation with our tech experts today.
Let’s Build TogetherExamples of AI in Insurance Sector
AI is being rapidly adopted by insurers worldwide to improve operations and services. These case studies highlight tangible impacts across key insurance functions.
Real-World Case Studies
 Liberty Mutual: AI-Powered Underwriting
Liberty Mutual: AI-Powered Underwriting
Liberty Mutual uses AI to automate commercial insurance underwriting. Their models assess risk factors and suggest policy terms based on real-time data. This reduced underwriting time by 40% and enhanced pricing accuracy.
The company also implemented AI to monitor exposure levels across portfolios. By integrating with Guidewire and Tableau, underwriters gained visibility into risk clusters. This improved decision-making and compliance readiness.
GEICO: Virtual Assistant for Claims Support
GEICO deployed an AI chatbot to assist customers during the claims process. The assistant guides users through FNOL, uploads photos, and tracks claim status. It resolved over 60% of support inquiries independently.
Built using AWS Lex and custom machine learning, the system integrates seamlessly with GEICO’s backend. The chatbot contributed to faster claims resolution and reduced workload for live agents.
Tokio Marine: AI for Auto Damage Estimation
Tokio Marine deployed computer vision models to assess vehicle damage from accident images. The AI compares photos to historical claim data and estimates repair costs. This reduced on-site inspections and claim cycle time.
Working with Tractable and Microsoft Azure, the solution processed thousands of claims weekly. The initiative improved customer experience and reduced settlement time by 50%.
These examples reflect the value of working with technology partners who understand both the technical and policy implications. If you’re considering a similar digital transformation, don’t hesitate to connect with AI implementation experts to explore what’s possible in your context.
Innovative AI Solutions
AI innovation in insurance is accelerating with new tools for decision support, automation, and customer engagement. These technologies reshape underwriting, servicing, and distribution.
Generative AI is being tested for policy drafting, claims narratives, and marketing content. Tools like ChatGPT help insurers create consistent and compliant documentation. This saves time for agents and speeds up customer communication.
Telematics and AI are converging to enable real-time risk assessment and behavior-based pricing. Insurers use sensors, apps, and vehicle data to personalize auto insurance. This creates new product models and incentivizes safe behavior.
Voice AI and biometric authentication are improving security and experience in customer interactions. Companies integrate voice assistants with KYC checks and claim tracking. These tools reduce fraud risk and enhance accessibility.
AI‑Driven Innovations Transforming the Insurance Sector
The insurance sector is experiencing a fundamental shift powered by artificial intelligence. According to the Global Insurance Survey by Goldman Sachs in 2024, approximately 29% of insurance companies globally were using AI, while U.S. adoption reached 42% in 2023—a rapid increase from earlier years. The Evident AI Insurance Index (June 2025) ranking places AXA, Allianz, and USAA at the top of AI maturity metrics, demonstrating leadership in innovation, talent, and transparency. As AI use cases in insurance sector proliferate—from underwriting to customer engagement—your role as a C-level executive or innovator is central to navigating the value journey. AI is no longer supplemental; it’s reshaping pricing models, risk management, claims workflows, and customer experience across the insurance value chain.
Insurers worldwide are embracing AI to drive faster decision-making and reduce operational costs. PwC estimates that sustainable implementation of generative AI with automation can contribute significantly to long-term growth and productivity—but only when integrated into broader organizational strategy, not isolated pilots. KPMG, BCG, and McKinsey echo that insurers must focus on high-impact, scalable use cases tied to measurable financial outcomes to avoid fragmented efforts and subscale ROI. As someone leading transformation, you are expected to craft an AI roadmap grounded in clear objectives—embedding AI into mission-critical insurance functions.
Emerging Technologies in AI for Insurance Sector
Generative AI and predictive analytics are redefining underwriting and pricing. According to McKinsey, insurers deploying AI for dynamic risk pricing achieve more accurate and personalized premiums, reducing loss ratios and improving customer trust. For example, Cytora (partnered with Markel) enabled a 113% productivity uplift in underwriting teams and cut quote turnaround from 24 hours to 2 hours. Haven Life—a digital-first insurer—uses AI-driven underwriting to issue policies in as little as 20 minutes, compared to traditional timelines of weeks or months.
Computer vision is transforming claims assessment. Tractable’s AI platform for auto and property damage enables insurers like GEICO to settle more claims remotely—settling about 60% of auto claims via photos compared to just 15% before the pandemic—boosting efficiency while facing technical accuracy challenges. Meanwhile, Google Cloud customers like Loadsure use Document AI and Gemini to automate claims extraction and classification with high accuracy—settling routine claims nearly in real-time and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Natural language processing powers customer communication. Allstate uses AI-generated emails powered by GPT models, resulting in language that’s more empathetic and less jargon-heavy. These emails—used across approximately 50,000 daily communications—are reviewed by humans for precision and have improved claimant experience significantly.
