1. Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to automation to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences. Two leading technologies in this space are Digital Process Automation (DPA) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). While both aim to improve efficiency, they serve distinct purposes and cater to different needs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key differences between DPA vs RPA, their use cases, and how to choose the right automation approach for your organization in 2025.
Explore what is process automation
1.1 What is Process Automation?
Process automation refers to the use of technology to perform repetitive tasks or workflows with minimal human intervention. By automating processes, businesses can save time, reduce errors, and focus on high-value activities. Whether it’s handling customer inquiries, processing invoices, or managing employee onboarding, automation has become a cornerstone of modern operations.
1.2 Why is Automation Essential for Modern Businesses?
In the competitive landscape of 2025, automation has emerged as a critical driver for business success, enabling organizations to optimize operations and meet the demands of a digital-first world. The adoption of technologies such as Digital Process Automation (DPA) or Robotic Process Automation (RPA) allows companies to streamline their workflows, significantly enhancing operational efficiency. A global retailer like Walmart, for instance, relies on automation to manage its extensive supply chain, ensuring that products are moved from warehouses to stores with precision and speed. This capability has enabled the company to save millions of hours annually, allowing its workforce to focus on strategic initiatives that drive growth rather than being bogged down by repetitive manual tasks.
Another compelling reason for businesses to embrace automation lies in its ability to deliver substantial cost savings while maintaining a high level of accuracy. By reducing the need for human intervention in routine processes, companies can lower labor expenses and minimize errors that often lead to financial setbacks. A financial services firm automating its accounts payable process can eliminate manual data entry errors, which previously resulted in late payment fees, saving the organization thousands of dollars each year.
Furthermore, automation ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, a crucial consideration in industries like healthcare. Mayo Clinic, a renowned healthcare provider, utilizes automation to manage patient billing processes, ensuring adherence to regulations like HIPAA and avoiding penalties that could amount to millions of dollars.
Equally important is the role automation plays in scaling operations and enhancing customer experiences, both of which are vital for maintaining a competitive edge. An e-commerce platform like Shopify employs automation to handle sudden spikes in order volumes during peak seasons, processing up to three times the normal workload without requiring additional staff. This scalability ensures uninterrupted service, even under pressure.
Similarly, Amazon leverages automation to provide instant responses to customer inquiries around the clock, a capability that has significantly boosted its customer satisfaction ratings. As market expectations continue to rise, with 85% of businesses projected to adopt automation by 2027 according to PwC, companies that integrate these technologies today will position themselves as leaders, capable of delivering efficiency, precision, and exceptional service in an increasingly demanding global market.
1.3 Overview of DPA and RPA: Definitions & Core Differences
Generally, RPA is task-oriented, while DPA is process-oriented, aiming for enterprise-wide transformation.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human interactions with digital systems. For example, an RPA bot can copy data from emails into a CRM system.
In contrast, Digital Process Automation (DPA) focuses on automating entire business processes from end to end, often integrating multiple systems and involving human decision-making. It’s ideal for complex workflows like loan approvals or supply chain management.
1.4 Common Misconceptions About DPA and RPA
A common misconception is that DPA and RPA are the same since both automate tasks. In reality, DPA optimizes entire processes, while RPA focuses on specific, repetitive tasks like data entry.
Another myth is that RPA can fully replace DPA. RPA offers quick fixes, such as automating invoice processing for a retailer like Target, but lacks DPA’s scalability for complex workflows, like customer onboarding at Verizon. DPA’s ability to integrate systems makes it ideal for larger operations.
Finally, some believe automation eliminates jobs, but it often redefines roles instead. At Google, automation of routine IT tasks allows employees to focus on strategic innovation, enhancing productivity without reducing employment.
2. What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
2.1 How RPA Works: An Overview
RPA uses software bots to interact with applications at the user interface (UI) level, just as a human would. For example, an RPA bot can log into a system, extract data from a spreadsheet, and input it into another application—all without human intervention.
2.2 Key Features of RPA

Explore the core features of Robotic Process Automation: UI-based automations, rule-based processes, quick deployment, and scalability.
One of its core strengths is UI-based automation, where RPA bots interact with applications at the front end, mimicking human actions like clicks, keystrokes, and screen scraping. This allows RPA to work with existing systems without requiring deep technical changes.
Furthermore, its rule-based approach enables RPA to excel at tasks with clear, predefined rules, such as “if an invoice exceeds $5,000, flag it for review.” This makes RPA ideal for straightforward automation needs. Additionally, RPA can be deployed rapidly, often within weeks, as seen with FedEx, which uses RPA to automate delivery route updates, saving on fuel costs.
