AI is rapidly transforming industries, with 70% of companies using AI in at least one business function. AI tools like chatbots and virtual assistants are at the forefront, enhancing customer experiences and improving efficiency. The global chatbot market is projected to reach $1.34 billion by 2024, while the virtual assistant market is expected to hit $18.8 billion by 2026. This growth highlights the critical role AI plays in modern business strategies.
While both technologies leverage AI, chatbots are designed for simple, task-specific interactions, whereas virtual assistants handle more complex, multi-step tasks. Understanding the difference is key for businesses to choose the right solution, whether for automating customer service or managing internal workflows.
This blog post explores the key differences between chatbots and virtual assistants, their applications across industries, and provides insights into choosing the right AI solution for your business.
1. What Are Chatbots?
1.1. Definition and Functionality
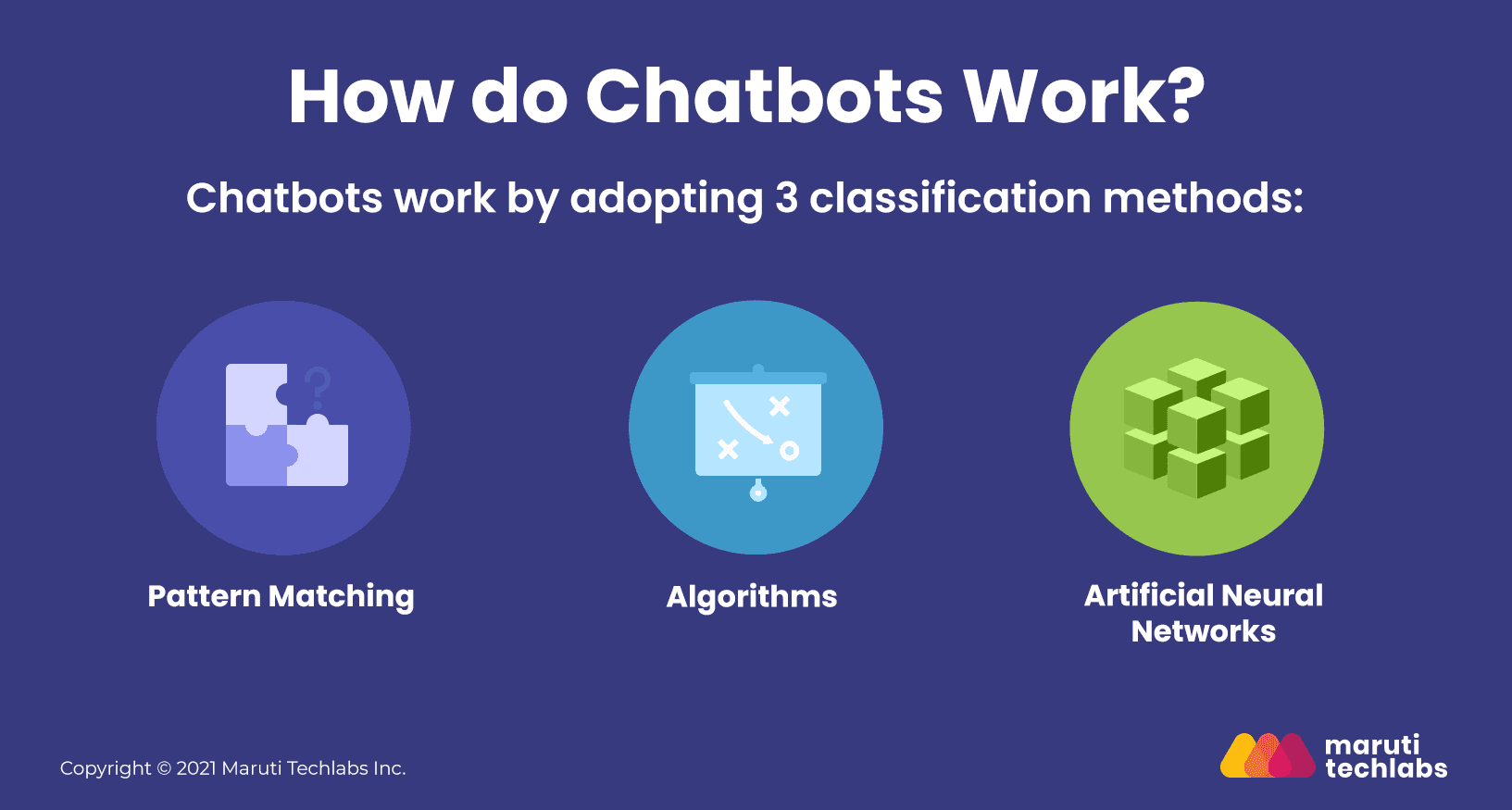
Chatbots are AI-powered tools designed to automate text-based communication, enabling businesses to interact with customers without human intervention. By mimicking human conversation, chatbots can handle a wide range of customer service inquiries, process orders, and provide assistance 24/7. A chatbot works by processing user input and delivering relevant responses based on a combination of pattern matching, algorithms, and artificial neural networks. Here’s how each of these concepts plays a role:
A chatbot primarily relies on pattern matching to process and respond to user inputs. This method involves comparing the text entered by the user against a database of predefined patterns or keywords. When a match is found, the chatbot delivers a corresponding response. Pattern matching works well for simple, repetitive tasks, where the chatbot is trained to recognize specific phrases and return fixed answers. However, it has limitations in terms of flexibility, as it can only handle queries that closely match its programmed patterns.
To overcome these limitations, more advanced chatbots use algorithms to assess the user’s input and determine the most appropriate response. Algorithms can range from basic decision trees to more sophisticated techniques, which analyze the user’s query based on a set of rules or logic.
The most advanced chatbots incorporate artificial neural networks (ANNs), which allow for more complex, context-aware interactions. ANNs simulate the way the human brain processes information by using interconnected layers of “neurons” to recognize patterns and make predictions.
1.2. Types of Chatbots
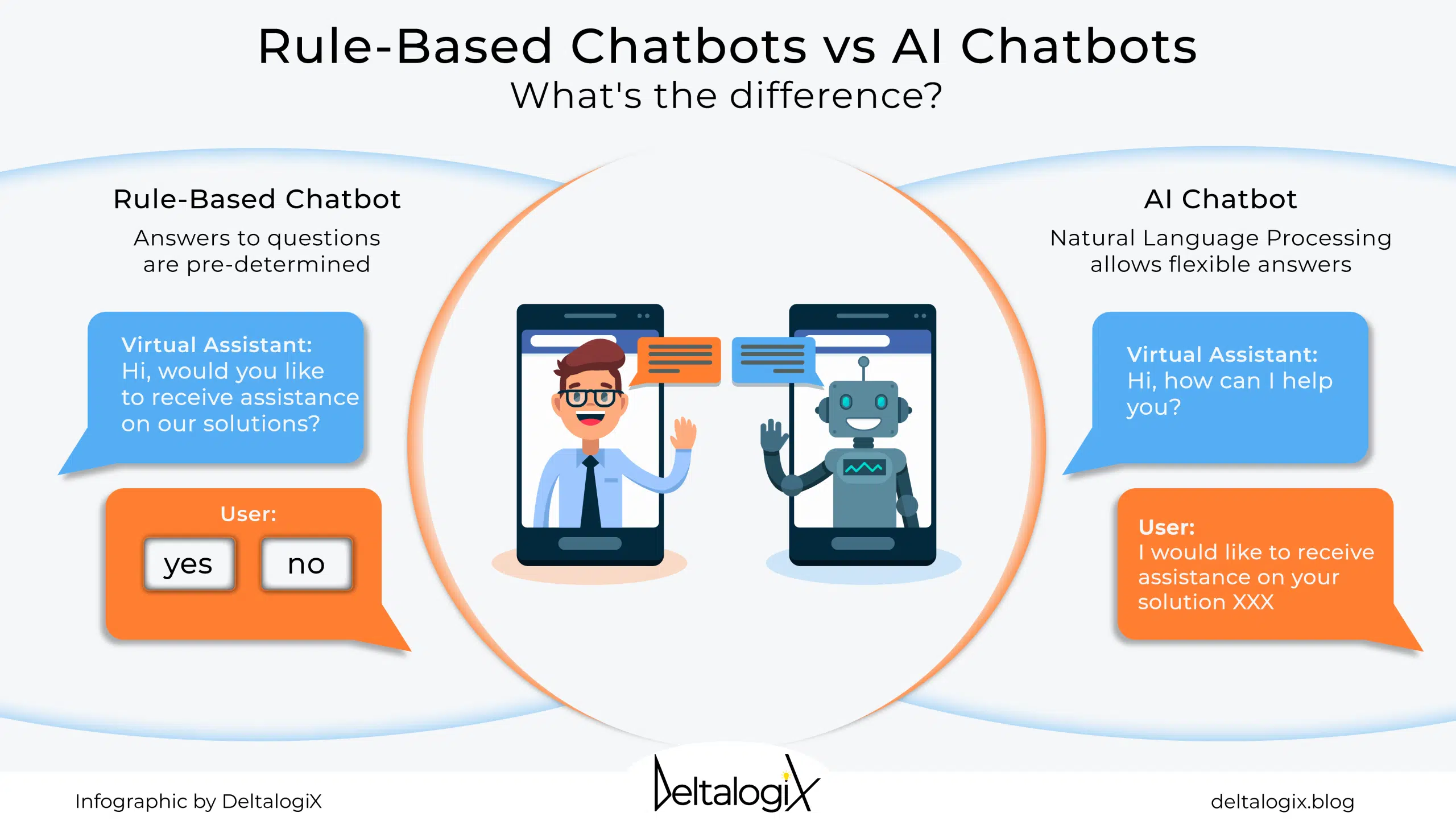
- Rule-based Chatbots
Rule-based chatbots follow predefined scripts and respond to specific keywords or phrases. They are reactive, providing answers based on fixed patterns. These bots are simple to implement and effective for answering basic queries, such as FAQs or order tracking. - AI-powered Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots, on the other hand, leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand and respond to complex, dynamic user queries. They can handle context-sensitive interactions and improve over time with use, making them suitable for more personalized customer service.
1.3. Use Cases and Industries
a. Customer Service
Chatbots have become a cornerstone of customer service automation, allowing businesses to offer continuous support without the need for human agents at all hours. Common uses include:
- Automating Ticket Generation: Chatbots can automatically create support tickets by collecting essential information from customers and logging it into a system. This reduces human intervention and accelerates the process of issue resolution.
- Responding to FAQs: Instead of relying on human staff to repeatedly answer common queries (e.g., store hours, shipping policies, return procedures), chatbots can provide instant responses based on a predefined knowledge base, improving efficiency.