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts in Insurance Sector
Predictive AI models support sustainable financial outcomes by reducing fraud, waste, and risk exposure. Fraud detection driven by sequence embeddings or graph-learning algorithms can uncover fraudulent insurance claims more efficiently: one method improved detection precision to 80% and flagged 44% more organized fraud rings than legacy rule-based systems. Using AI to streamline claims processing and pricing enhances operational efficiency, reducing unnecessary payouts and underwriting losses.
Data product marketplaces are emerging as a sustainable infrastructure investment. Insurers increasingly centralize data across silos—housing policyholder, claims, and partner data in unified marketplaces that reduce operational cost and unlock revenue potential via analytics and reuse across lines of business. This sustainable data architecture supports long-term scalability of AI solutions and aligns with regulatory transparency demands.
How to Implement AI in the Insurance Sector
 Step 1: Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Step 1: Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Your journey should begin by identifying high-volume, low-judgment tasks—like submission review, quotes, and claims triage—where AI can deliver early wins. A strategy-focused on these functions avoids wasted effort and preserves ROI clarity. PwC recommends defining specific business metrics—such as reducing submission review time by 50%—as benchmarks for success. McKinsey and BCG suggest pursuing high‑value use cases that embed AI into core insurance operations rather than pilot-only experiments.
Leadership alignment is equally critical. Establish cross-functional governance—underwriting, data, compliance, IT—to assure decision-makers share KPIs, risk appetite, and strategic clarity. NAIC’s 2023 Model Bulletin onboarding demonstrates how regulators require insurer governance frameworks covering transparency, bias mitigation, and oversight before deployment.
Step 2: Building a Strong Data Foundation
Clean, consolidated data is the bedrock. Insurance data is often fragmented—ACORD formats, manual forms, external partner systems. Successful AI implementation requires building a centralized data product marketplace, unifying policy, claims, and loss history data into a governed ecosystem with standard schemas and metadata tagging. Ensure compliance with NAIC and privacy guidelines, and invest in data quality efforts: classification, normalization, and secure storage accessible to AI pipelines while preserving auditability.
Legacy systems often hamper AI effectiveness—PwC warns that without data infrastructure modernization and integration, even the most advanced AI yields limited ROI.
Step 3: Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Vendor selection must balance innovation, regulatory compliance, and flexible integration. Leading insurers partner with AI platforms like Google Cloud’s Vertex AI—for instance, HDFC ERGO uses Vertex AI to power agent nudges and personalized pricing; Hiscox uses it to slash underwriting turnaround from days to minutes. Loadsure automates claims with Document AI and Gemini, enhancing accuracy and speed.
However, vendors must support governance—explainability, data lineage, audit logs—and align with NAIC model regulations. Driving tools in-house may be required for proprietary risk models or to satisfy regulatory scrutiny.
Step 4: Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Begin with focused pilots: for example, automate claims intake using Document AI, or deploy underwriting assistants in strategic product lines. Monitor metrics like time-per-claim, quote turnaround, fraud detection precision, processing speed. PwC and BCG emphasize the importance of piloting lightweight solutions via APIs or email ingestion—delivering ROI in weeks rather than months.
Once successful, scale across business lines—embedding reuse patterns across underwriting, claims, pricing, customer service—with centralized oversight and defined feedback mechanisms.
Step 5: Training Teams for Successful Implementation
Your workforce must evolve to become AI-literate. Train underwriters, claims adjusters, agents, and compliance staff to collaborate with AI: prompt review, exception handling, ethical oversight. Encourage human-in-the-loop workflows to validate outputs and maintain trust. PwC highlights that successful carriers reconceptualize roles as strategic portfolio managers rather than transaction processors—empowering upskilling and human‑AI synergy.
Upskilling should involve sandbox environments, vendor-led workshops, and iterative coaching—building institutional confidence and reducing adoption anxiety.
Whether you’re exploring your first pilot or scaling an enterprise-wide solution, our team is here to help. Get in touch with SmartDev and let’s turn your challenges into opportunities.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Insurance Sector
Key Metrics to Track Success
In insurance, ROI isn’t just about cost cuts. Focus your evaluation on metrics embedded in operational impact: average claims handling time, underwriting productivity, loss ratio improvements, fraud detection precision, policy issuance speed, customer satisfaction, and error reduction. For example, Cytora-enabled underwriting teams saw a gambit of productivity gains—quote turnaround reduced from 24 to 2 hours, doubling output and improving responsiveness. Loadsure’s real-time claims classification and Zurich’s new AI‑powered CRM (reducing service times by over 70%) exemplify dual gains in operational speed and customer satisfaction.
