Did you know that global e-commerce sales are projected to reach over $8 trillion by 2027? This staggering figure emphasizes the rapid growth of online retail, driven by evolving consumer behaviors and technological advancements. However, with this expansion, scalability has become a critical challenge for businesses, especially during peak shopping seasons or rapid growth phases, to maintain performance, reliability, and user satisfaction under high traffic and transaction volumes. So, how can e-commerce businesses ensure their platforms handle increasing traffic and transactions without compromising performance? What should business owners do? How does application engineering do anything related to scalability in e-commerce?
At SmartDev, we believe that application engineering is pivotal in building scalable, robust e-commerce solutions but not everyone is familiar with the term. In this blog, we’ll explore how strategic application engineering supports sustainable growth, ensuring your e-commerce platform remains responsive and reliable as your business expands.
Key Takeaways
- Scalability is the Foundation for Growth: A scalable platform ensures consistent performance, supports high traffic and transactions, and adapts to evolving business needs, making it essential for long-term success in e-commerce.
- Application Engineering as a Strategic Enabler: By implementing advanced architectures, automation, and AI, application engineering empowers businesses to handle growth efficiently while delivering seamless user experiences.
- Planning for Long-Term Success: Businesses must invest in scalable technologies like cloud computing, predictive analytics, and modular design, combined with a proactive strategy to adapt to market demands and future trends.
1. Introduction
Overview of E-commerce
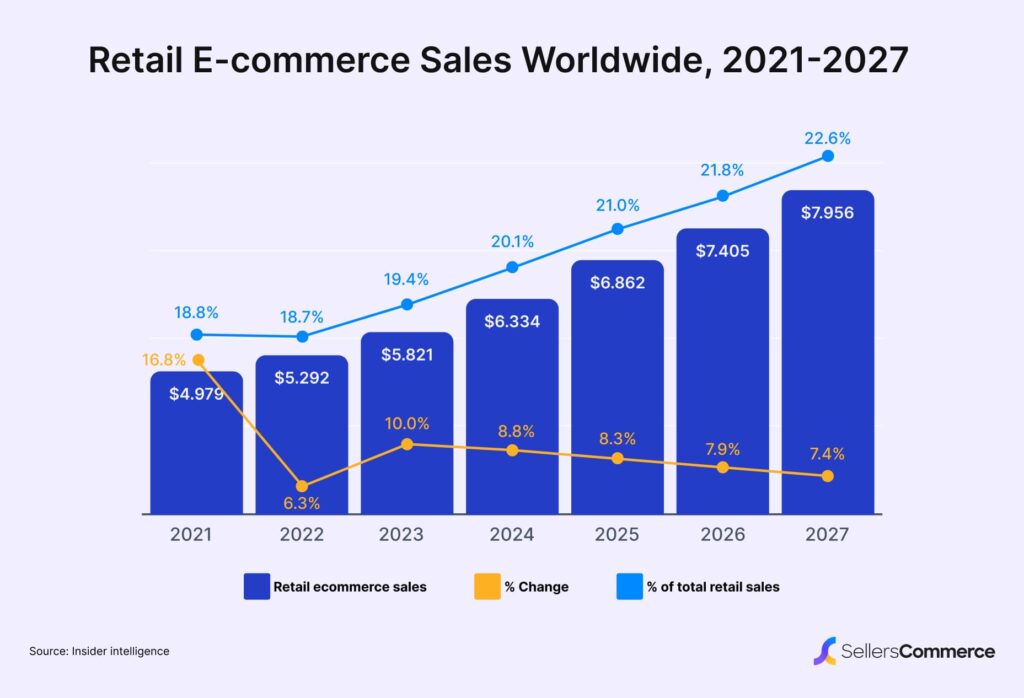
43 ECommerce Statistics In 2024 (Global And U.S. Data)
The e-commerce sector has experienced unprecedented growth over the past decade. In 2023, global e-commerce sales reached approximately $4.65 trillion, marking a 9.2% increase from the previous year. Projections indicate that by the end of 2024, the market will expand to $5.14 trillion, reflecting a robust growth rate of 10.4%. This rapid growth is fueled by these key factors:
- Technology Transformation: Increasing internet penetration and smartphone usage have made online shopping more accessible. As of 2023, over 5.3 billion people use the internet, with a significant percentage engaging in online transactions.
- Changing Preferences: Post-pandemic, consumers have shifted toward the convenience of online shopping. The rise of direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands and subscription-based services reflects this evolving behavior.
- Globalization: E-commerce platforms are expanding into new markets, creating a more interconnected global economy. Companies are targeting untapped markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, where e-commerce adoption is growing rapidly.
However, this rapid expansion brings significant challenges. E-commerce platforms must manage escalating web traffic, ensure seamless user experiences, and maintain robust security measures. The competitive landscape demands continuous innovation and the ability to adapt to evolving market trends. Additionally, businesses face logistical hurdles, including efficient inventory management and timely delivery, which are crucial for sustaining customer satisfaction.
Why Scalability?