- 24/7 Support: Unlike human agents, chatbots are available around the clock, ensuring customers can get assistance at any time of day or night, regardless of time zones. This helps businesses maintain high levels of customer satisfaction.
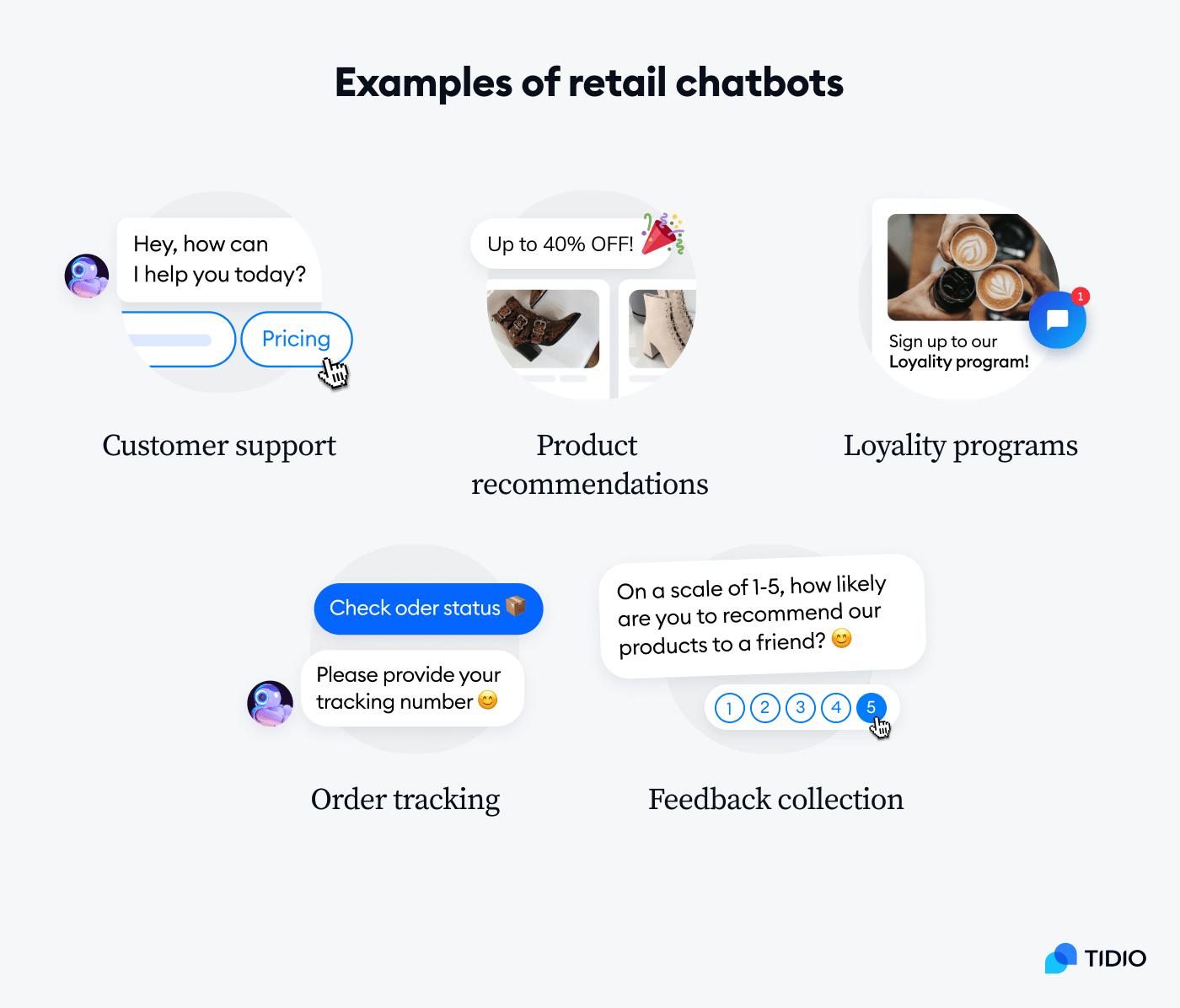
b. Retail
In the retail industry, chatbots are transforming how businesses interact with customers, enhancing both the shopping experience and operational efficiency:
- Product Recommendations: Using AI and machine learning algorithms, chatbots can analyze customer preferences and suggest products tailored to individual tastes. For example, chatbots on e-commerce websites can offer personalized clothing or electronics recommendations based on past purchases or browsing behavior.
- Order Inquiries: Chatbots can quickly provide customers with order status updates, including tracking numbers, estimated delivery times, and shipping status, without requiring direct interaction with a customer service representative.
- Post-purchase Support: After a purchase, chatbots can assist customers with follow-up questions such as return procedures, warranty information, and troubleshooting product issues. This automated support increases customer satisfaction and loyalty, reducing friction in post-purchase processes.
