In the era of digital transformation, businesses are continuously seeking innovative ways to enhance customer interactions, improve efficiency, and streamline operations. One of the most significant advancements in this space is the adoption of AI-driven conversational technologies.
Among the most widely used solutions are chatbots and conversational AI, both of which aim to automate interactions between businesses and customers. However, while they may seem similar at first glance, their capabilities and complexities are vastly different.
As businesses strive to deliver more personalized and efficient customer experiences, understanding the differences between chatbots and conversational AI becomes crucial. The decision to implement one over the other can significantly impact user satisfaction, operational efficiency, and long-term business success.
A simple chatbot might be sufficient for handling structured, repetitive queries, but as customer expectations rise, businesses need solutions that provide more dynamic, intelligent, and context-aware interactions. This is where conversational AI comes into play. By understanding the nuances between these technologies, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their customer service goals and long-term growth strategies.
In this article, we will explore its significance, and the benefits these tools offer to businesses like SmartDev, enabling you to leverage AI effectively.
1. What are Chatbots?
Imagine having a virtual assistant available 24/7, ready to answer your questions, assist with tasks, and even hold meaningful conversations—all without human intervention. This is the power of chatbots. These AI-driven tools are transforming the way businesses interact with customers, streamlining communication, and automating processes with remarkable efficiency. From simple scripted responses to advanced AI models capable of understanding context and emotions, chatbots are revolutionizing industries like customer service, e-commerce, and healthcare.
1.1 Definition and Brief History of Chatbots
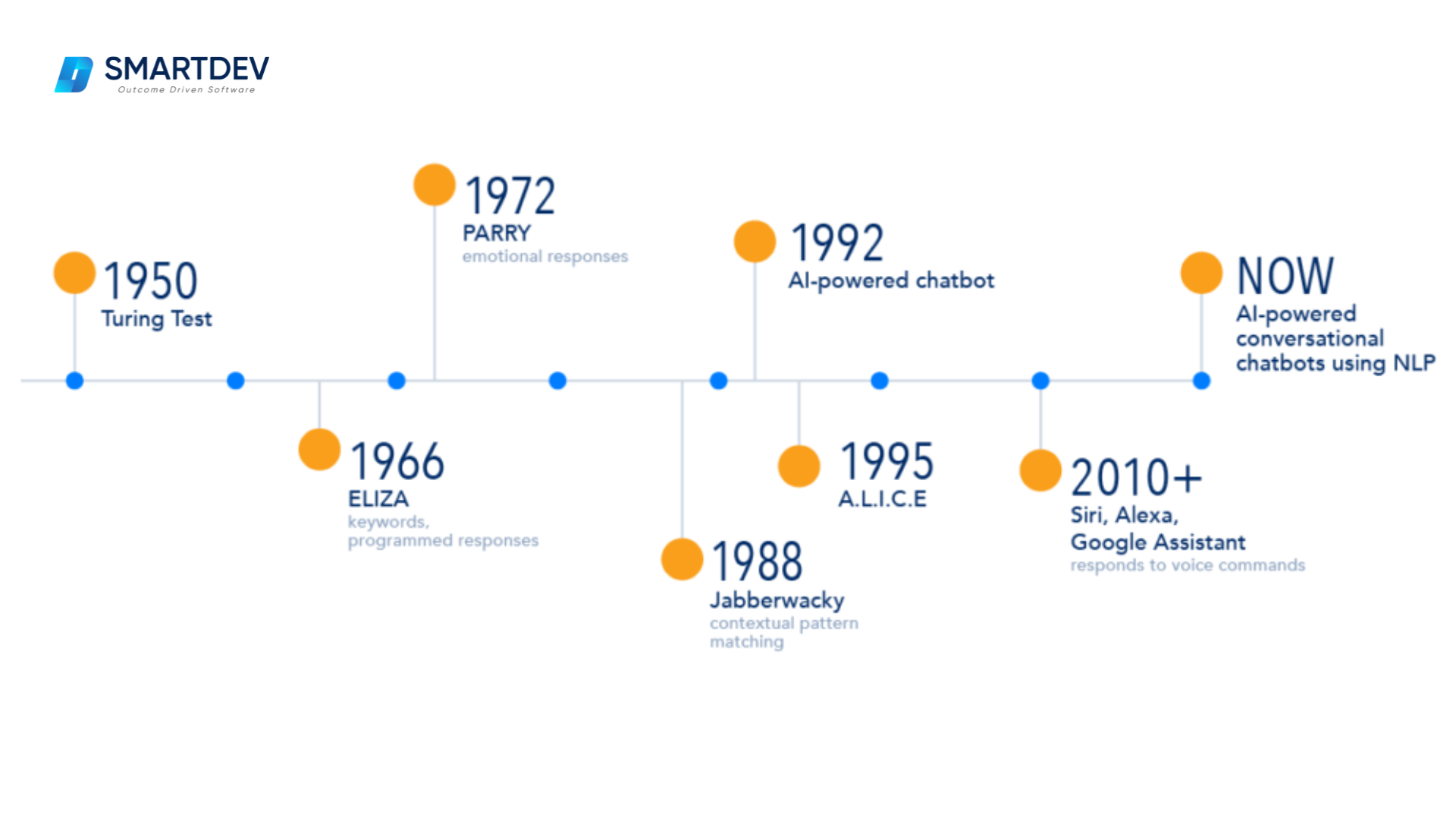
Chatbots are software applications designed to simulate human conversation, primarily through predefined rules, scripts, or AI-powered logic. The earliest chatbot, ELIZA, developed in the 1960s at MIT, used basic pattern-matching techniques to simulate conversation, but its ability to engage in meaningful interactions was limited.
ELIZA was designed to simulate human conversation by employing pattern matching and substitution techniques, creating the illusion of understanding without genuine comprehension. The scientist’s experience with ELIZA led him to critically assess the implications of artificial intelligence, cautioning against overestimating machine understanding and the potential consequences of integrating AI into human-centric domains. (Pierce, 2024).

The first Chatbot – Eliza in the talking (1966)
Fast forward to the 21st century, chatbots have evolved significantly, with modern versions leveraging natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to enhance user experiences. While traditional chatbots follow strict, rule-based responses, newer AI-powered chatbots attempt to understand user intent, though they still have significant limitations in adaptability and contextual understanding.
1.2 Types of Chatbots
Chatbots come in various forms, each designed to serve different use cases based on their complexity and capabilities. Below are the four primary types of chatbots, ranging from simple rule-based systems to more advanced AI-powered models.
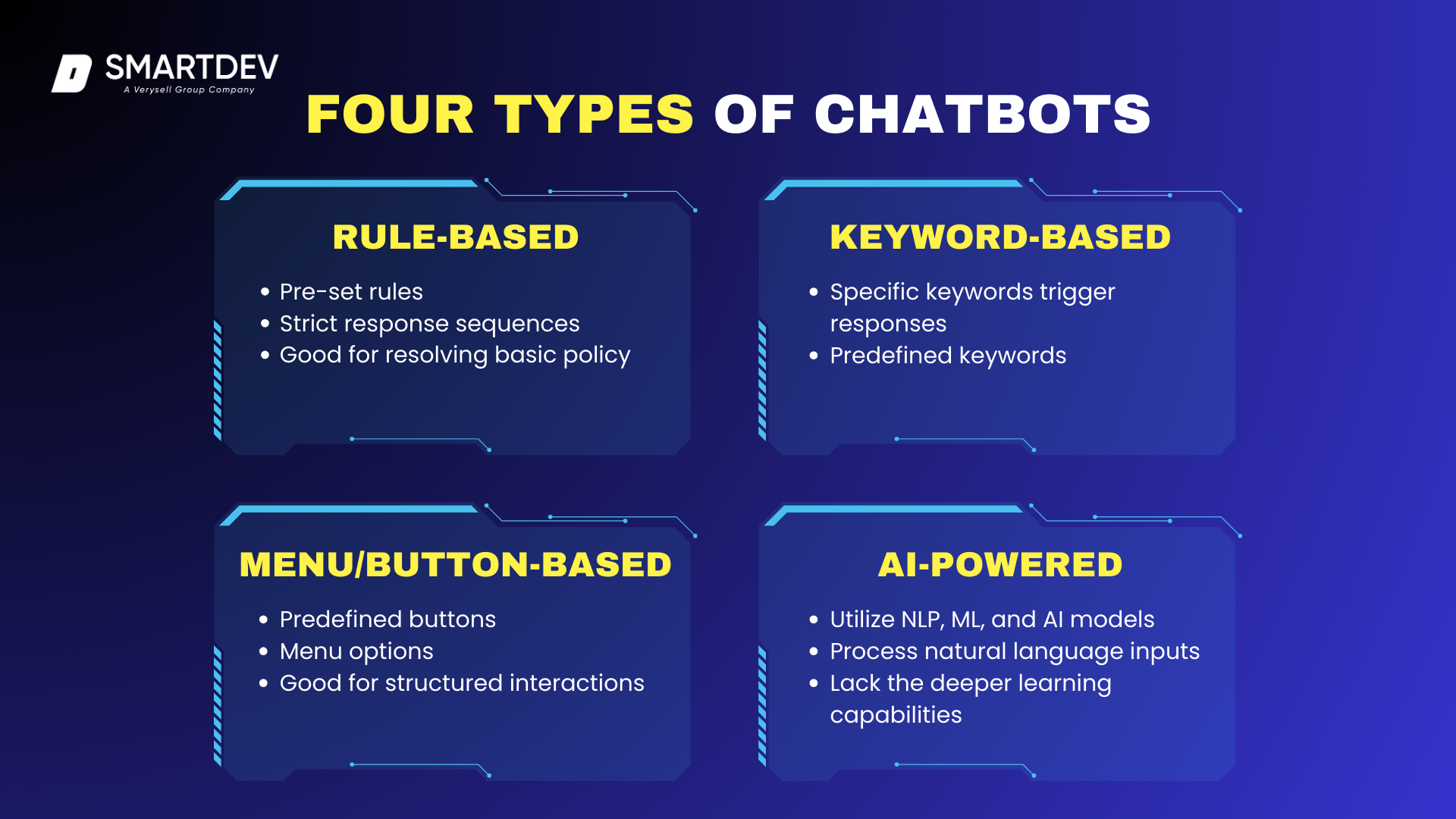
1.2.1. Rule-Based Chatbots
These chatbots operate on predefined rules and structured decision trees, making them highly predictable but limited in flexibility. They function by following a set of pre-programmed responses based on specific user inputs. Since they do not learn from interactions, they are best suited for handling repetitive tasks where responses are straightforward and do not require contextual understanding.
Example: A basic customer service chatbot for an e-commerce store that helps users with refund policies, order tracking, and store hours by navigating a structured flow of questions and answers.
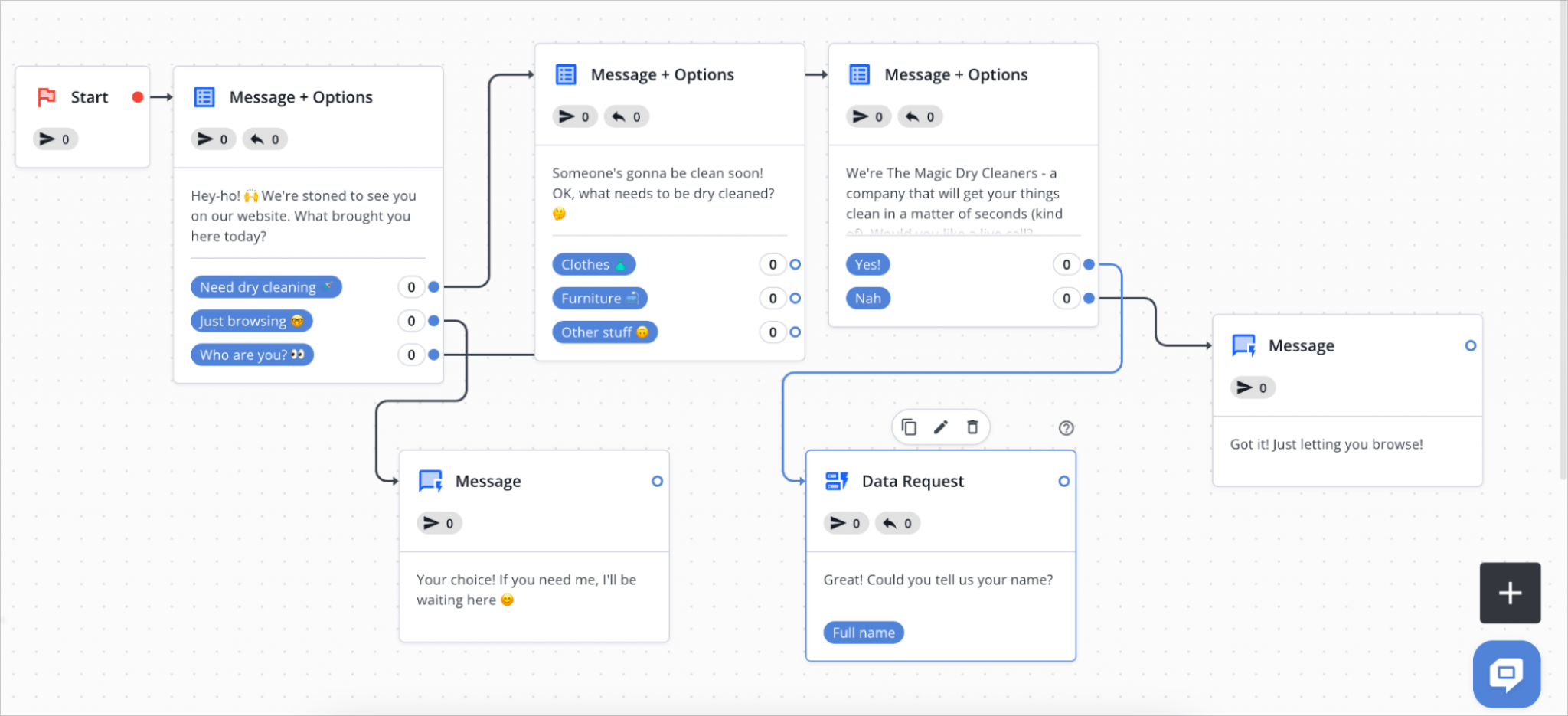
The process of rule-based Chatbots
1.2.2. Keyword-Based Chatbots
Keyword-driven chatbots recognize specific words or phrases within user input and trigger pre-assigned responses. These chatbots use pattern matching but do not possess true contextual awareness, meaning they work best when users input expected terms. While they offer more flexibility than rule-based chatbots, they may struggle with varied sentence structures or ambiguous queries.
Example: A telecom chatbot that recognizes keywords like “data plan” or “international roaming” to provide relevant plan details, pricing, or upgrade options.