In the context of e-commerce, scalability refers to a platform’s ability to handle increasing numbers of users, transactions, and data without degradation in performance. This involves both vertical scalability (enhancing the capacity of existing servers) and horizontal scalability (adding more servers to distribute the load). During peak shopping periods, such as Black Friday or Singles’ Day, platforms often experience traffic surges that can overwhelm unprepared systems, leading to slow load times or crashes. Such incidents can result in significant revenue losses and damage to brands’ reputation.
Why Application Engineering?
Application engineering is the backbone of scalable and efficient e-commerce platforms. It focuses on designing software solutions that not only meet immediate business requirements but also adapt to growth and market changes. In e-commerce, this involves creating applications that can handle high transaction volumes, integrate seamlessly with other systems, and deliver exceptional user experiences.
Key aspects of application engineering in e-commerce include developing modular architectures like microservices for flexibility, optimizing databases for faster processing, and implementing advanced security measures to protect sensitive customer data. Engineers also leverage technologies like cloud computing for dynamic scalability and AI for personalized shopping experiences.
Curious to learn more about how application engineering works and its impact on different industries? Check out our in-depth blog: Application Engineering 101: Key Skills, Challenges, and Trends | SmartDev
Understanding Scalability in E-Commerce
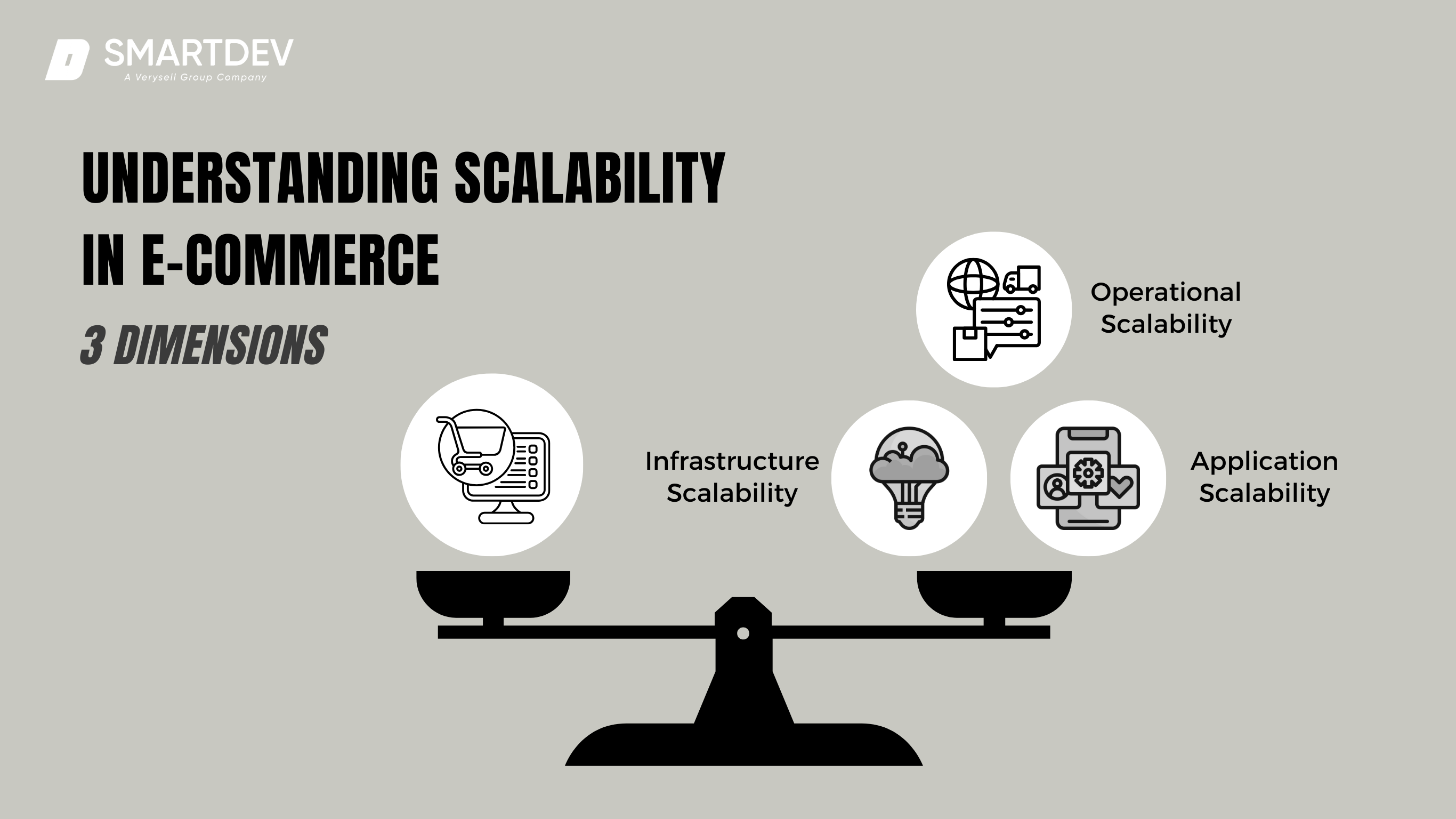
3 Key Dimensions of Scalability in E-Commerce
Scalability in e-commerce is more than just handling an increase in users; it’s about ensuring seamless operations across the board, from the backend infrastructure to the customer-facing interface. Scalability can be categorized into three key dimensions:
- Infrastructure Scalability: This involves using cloud-based solutions to dynamically allocate resources. For example, platforms like AWS and Azure allow businesses to scale storage and computing power in real-time, ensuring that server capacity meets demand.