RPA also supports scalability, allowing businesses to adjust the number of bots based on workload. This flexibility ensures companies can respond to demand fluctuations efficiently, making RPA a practical choice for tactical automation.
2.3 Benefits of RPA in Business Processes
First off, RPA bots operate 24/7, completing tasks much faster than humans. For instance, a retailer like Target uses RPA to update inventory records, saving hours of manual work weekly. RPA is also cost-effective, reducing the need for manual labor in repetitive tasks such as data entry or report generation. This lowers operational expenses considerably. Additionally, RPA minimizes human errors in tasks like calculations, ensuring greater accuracy in business processes.
Another advantage is its non-invasive nature, allowing RPA to work seamlessly with legacy systems without requiring major changes. This makes RPA an accessible solution for companies looking to automate quickly, providing immediate efficiency gains without disrupting existing infrastructure.
2.4 Limitations & Challenges of RPA
RPA is fantastic for simple, repetitive tasks, but it can struggle with more complex processes that need decision-making. For example, if you’re trying to automate a customer support system with dynamic queries, RPA might not keep up on its own.
Another thing to keep in mind is that RPA works at the UI level, so it doesn’t integrate deeply with systems, which can be a limitation for bigger workflows. Also, if an application’s UI changes—like after a software update—the bots might stop working, needing regular maintenance. Scaling up can get tricky too; a company like FedEx, which uses RPA for route updates, might find costs and complexity rise as they add more bots, so planning ahead is key.
3. What is Digital Process Automation (DPA)?
3.1 How DPA Works: An Overview
DPA automates entire business processes by integrating systems, data, and human actions into a seamless workflow. It often uses low-code platforms and APIs to connect applications, enabling end-to-end automation. For example, DPA can manage a customer onboarding process by coordinating between CRM, email systems, and compliance checks.
3.2 Key Features of DPA
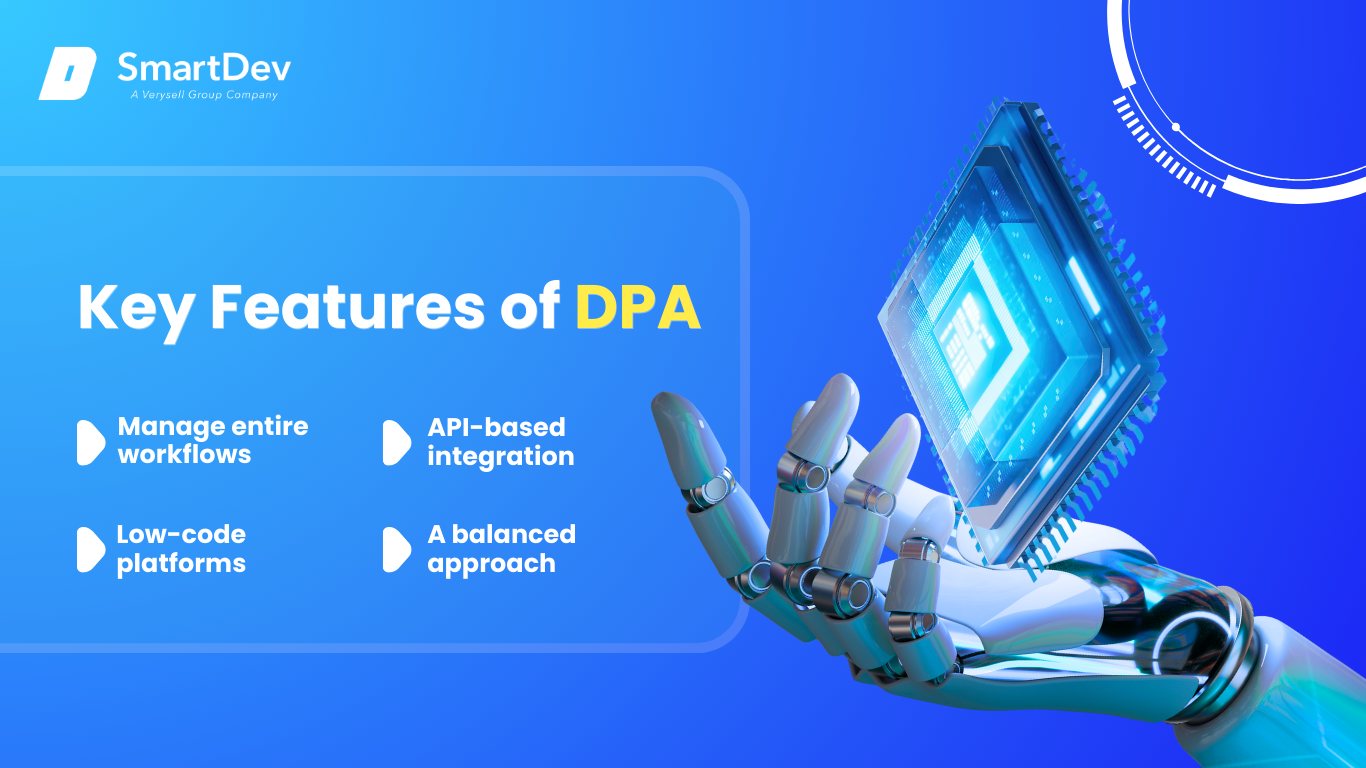
Explore the core features of Digital Process Automation: Manage entire workflows; API-based integration; Low-code platforms; A balanced approach
A core strength of DPA is its ability to manage entire workflows, ensuring end-to-end automation across systems and departments. Unlike tools focused on individual tasks, DPA integrates every step of a process, enhancing efficiency and reducing delays.