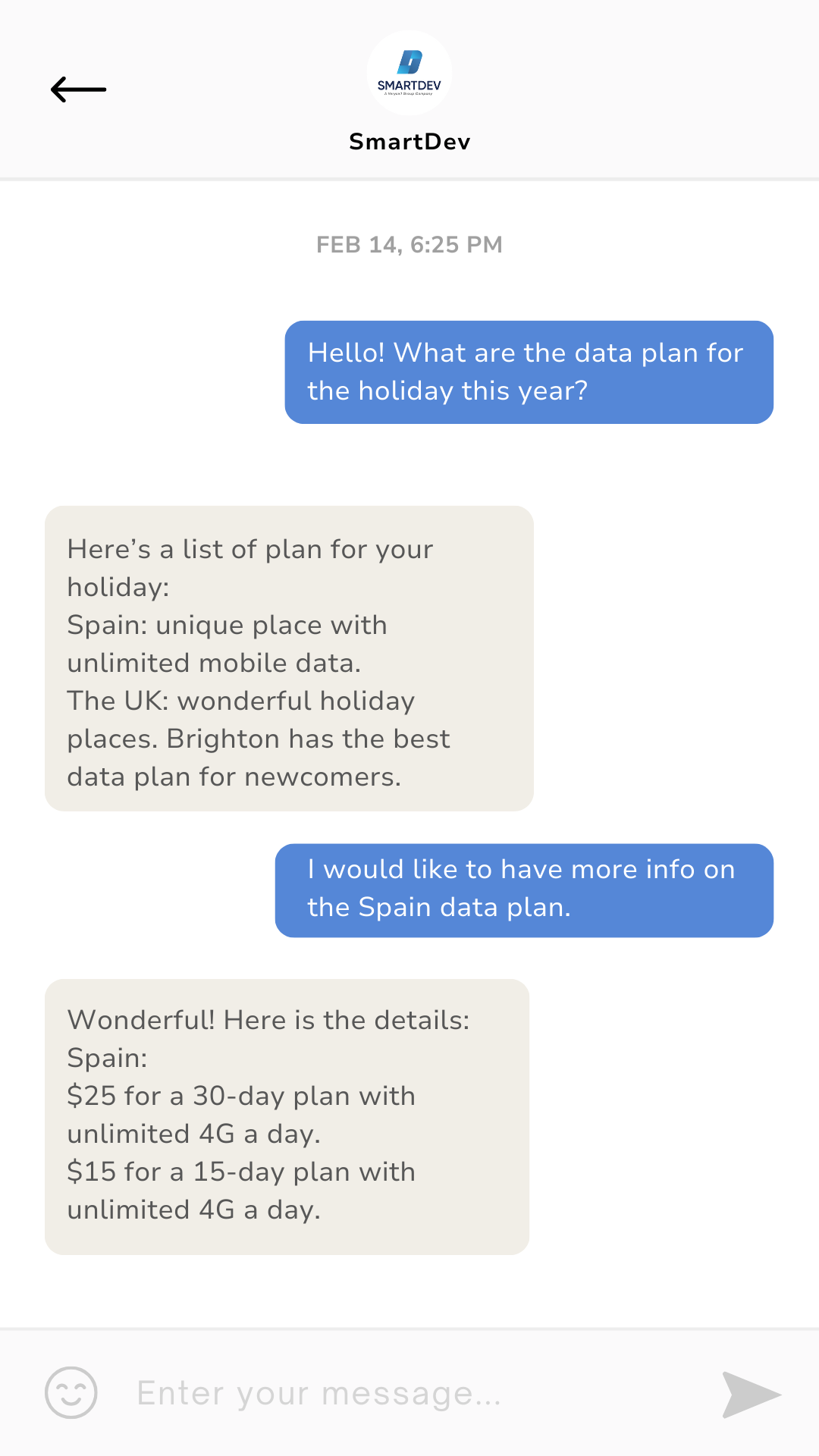
Example of a Keyword-based chatbot
1.2.3. Button-Based Chatbots
These chatbots present users with a list of predefined buttons or menu options, allowing them to navigate through a structured conversation without requiring free-text input. This design is ideal for scenarios where user interactions follow a fixed flow, such as booking services, surveys, or guided customer support.
Example: An airline booking chatbot that presents users with options to “Search Flights,” “Check-in Online,” or “View Baggage Policies,” guiding them step by step through the booking or inquiry process.

Menu/Button-based chatbot example
1.2.4. AI-Powered Chatbots
Leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and advanced AI models, these chatbots are designed to understand and respond to user inputs in a more natural and dynamic manner. They can analyze context, intent, and even sentiment, making them highly adaptive. While they are significantly more advanced than rule-based systems, their accuracy depends on training data, AI model sophistication, and continuous learning. (Hubspot, 2025).
Example: A banking chatbot capable of answering complex customer inquiries about loan eligibility, investment advice, or fraud detection by understanding the intent behind user questions rather than relying solely on predefined scripts.
Each of these chatbot types has its strengths and limitations, with the choice depending on the specific needs of a business or service.
Regular chatbot vs AI-powered chatbot
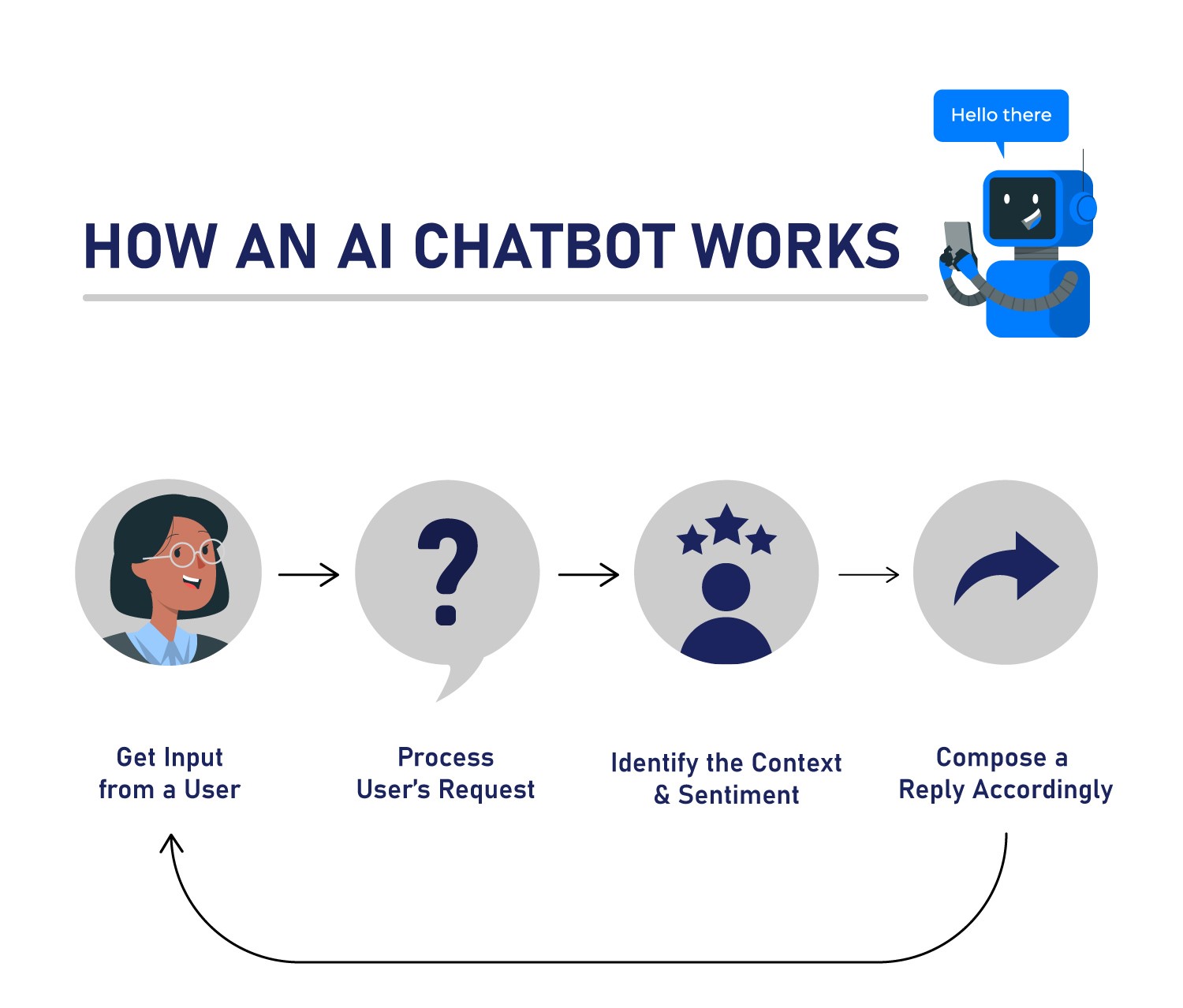
The process of AI-based chatbots
1.3 Common Use Cases for Chatbots
1.3.1. Customer Support & Service
One of the most prevalent applications of chatbots is in customer service, where they assist users with common inquiries, reducing response times and alleviating the workload of human agents. Chatbots can handle frequently asked questions such as order tracking, refund policies, troubleshooting product issues, and store hours—providing instant support 24/7.
Example: E-commerce giants like Amazon and Walmart use AI chatbots to handle customer complaints, track deliveries, and initiate returns without requiring human intervention.
Impact:
- 67% of customers worldwide have interacted with a chatbot for customer support (Salesforce, 2023).
- Businesses using chatbots for customer service report an average 30% reduction in support costs (IBM, 2022).
1.3.2. Lead generation & qualification
Businesses use chatbots to engage website visitors, capture lead information, and qualify potential customers before transferring them to human sales representatives. By automating this process, companies can efficiently filter out unqualified leads and focus on high-value prospects.
Example: Real estate firms deploy chatbots on their websites to ask potential buyers about their budget, preferred locations, and property requirements, then schedule appointments with agents.
Impact:
- Companies using AI-powered chatbots for lead qualification experience a 3x increase in conversion rates (Drift, 2022).
- 55% of businesses state that chatbot-driven lead generation has significantly improved their sales funnel efficiency (HubSpot, 2023).
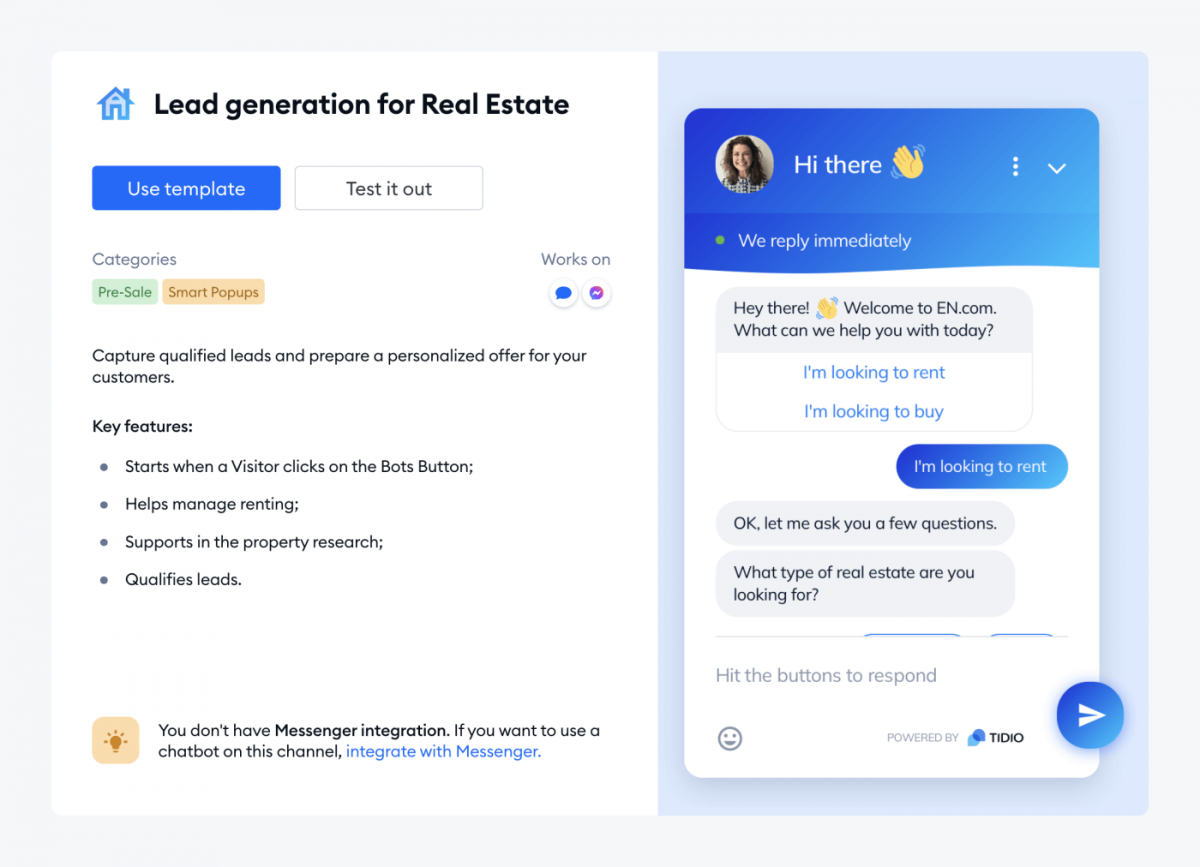
Real Estate chatbots
1.3.3. FAQ Automation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) chatbots help businesses provide instant answers to common customer inquiries without requiring human intervention. These chatbots are programmed with a database of frequently asked questions and use NLP (Natural Language Processing) to match customer queries with the most relevant response.
Example: Universities and government agencies use FAQ chatbots to answer questions about admissions, tuition fees, or public services, reducing the burden on call centers and administrative staff.
Impact:
- 80% of routine questions can be automated with chatbots, significantly improving response times (Gartner, 2023).
- Businesses using FAQ chatbots report a 40% decrease in email and phone inquiries, freeing up support teams for more complex issues (HubSpot, 2023).
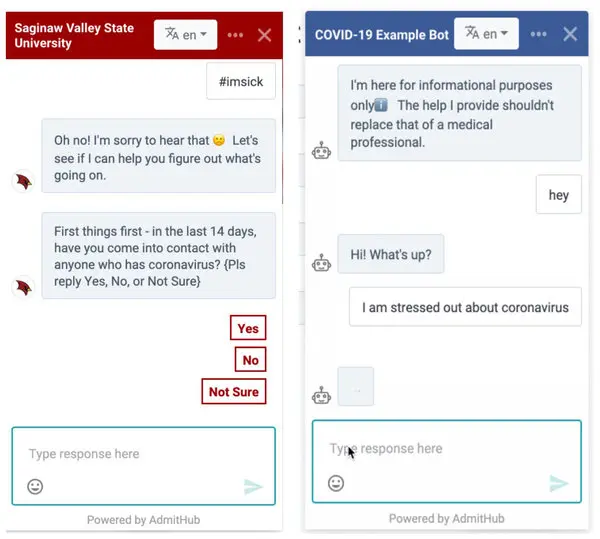
University chatbots
1.4 Limitations of Traditional Chatbots
While traditional chatbots streamline customer interactions and automate tasks, they have several inherent limitations that restrict their effectiveness (BaaJ, El Bakkali, and Amine Lahiala, 2024)
- Struggle with Complex Queries
Rule-based and keyword-driven chatbots operate within predefined scripts, making them ineffective when handling ambiguous, multi-part, or unexpected user inputs. Their rigid structure prevents them from adapting to varied language patterns or nuanced questions.
- Lack of Contextual Understanding
Traditional chatbots process each query in isolation, without memory of previous interactions. This results in repetitive and impersonal responses, forcing users to rephrase or re-enter information, reducing efficiency and engagement.
- Cannot Learn and Improve Over Time
Unlike AI-powered chatbots, traditional versions do not self-improve based on past conversations. They require manual updates to expand their knowledge base, making them inflexible and resource-intensive to maintain.
Although effective for handling repetitive, structured tasks, traditional chatbots lack the adaptability needed for deeper engagement. Businesses requiring personalized and dynamic interactions may benefit from conversational AI solutions.
2. What Is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI refers to AI-powered systems that understand, process, and respond to human language in a natural, intelligent, and contextual manner. Unlike traditional chatbots, which follow predefined scripts and limited keyword recognition, conversational AI employs advanced natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and deep learning to interpret and generate human-like responses. It continuously learns from interactions, enabling more refined and personalized conversations over time.
Conversational AI systems can handle complex queries, recognize speech patterns, detect user intent, and even understand sentiment and emotions. This makes them particularly effective in customer service, virtual assistants, and business automation scenarios, where dynamic and meaningful interactions are crucial.