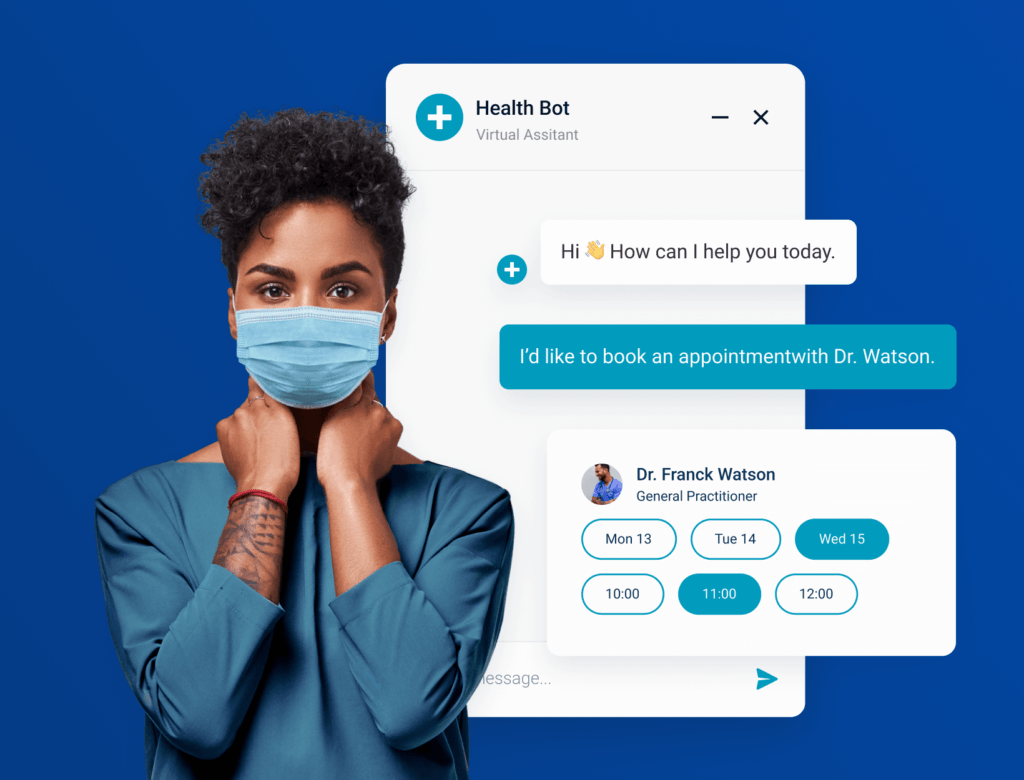
c. Healthcare
The healthcare sector is rapidly adopting chatbots to improve patient engagement, streamline administrative tasks, and ensure timely access to information:
- Appointment Bookings: Chatbots can schedule, reschedule, and cancel appointments autonomously by integrating with the healthcare provider’s calendar system. This makes appointment management easier for both patients and administrative staff.
- Answering Medical Queries: Chatbots can provide general medical information, such as symptoms, treatment options, and medication instructions. They can also offer answers to frequently asked questions about clinic policies, insurance coverage, or doctor availability.
- Health-related Information: Some chatbots are capable of tracking health metrics, reminding patients to take medications, or offering wellness tips based on their health profile. More advanced bots may even assist in monitoring chronic conditions by integrating with wearable health devices.
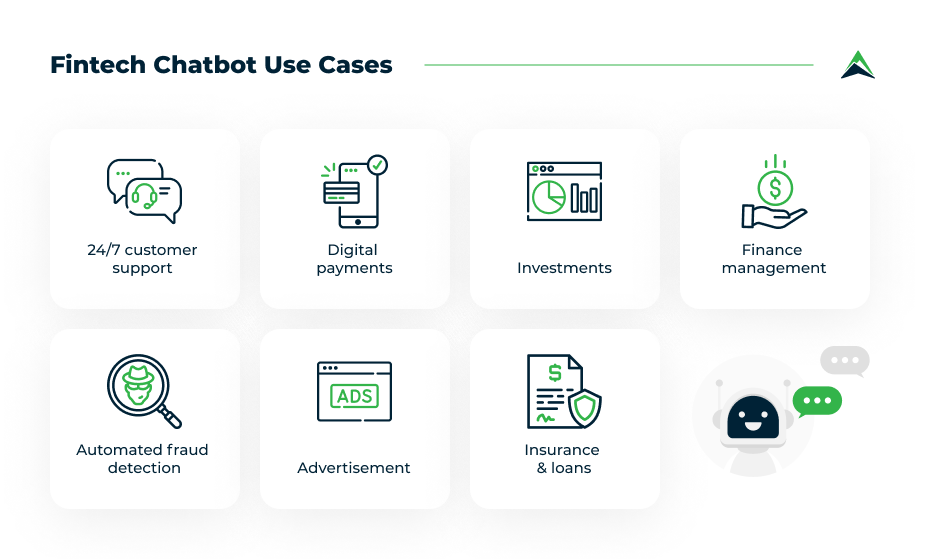
d. Banking & Finance
Chatbots are making banking and financial services more accessible, improving both customer experience and operational productivity:
- Account Balances and Transaction History: Chatbots can provide instant access to account balances, recent transactions, and pending payments, helping customers manage their finances without needing to call or visit a branch.
- General Financial Assistance: Chatbots can guide users through banking processes such as transferring funds, applying for loans, or setting up recurring payments. They can also provide real-time financial advice or insights, such as savings tips or investment suggestions based on the user’s spending patterns.
- Fraud Detection and Alerts: AI-powered chatbots can proactively detect unusual spending patterns or security risks and alert customers immediately. In some cases, chatbots can even initiate fraud prevention measures by blocking transactions or freezing accounts until human intervention occurs.