- Application Scalability: A scalable application is built on flexible architectures like microservices and uses efficient coding practices to manage increasing workloads. This approach ensures that adding features or supporting new users doesn’t compromise existing functionality.
- Operational Scalability: Beyond technology, scalability also depends on efficient workflows. Automating processes like inventory management, order fulfillment, and customer support ensure that operations keep pace with growth.
For example, a medium-sized retailer experiencing 200% growth in sales over a year might face challenges like delayed load times or database bottlenecks. Consequently, application engineers can redesign the system using cloud-native solutions, ensuring the platform can handle the increased traffic and transaction volume without disruptions.
2. What is Scalability?
As mentioned above, for e-commerce businesses, scalability ensures that operations remain efficient, user experiences stay consistent, and platforms continue to deliver reliable performance as the business grows or faces sudden traffic spikes.
The Cost of No Scaling: Common Pitfalls and Risks
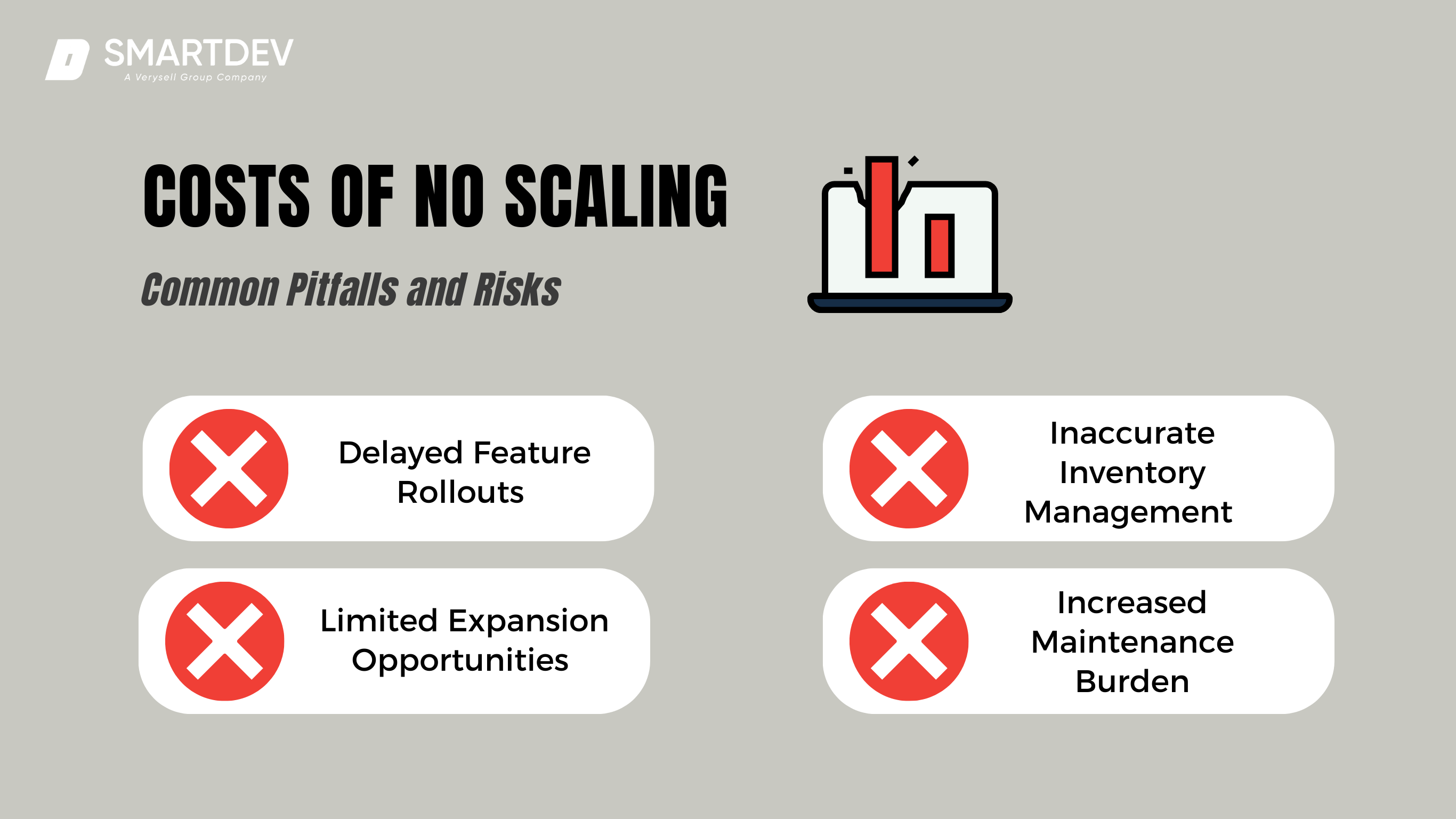
Costs of No Scaling
Failing to prioritize scalability early can lead to cascading problems that affect customer satisfaction and business operations. Here are some lesser-discussed but equally critical pitfalls:
Delayed Feature Rollouts
As your platform grows, introducing new features, like dynamic pricing or AI-driven recommendations, can become significantly slower on an unscalable architecture. Delayed rollouts hinder your ability to stay competitive in a fast-paced market.
Inaccurate Inventory Management
Unscalable systems may struggle to process real-time inventory updates during peak demand, leading to issues like overselling or stockouts. This frustrates customers and complicates fulfillment processes.
Limited Expansion Opportunities
If your system can’t handle growth, entering new markets or onboarding more products becomes a risky endeavor. Businesses often miss out on lucrative opportunities because their platforms aren’t equipped for expansion.
Increased Maintenance Burden
As an unscalable system grows in complexity, maintenance efforts increase disproportionately. Engineers may spend excessive time patching performance issues instead of focusing on innovation.
Examples of Scalability Challenges During Peak Demand
Holiday Promotions

During the holiday season, businesses often launch promotional campaigns that attract thousands of visitors in minutes. For instance, in Target’s 2019 Black Friday sales, their website experienced a significant outage due to overwhelming traffic. Customers faced difficulties accessing the site, leading to frustration and potential revenue loss. The incident highlighted the importance of robust infrastructure to handle peak shopping periods.
Live Streaming Commerce
Livestream shopping is becoming a popular trend, particularly in regions like Asia. Platforms hosting live events often face simultaneous high video streaming traffic and real-time purchasing demands. In one instance, Alibaba’s Taobao platform faced technical glitches during the 2020 Singles’ Day live-streaming event. The platform struggled to manage the massive influx of viewers and real-time transactions, resulting in delays and a suboptimal user experience. This incident underscored the challenges of scaling live-streaming commerce platforms.
Unforeseen Viral Campaigns
Viral trends or social media campaigns can lead to unexpected traffic surges. For instance, a small clothing brand went viral on TikTok, resulting in a tenfold increase in traffic overnight. Take Kylie Jenner’s cosmetics brand as a lesson. The brand experienced a website crash during the launch of its lip kits in 2015. The unexpected surge in traffic from fans eager to purchase the products overwhelmed the site’s capacity, leading to downtime and customer dissatisfaction. This event highlighted the need for scalable solutions to accommodate sudden spikes in demand.
High-Volume Flash Deals
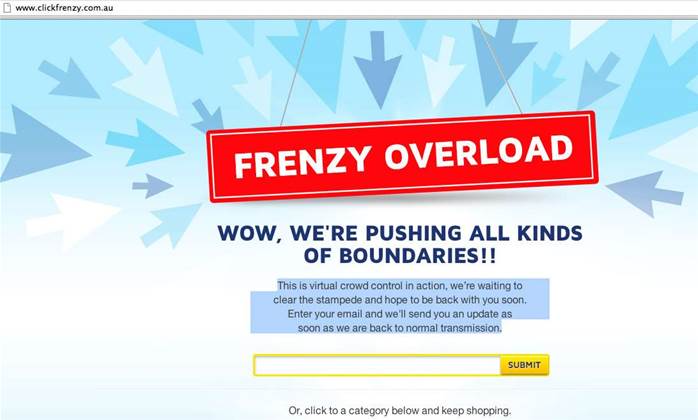
Platforms like Amazon manage millions of transactions during events like Prime Day. Smaller businesses trying to replicate these sales models often encounter issues with queuing systems or checkout failures, as their infrastructure isn’t designed for such concentrated demand.
Australia’s Click Frenzy is one of them. They, inspired by the U.S. Cyber Monday, launched their first online sales event in 2012. The website crashed within moments of launching due to an inability to handle the anticipated heavy traffic, rendering it unavailable for most of the night. This incident emphasized the critical importance of preparing for high-volume flash sales.