Weak ROI often stems from narrow KPIs or disregarded governance structures. McKinsey notes that insurers must align AI initiatives with domain‑wide strategy to prevent fragmented, non‑scalable outcomes.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Markel’s partnership with Cytora enabled a 113% rise in productivity for underwriting teams, while shortening quote SLA from a full day to mere hours—representing both faster service and lower quote cost.
Policybazaar for Business launched ClaimSetu on August 1, 2025: an AI-led claims scoring engine for group health insurance. It enhances transparency, accelerates reimbursement, and reduces friction for corporate clients—delivering measurable ROI in claims maturity and client retention.
Omega Healthcare (though in healthcare payments) provides a parallel: in insurance billing, UiPath AI-powered tools saved over 15,000 employee hours per month, cut documentation time by 40%, turnaround by 50%, with 99.5% accuracy—resulting in 30% ROI for clients. This mirrors potential outcomes when insurers automate internal claims workflows with similar tools.
Zurich Insurance Group rolled out an AI-powered CRM across four markets, slashing service times by over 70% while enabling agents to recommend products more intelligently—enhancing customer trust and agent productivity.
Understanding ROI is possibly a challenge to many businesses and institutions as different in background, cost. So, if you need to dig deep about this problem, you can read AI Return on Investment (ROI): Unlocking the True Value of Artificial Intelligence for Your Business
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Many insurers stumble by over-focusing on pilots without scalable strategy—leading to isolated successes but limited impact. McKinsey warns that underestimating investment needs and ignoring reusable components hampers long‑term AI value.
Insurers also falter when data is siloed or governance weak—causing biased models or regulatory friction. PwC emphasizes that insufficient data infrastructure and siloed deployment frequently result in disappointing ROI.
To avoid these pitfalls, define clear KPIs with cross-functional ownership, establish governance frameworks aligned with NAIC model regulations, invest in data modernization, and prioritize early wins that scale into enterprise-wide applications.
Future Trends of AI in Insurance Sector
Predictions for the Next Decade
In the next decade, AI will transition from automating workflows to enabling intelligent ecosystems. We’ll see underwriting bots that autonomously gather exposure data, price portfolios, and dynamically adjust policies continuously. Customer-facing GenAI agents will handle claims triage, appeals, and renewal engagements—citing sources and resolving queries in near real-time.
Fraud detection will shift to network-based anomaly detection using graph-learning and embeddings across policy exposures and claims histories—delivering earlier, more precise identification of organized fraud rings. Sustainability will emerge through predictive risk scoring—factoring climate data, behavior, and market trends into pricing and underwriting decisions.
Enterprise AI maturity will depend on data marketplaces becoming standard architecture—supporting interoperability, reuse, and innovation across underwriting, claims, and customer service.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To lead, you must treat AI use cases in insurance sector as a strategic pillar—not a shiny technology. Begin by investing in robust data infrastructure, cross-functional governance, and human-in-the-loop capabilities. Build reusable AI components—such as document-extraction pipelines, pricing models, or communication assistants—that scale across departments.
Regularly benchmark against industry leaders (AXA, Allianz, USAA) via indexes like Evident AI to assess AI maturity across talent, transparency, leadership, and innovation. Stay informed about evolving regulation (e.g., NAIC model bulletin) and anticipate human-oversight mandates in critical decisions.
Foster a culture that sees AI as augmentation—upskilling underwriters and agents to collaborate with AI rather than be threatened by it. As AI capabilities mature, you’ll unlock sustainable ROI that compounds through productivity, customer loyalty, and operational resiliency.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Takeaways on AI Use Cases in Insurance Sector
AI use cases in insurance sector are broadening rapidly—from automated underwriting and pricing, robotic claims processing, fraud detection, to empathetic client communication and agent decision support. Evidence from Markel, Haven Life, Zurich, and Omega Healthcare demonstrates that AI delivers tangible ROI: measurable productivity gains, accelerated service delivery, fraud reduction, and improved customer satisfaction. True value emerges when AI is embedded within a strategic vision—backed by data foundations, governance, and human-AI collaboration.
Moving Forward: A Path to Progress for Businesses Considering AI Adoption
Now is the time to act. Start with a strategic readiness assessment—identify inefficiencies across underwriting, pricing, claims, and customer experience. Pilot AI solutions in targeted workflows with clear KPIs. Invest in data modernization and governance aligned with regulatory mandates.