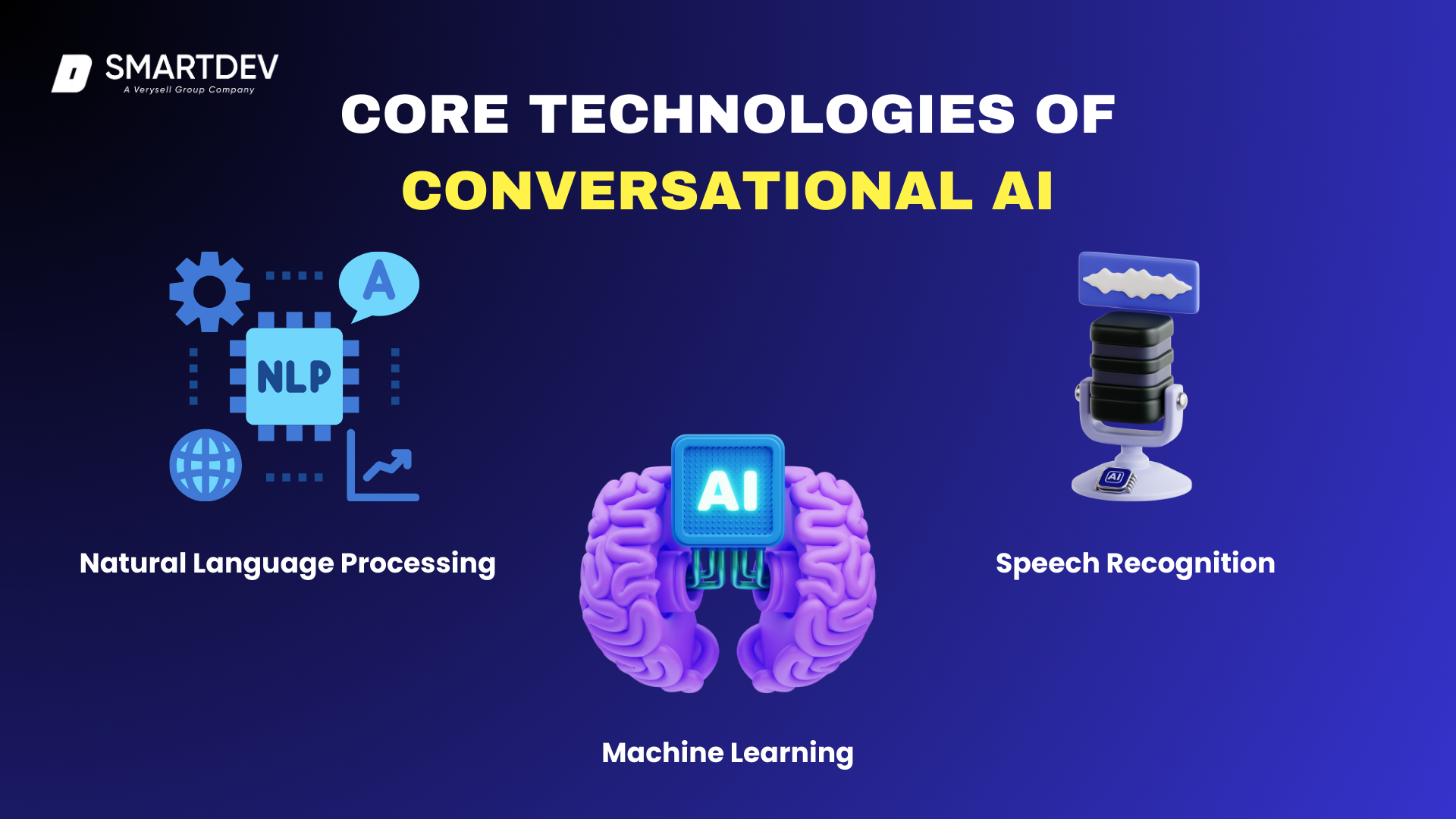
2.1 Core Technologies in Conversational AI
Conversational AI relies on a combination of advanced technologies to process, understand, and respond to human input effectively. These technologies work together to enhance chatbot and virtual assistant capabilities, allowing for more natural and engaging interactions. Below are the key components that power conversational AI systems. (Abdullahi et al., 2023)
2.1.1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a critical technology that enables AI systems to understand and process human language. It breaks down input into syntax (grammar and sentence structure), semantics (meaning), and intent (the user’s goal) to generate accurate and context-aware responses. NLP allows chatbots to handle diverse language variations, detect sentiment, and interpret conversational nuances.
Key Functions:
- Tokenization: Splitting sentences into words or phrases.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifying proper names, locations, dates, etc.
- Intent Recognition: Determining the purpose behind user queries.
- Sentiment Analysis: Understanding user emotions (e.g., frustration, excitement).
Use Cases:
- AI chatbots in customer support responding to complex inquiries.
- Virtual assistants understanding and executing user commands.
- Sentiment-based responses in social media monitoring tools.
2.1.2. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning (ML) is the backbone of AI-driven improvements in conversational systems. Unlike rule-based chatbots that rely on predefined scripts, ML models learn from historical interactions and user behavior, continuously refining their responses and decision-making processes. Through supervised and unsupervised learning techniques, AI can detect patterns, predict user intent, and adapt its responses over time.
Key Functions:
- Training Models: AI is trained on large datasets to understand diverse conversational patterns.
- Personalization: Chatbots tailor responses based on user history and preferences.
- Continuous Learning: AI refines its accuracy through feedback and new interactions.
Use Cases:
- AI-powered customer service chatbots improving response accuracy over time.
- Smart recommendation systems suggesting products based on user behavior.
- Fraud detection in financial AI assistants based on anomaly recognition.
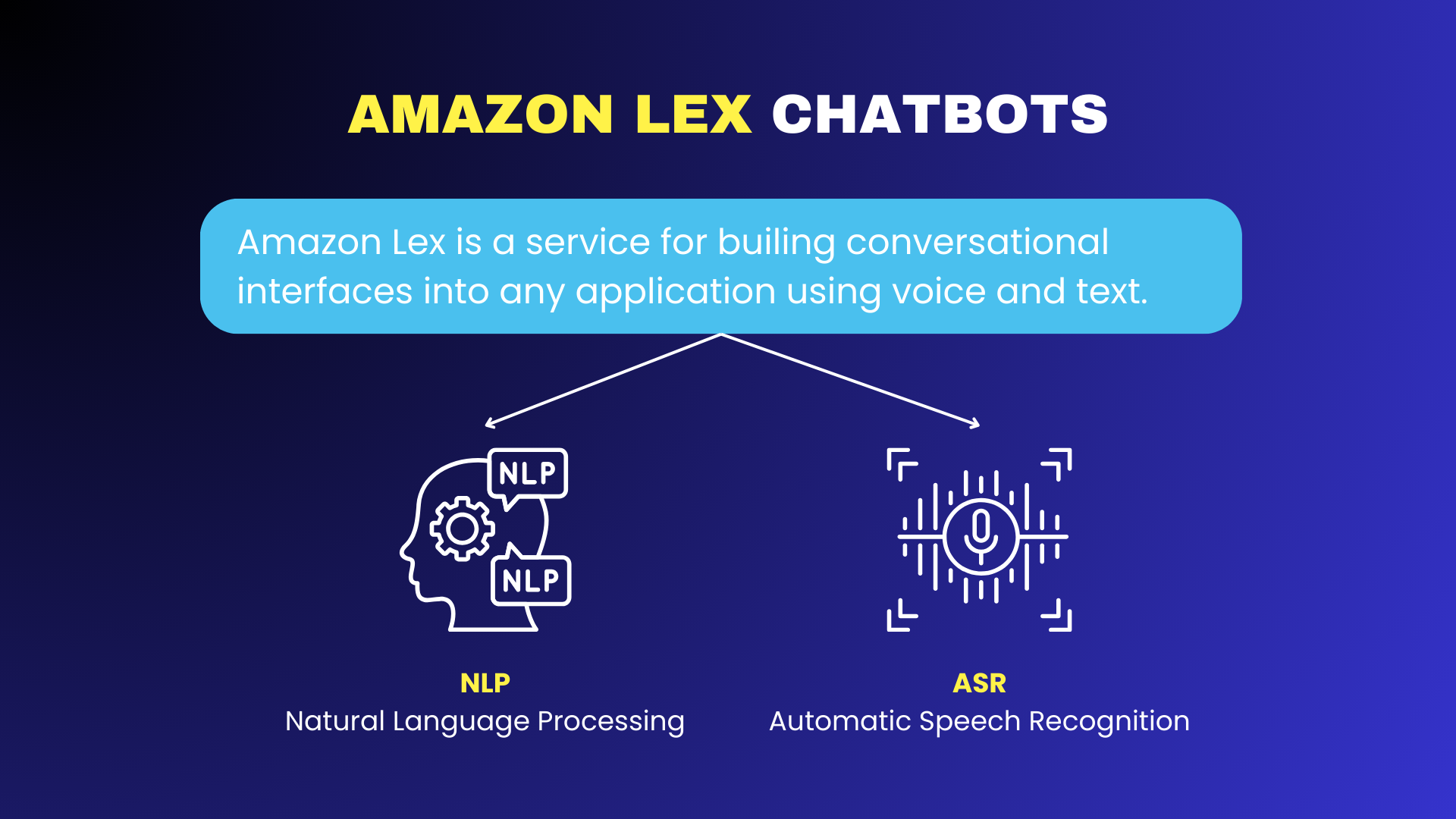
2.1.3. Speech Recognition
Speech recognition, also known as Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), enables AI to convert spoken language into text, allowing users to interact with virtual assistants and chatbots using voice commands. This technology is essential for hands-free applications and accessibility, bridging the gap between humans and machines in natural communication.
Key Functions:
- Voice-to-Text Conversion: Transcribing spoken words into digital text.
- Language and Accent Adaptation: Recognizing various accents and dialects.
- Noise Reduction: Filtering out background noise for improved accuracy.
Use Cases:
- Voice-activated virtual assistants like Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa.
- AI-powered transcription services for meetings and lectures.
- Voice command functionality in smart home devices and automotive assistants.
2.2 Features That Set Conversational AI Apart
Chatbots have long been used to automate conversations, but the evolution of artificial intelligence has given rise to conversational AI, a more sophisticated and intelligent system that surpasses traditional rule-based chatbots.
Unlike simple bots that follow scripted responses, conversational AI understands context, engages in multi-turn conversations, and integrates seamlessly with other AI tools to provide a much richer user experience. Here’s how these key features differentiate conversational AI from traditional chatbots (Gentsch, 2019).
2.2.1. Contextual Understanding: The Ability to Remember and Adapt
One of the biggest shortcomings of traditional chatbots is their inability to remember past interactions or adjust responses based on previous user inputs. They treat every query as an isolated event, which often leads to repetitive or irrelevant answers. Conversational AI, however, is designed to retain context throughout an interaction, ensuring that responses are logical, relevant, and personalized.
By leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning, conversational AI can analyze user intent, track past exchanges, and generate responses that align with the conversation’s flow. For example, if a customer previously inquired about a product’s price and later asks about payment options, the AI understands that both questions are related and responds accordingly without requiring the user to re-explain their request.
Contextual awareness is particularly important in customer service, where users expect chatbots to recognize past issues, preferences, or ongoing support tickets. This creates a more seamless and human-like interaction, reducing frustration and improving overall engagement.
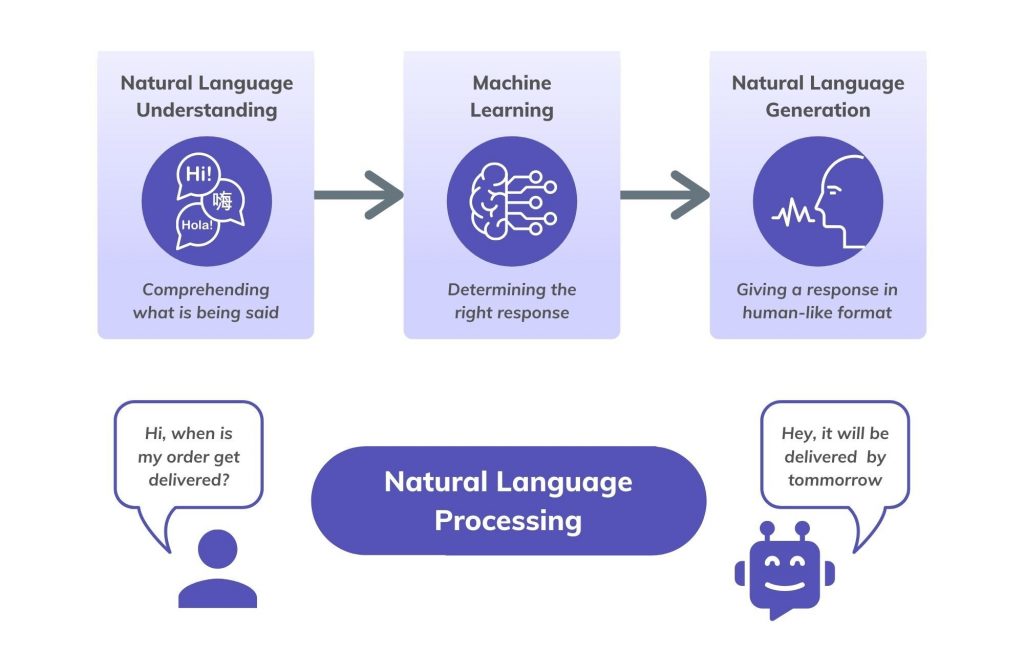
Natural Language Processing in Conversational AI
2.2.2. Multi-Turn Conversations: Engaging in More Human-Like Dialogues
Traditional chatbots are primarily built for single-turn interactions, meaning they can only handle one question at a time and often struggle with complex, multi-step requests. If a user asks a follow-up question, a rule-based chatbot may fail to connect it to the initial query, leading to disjointed and frustrating exchanges.
Conversational AI, on the other hand, is designed to manage multi-turn conversations, allowing it to handle layered interactions in a natural and intuitive way. Instead of simply providing one-off answers, it guides users through a structured dialogue, adapting its responses as the conversation progresses.
The ability to maintain fluid back-and-forth discussions makes conversational AI more effective in handling complex inquiries, troubleshooting issues, and delivering personalized recommendations.