e. Travel & Hospitality
In the travel industry, chatbots are enhancing the customer journey from booking to post-trip support:
- Flight and Hotel Bookings: Chatbots can help customers find the best flight and hotel options based on their preferences, making recommendations based on budget, travel dates, and other preferences. They can also assist with booking confirmations, cancellations, or modifications.
- Travel Information & Itinerary Management: Chatbots can provide real-time updates on flight statuses, gate changes, and weather forecasts, ensuring travelers are well-informed. They can also send reminders about upcoming flights, check-in times, and hotel check-ins.
- Customer Support: For issues like lost luggage, itinerary changes, or emergencies, chatbots offer customers immediate assistance, reducing frustration and wait times associated with traditional customer support channels.
1.4. Advantages of Chatbots
- Scalability
One of the primary advantages of chatbots is their ability to handle large volumes of interactions simultaneously. Unlike human agents, chatbots can engage with multiple users at once, making them ideal for businesses with high customer interaction volumes. 65% of consumers now expect chatbots to assist them with customer service (Salesforce, 2022), and this number continues to grow. This scalability allows businesses to efficiently serve a larger customer base without increasing the headcount of customer support teams. - Availability
Chatbots are available 24/7, offering round-the-clock support and ensuring that customers can receive assistance at any time. Whether it’s early morning or late at night, chatbots help ensure that businesses maintain a high level of customer satisfaction, especially in regions with varying time zones. This constant availability also reduces wait times and supports the growing consumer expectation of instant responses. - Cost-efficiency
Chatbots can reduce customer service costs by automating routine tasks such as answering FAQs, processing orders, or updating account information. According to Juniper Research, businesses could save up to $11 billion annually by 2023 by implementing chatbots in customer service roles. By offloading simple inquiries to bots, businesses can allocate human resources to more complex tasks, ultimately improving operational efficiency and reducing overhead.
1.5. Limitations of Chatbots
- Lack of Emotional Intelligence
Despite advancements in AI, chatbots still lack emotional intelligence, which can limit their ability to handle nuanced or sensitive conversations. For example, if a customer is frustrated or upset, chatbots often fail to empathize or provide the level of comfort that a human agent could. This lack of emotional depth can lead to customer dissatisfaction, particularly in scenarios where empathy and understanding are crucial, such as handling complaints or sensitive issues. - Dependency on Predefined Scripts (Rule-Based Bots)
Rule-based chatbots, which operate based on predefined scripts and keyword matching, have significant limitations in addressing complex or unexpected queries. These bots can only respond to the scenarios they have been programmed for and struggle with context or ambiguity. As a result, businesses that rely on rule-based chatbots may find them ineffective in providing accurate or helpful responses to customers outside of simple, scripted interactions.
2. What Are Virtual Assistants?
2.1. Definition and Capabilities
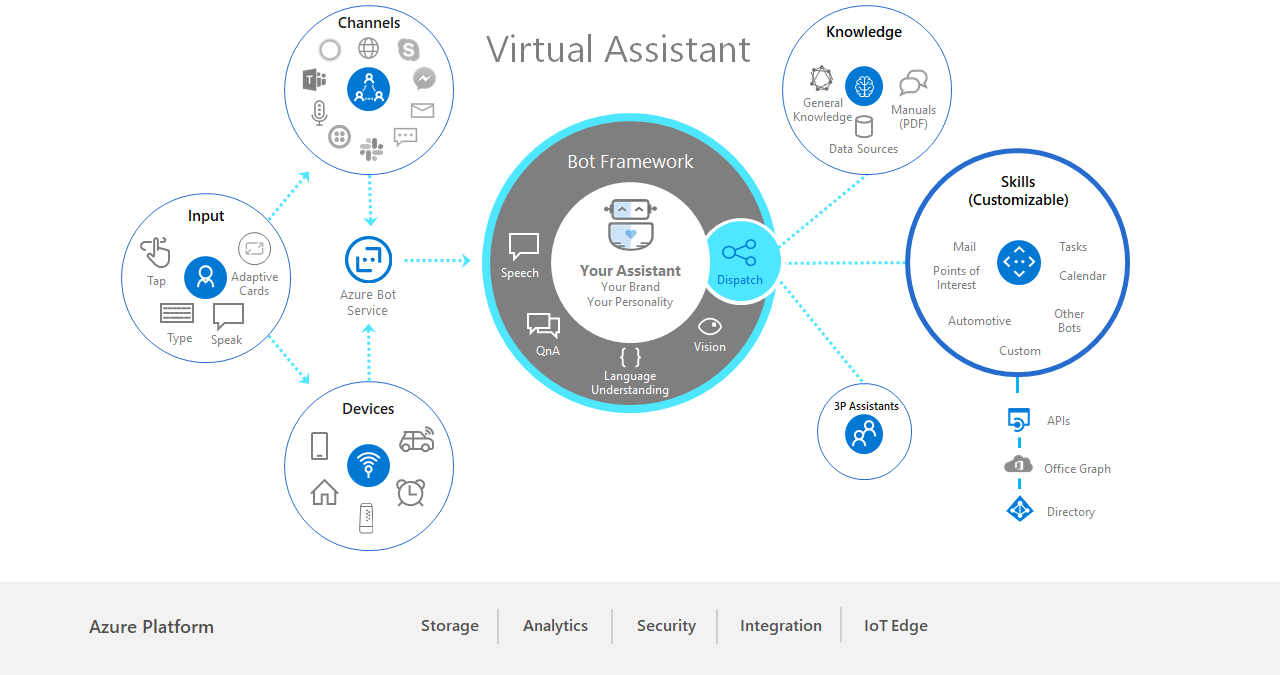
Virtual assistants (VAs) are advanced AI-powered tools designed to assist users in managing a wide range of tasks, from scheduling appointments and sending emails to controlling smart devices and retrieving information. Unlike chatbots, which focus primarily on text-based interactions, virtual assistants are more versatile and integrated, handling both simple and complex functions through voice or text. They are built to be context-aware, capable of processing and understanding user requests in a more sophisticated manner.