Train your workforce for human-in-loop AI collaboration. And scale wins across the enterprise using reusable patterns, transparent metrics, and incremental rollout. AI isn’t a bolt-on—it’s a transformative platform. With disciplined execution and bold vision, you can lead the insurance sector into a smarter, faster, customer-centered future.
References
- https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/the-future-of-ai-in-the-insurance-industry
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-insurance
- https://assets.kpmg.com/content/dam/kpmg/my/pdf/ai-in-the-insurance-industry.pdf
- https://www.ey.com/en_us/insights/insurance/how-insurers-can-leverage-the-power-of-generative-ai
- https://www.ibm.com/thought-leadership/institute-business-value/en-us/report/insurance-generative-ai
- https://www.bcg.com/publications/2025/how-insurers-can-supercharge-strategy-with-artificial-intelligence
- https://www.insuranceeurope.eu/publications/2608/artificial-intelligence-ai-in-the-insurance-sector/


 1. Faster, Smarter Underwriting
1. Faster, Smarter Underwriting Use case 1. Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment and Pricing
Use case 1. Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment and Pricing Liberty Mutual: AI-Powered Underwriting
Liberty Mutual: AI-Powered Underwriting 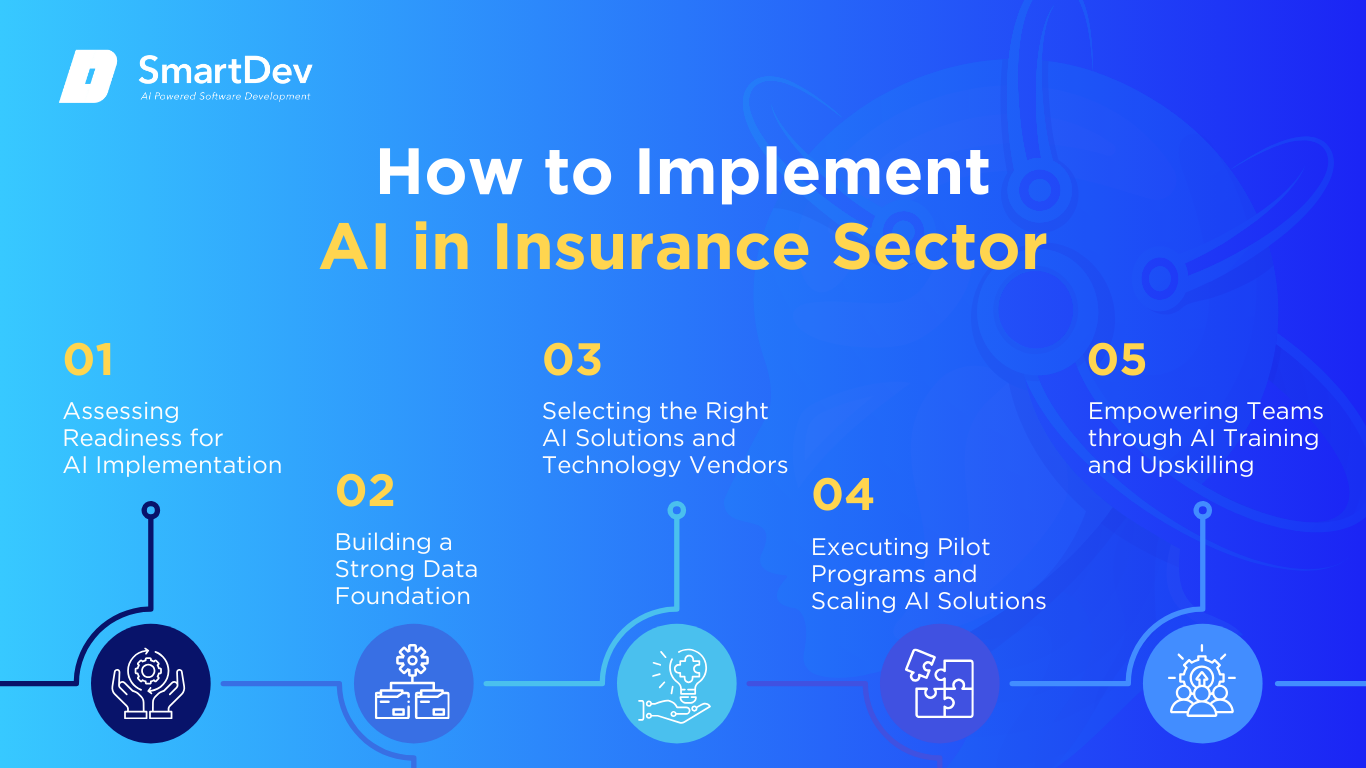 Step 1: Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Step 1: Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption