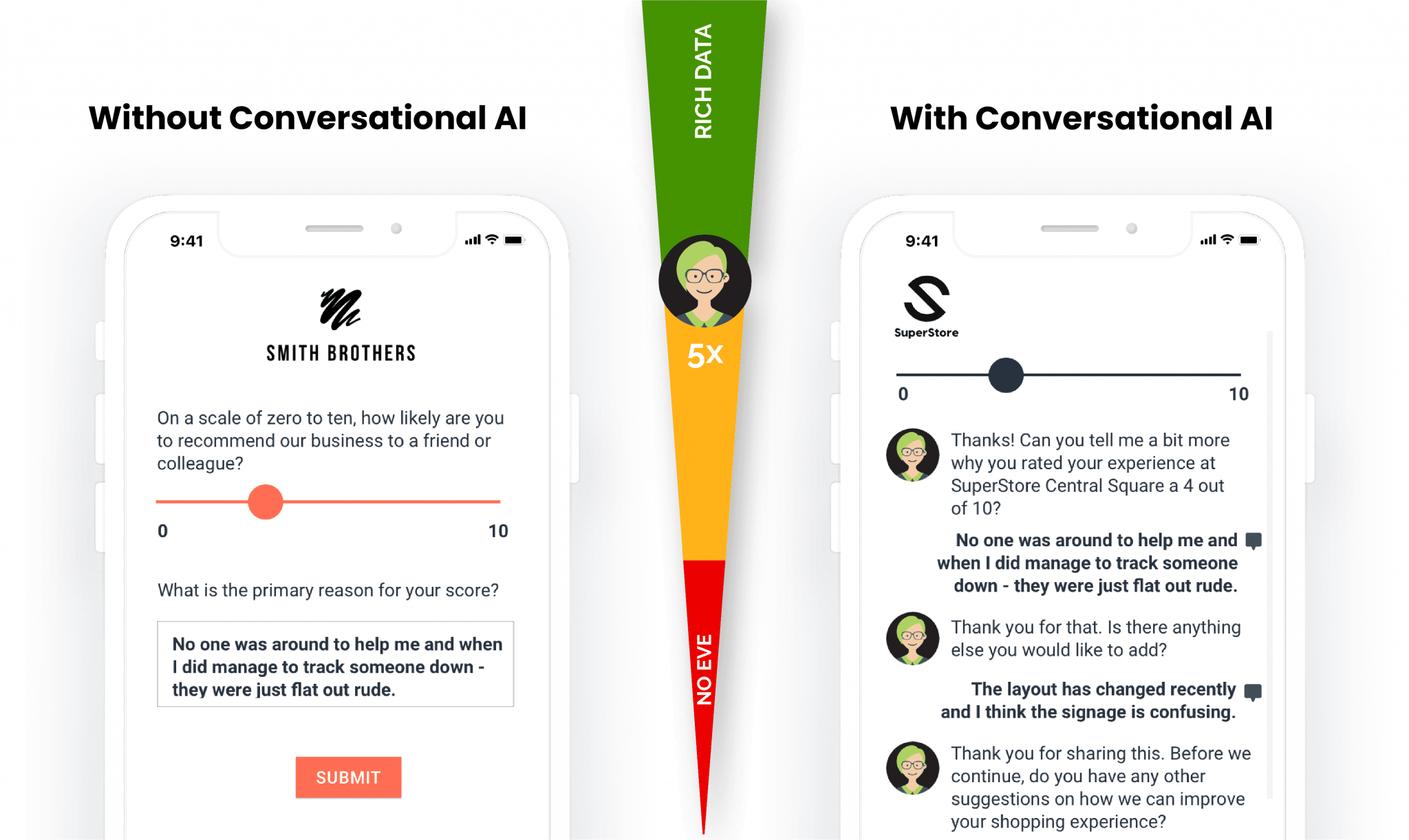
Human-like conversation optimization
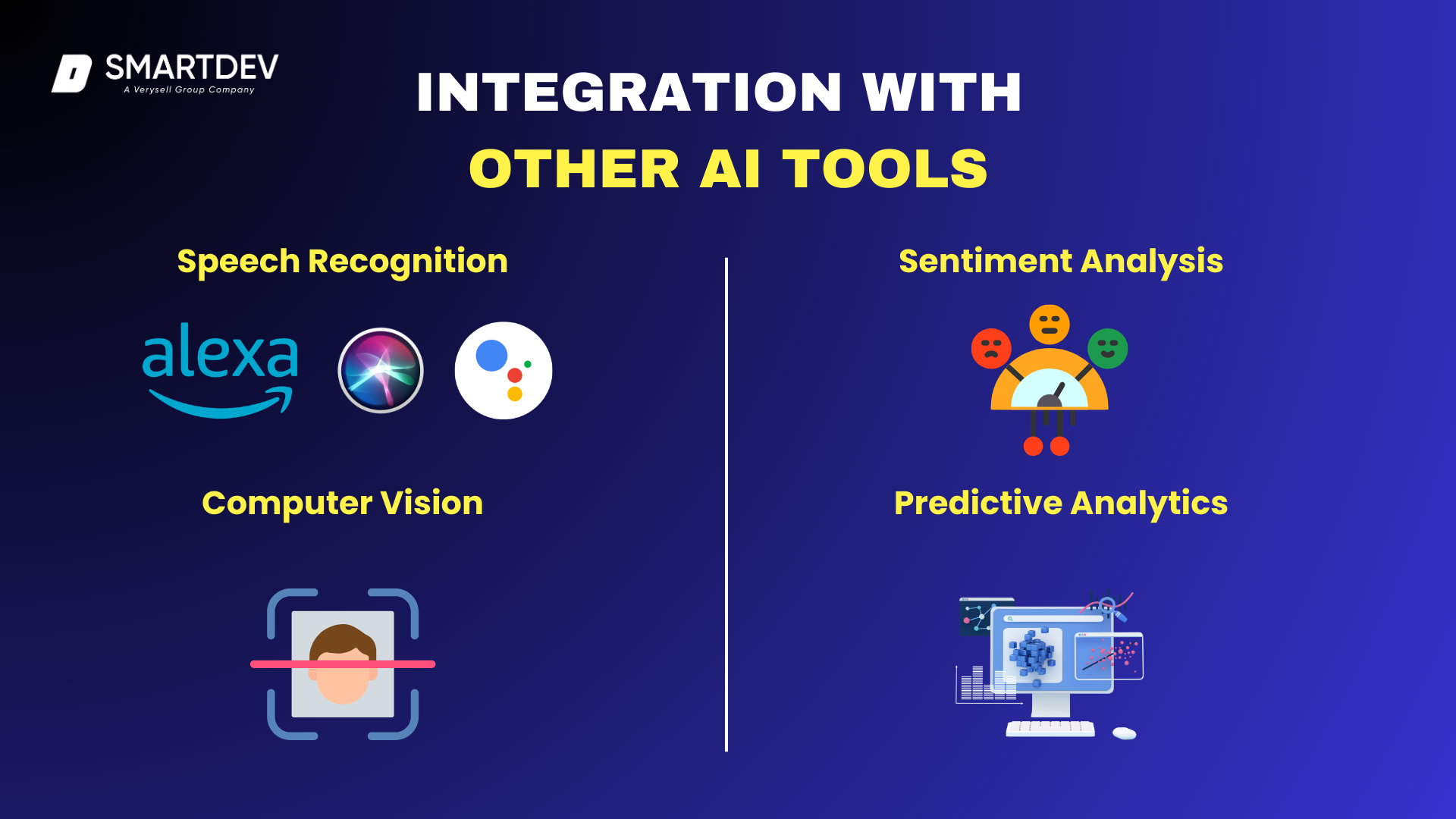
2.2.3. Integration with Other AI Tools: Expanding Capabilities Beyond Text
Conversational AI is not just limited to handling text-based queries—it integrates seamlessly with various AI-driven tools to enhance its functionality and provide more robust support. Unlike traditional chatbots that operate in isolation, conversational AI can work alongside:
- Speech Recognition: Enabling voice interactions for virtual assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri.
- Sentiment Analysis: Detecting user emotions to adjust responses accordingly (e.g., providing empathetic replies in customer complaints).
- Computer Vision: Allowing AI to interpret images and videos in applications like facial recognition for security or analyzing product photos in e-commerce.
- Predictive Analytics: Anticipating user needs based on behavior and previous interactions to suggest relevant actions or products.
By integrating with CRM systems, knowledge bases, automation tools, and IoT devices, conversational AI can perform tasks beyond simple text interactions. A banking AI, for instance, can pull real-time account details, process transactions, and alert users about suspicious activity, making it a truly intelligent digital assistant rather than just a scripted chatbot.
2.3 Typical Use Cases for Conversational AI
Conversational AI is transforming industries by making digital interactions more human-like, efficient, and responsive. Unlike traditional chatbots, which rely on predefined scripts, conversational AI leverages natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and deep learning to understand user intent, retain context, and provide personalized experiences.
Here are three key areas where conversational AI is making a significant impact. (Khan et al., 2023)
2.3.1. Virtual Assistants: A Smarter Way to Interact with Technology
Virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri are among the most widely recognized applications of conversational AI. These AI-driven assistants have become an integral part of daily life, helping users perform tasks, control smart devices, retrieve information, and even entertain.
How It Works
Virtual assistants use speech recognition, NLP, and contextual understanding to process spoken commands and respond accordingly. Over time, they refine their accuracy by learning from user interactions and adapting to personal preferences.
Common Applications
- Smart Home Control: Users can control lights, thermostats, and appliances with voice commands.
- Information Retrieval: Providing real-time news updates, weather forecasts, and general knowledge responses.
- Productivity Assistance: Scheduling appointments, setting reminders, and managing to-do lists.
- Entertainment & Media: Playing music, audiobooks, and streaming content on demand.

Virtual assistant use cases
2.3.2. Personalization in E-Commerce: Creating a Tailored Shopping Experience
Conversational AI is redefining e-commerce by offering highly personalized shopping experiences. Unlike traditional recommendation engines that rely solely on browsing history, AI-powered shopping assistants engage customers in dynamic, real-time conversations to better understand their preferences and needs.
How It Works
Conversational AI in e-commerce combines NLP, behavioral analytics, and customer profiling to offer tailored product recommendations and support. Instead of static filters, AI interacts with shoppers directly, helping them find products that match their tastes, budget, and past purchases.
 Common Applications
Common Applications
- Personalized Product Recommendations: AI suggests items based on user preferences, past purchases, and trending products.
- Conversational Shopping Assistants: Chatbots assist customers in finding the right size, style, or brand based on interactive conversations.
- Cart Abandonment Recovery: AI follows up with users who left items in their cart, offering personalized discounts or assistance to complete the purchase.
- Voice Shopping: Customers can search for and purchase items using voice-enabled AI assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant.
2.3.3. Advanced Customer Support: AI-Powered Conversations That Feel Human
One of the most impactful applications of conversational AI is customer support automation, where AI-driven chatbots and voice assistants help resolve inquiries quickly and efficiently. Unlike traditional support chatbots, which often rely on predefined scripts, conversational AI is capable of handling complex, multi-turn conversations while retaining context.
How It Works
AI-driven customer support systems use NLP, sentiment analysis, and deep learning models to interpret customer concerns and provide accurate responses. They can understand intent, analyze past interactions, and escalate issues to human agents when necessary.

Common Applications
- 24/7 Automated Support: AI handles routine customer queries without human intervention, providing instant assistance.
- Sentiment-Based Responses: AI detects frustration or urgency in customer messages and adapts its tone accordingly.
- Multi-Language Support: Businesses can serve global customers by deploying AI chatbots with multilingual capabilities.
- Seamless Human Escalation: When AI cannot resolve a query, it smoothly transfers the conversation to a human agent, providing them with relevant context.
Selecting the right solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and optimize operations.
Ready to explore more on AI virtual assistants in the workplace environment? Read more here:
3. Key Differences Between Chatbots and Conversational AI
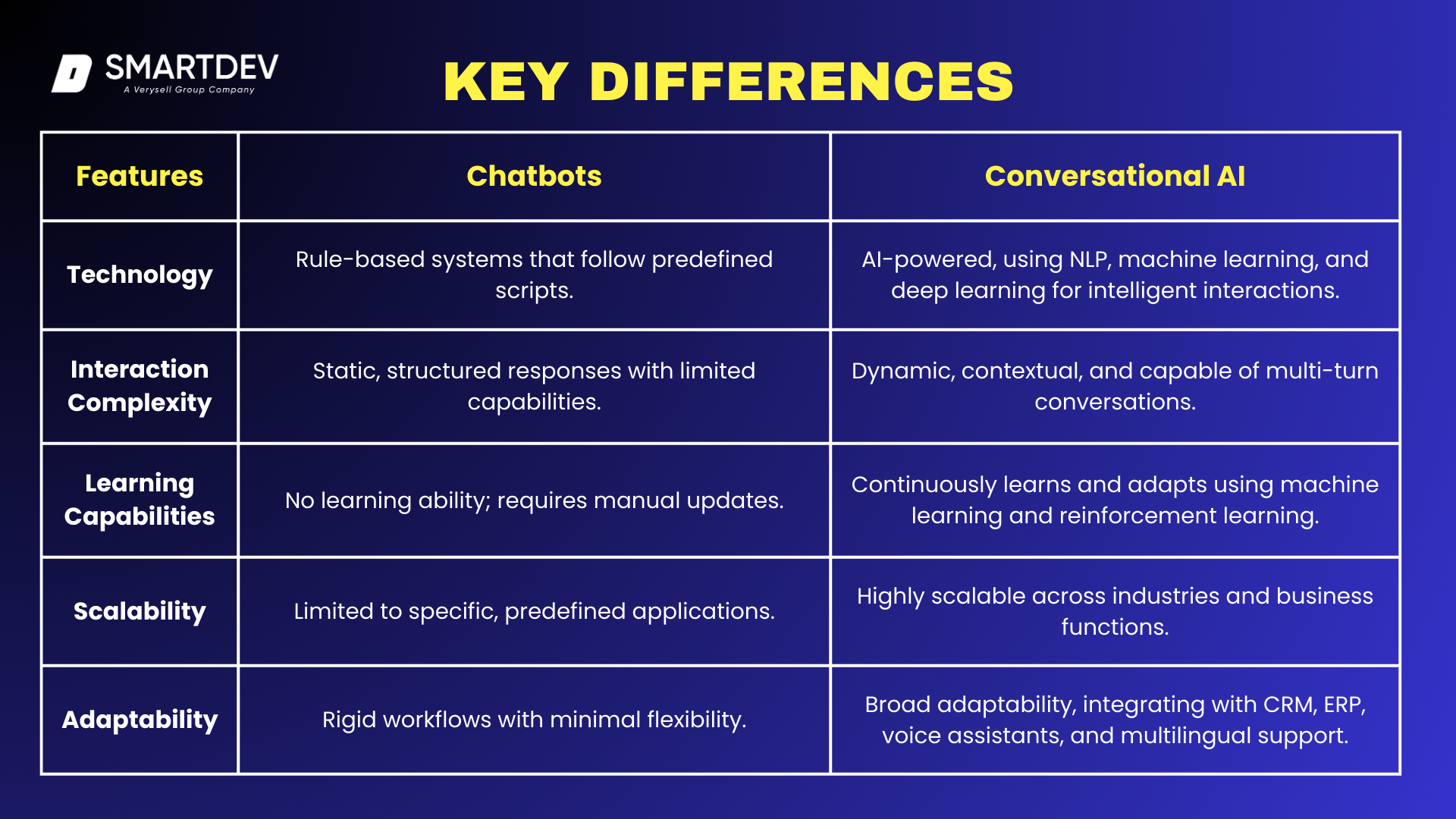
Chatbots and conversational AI are often used interchangeably, but they differ significantly in technology, complexity, learning ability, scalability, and adaptability. While both serve the purpose of automating conversations, their capabilities vary drastically.
Traditional chatbots rely on predefined rules and scripts, while conversational AI is powered by machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and deep learning to enable more human-like, adaptive, and context-aware interactions.
Let’s explore these key differences in detail.
3.1 Technology: Rule-Based Systems vs. AI and NLP
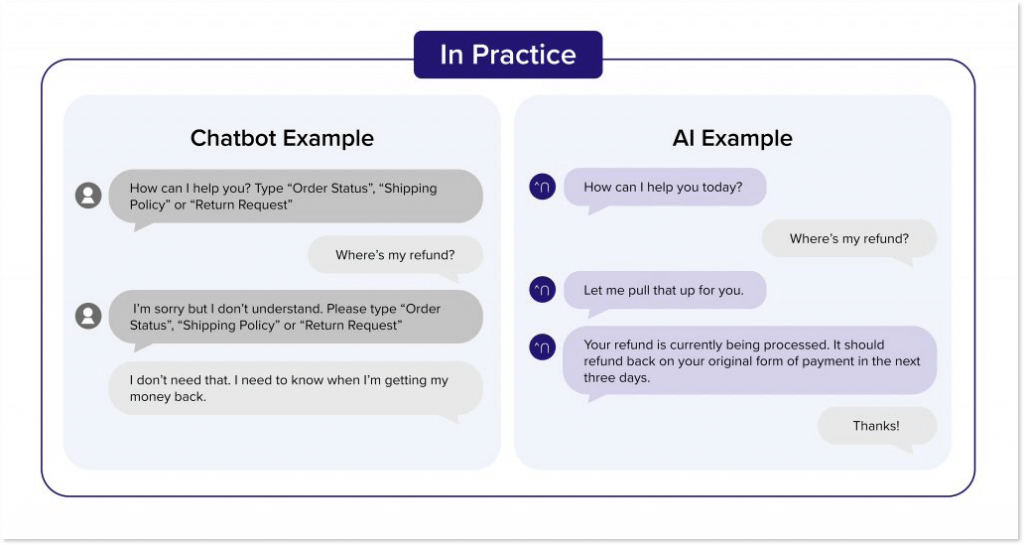
One of the fundamental differences between chatbots and conversational AI lies in the underlying technology. Traditional chatbots operate on rule-based frameworks where they follow a set of predefined scripts. They respond to user inputs by matching them with preprogrammed keywords or phrases. If a query does not fit within these predefined rules, the chatbot often fails to provide an accurate response.
Conversational AI, however, leverages advanced AI models, NLP, and machine learning to understand, interpret, and generate human-like responses. It goes beyond keyword matching by analyzing sentence structure, intent, and sentiment to deliver more natural and intelligent conversations. Unlike rule-based chatbots, conversational AI continuously learns and adapts, improving over time through data-driven insights.