3. The Role of Application Engineering in Scalability
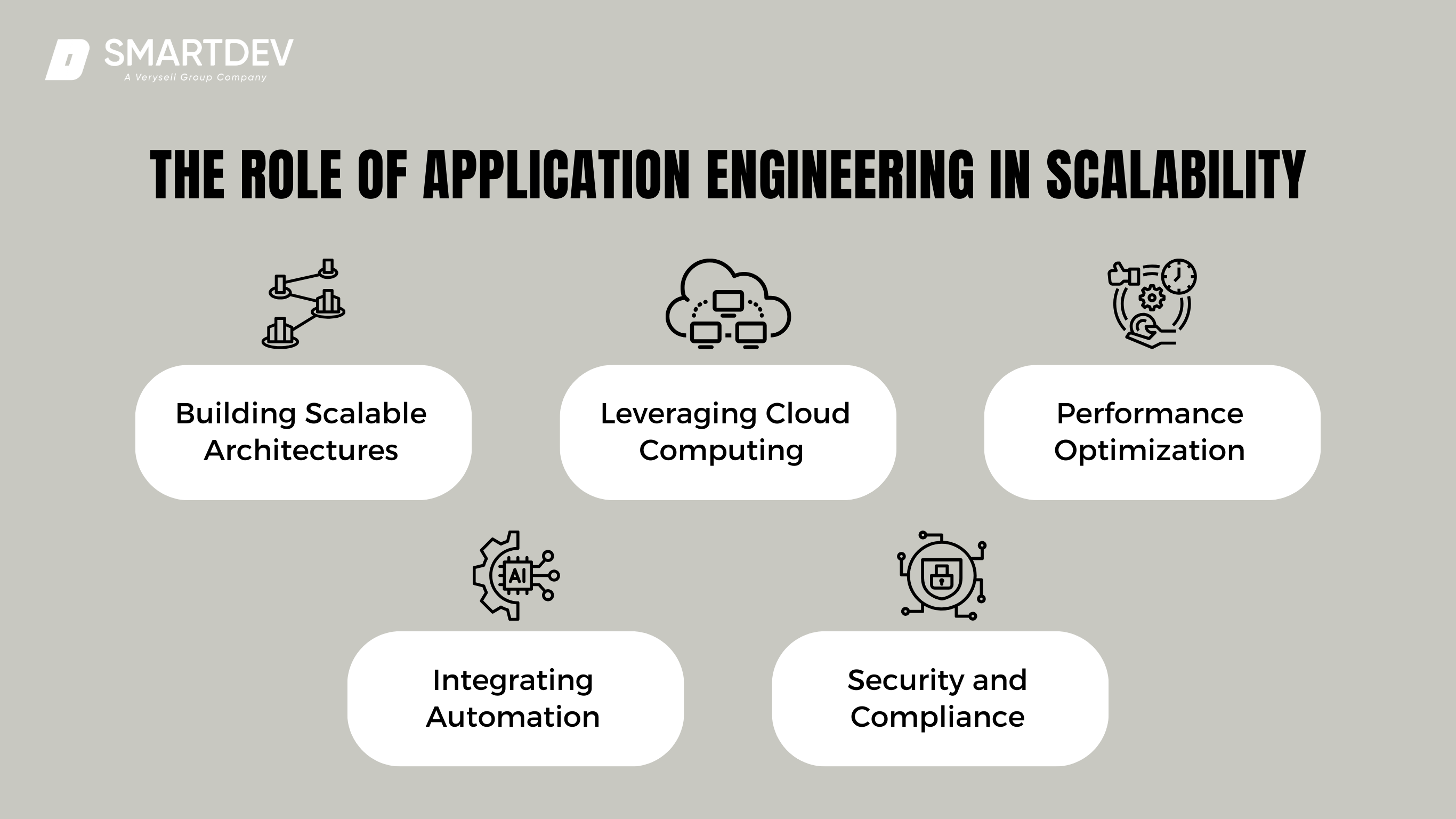
The Role of Application Engineering in Scalability
Application engineering plays a crucial role in ensuring not only e-commerce platforms but also many other sectors designed to handle growth, traffic surges, and complex operations without sacrificing performance or user experience. By leveraging cutting-edge strategies and technologies, application engineers build systems that are resilient, efficient, and adaptable. Below, we explore keyways in which application engineering drives scalability in e-commerce.
Building Scalable Architectures: Microservices and Modular Design
One of the most effective approaches to building scalable e-commerce platforms is through microservices and modular design. These architectures break down an application into smaller, independent components that can operate and scale independently.
- Microservices
In a microservices architecture, each service is responsible for a specific function, such as user authentication, product catalogs, or payment processing. This separation allows individual services to scale based on demand without affecting the performance of other components. For example, during a flash sale, the inventory service can scale to manage product availability updates while other services remain unaffected.
- Modular Design
Modular design enables engineers to add or modify features without disrupting the entire application. This approach is particularly useful for e-commerce platforms that frequently introduce new functionalities, such as loyalty programs or AI-powered recommendations.
Leveraging Cloud Computing for Dynamic Workloads
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way e-commerce platforms manage scalability. With cloud infrastructure, businesses can dynamically allocate resources to handle varying workloads, ensuring consistent performance even during traffic spikes.
- Elastic Scalability
Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide auto-scaling capabilities, allowing resources to expand or contract based on real-time demand. This flexibility eliminates the need for businesses to invest in expensive on-premises hardware.
- Global Reach
Cloud services offer distributed data centers, reducing latency for users in different geographical locations. This is especially critical for e-commerce businesses expanding into international markets.
Performance Optimization: Load Balancing and Caching
Performance optimization is another critical aspect of scalability, and application engineers rely on techniques like load balancing and caching to maintain fast, seamless experiences for users.
- Load Balancing
Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload and ensure even resource utilization. This is particularly important during high-traffic periods, where a single server may otherwise become a bottleneck.
- Caching
By storing frequently accessed data temporarily in memory, caching reduces server load and speeds up response times. For instance, caching product images, search results, or checkout information can significantly improve the user experience during peak demand.