In 2023, 44% of U.S. households reported using voice-activated virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant (Statista). These tools are increasingly becoming essential in both personal and business environments, with their ability to automate tasks, answer questions, and provide personalized experiences, creating immense value for users and businesses alike.
Virtual assistants excel in their ability to integrate with a wide variety of systems, from calendars and emails to smart home devices and business applications. They use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand context, process commands, and offer intelligent, personalized responses. Their ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously and adapt to user preferences makes them powerful tools for both consumer and enterprise use.
2.2. Types of Virtual Assistants
a. Voice-activated Virtual Assistants
Voice-activated virtual assistants, such as Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google Assistant, are designed to respond to spoken commands, allowing users to perform tasks hands-free. These assistants are often integrated into smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices, making them highly accessible and convenient.
For instance, Siri can help you send a message or play music, while Alexa can control smart home devices like thermostats, lights, and security cameras. In 2023, there were over 4.2 billion voice assistant devices in use globally, highlighting the growing reliance on voice-driven AI
b. Enterprise-focused Virtual Assistants
On the business side, virtual assistants like Microsoft’s Cortana and Google Assistant for Workspace are designed to support enterprise-level tasks. These assistants integrate with business systems, such as email platforms, calendar applications, and project management tools, to help employees streamline their workflows.
Enterprise-focused assistants can schedule meetings, manage emails, set reminders, and provide updates on tasks or deadlines, all while adapting to the specific needs of a workplace environment. 40% of productivity software users will interact with an AI assistant by 2026, making these tools a growing fixture in business operations.
2.3. Applications in Businesses and Homes
Virtual assistants (VAs) are increasingly becoming essential tools in both personal and business environments due to their ability to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and simplify complex tasks. In homes, voice-activated virtual assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant provide convenience by automating daily activities such as controlling smart home devices, playing music, or setting reminders.
In the business world, virtual assistants are transforming how organizations handle routine administrative tasks. For instance, Cortana and Google Assistant are integrated into enterprise systems to assist with scheduling meetings, managing calendars, sending reminders, and even responding to emails. Virtual assistants are also being used in customer support, data retrieval, and project management.
Virtual assistants can also optimize team collaboration by providing real-time insights, tracking deadlines, and managing documents. The ability of these tools to integrate with a wide array of third-party applications—ranging from CRM systems to cloud-based file storage—makes them indispensable in modern workplace environments.
2.4. Strengths and Challenges of Virtual Assistants

Strengths
- Contextual Understanding
Virtual assistants are built with Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities, which enable them to understand context and user intent beyond simple commands. This allows them to process complex requests and provide more accurate, relevant responses. Unlike basic chatbots, which rely on scripted interactions, virtual assistants can adapt to evolving conversations, making them ideal for a wide variety of tasks. - Multi-tasking
One of the standout features of virtual assistants is their ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. Whether managing emails, setting reminders, or retrieving important documents, these tools can juggle various functions without losing efficiency. This multi-tasking capability boosts productivity, especially in high-demand environments like corporate offices, where time-sensitive decisions and quick responses are often critical.
Challenges
- Requires Sophisticated AI Training
While virtual assistants have advanced capabilities, they still require sophisticated AI and machine learning models to function effectively. They need to be trained on vast amounts of data to understand context, handle multi-step tasks, and refine their accuracy. The complexity involved in training these models means that virtual assistants must continuously evolve and improve to meet user expectations, which can lead to significant development and maintenance costs. - Privacy Concerns
The use of voice-activated virtual assistants raises valid concerns about user privacy and data security. Devices like Alexa and Siri are constantly listening for voice commands, which can sometimes result in unintended data collection. A study by Pew Research Center found that 45% of Americans are concerned about privacy risks associated with smart devices. This has led to growing concerns about how companies handle and store voice data, and what measures are in place to protect users’ personal information.