Another key feature is its API-based integration, which connects systems at a deeper level for seamless data flow. This allows DPA to link platforms like CRM and ERP systems, ensuring real-time information sharing. For example, a global firm like Accenture uses DPA to integrate client data across platforms, improving accuracy in its onboarding processes.
Additionally, DPA provides low-code platforms, enabling non-technical users to design and modify workflows with ease, which speeds up implementation. It also incorporates human decision-making into automated processes, ensuring a balanced approach where employees can focus on critical choices while routine tasks are handled efficiently.
3.3 Benefits of DPA for End-to-End Workflow Automation
Digital Process Automation (DPA) offers compelling advantages for businesses aiming to streamline their operations comprehensively. It excels at holistic optimization, enhancing entire processes rather than just individual tasks, which drives significant efficiency gains. A global leader like HSBC, for example, uses DPA to manage loan approvals, reducing the process from weeks to days by seamlessly connecting every step, ensuring faster service and higher customer satisfaction.
Moreover, DPA provides exceptional scalability, enabling businesses to adapt to growing demands and complex workflows without disruption. Its ability to deliver better customer experiences through streamlined processes, such as order fulfillment, is a key differentiator in today’s competitive market.
Additionally, DPA’s built-in analytics offer data-driven insights, empowering organizations to monitor performance and make informed improvements, ensuring they stay ahead of the curve with smarter, more efficient operations.
3.4 Limitations & Challenges of DPA
While delivering substantial benefits, DPA also presents challenges that require careful consideration. A primary concern is the higher initial investment compared to RPA, as DPA demands significant upfront planning and resources. For a mid-sized company, implementing DPA for complex workflows can easily exceed $50,000, covering integration and training costs, which may strain budgets without proper preparation.
The implementation process additionally can be complex and time-consuming, particularly for large-scale operations, often taking months to fully integrate systems. Teams may also face a learning curve when using DPA’s low-code platforms, requiring dedicated training to maximize effectiveness.
Furthermore, DPA’s success hinges on the quality of system integrations—a fragmented infrastructure, as seen in some global firms like Verizon during customer onboarding, can lead to delays and additional expenses, underscoring the need for thorough planning.
4. Key Differences Between DPA and RPA
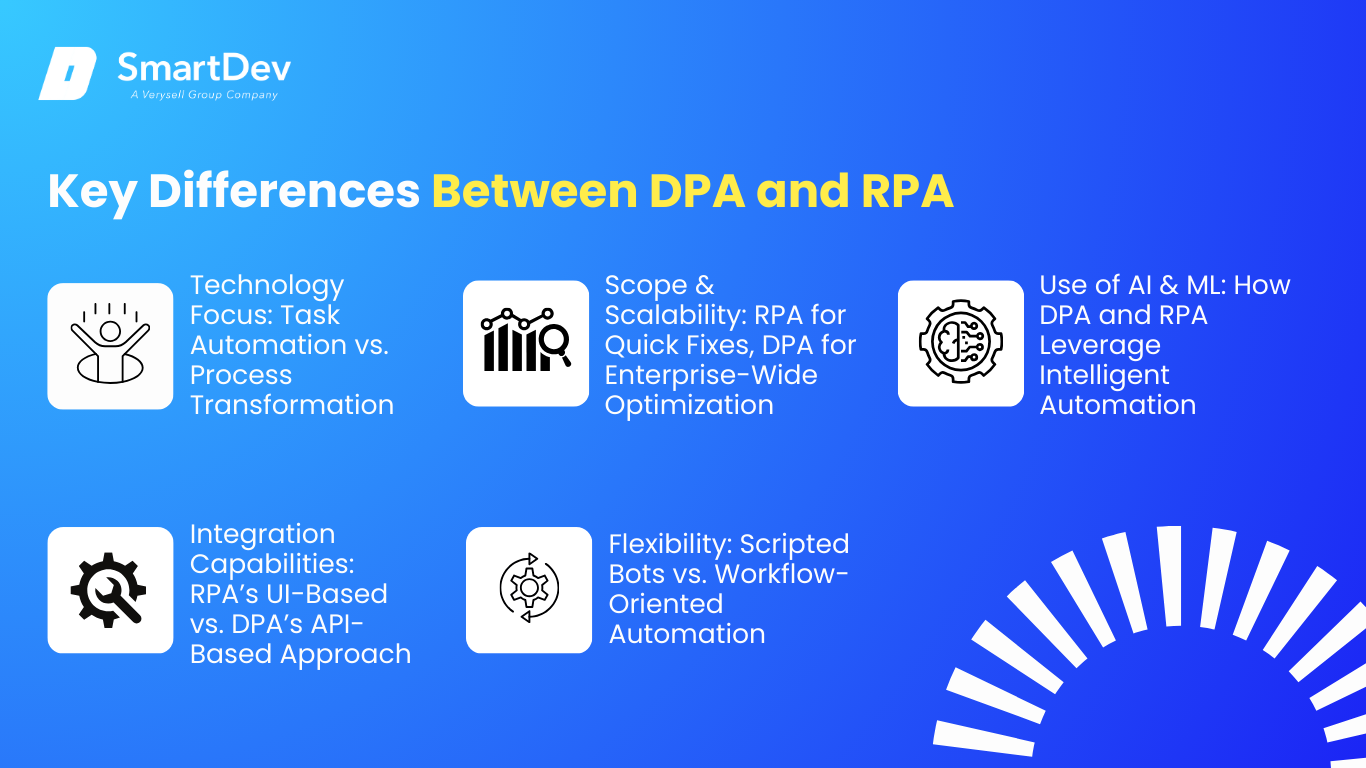
The main differences between DPA and RPA
4.1 Technology Focus: Task Automation vs. Process Transformation