Integrating Automation for Seamless Scalability
Automation plays an increasingly important role in scalability by streamlining resource management and deployment processes.
- CI/CD Pipelines
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines automate the testing and deployment of updates, allowing businesses to roll out new features quickly and efficiently.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Engineers use IaC tools like Terraform and Ansible to automate infrastructure provisioning. This ensures that additional resources can be deployed instantly during traffic surges.
Enhancing Security and Compliance
Scalability is not just about performance; it also involves ensuring that platforms remain secure as they grow. Application engineers implement robust security measures to protect sensitive customer data while complying with industry regulations like GDPR or PCI DSS.
- Secure Architectures
Scalable platforms integrate encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication to prevent data breaches during high-traffic periods.
- Regular Vulnerability Assessments
Automated tools are used to identify and resolve potential security risks as the platform scales.
4. Challenges in Scaling E-Commerce Platforms
High Traffic and Transaction Volumes
While managing server loads is a well-documented challenge, the ripple effects of high traffic go beyond backend overloads:
- Checkout Failures: Transaction processing systems often struggle to handle thousands of simultaneous payments, leading to errors or abandoned carts. This can result in substantial revenue losses during critical sales windows.
- API Limitations: Many platforms rely on third-party APIs for payment gateways, shipping calculations, or analytics. During traffic spikes, these APIs may reach their request limits, disrupting user workflows.
Database Bottlenecks and Slow Performance
As an e-commerce platform grows, so does the volume of data it processes. This includes product inventories, customer accounts, order histories, and real-time updates. Without optimized database management, bottlenecks can occur, leading to:
- Slow Search Queries: As product catalogs expand, search functionalities can slow down, frustrating users looking for specific items.
- Concurrent Transaction Failures: A lack of concurrency support in the database can result in delayed or failed transactions, especially during busy periods.
- Data Inconsistencies: High transaction volumes can lead to mismatches between inventory levels, order confirmations, and actual availability, creating logistical nightmares.
User Experiences Across Devices
With over 50% of global e-commerce transactions occurring on mobile devices, delivering a seamless multi-device experience is no longer optional. However, ensuring performance consistency across desktops, tablets, and smartphones presents unique challenges:
- Responsive Design Limitations: Platforms often face issues with inconsistent layouts, misplaced elements, or broken functionality on smaller screens.
- Performance Optimization for Mobile: Mobile users frequently encounter slower load times, especially on image-heavy e-commerce sites. Mobile-specific caching and compression solutions are sometimes overlooked during scaling efforts.
- Payment and Checkout Compatibility: Payment gateways or checkout systems may behave inconsistently across devices, leading to drop-offs in mobile transactions.
Subsequently, Google research indicates that 53% of users abandon mobile sites that take longer than 3 seconds to load, underscoring the importance of optimizing for speed and responsiveness.
Personalization and Recommendations
As e-commerce businesses grow, customers expect more personalized shopping experiences. While AI-driven recommendation engines can deliver tailored product suggestions, they require immense processing power and data handling capabilities:
- Real-Time Processing: Generating personalized recommendations in real time during high traffic periods can strain servers and delay responses.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Scaling personalization features often involves managing sensitive customer data, which must comply with regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
- System Lag in Recommendation Updates: Frequent catalog changes during sales events can cause recommendation algorithms to lag, leading to irrelevant suggestions.
Logistical Scaling and Order Fulfillment
Even with a perfectly scaled digital platform, scaling logistical operations can be a significant bottleneck. As order volumes grow, ensuring timely fulfillment becomes increasingly complex:
- Inventory Synchronization Issues: Inaccurate or delayed inventory updates can lead to overselling or out-of-stock errors.
- Warehouse and Shipping Capacity: Without scalable operational processes, warehouses can become overloaded, leading to delayed shipments and unhappy customers.
Ensuring Security and Fraud Prevention
Scaling a platform also increases exposure to cybersecurity threats. Larger platforms with higher transaction volumes become prime targets for fraud, data breaches, and other malicious activities.
- Fraudulent Transactions: High transaction volumes make it harder to identify suspicious activity in real-time.
- Data Breaches: Scaling systems often means integrating multiple third-party tools and APIs, which can inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities.
- Compliance with Expanding Regulations: Growing businesses often enter new markets, each with its own data protection laws, adding complexity to compliance.
In the next section, we’ll explore actionable solutions and strategies to overcome these hurdles effectively.
5. Technological Solutions for E-Commerce Scalability
Scaling an e-commerce platform requires leveraging advanced technological solutions to ensure consistent performance, seamless user experiences, and efficient resource utilization. Application engineering lies at the heart of implementing these solutions, tailoring them to meet business-specific challenges and growth needs. Below, we explore key technologies driving scalability in e-commerce.
Cloud-Native Development
Cloud-native development allows e-commerce platforms to dynamically adjust resources based on demand. With providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, businesses can scale server capacity automatically during traffic spikes, ensuring smooth user experiences. Elastic scalability eliminates over-provisioning, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Additionally, the pay-as-you-go model offered by cloud platforms ensures that businesses only pay for the resources they use. This is particularly beneficial for startups or growing businesses that experience seasonal surges but don’t need year-round maximum capacity.