Example: A rule-based chatbot for an e-commerce store might recognize “order status” as a trigger phrase and provide a static response. In contrast, a conversational AI assistant can handle variations like “Where’s my package?”, “Has my order shipped yet?”, or “Track my last purchase”, and respond contextually.
3.2 Complexity of Interactions: Static Responses vs. Contextual Conversations
Traditional chatbots are highly structured and limited in scope. They rely on decision trees and static, pre-programmed responses, which means they can only handle straightforward, repetitive queries. If a user deviates from the expected input format, the chatbot often responds with “I don’t understand” or prompts the user to rephrase their question.
Conversational AI, on the other hand, enables dynamic and contextually aware interactions. It can manage multi-turn conversations, where it remembers the user’s previous inputs and provides responses that align with the broader context of the conversation. This allows for more natural, human-like interactions, reducing user frustration and increasing efficiency.
Example:
- Chatbot: A traditional banking chatbot can answer simple questions like “What’s my balance?” but struggles with follow-up inquiries.
- Conversational AI: A smart banking assistant can handle a sequence of requests:
- “What’s my balance?”
- “Can you show my last five transactions?”
- “Set up a payment for my electricity bill from my savings account.”
- The AI retains context and responds intelligently, making the experience seamless.
3.3 Learning Capabilities: Pre-Programmed Responses vs. Machine Learning
Traditional chatbots do not learn from interactions—they require manual updates and programming whenever a business needs to expand their capabilities. Their responses remain static and predictable, which means businesses must frequently adjust scripts to accommodate new inquiries.
Conversational AI, however, continuously learns and evolves using machine learning algorithms. It analyzes past interactions, customer behavior, and data patterns to refine its responses over time. With reinforcement learning, conversational AI can detect inefficiencies in conversations, adapt to user preferences, and improve accuracy with each interaction.
Example:
- Chatbot: A FAQ-based chatbot for a retail store might require manual updates when new promotions are introduced.
- Conversational AI: An AI-powered assistant can learn from purchase trends and automatically update its recommendations based on seasonal changes, user preferences, or recent customer interactions.
3.4 Scalability: Limited Applications vs. Versatile Use Cases
A traditional chatbot is usually built for a specific purpose, such as answering FAQs, handling basic customer support queries, or assisting with website navigation. While effective for small-scale applications, these chatbots struggle to scale as businesses grow and customer needs evolve.
Conversational AI, in contrast, offers scalability across multiple functions and industries. It can handle thousands of conversations simultaneously, process complex requests, and integrate with various business applications, databases, and third-party services. AI-powered assistants can support customer service, sales, marketing, HR, healthcare, finance, and more—making them a versatile tool for enterprises looking to enhance digital interactions.
Example:
- Chatbot: A chatbot designed for a telecom company might only answer questions about mobile data plans.
- Conversational AI: A telecom AI assistant can provide plan recommendations, assist with billing, troubleshoot technical issues, offer multilingual support, and even cross-sell additional services based on the user’s past interactions.
3.5 Adaptability: Narrow Use Cases vs. Broad Integration
Traditional chatbots are rigid and limited in adaptability, meaning they work well within predefined workflows but struggle to handle unexpected queries or integrate with other tools. If a chatbot is designed to answer order-related questions, it cannot suddenly start assisting users with refund policies unless it has been manually programmed to do so.
Conversational AI, however, is highly adaptive and capable of integrating with various AI-driven systems. It can connect with CRM platforms, ERP systems, analytics tools, voice recognition software, and IoT devices, making it a dynamic and scalable solution for businesses looking to enhance customer interactions.
Additionally, conversational AI supports multilingual conversations, sentiment analysis, and voice-to-text capabilities, making it far more versatile than traditional chatbots. It can understand slang, regional dialects, and cultural nuances, ensuring more effective and inclusive communication.
Example:
- Chatbot: A travel chatbot can answer pre-programmed FAQs about flight schedules but cannot handle personalized itinerary planning.
- Conversational AI: An advanced AI-powered travel assistant can provide personalized recommendations, book flights, suggest hotels, notify users of weather changes, and even analyze past trips to offer better suggestions for future travel.
4. Real-life Examples
4.1 Successful use cases of chatbots
4.1.1. Tidio Chatbot
Tidio is a widely used chatbot solution, particularly in the e-commerce space. It enables small and medium-sized businesses to automate customer support, engage website visitors, and capture leads efficiently. Tidio’s chatbot can provide instant responses to frequently asked questions, handle basic order tracking, and integrate with messaging apps like Facebook Messenger and email. One of its standout features is its hybrid approach, allowing live agents to step in seamlessly when a chatbot cannot resolve an issue.
For example, an online clothing retailer using Tidio might set up automated responses for common inquiries such as “Where is my order?” or “What is your return policy?” Without human intervention, the chatbot provides quick, accurate responses, improving customer satisfaction and reducing support costs.
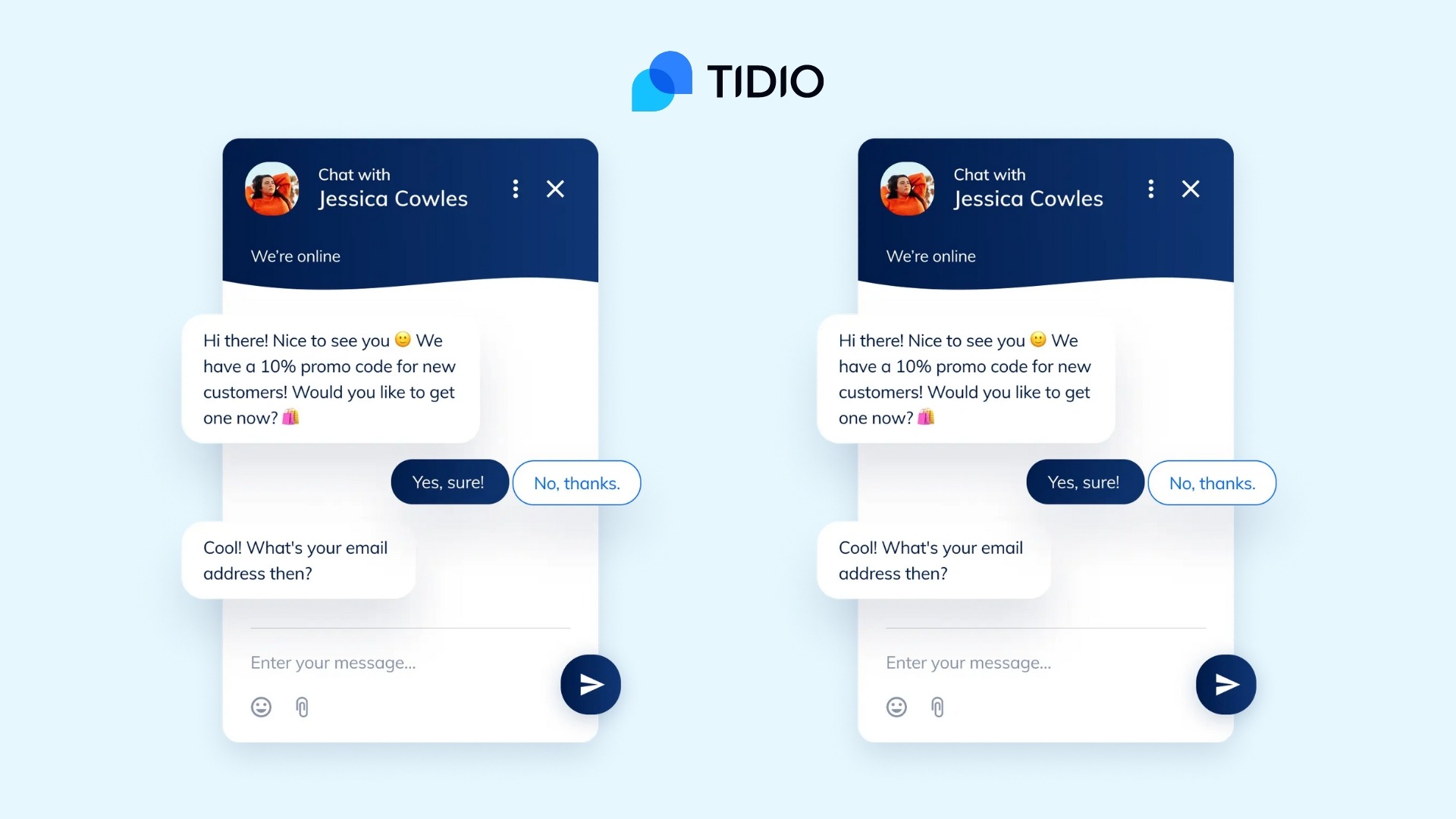
Tidio Chatbot
4.1.2. Drift
Drift is a powerful conversational marketing chatbot that is widely adopted in B2B sales and marketing environments. Unlike standard support chatbots, Drift’s AI-driven chatbots are designed to qualify leads, book meetings, and personalize customer interactions. Companies use Drift to engage website visitors in real-time, guiding them through the sales funnel without requiring human input at every stage.
For instance, a SaaS company might use Drift to initiate a conversation with a visitor based on their browsing behavior. If the visitor downloads an e-book, Drift’s chatbot can follow up with a personalized message offering a demo. This level of proactive engagement significantly increases conversion rates and enhances the customer journey.
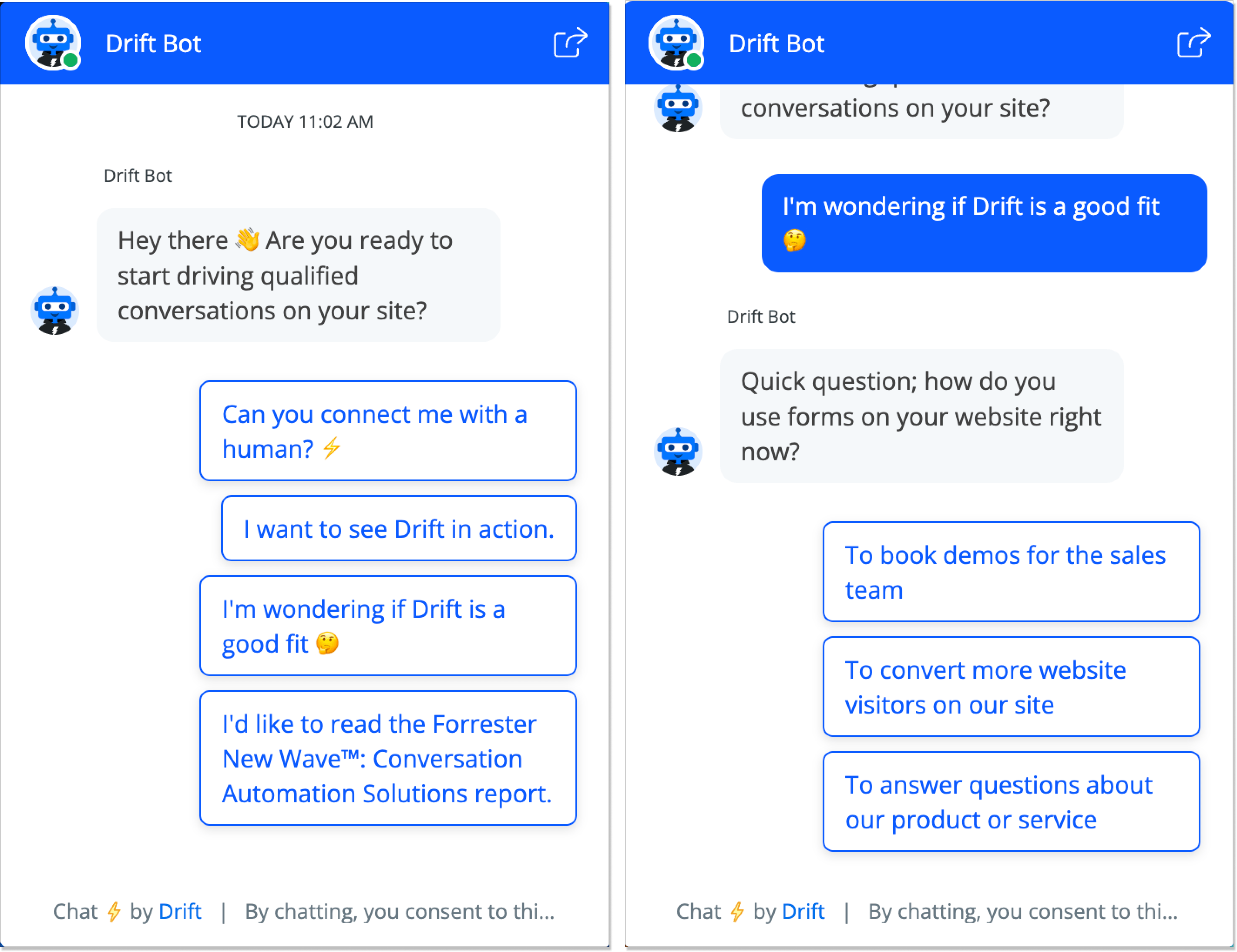
Drift Chatbot
4.1.3. HubSpot’s Sales Bot
HubSpot’s Sales Bot is integrated within HubSpot’s CRM, offering an intelligent way to streamline sales and customer service interactions. It helps businesses capture leads, route them to the right teams, and automate follow-ups.
A marketing agency, for example, can use HubSpot’s chatbot to qualify potential clients by asking pre-set questions such as “What is your budget?” or “What services are you interested in?” Based on the responses, the bot automatically assigns the lead to the appropriate sales representative, ensuring a smooth and efficient sales process.
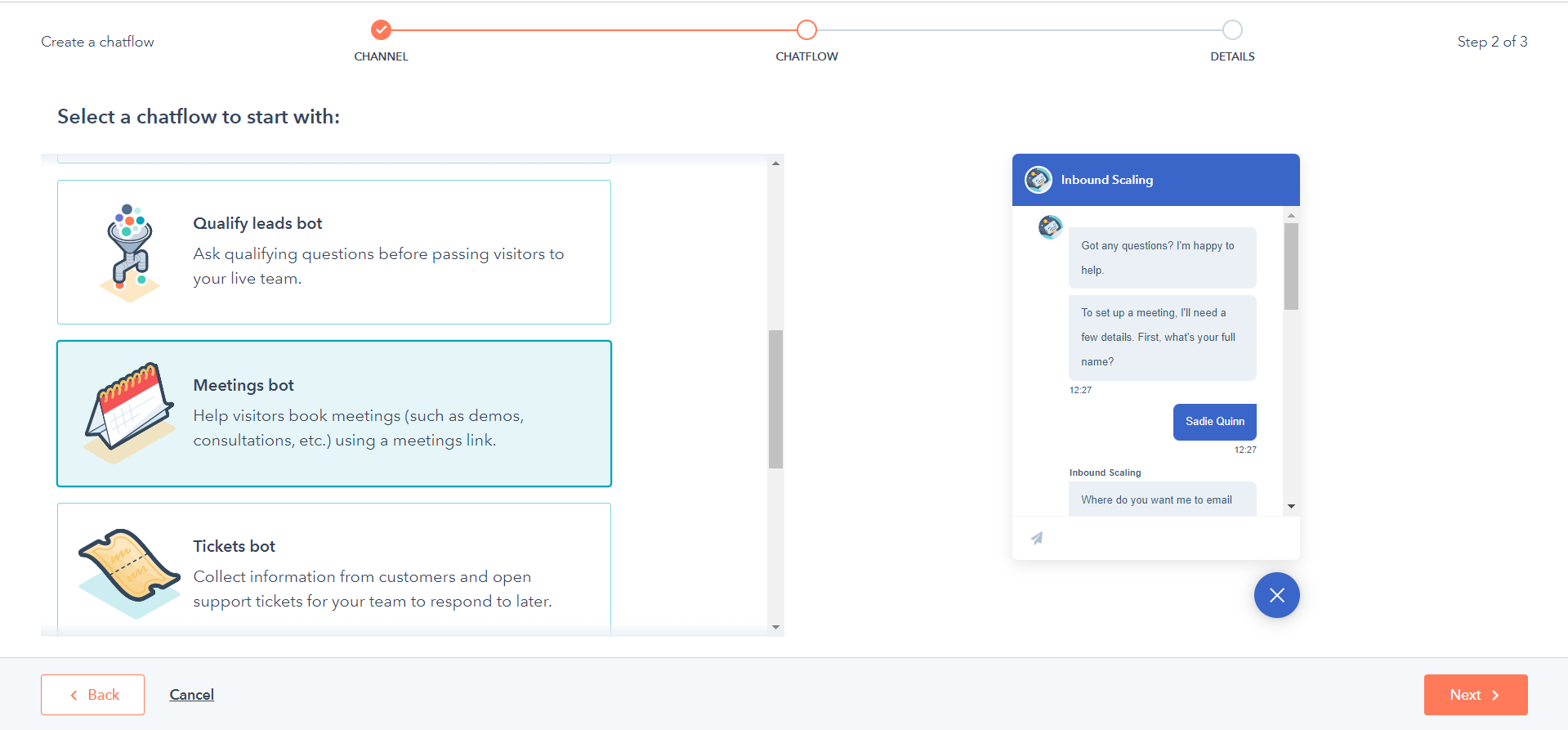
HubSpot Chatflow Bot
4.2 Top Conversational AI
4.2.1. Siri and Alexa
Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa are two of the most widely recognized conversational AI assistants. Unlike traditional chatbots, these AI-driven systems utilize natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand and respond to user requests in a conversational manner.