RPA is designed to automate individual tasks, making it ideal for quick, repetitive actions. For instance, in a customer support setting, an RPA bot can extract customer details from an email and input them into a ticketing system, saving time on manual entry. However, RPA stops there—it doesn’t handle the broader workflow.
In contrast, DPA focuses on process transformation, optimizing entire workflows across departments for maximum efficiency. In the same customer support scenario, a global firm like Verizon uses DPA to manage the full ticket process: receiving the query, assigning it to the right team, tracking progress, and sending a follow-up survey after resolution. DPA ensures every step is seamlessly connected, often incorporating human decision-making where needed, making it a powerful choice for comprehensive automation.
4.2 Scope & Scalability: RPA for Quick Fixes, DPA for Enterprise-Wide Optimization
And what about the differences in scope and scalability between DPA vs RPA? In the one hand, RPA is perfect for short-term, tactical fixes, focusing on automating isolated tasks with minimal disruption. A retailer like Target, for example, uses RPA to update inventory levels by pulling data from supplier emails and entering it into their system, saving time without needing complex setups. However, RPA can struggle as the scope grows, especially when managing multiple systems or bots, leading to challenges like “bot sprawl.”
On the other hand, DPA is built for long-term, enterprise-wide optimization, handling large-scale processes across departments. In manufacturing, a company like Siemens uses DPA to streamline supply chain management, connecting procurement, logistics, and sales, ensuring efficiency, compliance, and scalability across the board.
4.3 Integration Capabilities: RPA’s UI-Based vs. DPA’s API-Based Approach
Understanding integration capabilities is key when comparing DPA vs RPA for your business needs. RPA operates at the UI level, mimicking human actions without deep system integration. For example, an RPA bot can log into a legacy system, extract data, and paste it into a modern cloud application, even if the two systems don’t natively integrate. However, this approach has limitations: if the UI changes (e.g., a button moves after a software update), the bot may fail, requiring manual updates to its script.
Conversely, DPA uses APIs to integrate systems, enabling seamless data flow and collaboration. This enables DPA to handle complex workflows that require real-time data exchange. For instance, in a customer onboarding process, DPA can pull customer data from a CRM, verify it against a compliance database, and update the status in an ERP system—all without relying on UI interactions. This makes DPA more robust and less prone to breaking when systems change.
4.4 Flexibility: Scripted Bots vs. Workflow-Oriented Automation
When it comes to flexibility, RPA and DPA take very different paths, impacting their fit for your business. RPA relies on scripted bots that follow strict rules, which can limit adaptability. For instance, a retailer like Walmart might use an RPA bot to extract invoice numbers from emails, but if the email format changes, the bot fails, needing a script update to keep working.