Automation for Faster Deployment
Automation accelerates scalability by streamlining deployment and infrastructure management. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines automate testing and rollout of updates, reducing time-to-market for new features. This approach ensures that platforms adapt quickly to evolving user needs.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) further simplifies scalability by automating resource provisioning. Engineers can deploy additional infrastructure instantly during high-traffic events without manual intervention, minimizing downtime and enhancing reliability.
Case for AI and Predictive Analytics in Resource Management
AI and predictive analytics provide valuable insights to optimize resource management. Algorithms analyze historical data to forecast traffic patterns, enabling pre-scaling of resources ahead of peak demand. This proactive approach prevents disruptions and ensures consistent performance.
Predictive tools also enhance inventory and pricing management, aligning stock levels with customer demand and dynamically adjusting prices to maximize revenue. AI-driven solutions make platforms smarter, enabling better decision-making at a scale.
Serverless Architectures for On-Demand Scalability
Serverless computing offers a flexible, cost-efficient solution for handling unpredictable workloads. Platforms like AWS Lambda execute functions only when needed, ensuring resources are used efficiently. This reduces operational complexity and allows application engineers to focus on development.
Serverless architectures are particularly effective for managing backend tasks like payment processing during flash sales. They allocate resources dynamically, ensuring fast and reliable performance even during traffic surges.
Edge Computing for Faster Data Processing
Edge computing minimizes latency by processing data closer to users. This approach is critical for global e-commerce platforms, ensuring fast load times and a seamless experience for geographically dispersed customers.
Real-time analytics enabled by edge computing supports features like personalized recommendations and live shopping. By reducing the reliance on centralized servers, edge computing enhances both speed and reliability, particularly during high-demand events.
6. Case Studies: Application Engineering in Action
A notable example is BOLDR, a company dedicated to combating climate change through innovative energy efficiency solutions. Partnering with SmartDev, BOLDR successfully developed and scaled an energy efficiency app, demonstrating the pivotal role of application engineering in e-commerce scalability.
Challenges Faced by BOLDR
BOLDR aimed to revolutionize home climate management by introducing an app capable of delivering substantial energy savings and automated control. The primary challenges included:
- Rapid Development Needs: To gain a competitive edge, BOLDR required swift development of a sophisticated minimum viable product (MVP) that could be scaled as the user base expanded.
- Integration with Diverse Devices: Ensuring compatibility with various air conditioning systems and smart home devices was essential for broad market adoption.
- User Experience Optimization: Creating an intuitive and seamless user experience was crucial to encourage widespread usage and engagement.
Application Engineering Solutions Implemented
SmartDev addressed these challenges through targeted application engineering strategies:
- IoT System Development: An innovative Internet of Things (IoT) system was developed, integrating mobile applications for both iOS and Android platforms. This system utilized MQTT for efficient real-time device communication, ensuring responsiveness and reliability.
- Microservices Architecture: Employing a microservices architecture allowed for scalability and ease of maintenance. This design enabled individual components to be updated or scaled independently, facilitating rapid adaptation to user growth and technological advancements.
- Ongoing Support and Expertise: Beyond initial development, SmartDev provided continuous support and expert guidance, ensuring the platform’s performance remained exceptional and aligned with BOLDR’s strategic goals.
Outcomes and Successes
- Seamless Integration: The app achieved universal compatibility, connecting with a wide range of air conditioning systems through infrared technology.
- Enhanced User Experience: Features such as smart climate control, remote access, and voice command integration with platforms like Alexa and Google Assistant were implemented, enhancing user convenience and engagement.
- Scalable and Maintainable Platform: The microservices architecture ensured that the platform could scale efficiently with user growth, maintaining high performance and reliability.
BOLDR’s journey underscores the critical role of application engineering in scaling e-commerce solutions. By leveraging advanced technologies and strategic development practices, small businesses can overcome scalability challenges, deliver exceptional user experiences, and achieve rapid growth in competitive markets.
Read more at Scaling BOLDR with AWS: A Secure and Flexible Infrastructure | SmartDev
7. Future Trends in E-Commerce Scalability
The e-commerce landscape is continually evolving, with scalability remaining a central focus for businesses aiming to meet growing consumer demands. Emerging trends are shaping how companies approach scalability, ensuring robust and flexible platforms.