Siri, integrated into Apple devices, assists users with tasks such as sending messages, setting reminders, and providing weather updates. Its ability to recognize voice commands and learn user preferences makes it a valuable personal assistant. Similarly, Alexa powers Amazon Echo devices, enabling voice-activated control over smart home devices, music playback, and shopping experiences.
For example, a user can say, “Alexa, reorder my last purchase from Amazon,” and the AI assistant will process the request based on past shopping behavior. This level of personalization and automation enhances user convenience, setting Conversational AI apart from basic chatbots. (Espinoza-Hernández, 2023)
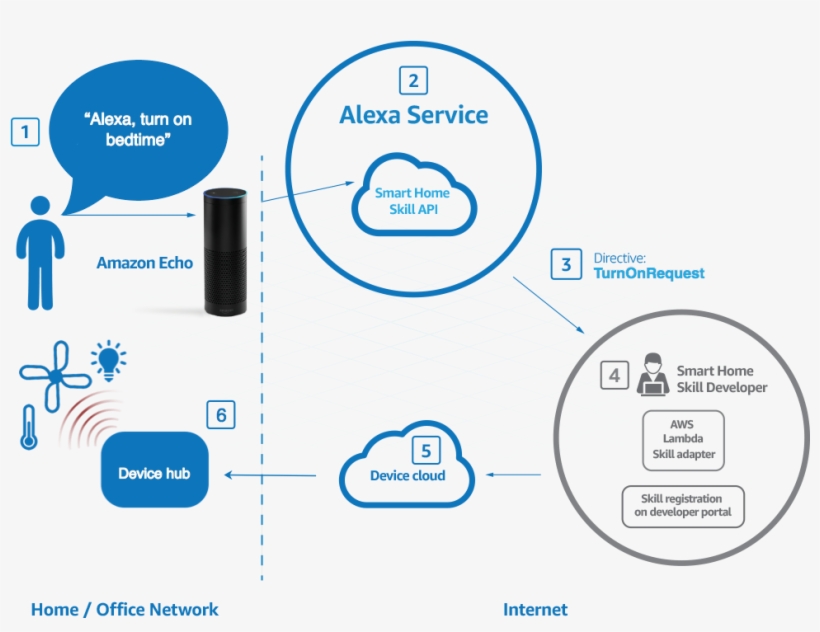
How Alexa works
4.2.2. Google Duplex
Google Duplex is an advanced AI-powered system capable of engaging in human-like conversations to complete real-world tasks. One of its most impressive applications is making phone calls on behalf of users for tasks such as booking restaurant reservations or scheduling hair appointments.
For example, a user can say, “Hey Google, book a haircut appointment for Saturday at 10 AM.” Google Duplex then calls the salon, interacts with the receptionist using natural speech patterns, and confirms the booking. Unlike chatbots, which follow predefined scripts, Google Duplex can understand nuances, respond dynamically, and handle real-time scheduling conflicts.

How Google Duplex works
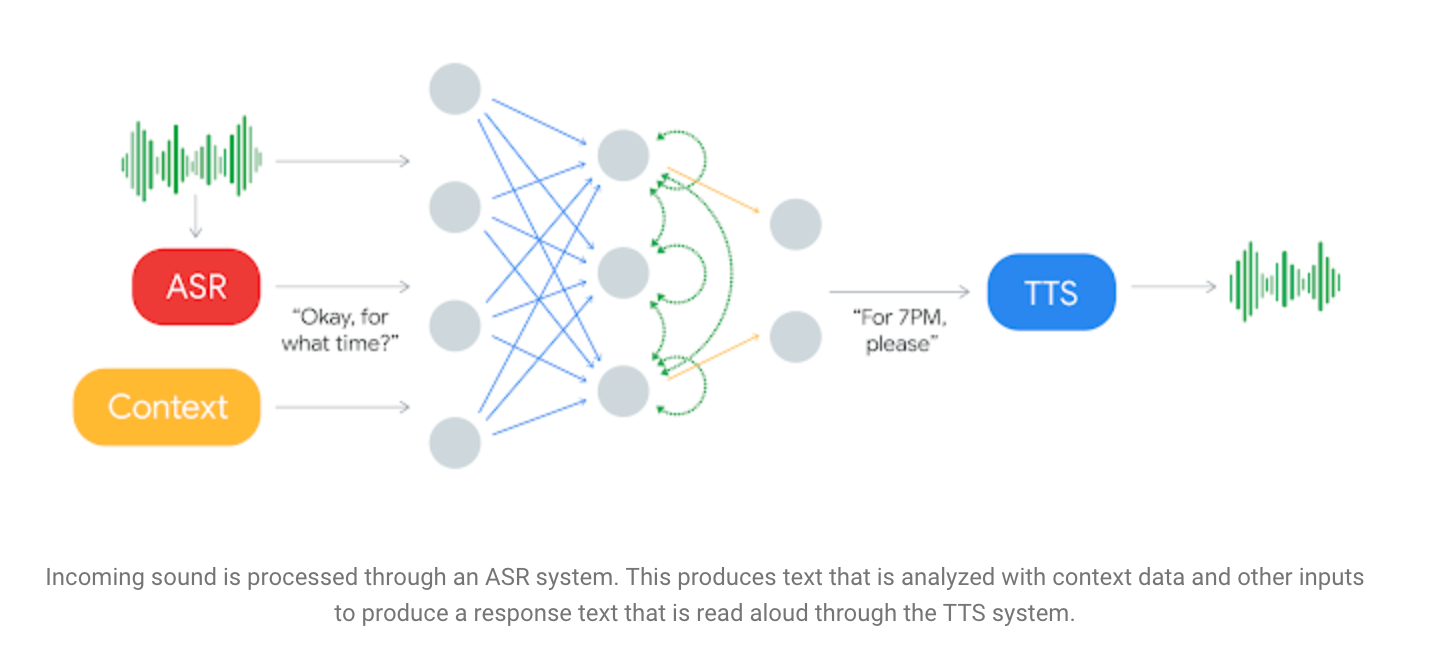
The ASR system of Google Duplex
4.2.3. Zendesk AI
Zendesk AI enhances customer support by leveraging machine learning and NLP to provide accurate and context-aware responses. Unlike traditional chatbots that rely on preset decision trees, Zendesk AI continuously learns from customer interactions, improving its ability to resolve inquiries over time.
For instance, a large e-commerce platform using Zendesk AI can automate responses to support tickets related to order tracking, refunds, and product recommendations. If a customer asks, “I received a damaged product; what should I do?” the AI can analyze previous interactions, suggest solutions, and escalate the case if necessary, ensuring a seamless support experience.
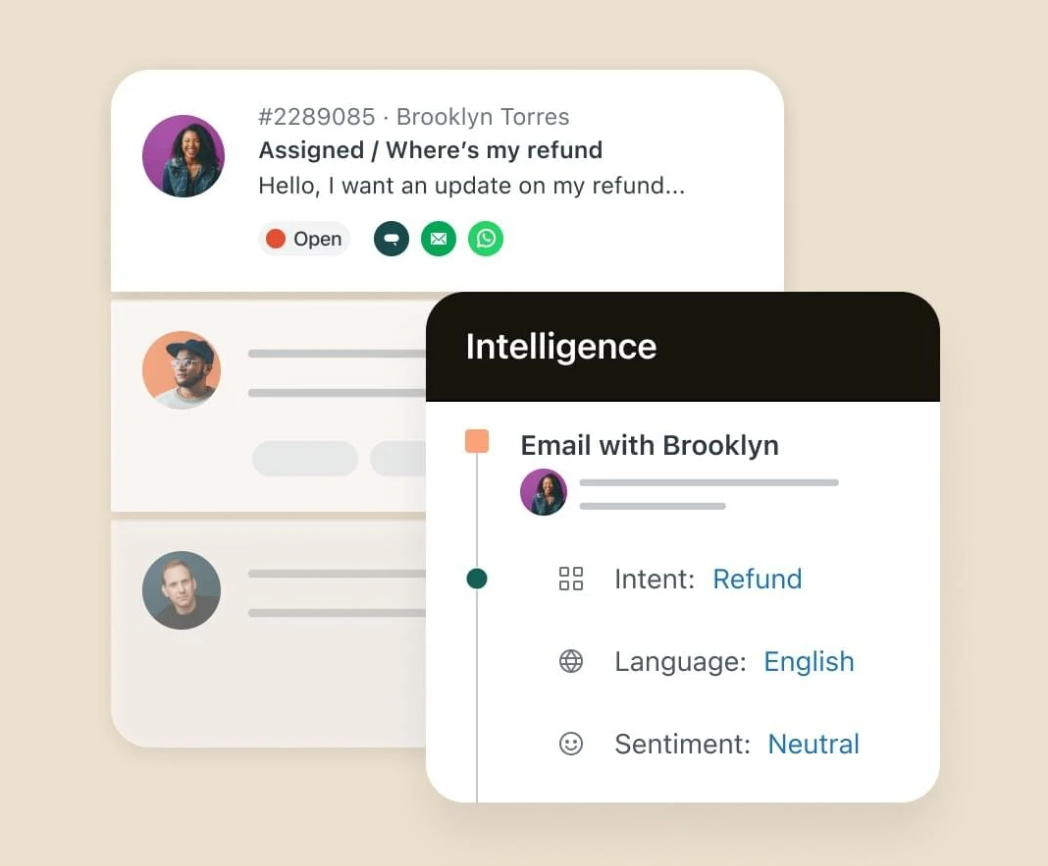
Zendesk AI
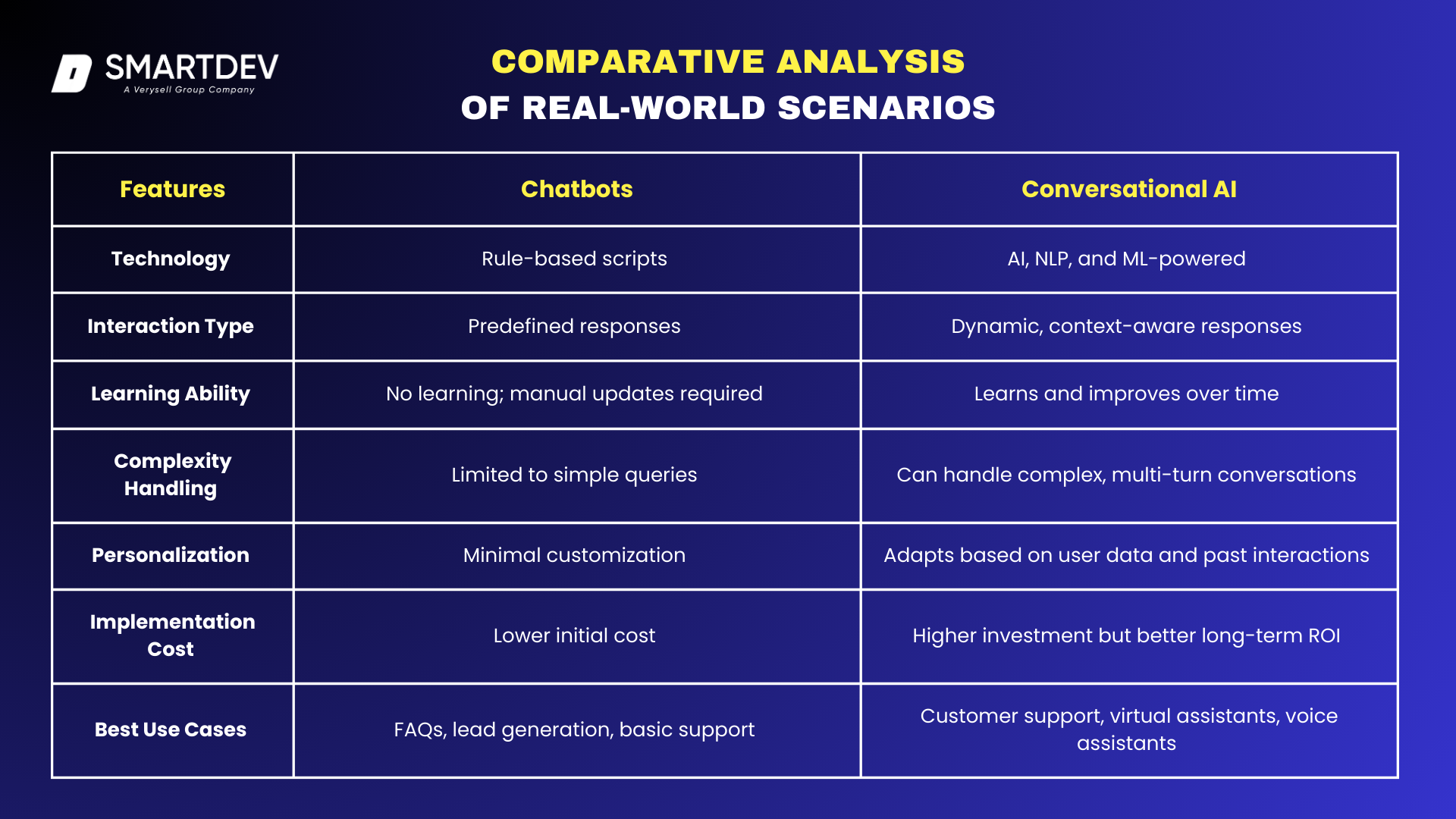
4.3 Comparative Analysis of Real-World Scenarios
4.3.1. Customer Support in E-Commerce
A small online store might implement Tidio Chatbot to answer FAQs about order tracking and return policies. While effective for routine inquiries, it struggles with handling complex or nuanced customer complaints. In contrast, a large e-commerce platform like Amazon leverages Conversational AI (Alexa and Zendesk AI) to provide a far more personalized experience. Alexa can understand a user’s past shopping behavior and make recommendations, while Zendesk AI continuously improves its customer support interactions based on user history.
4.3.2. Booking Appointments
Many businesses use basic chatbots to handle appointment scheduling by allowing customers to select available time slots. However, these bots fail when an appointment conflict arises. Google Duplex, on the other hand, can call a business on behalf of a user, negotiate timing, and make real-time adjustments based on availability. This demonstrates the key advantage of Conversational AI: handling dynamic, real-world situations more effectively than rule-based chatbots.
4.3.3. Lead Generation and Sales
Companies like SaaS providers use Drift Chatbot to qualify leads based on pre-defined questions. This is effective for initial engagement but may feel impersonal if the chatbot cannot respond beyond its script. HubSpot’s Sales Bot, which integrates with a CRM, offers a slightly more advanced approach by routing leads to appropriate teams. However, a fully AI-driven system that utilizes NLP and machine learning could go a step further, offering personalized responses based on previous interactions and customer data.