DPA, however, offers workflow-oriented automation, designed for dynamic processes with greater adaptability. In a procurement scenario, a company like Siemens uses DPA to manage exceptions—like a supplier delay—by rerouting the workflow to a human approver or sourcing from a backup supplier. With low-code interfaces, DPA allows users to adjust processes easily, making it a strong choice for evolving workflows that need human oversight.
4.5 Use of AI & ML: How DPA and RPA Leverage Intelligent Automation
The use of AI and ML sets RPA and DPA apart in their automation capabilities, offering unique value. RPA can incorporate AI for basic tasks like OCR (Optical Character Recognition) or simple decision-making.
Traditional RPA is rule-based, meaning it follows predefined logic (e.g., “If the invoice amount is over $10,000, flag it for review”). However, modern RPA platforms are increasingly incorporating AI capabilities, such as:
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): To extract data from scanned documents.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): To understand and process unstructured text, like customer emails.
- Basic Decision-Making: For example, an RPA bot might use AI to classify emails as “urgent” or “non-urgent” based on keywords. Despite these advancements, RPA’s AI usage is often limited to enhancing specific tasks rather than transforming entire processes.
DPA, however, leverages AI and machine learning more extensively for predictive analytics, process optimization, and intelligent decision-making. DPA platforms are designed to integrate AI and ML at a deeper level, enabling more sophisticated automation. Examples include:
- Predictive Analytics: DPA can analyze historical data to predict process bottlenecks. For instance, in a supply chain workflow, DPA might predict delays based on past supplier performance and suggest alternative actions.
- Intelligent Decision-Making: DPA can use ML to make dynamic decisions. For example, in a loan approval process, DPA might use ML to assess an applicant’s risk profile and recommend approval or rejection.
- Process Optimization: DPA can continuously learn from process data to improve efficiency. For example, if a customer support workflow consistently experiences delays at a certain step, DPA can suggest reordering the steps or allocating more resources.
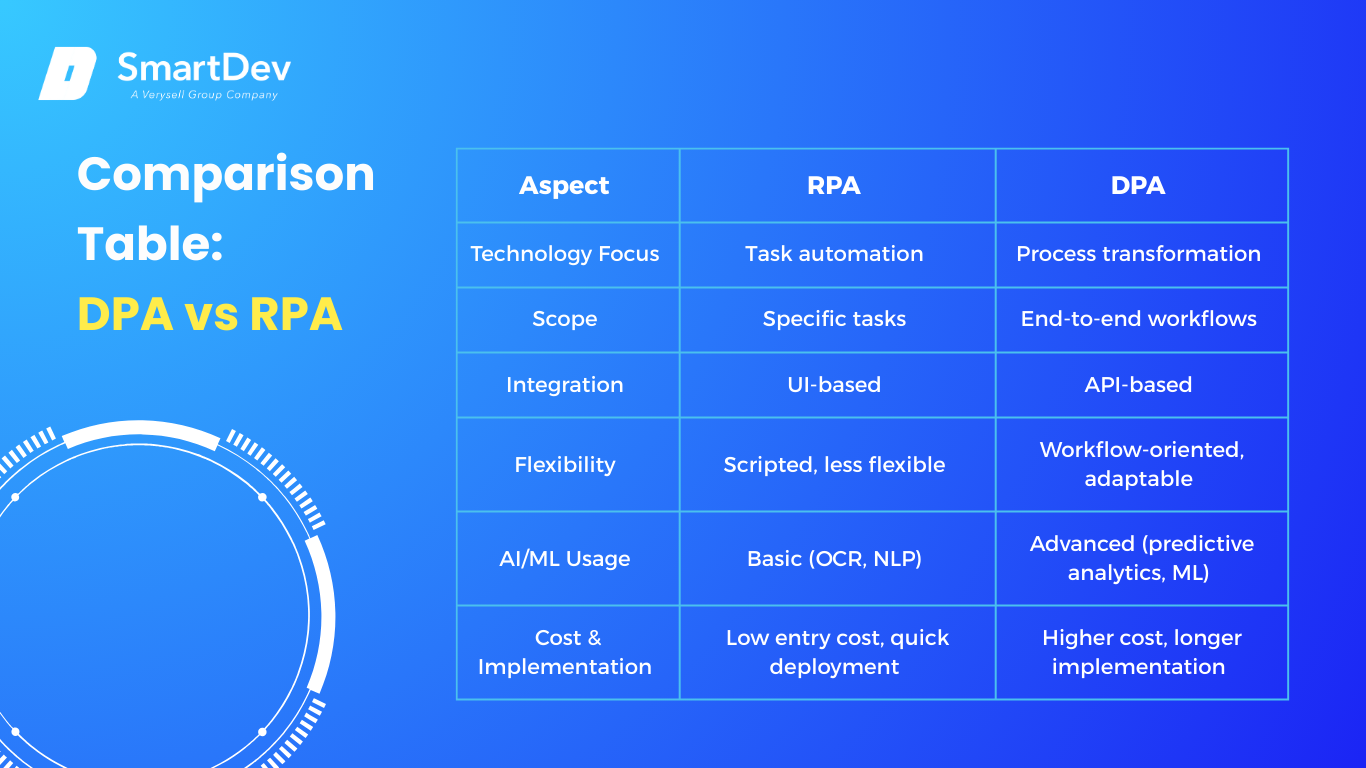
Comparing DPA and RPA across key aspects.