Trend No. 1: Headless Commerce
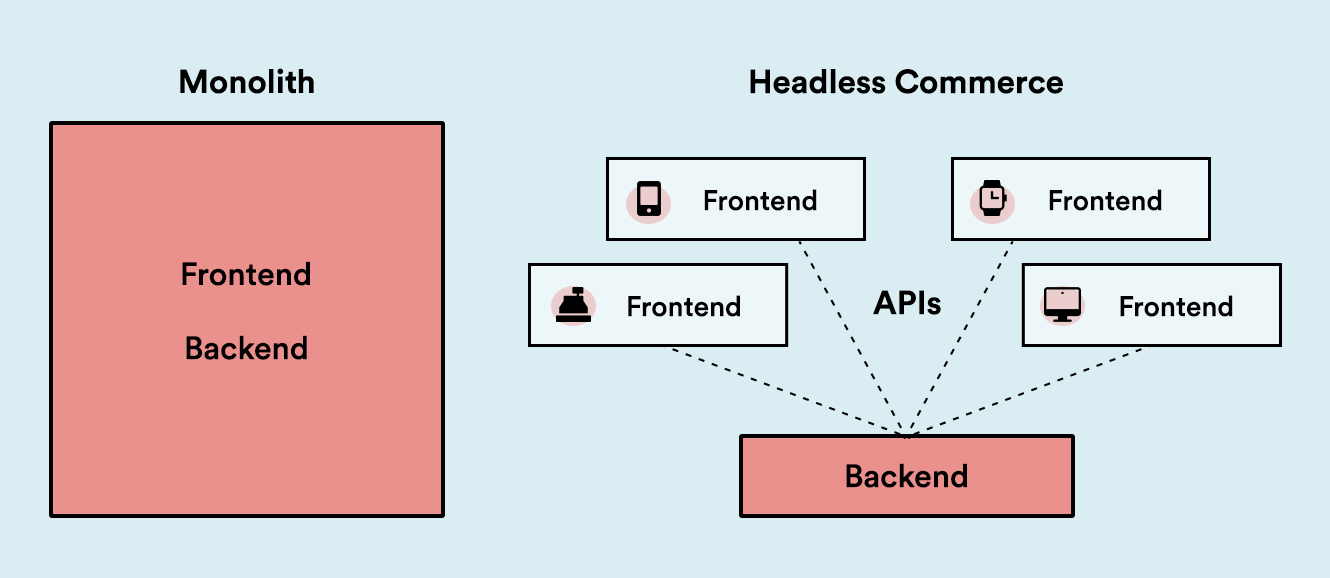
Headless commerce decouples the front-end presentation layer from the back-end e-commerce functionality, allowing businesses to deliver content across various channels seamlessly. This architecture enhances scalability by enabling independent updates and integrations without disrupting the entire system. As consumer touchpoints diversify, headless commerce offers the flexibility needed to maintain consistent experiences across platforms.
Trend No. 2: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)

AI and machine learning are becoming integral in optimizing e-commerce operations. These technologies facilitate personalized shopping experiences, predictive analytics for inventory management, and dynamic pricing strategies. By automating complex processes, AI and machine learning contribute to scalable solutions that can adapt to market fluctuations and consumer behaviors.
Trend No.3: Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)

AR and VR technologies are transforming online shopping by providing immersive experiences that bridge the gap between physical and digital retail. Implementing AR and VR requires scalable infrastructure to handle high-quality graphics and real-time interactions, ensuring a seamless user experience as these technologies become more prevalent.
Trend No. 4: Sustainability and Ethical Practices

Consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability and ethical considerations in their purchasing decisions. E-commerce platforms are scaling operations to include transparent supply chains, eco-friendly packaging, and sustainable sourcing. Integrating these practices requires scalable systems that can adapt to new compliance standards and consumer expectations.
Trend No. 5: Social Commerce

Social media platforms are evolving into significant e-commerce channels, enabling direct purchases through social apps. This trend necessitates scalable solutions that can integrate social commerce functionalities, manage increased traffic from social channels, and provide seamless checkout experiences within these platforms.
Trend No. 6: Blockchain Technology

Blockchain offers enhanced security and transparency in transactions, supply chain management, and data integrity. Adopting blockchain requires scalable architectures capable of handling decentralized databases and ensuring real-time processing, which is crucial for maintaining trust and efficiency in e-commerce operations.
Staying abreast of these trends is essential for businesses aiming to scale effectively in the dynamic e-commerce environment. By embracing innovative technologies and practices, companies can build resilient platforms that meet evolving consumer expectations and sustain growth.
8. Conclusion
Scalability is no longer a luxury for e-commerce businesses; it’s a necessity for growth and long-term success. Throughout this blog, we’ve explored how application engineering serves as a powerful enabler of scalability, helping businesses handle increasing demands, optimize performance, and enhance user experiences. From microservices architectures to AI-driven insights, application engineering ensures platforms are not just prepared for today’s challenges but also adaptable for tomorrow’s opportunities.
At SmartDev, we specialize in crafting scalable, custom e-commerce solutions tailored to your business needs. Whether you’re preparing for rapid growth or looking to future-proof your platform, our expert team is ready to help. Partner with us to build a robust, scalable e-commerce platform that drives success and meets the evolving demands of the market. Contact us today to get started!
References
- Ecommerce Statistics You Need to Know in 2024 | HubSpot Marketing Blog
- Global E-Commerce Market 2024: Size, Market Growth, and Online Share | EcommerceDB Insights
- Scalability Definition | Gartner IT Glossary
- Headless Commerce | Wikipedia
- Modern E-Commerce Architecture Trends and Services: A Comprehensive Guide | FocusReactive Blog
- E-Commerce in 2024: Growth Trends and Challenges | Alfred24 Blog
- How Web3 is Shaping the Future of Shopping | Vogue Business