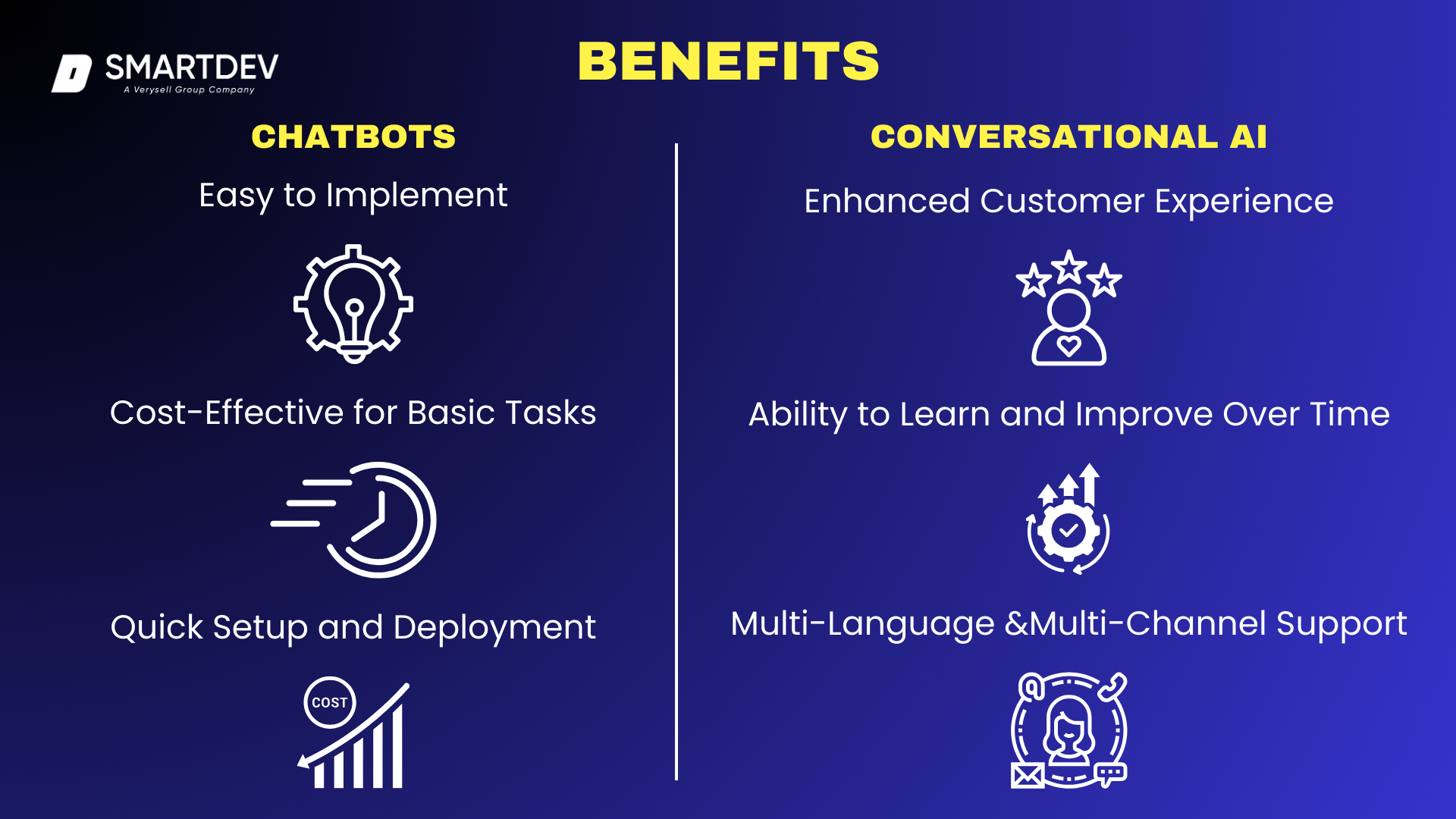
5. Benefits of Chatbots vs Conversational AI
5.1 Benefits of Chatbots
Easy to Implement
Chatbots are one of the most accessible automation tools for businesses. They can be quickly deployed on websites, social media platforms, and messaging apps, helping businesses provide immediate assistance to users.
Many chatbot platforms offer pre-built templates and drag-and-drop interfaces, allowing businesses to set up a chatbot with minimal technical expertise. This ease of implementation ensures that even small businesses can leverage chatbot technology without requiring extensive IT support or development resources.
Cost-Effective for Basic Tasks
For businesses looking to reduce operational costs, chatbots provide a highly affordable solution. Unlike human agents, who require salaries, training, and infrastructure, chatbots can handle thousands of inquiries simultaneously at no additional cost. They are particularly useful for repetitive and predictable interactions, such as responding to frequently asked questions (FAQs), scheduling appointments, processing simple transactions, and capturing lead information.
By automating these basic tasks, businesses can free up human agents to focus on more complex and high-value interactions, improving overall efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Quick Setup and Deployment
Unlike Conversational AI, which requires extensive data training and optimization, chatbots can be deployed within hours or days. This makes them an attractive solution for businesses that need an immediate automation tool to handle customer interactions.
Chatbots can be integrated with CRM systems, e-commerce platforms, and customer service tools, ensuring seamless interaction between automation and human support. Additionally, their predefined workflows ensure a smooth onboarding process, making them a practical choice for businesses looking to implement AI-driven interactions without significant development time.
5.2 Benefits of Conversational AI
Enhanced Customer Experience
Conversational AI provides a significantly more sophisticated and engaging customer experience than traditional chatbots. Unlike scripted responses, Conversational AI understands intent, context, and sentiment, enabling it to engage in human-like interactions. It can manage multi-turn conversations, follow up on previous interactions, and provide personalized recommendations based on user behavior.
This ability to offer natural, fluid, and context-aware conversations leads to higher customer satisfaction and a more seamless experience across digital touchpoints.
Multi-Language and Multi-Channel Support
One of the most powerful features of Conversational AI is its ability to support multiple languages and operate across various communication channels. Unlike basic chatbots that may require separate implementations for different platforms, Conversational AI can be integrated seamlessly across websites, mobile apps, social media, voice assistants, and even call centers. With natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, it can understand and respond in multiple languages, making it an ideal solution for global businesses that serve diverse customer bases.
For example, a multinational retail company using Conversational AI can provide real-time, localized support in different languages, ensuring that customers from different regions receive the same level of service. This enhances brand trust and eliminates the need for large multilingual support teams.
Ability to Learn and Improve Over Time
Unlike traditional chatbots, which operate on fixed decision trees, Conversational AI systems utilize machine learning (ML) and natural language understanding (NLU) to continuously refine their responses. Every interaction provides new data for AI models to learn from, improving their accuracy and relevance over time. This means that instead of requiring manual updates, Conversational AI can self-optimize to provide better responses based on user interactions.
For example, an AI-powered customer support assistant using Zendesk AI can analyze thousands of customer queries and automatically suggest improved responses based on past resolutions. Over time, it identifies common patterns, understands user intent more accurately, and reduces the need for human intervention. This adaptive learning capability makes Conversational AI a powerful long-term investment for businesses seeking to enhance automation and efficiency.
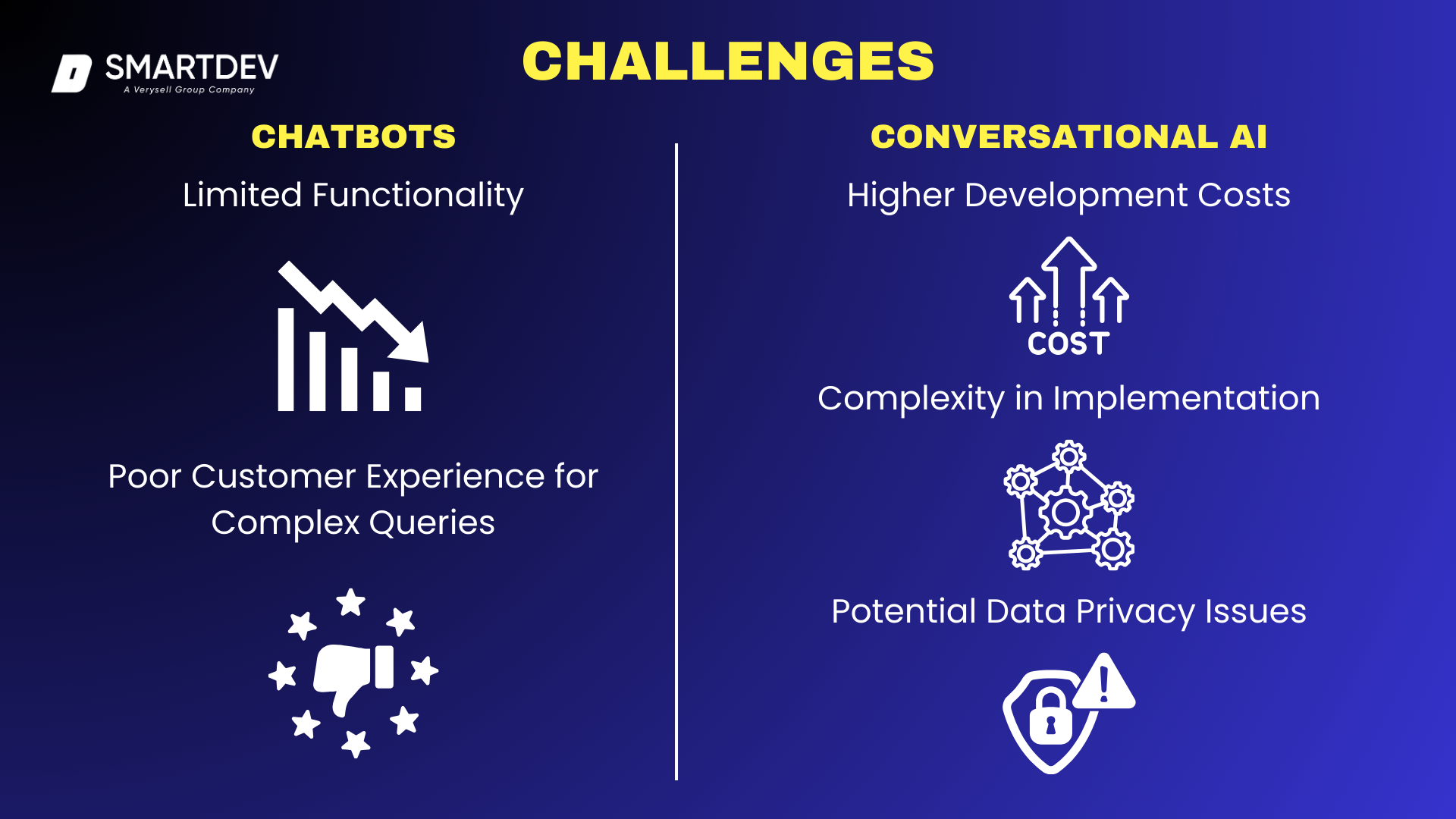
6. Challenges and Limitations
6.1 Challenges of Chatbots
Limited Functionality
While chatbots are effective at handling predefined tasks, their capabilities are inherently limited. They operate using a rule-based approach, meaning they can only respond to inquiries they have been programmed for. If a customer asks a question outside of the chatbot’s scope, it may provide inaccurate or irrelevant answers, leading to frustration.
For example, a banking chatbot may effectively answer “What is my account balance?” but struggle with complex queries like “What are the best investment options for my financial profile?”
Poor Customer Experience for Complex Queries
Since chatbots lack the ability to understand nuanced or multi-layered queries, they often fail in customer service scenarios requiring deeper contextual awareness. When users encounter problems beyond the chatbot’s programmed capabilities, the experience can become frustrating, leading to higher customer churn.
Customers often expect quick solutions, and if a chatbot forces them to navigate a rigid menu without resolving their concerns, they may abandon the interaction altogether.
6.2 Limitations of Conversational AI
Higher Development Costs
Implementing Conversational AI requires significant investment in data training, AI model development, and system integration. Unlike basic chatbots, which can be set up quickly, Conversational AI solutions involve natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, which require substantial time and resources to develop and refine.
Businesses must invest in AI training, data labeling, and ongoing improvements, making it a costly solution, particularly for small and mid-sized enterprises.
Complexity in Implementation
Unlike simple rule-based chatbots, which can be integrated into customer service workflows with minimal effort, Conversational AI requires complex backend systems to function effectively. This includes API integrations, data analytics pipelines, and AI model training processes.
Businesses must also continuously fine-tune their AI models to ensure they remain relevant and accurate. Furthermore, AI-driven virtual assistants require robust monitoring and maintenance to handle evolving user behavior and preferences.
Potential Data Privacy Issues
Since Conversational AI collects and processes large volumes of user data, businesses must implement strict security and compliance measures to protect customer privacy. AI-driven assistants analyze and store sensitive information, such as personal details, payment history, and conversation logs, making them attractive targets for cyber threats.
Organizations deploying Conversational AI must comply with stringent data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, to ensure user data is safeguarded from breaches and misuse.
7. How to Choose Between Chatbots and Conversational AI
Selecting the right solution between chatbots and Conversational AI depends on several critical factors. While chatbots are suitable for basic automation, Conversational AI is designed for more complex, human-like interactions. Businesses must analyze their specific needs before deciding which technology to implement.