5. DPA vs. RPA: Which One is Right for Your Business?
5.1 When to Use RPA (Ideal Use Cases)
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, is best suited for tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and time-consuming. Think of processes like entering data into spreadsheets, generating reports, or processing invoices. These tasks don’t require human judgment or complex decision-making—they just need to get done quickly and accurately.
One of RPA’s biggest advantages is its ability to work with legacy systems. If your business relies on older software that doesn’t support modern integrations, RPA can act as a bridge, automating tasks without the need to overhaul your entire IT infrastructure. This makes it a great option for businesses looking for quick wins and short-term automation solutions that can be implemented without a full digital transformation.
Our RPA services help you get fast, accurate results, get expert insights on RPA strategy
5.2 When to Use DPA (Ideal Use Cases)
Digital Process Automation, on the other hand, is designed to manage more complex, end-to-end workflows. If you’re dealing with processes like customer onboarding, loan approvals, or internal compliance procedures—where multiple steps, approvals, and departments are involved—DPA is the better fit.
It’s particularly valuable for organizations that are committed to long-term digital transformation. DPA doesn’t just automate tasks—it rethinks and optimizes the entire process. It also integrates deeply with various systems across your organization, helping to break down silos and improve overall efficiency.
5.3 Hybrid Approaches: Combining RPA and DPA for Maximum Efficiency
In reality, many businesses find that the most effective approach is a combination of both RPA and DPA. For example, you might use RPA bots to handle specific, repetitive tasks—like pulling customer data from different systems—while DPA orchestrates the broader workflow, ensuring that the right information reaches the right people at the right time.
This hybrid model allows you to leverage the speed and simplicity of RPA alongside the strategic capabilities of DPA. The result? A more agile, scalable, and intelligent automation solution that aligns with both your short-term goals and long-term vision.
6. Real-World Use Cases: How Businesses Use DPA and RPA

How businesses apply DPA and RPA across industries.
6.1 Finance & Accounting: Automating Invoice Processing & Approval Workflows
In the finance and accounting world, RPA is a game changer, especially when it comes to tasks like invoice processing. For example, a mid-sized manufacturing company processing 5,000 invoices every month found itself spending a staggering 200 hours just on manual data entry. With an error rate of 5%, it wasn’t just time-consuming—it was costly.
Once the company implemented an RPA solution using UiPath, the results were immediate. RPA automated 80% of the data entry, slashing processing time to just 40 hours per month and reducing errors to less than 1%. This resulted in significant savings—around $50,000 annually—while also improving vendor relationships by ensuring accurate, on-time payments.
On the DPA side, a global retail chain with 50 stores was grappling with an inefficient invoice approval process. It took them 15 days to process and approve invoices due to delays caused by manual routing and communication issues between departments. After adopting a DPA solution through Microsoft Power Automate, they cut the approval cycle down to just 3 days. The system not only flagged discrepancies, such as mismatched purchase orders, but also sent real-time notifications to approvers, ensuring compliance with payment terms and streamlining the entire process.
6.2 Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Records Management
Healthcare organizations are also reaping the benefits of automation. A regional hospital in the U.S. was managing 10,000 patient records every month, and its staff was spending 150 hours just updating these records across multiple systems. But this led to costly billing errors, as 3% of claims were rejected due to incorrect insurance information.
By implementing RPA with Automation Anywhere, the hospital automated 90% of the data entry tasks. This reduced manual work to just 15 hours per month and improved billing accuracy, cutting rejections to only 0.5%.
Meanwhile, DPA is helping healthcare providers improve patient onboarding. A large healthcare network with 20 clinics was facing long delays, taking up to 48 hours to process new patients due to manual coordination between departments. By introducing a DPA solution, the network reduced onboarding time to just 4 hours. The system automatically flagged missing insurance details and sent notifications, while also integrating with SMS platforms to remind patients of their appointments—resulting in a 20% decrease in no-show rates.