3. Key Differences Between Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
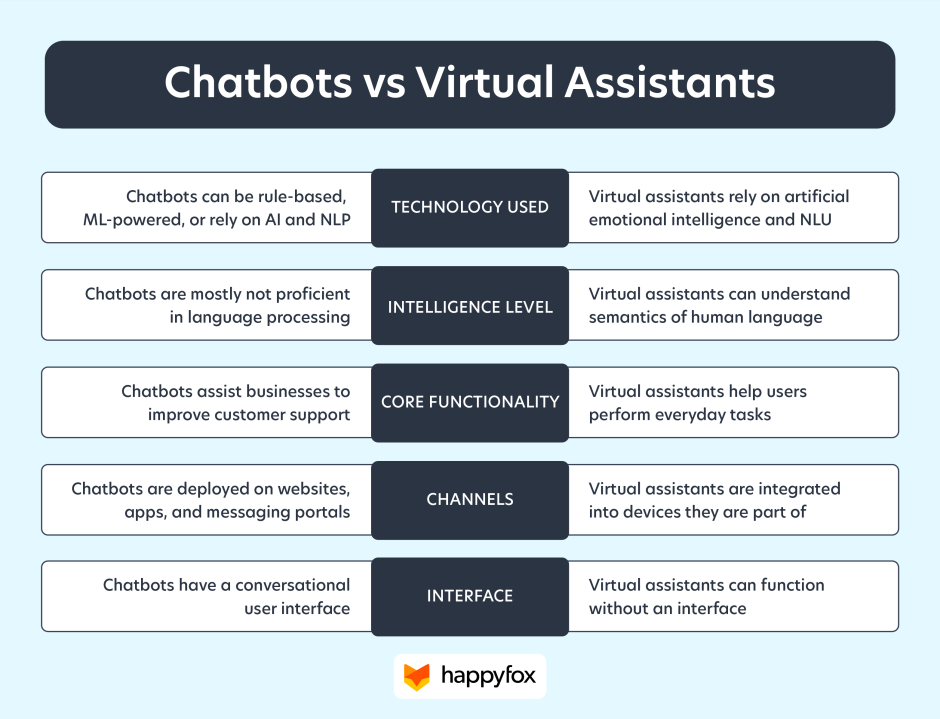
While both chatbots and virtual assistants are powered by AI and designed to automate tasks and enhance user experiences, they serve distinct functions and are built on different technological foundations. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their digital strategies and select the right tool for their needs.
3.1. Technology
Chatbots typically rely on either rule-based logic or more limited forms of AI, depending on their complexity. Rule-based chatbots follow predefined scripts and are designed to respond to specific commands or keywords. They can handle straightforward tasks such as answering FAQs or guiding users through a simple process. On the other hand, AI-powered chatbots use basic machine learning techniques to process natural language but still remain relatively simple compared to virtual assistants.
Virtual assistants, however, utilize advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning to interpret and respond to more complex requests. Virtual assistants can analyze context, understand nuanced language, and improve their responses over time through continuous learning. This makes virtual assistants more sophisticated, capable of handling complex conversations and interacting in a more human-like manner.
3.2. Interaction
The scope of interaction is another key difference. Chatbots are generally designed for task-specific queries, such as providing customer support or processing orders. They excel in environments where simple, transactional conversations are needed. For instance, chatbots can handle requests like order status updates, simple troubleshooting, or booking appointments, and they are typically used in areas like e-commerce, customer service, and support.
In contrast, virtual assistants can engage in complex, multi-step conversations. They are designed to manage more sophisticated tasks like setting up meetings, retrieving documents, managing emails, and even integrating with smart home devices. Virtual assistants offer a more holistic interaction, capable of handling requests across various domains simultaneously, making them invaluable in both personal and business environments.
3.3. Integration
One of the most significant distinctions between chatbots and virtual assistants is their level of integration into larger systems. Chatbots are often deployed in customer service or specific, predefined use cases. They are commonly found in messaging apps, on websites, or within social media channels, primarily supporting customer inquiries and troubleshooting. Their integration is typically limited to the channels they serve, and their role is often focused on first-line support or assisting users through simple tasks.
Virtual assistants, on the other hand, are deeply integrated into both business operations and IoT systems. They can interact with enterprise software, manage complex workflows, and even interface with Internet of Things (IoT) devices. For instance, virtual assistants like Google Assistant for Workspace and Cortana can schedule meetings, retrieve project information, and control connected devices all within the same ecosystem. This integration allows virtual assistants to become central hubs for both personal and professional productivity, enhancing both individual and organizational efficiency.
3.4. Personalization and Adaptability
Virtual assistants offer a much higher degree of personalization and adaptability compared to chatbots. Thanks to advanced AI and machine learning, virtual assistants can learn from user interactions, adapt to preferences, and provide more personalized responses over time. They can also handle a broader range of scenarios, from managing emails to controlling smart home devices, all while offering a more tailored experience based on user behavior and preferences.
In contrast, chatbots have more limited adaptability. While AI-powered chatbots can improve their responses through machine learning, they still rely heavily on predefined scripts and rules. Their ability to handle new or unexpected scenarios is often restricted unless they are specifically trained on those situations. As such, chatbots are less flexible and capable of personalization than virtual assistants.
4. Chatbot vs. Virtual Assistant: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business

When deciding between chatbots and virtual assistants for your business, it’s essential to consider several key factors, including the complexity of tasks, customer experience needs, budget constraints, and data security concerns. The right choice can significantly impact your operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and bottom line. As AI technologies continue to evolve, businesses are increasingly relying on these solutions to streamline workflows and enhance customer interactions.
4.1. Identifying Task Complexity and Goals
The first step in selecting the right AI solution is to evaluate the scope of tasks you want to automate. If your business needs to handle simple queries, such as answering frequently asked questions (FAQs) or processing routine requests, a chatbot may be sufficient. Chatbots are ideal for tasks that require limited decision-making, such as order status inquiries or appointment scheduling.
However, if your operations require handling more complex interactions—such as managing customer support tickets, processing multi-step workflows, or assisting in decision-making—virtual assistants are better equipped to handle these advanced tasks. Virtual assistants utilize sophisticated Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning, enabling them to process more nuanced information and provide multi-step, personalized solutions.