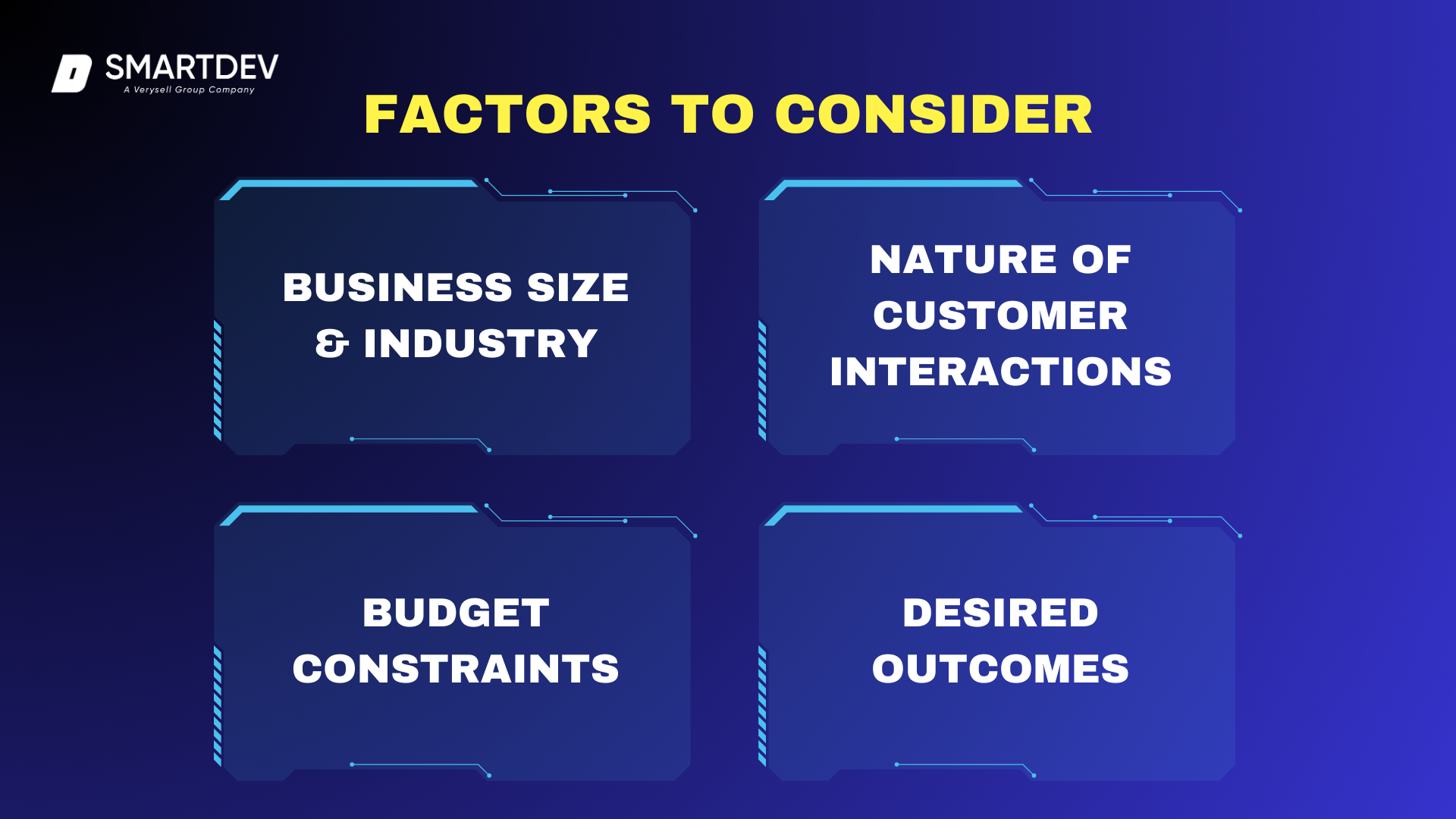
7.1 Factors to Consider
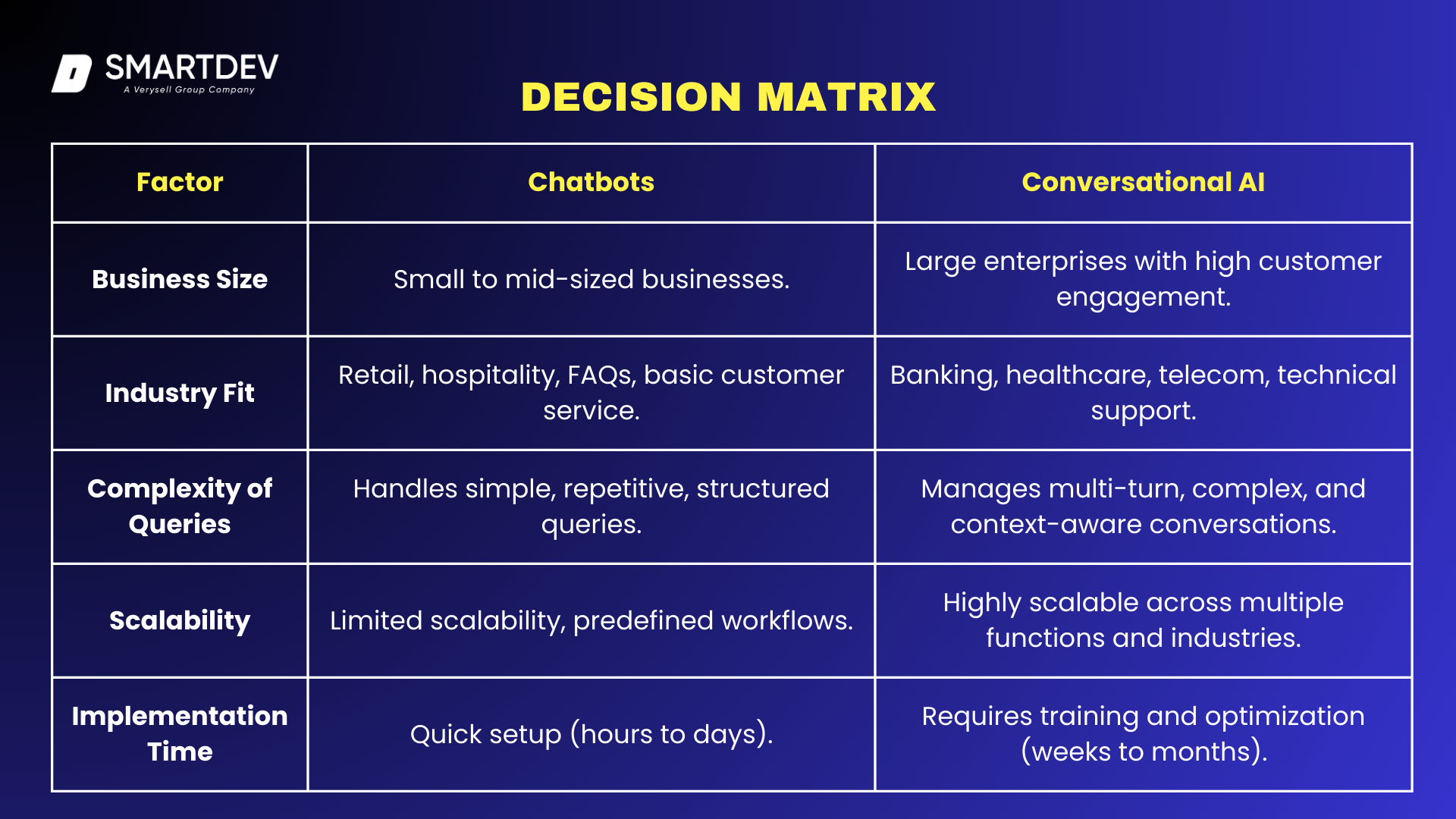
Business Size and Industry
The size of a business and the industry it operates in significantly impact whether chatbots or Conversational AI is the right fit. Small businesses and startups with limited resources often find chatbots a cost-effective way to automate customer service without requiring a large technical team. Industries with straightforward customer inquiries, such as retail and hospitality, benefit from chatbots for handling tasks like FAQs, order tracking, and simple bookings.
Conversely, enterprises dealing with high-volume, complex customer interactions, such as banking, healthcare, and telecommunications, require Conversational AI to offer personalized and context-aware interactions. Industries that rely on voice-based assistants, such as smart home technology or automotive services, also benefit from Conversational AI due to its ability to process natural language efficiently.
Nature of Customer Interactions
The complexity of customer inquiries is a key factor in choosing between chatbots and Conversational AI. If customer queries are mostly predictable, structured, and repetitive, chatbots are highly effective. For example, an airline company might use a chatbot to assist customers with check-in procedures, baggage policies, and flight status inquiries.
However, businesses handling multi-turn conversations with varying customer needs, such as technical support, medical consultations, or financial advisory services, require Conversational AI. AI-driven virtual assistants can analyze past interactions, detect intent, and provide more tailored responses, making them superior for customer engagement requiring deeper context.
Budget Constraints
Budget is often a deciding factor when selecting between chatbots and Conversational AI. Chatbots are generally more affordable since they are rule-based, require minimal customization, and can be implemented quickly. Businesses looking for a low-cost automation solution for customer support and lead generation may find chatbots to be the most feasible option.
On the other hand, Conversational AI requires significant investment in terms of AI model training, data processing, and system integration. Large enterprises with high customer engagement levels and long-term automation goals may find that the higher initial cost of Conversational AI pays off through improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Desired Outcomes
Companies must define their goals before implementing either technology. If the primary objective is to reduce human workload for repetitive inquiries and streamline simple transactions, chatbots provide an effective solution. However, if the goal is to enhance customer relationships, provide multilingual support, and improve customer retention through personalized engagement, Conversational AI offers more value in the long run.
7.2 Decision Matrix: When to Use Chatbots vs Conversational AI
Ultimately, the decision to implement chatbots or Conversational AI depends on business needs and long-term automation goals. Chatbots provide an entry-level automation solution for handling common queries, while Conversational AI offers advanced capabilities to enhance customer interactions, understand complex queries, and improve service quality over time.
By evaluating these factors carefully, businesses can make a well-informed decision that aligns with their budget, customer engagement strategy, and growth objectives.
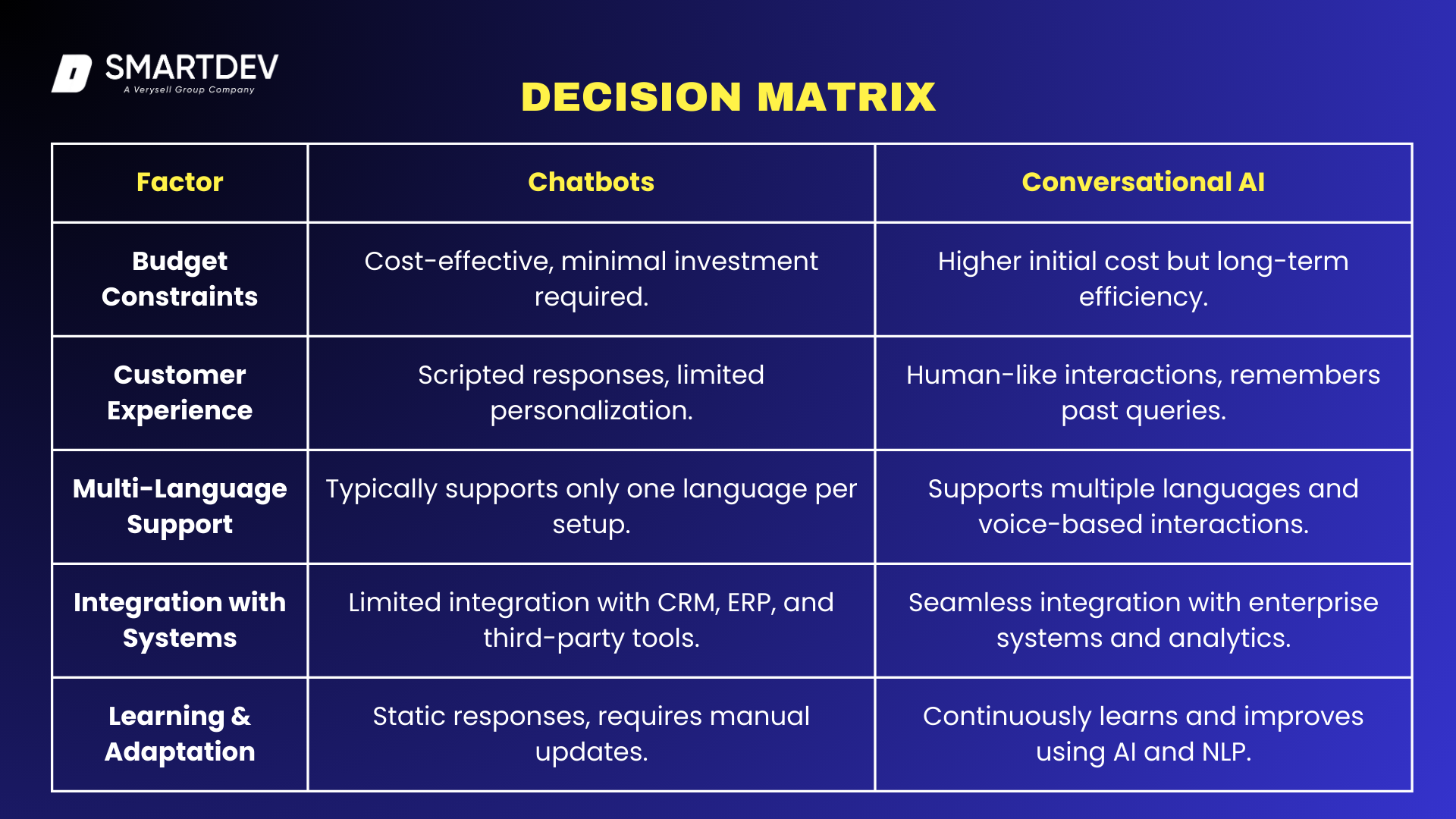
If most of your answers align with the Chatbots column → A chatbot is the right choice for your business. If most of your answers align with the Conversational AI column → Investing in Conversational AI is the better option. This decision matrix ensures businesses align their choice with their budget, customer engagement strategy, and long-term growth objectives.
Still have considerations? Explore our article on which AI Solution is Right for Your Business here:
8. The Future of Conversational AI and Chatbots
As technology advances, both chatbots and Conversational AI are undergoing rapid transformation, becoming more intelligent, adaptive, and human-like in their interactions. Businesses across industries are investing in these technologies to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and automate complex workflows.
8.1 The Evolution of Chatbots: Becoming More AI-Powered
Traditional chatbots have relied primarily on rule-based programming and scripted responses. However, modern advancements in natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI) are enabling chatbots to evolve into more sophisticated conversational agents.
Today’s chatbots can process unstructured data, analyze context, and even predict user intent, making them more efficient and capable of handling dynamic conversations. AI-powered chatbots are no longer limited to predefined queries but can now learn from interactions, recognize patterns, and adapt responses over time. This shift is transforming how businesses automate customer support, sales, and internal operations.
For example, AI-driven chatbots are now being used in healthcare to provide symptom assessments and appointment scheduling, in finance to offer investment advice and fraud detection alerts, and in e-commerce to enhance shopping recommendations through personalized engagement.
8.2 How Conversational AI is Shaping the Future of Customer Interactions
Conversational AI is at the forefront of revolutionizing customer engagement. Unlike chatbots, which operate on predefined scripts, Conversational AI solutions understand human emotions, respond contextually, and facilitate meaningful conversations with users. This is particularly evident in industries like banking, healthcare, and customer service, where human-like interaction is critical.
By integrating deep learning and sentiment analysis, Conversational AI can detect frustration or satisfaction in a user’s tone and adjust its responses accordingly. This leads to more empathetic and personalized interactions, bridging the gap between automated systems and human touch.
Additionally, Conversational AI is expanding beyond text-based communication and moving into multimodal interactions—combining text, voice, and even visual inputs. This enables businesses to develop AI-powered customer service representatives, virtual assistants, and interactive voice response (IVR) systems that provide seamless user experiences across multiple platforms.
8.3 Trends to Watch
Integration with Voice Assistants
http
Voice-enabled AI assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri are becoming an integral part of Conversational AI solutions. Businesses are increasingly integrating voice-based AI into their customer service workflows to provide hands-free assistance. Voice assistants are being used for a range of applications, from smart home automation and healthcare diagnostics to retail shopping experiences and automotive infotainment systems.
Emotion Recognition
AI is now capable of analyzing user sentiment through tone, word choice, and even facial expressions. Emotion recognition allows Conversational AI to provide tailored responses based on a user’s emotional state. This is particularly valuable in mental health applications, customer service interactions, and HR support systems, where AI can identify stress, frustration, or excitement and respond accordingly.
For instance, a virtual therapist using Conversational AI can detect stress levels based on speech patterns and adjust its recommendations accordingly. Similarly, a customer support AI assistant can escalate a conversation to a human agent when it detects frustration, ensuring that customers receive the best possible experience.
Real-Time Data Analysis
Another major trend shaping the future of Conversational AI is the ability to analyze real-time data and provide instant insights. Businesses can use AI-powered chatbots to collect and interpret customer data, enabling predictive analytics that drive better decision-making.
For example, Conversational AI in e-commerce can analyze browsing behavior, past purchases, and social media interactions to offer personalized product recommendations in real-time. In finance, AI-powered chatbots can monitor spending habits and provide instant alerts for unusual transactions, enhancing security and user engagement.
Conclusion
Chatbots and Conversational AI serve different purposes. Chatbots are rule-based, best suited for handling structured, repetitive tasks such as FAQs and appointment scheduling. Conversational AI, with its machine learning and natural language processing capabilities, provides context-aware, human-like interactions ideal for industries requiring deep engagement, such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce.
Businesses should consider their size, industry, customer interaction complexity, and budget when deciding between chatbots and Conversational AI. Chatbots are cost-effective and easy to deploy, while Conversational AI is ideal for scalable, dynamic interactions that require long-term learning and adaptation.
Selecting the right solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and optimize operations. At SmartDev, we specialize in designing and implementing custom AI-powered solutions tailored to your business goals. Whether you need a simple chatbot to streamline support or an advanced Conversational AI system to drive customer engagement, our team can guide you through the decision-making process and implementation strategy.
Ready to integrate AI into your business? Contact us today to find the best solution for your needs.
—
References:
- From Eliza to ChatGPT: the 60-year history of chatbots | The Verge
- AI Chatbots: My Top 23 Picks for 2025
- Chatbots and crisis communication: effectiveness and limitations in the educational sector
- Conversational artificial intelligence in the AEC industry: A review of present status, challenges and opportunities
- Conversational AI: How (Chat)Bots Will Reshape the Digital Experience
- Impact of Conversational and Generative AI Systems on Libraries: A Use Case Large Language Model (LLM)
- When Healthcare Meets Conversational AI: A Narrative Review of Amazon Alexa Devices in Healthcare