6.3 Human Resources: Onboarding Employees & Payroll Automation
In human resources, RPA is making processes like payroll automation faster and more accurate. A tech startup with 200 employees was spending 30 hours each month processing payroll manually, and errors like incorrect deductions were affecting employee satisfaction. After introducing an RPA solution with Blue Prism, the company automated 85% of payroll tasks, reducing time spent on payroll to just 5 hours per month and minimizing errors to 0.2%. Additionally, the system sent pay stub emails automatically, saving even more administrative time.
For larger HR processes, like onboarding, DPA is proving invaluable. A financial services firm with 1,000 employees faced significant delays in getting new hires onboard due to manual coordination between HR, IT, and training departments. With a DPA solution from Appian, the company reduced onboarding time from 10 days to just 2 days. The system automated tasks like IT provisioning and training schedule assignments, ensuring a smoother and faster onboarding process for new hires.
6.4 Customer Service: Improving Response Times & Workflow Efficiency
RPA is also transforming customer service, especially when it comes to handling repetitive inquiries. An e-commerce company that receives 2,000 customer inquiries daily found that 60% of these were repetitive questions. Their support team was spending a whopping 80 hours each week answering these queries, delaying responses for more complex issues. By implementing RPA through UiPath, the company automated 70% of these repetitive inquiries, reducing the team’s workload to just 24 hours per week. This freed up time for agents to focus on high-priority, complex issues.
On the DPA side, a telecom provider with 500,000 customers was struggling with ticket management, taking up to 24 hours to resolve issues due to manual routing and lack of visibility. By using Microsoft Power Automate, the company cut resolution times to just 6 hours. The system intelligently prioritized tickets based on urgency, such as outages affecting multiple customers, and integrated with SMS to provide real-time updates to customers. This reduced follow-up inquiries by 30%, significantly improving customer satisfaction.
6.5 IT & Operations: Automating Software Deployments & Security Checks
Even in IT and operations, automation is proving crucial for routine tasks. A software company with 50 servers was spending 20 hours per week manually performing security scans, and the 2% error rate meant that vulnerabilities were sometimes overlooked. After introducing RPA with Automation Anywhere, the company automated 95% of these scans, reducing time spent on security checks to just 1 hour per week and eliminating errors. Additionally, the bot sent alerts whenever critical vulnerabilities were detected, enabling faster responses to potential threats.
In software deployment, DPA is helping companies like a fintech firm with 10 development teams. Previously, the manual coordination required to deploy software updates took 5 days. By implementing DPA with Nintex, the company streamlined the process, reducing deployment time to just 12 hours. The system automated testing, approval workflows, and rollback procedures, ensuring compliance with strict financial regulations and significantly speeding up time-to-market.
To explore how DPA & RPA apply on your business, read more about Our successful projects and solutions we’ve developed in collaboration with our valued clients.
7. Choosing the Right Automation Tool: DPA vs. RPA Software Comparison
7.1 Leading RPA Platforms (UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism)
UiPath has earned a reputation for its clean, user-friendly interface that makes it easy for both IT teams and business users to build automation workflows. It also comes with an extensive library of ready-made bots, which speeds up deployment and reduces the learning curve.
Automation Anywhere, on the other hand, stands out with its advanced AI integrations. For businesses looking to move beyond simple rule-based automation into more intelligent, data-driven workflows, it’s a go-to choice.
Meanwhile, Blue Prism appeals strongly to large enterprises with its focus on security, compliance, and scalability. If your business requires enterprise-grade solutions that can support mission-critical operations, Blue Prism is often the preferred option.
7.2 Leading DPA Platforms (Appian, Microsoft Power Automate, Nintex
Appian leads the way in the DPA world with its low-code platform that allows businesses to build and manage end-to-end workflows without heavy developer involvement. It’s especially valuable for organizations that want a unified, centralized way to manage complex operations.
Microsoft Power Automate brings a strong advantage if your organization is already embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem. It integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 tools, enabling teams to automate daily workflows with minimal setup.
Nintex offers a different strength — it’s particularly powerful in process mapping and managing complex workflows. Businesses with detailed approval chains or multi-layered processes often choose Nintex to bring structure and visibility to their operations.
7.3 Cost & Implementation Considerations for RPA & DPA
When weighing RPA against DPA, cost and implementation timeline are two key factors to consider. RPA typically requires a lower upfront investment. It’s quick to roll out — often in a matter of weeks — which makes it ideal for businesses seeking rapid results. However, costs can add up over time as you scale the number of bots and increase maintenance demands.
DPA, by contrast, usually involves a higher initial cost. Implementing a DPA solution means rethinking workflows, integrating with multiple systems, and involving several departments — which can take months. But the payoff is a long-term, scalable solution that supports enterprise-wide transformation.