4.2. Assessing Customer Experience Needs
Your choice of AI solution also depends on the customer experience you want to deliver. If you’re looking to provide a simple, self-service option for customers, a chatbot may be the best fit. They excel in handling straightforward, transactional queries, such as product inquiries or booking confirmations.
However, if you want to offer a more seamless, engaging experience, a virtual assistant may be necessary. Virtual assistants are capable of understanding more complex commands, offering personalized recommendations, and assisting with a broader range of tasks, making them an ideal solution for businesses looking to provide an advanced customer journey.
4.3. Budget Considerations
When evaluating the cost-effectiveness of chatbots vs. virtual assistants, it’s important to factor in both initial deployment costs and long-term maintenance expenses. Chatbots are typically less expensive to develop and deploy, making them an attractive option for businesses with more limited budgets. They also have lower maintenance costs because they rely on predefined rules and processes, reducing the need for ongoing AI training and updates.
Virtual assistants, while more expensive to implement, offer greater scalability and can support a broader range of business needs. Their advanced AI capabilities, such as natural language processing and machine learning, require more significant investments in development, training, and ongoing optimization. However, the long-term benefits of virtual assistants—such as improved customer satisfaction, increased efficiency, and the ability to scale—may outweigh the initial costs for larger enterprises or those with complex operations.
4.4. Addressing Data Security and Privacy Concerns
In industries that handle sensitive customer data, such as healthcare, finance, and legal services, data security and privacy should be a top priority when deploying AI solutions. Chatbots and virtual assistants collect vast amounts of personal and financial information, making them potential targets for data breaches. It’s crucial to implement strong encryption protocols, secure cloud storage, and compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
5. Future Trends in AI-Driven Automation
5.1. Advances in NLP and Contextual Understanding
The continued advancements in NLP are transforming how AI tools like chatbots and virtual assistants interpret and respond to human language. NLP, which allows machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, is becoming more sophisticated, enabling AI systems to engage in more fluid, human-like conversations. As contextual understanding improves, chatbots and virtual assistants will be able to recognize nuances such as tone, sentiment, and intent, allowing for more personalized and accurate interactions.
In fact, Gartner forecasts that by 2025, 80% of all customer interactions will involve some form of AI, with NLP at the forefront of this transformation. This means businesses will be able to automate not just transactional queries, but complex, multi-step conversations that require deeper understanding. The ability of AI systems to adapt and learn from these interactions will drive customer satisfaction and operational efficiency to new heights.
5.2. Integration of IoT and Multi-modal AI Tools
As IoT devices become increasingly ubiquitous, the integration of IoT-connected virtual assistants is expected to revolutionize the way businesses and consumers interact with technology. Virtual assistants will be able to seamlessly integrate with various IoT systems—from smart home devices to industrial IoT platforms—enabling a more connected and automated ecosystem. Imagine a scenario where a virtual assistant not only manages your calendar but also controls your office lighting, adjusts heating, monitors inventory levels, and coordinates machine maintenance, all through a single interface.
The future of multi-modal AI tools—systems that combine text, voice, and visual inputs—will take this further by allowing users to interact with machines in a more natural, intuitive manner. With the rise of voice-controlled AI assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, the next step will be cross-platform integration, allowing businesses to unify various devices and applications into a single, cohesive experience. According to a report by Statista, the global number of IoT-connected devices is expected to reach 75 billion by 2025, creating immense opportunities for AI-driven automation.
5.3. Industry-Specific Innovations
AI-driven automation is set to have a transformative impact across various industries. In healthcare, for example, AI-powered virtual assistants are already helping healthcare professionals schedule appointments, analyze medical records, and even assist in diagnostics. These systems are becoming increasingly adept at interpreting medical language and providing decision support, making them invaluable in improving patient care and operational efficiency.
In finance, AI is enhancing fraud detection, automating customer service, and streamlining risk assessments. Virtual assistants are also helping financial institutions provide more personalized financial advice by analyzing customers’ financial data and offering tailored recommendations.
In retail, AI is already revolutionizing how businesses interact with customers. Virtual assistants are being used for personalized shopping experiences, from product recommendations to inventory management and customer support. AI-driven chatbots are also helping brands engage customers in real-time, enhancing both sales conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Why Choose SmartDev for AI Solutions?

We understand that not every business is the same, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Choosing between chatbots and virtual assistants depends on your specific needs, goals, and industry. If you’re still unsure which solution best fits your business, we recommend scheduling a 30-minute consulting session with our AI experts. We’ll assess your unique business situation and provide personalized recommendations to help you make the most informed choice.
Choosing SmartDev means choosing a future-ready AI solution that is tailored to your business needs, backed by expert knowledge and industry experience. With a portfolio of successful projects across various sectors, SmartDev is a trusted partner for AI-driven transformations. Our case studies highlight tangible results in improving customer engagement and reducing costs.
Whether you are looking to implement a chatbot, a virtual assistant, or a more complex AI-driven system, SmartDev’s holistic approach ensures that every aspect of your solution is designed with your business goals in mind.
References
- The State of AI in 2023: Generative AI’s Breakout Year
- Chatbot Market – Global Forecast to 2028
- State of the Connected Customer
- Chatbots to Deliver $11bn Cost Savings by 2023
- Voice Assistant Users in the U.S. 2023
- Productivity Management Software Market
- Virtual Assistants: The Future of Work
- Americans and Privacy: Concerned, Confused, and Feeling Lack of Control Over Their PersonalInformation