7.4 How to Decide: Key Questions to Ask Before Choosing
Before making your final decision, it’s essential to ask the right questions. First, what are you trying to automate — a single task or an entire process? RPA shines in task automation, while DPA is designed for end-to-end process management.
Second, consider whether your automation requires deep system integration. If your processes span multiple departments and systems, DPA will serve you better.
Then, evaluate your budget and your timeline. If you’re under time pressure and need results fast, RPA may be the better fit. If you’re investing in long-term operational change, DPA is worth the wait.
And finally, think about your broader vision. Are you looking for a quick operational fix, or are you aiming to build a digitally transformed organization over time. Find out how SmartDev crafts solutions for your needs at Digitalization | SmartDev
8. The Future of Process Automation: What’s Next for DPA and RPA?
8.1 The Rise of Hyperautomation: Merging RPA, DPA, AI, and ML
Hyperautomation combines RPA, DPA, AI, and machine learning to create fully automated, intelligent systems. For example, a hyperautomated system could use RPA to extract data, DPA to manage workflows, and AI to predict outcomes.
8.2 The Role of No-Code & Low-Code Automation in Business Growth
No-code and low-code platforms (like those used in DPA) are democratizing automation, allowing non-technical users to build workflows. This trend is accelerating business growth by enabling faster innovation.
8.3 How AI-Powered Automation is Shaping the Future
AI is enhancing both DPA and RPA by enabling predictive analytics, natural language processing, and intelligent decision-making. For example, AI-powered DPA can predict bottlenecks in a supply chain and suggest optimizations.
8.4 Predictions: Will DPA Replace RPA in the Long Run?
While DPA offers greater scalability and integration, RPA will remain relevant for quick, tactical automation. The future likely lies in hybrid solutions that combine the strengths of both.
9. Conclusion & Next Steps
9.1 How to Get Started with Automation in Your Organization
If you’re just beginning your automation journey, it’s important to start with clarity — not complexity. Business automation doesn’t require a complete overhaul overnight; in fact, the most successful transformations often begin with small, focused steps. Here’s how to lay the groundwork:

How to Get Started with Automation in Your Organization
Step 1: Assess Your Needs Thoughtfully
Before introducing any technology, take the time to identify operational bottlenecks. Are your teams spending too much time on repetitive, manual tasks like invoice processing, customer data updates, or employee onboarding? Look for processes that are rule-based, time-consuming, and prone to human error — these are strong candidates for automation.
Don’t just look at isolated tasks — map the broader process. A payroll entry might seem like a standalone task, but it may be part of a larger workflow involving approvals, compliance checks, and notifications. Understanding the full scope helps determine whether you need RPA for task automation or DPA for end-to-end process redesign.
Step 2: Select the Right Tool for the Right Job
Choosing between RPA and DPA (or a hybrid of both) depends on your objectives. RPA is excellent for quick wins: automating highly repetitive tasks without altering your existing systems. DPA, however, delivers deeper value by streamlining complex processes and improving cross-departmental collaboration through structured workflows.
If you’re unsure where to start, our team at SmartDev can help you evaluate your current systems and workflows to recommend a tailored automation solution that fits both your short-term needs and long-term growth.
Step 3: Run a Pilot Project
Start with a contained, low-risk use case. For example, automating invoice data entry with RPA or digitizing a basic approval process using DPA. This approach gives you a clear picture of the technology’s potential impact, helps your team get familiar with the tools, and builds internal support for scaling.
Step 4: Plan to Scale
Once the pilot proves successful, it’s time to expand. Build a roadmap to introduce automation gradually across departments — HR, finance, operations, customer service — while ensuring that change management and employee training are part of the process.
9.2 Key Takeaways: Making an Informed Decision
RPA shines when speed and simplicity matter. It’s ideal for businesses that want fast wins by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks with minimal disruption.
DPA, on the other hand, is a game-changer for organizations ready to rethink and optimize entire processes. It’s the foundation of true digital transformation, providing structure, transparency, and control over how work gets done.
In many cases, the most effective approach is a blend of both — using RPA for quick automation wins and DPA for long-term process redesign and optimization.
9.3 Final Thoughts on the Evolution of Business Automation
The question is no longer whether to automate — but how to do it in a way that aligns with your business vision. The conversation around RPA vs DPA isn’t about choosing sides; it’s about identifying what combination best supports your team, your systems, and your goals.
Organizations that take action today are setting themselves up to lead tomorrow. In a world where agility, accuracy, and efficiency define success, automation is your catalyst for change.
Curious about what automation could look like for your business? At SmartDev, we help companies like yours move from insight to impact. Right now! Discover SmartDev’s Custom Automation Solutions
References







