The artificial intelligence revolution has fundamentally transformed how organizations approach product development, yet it has introduced a new category of challenges that traditional software engineering never encountered. While AI product development challenges share surface-level similarities with conventional software projects, the underlying dynamics operate on entirely different principles-ones defined by probabilistic outcomes, continuous experimentation, and irreducible uncertainty.
Recent industry data reveals a sobering reality: 42% of companies abandoned most of their AI initiatives in 2025, a dramatic spike from just 17% the previous year. More alarming, the failure rate of traditional IT projects. These statistics aren’t merely indicators of immature technology; they reflect a fundamental misunderstanding of what distinguishes AI product development from the software engineering practices that have worked for decades.
The stakes have never been higher. Organizations investing in AI expect transformational impact, yet most initiatives stall before reaching production. Understanding the unique dynamics of the AI product lifecycle, recognizing the critical differences between AI and software development, and implementing robust strategies for managing uncertainty in AI product development separate successful AI initiatives from the 42% headed for abandonment.

Why AI Product Development Isn’t Just “Software 2.0”
The Fundamental Mindset Shift
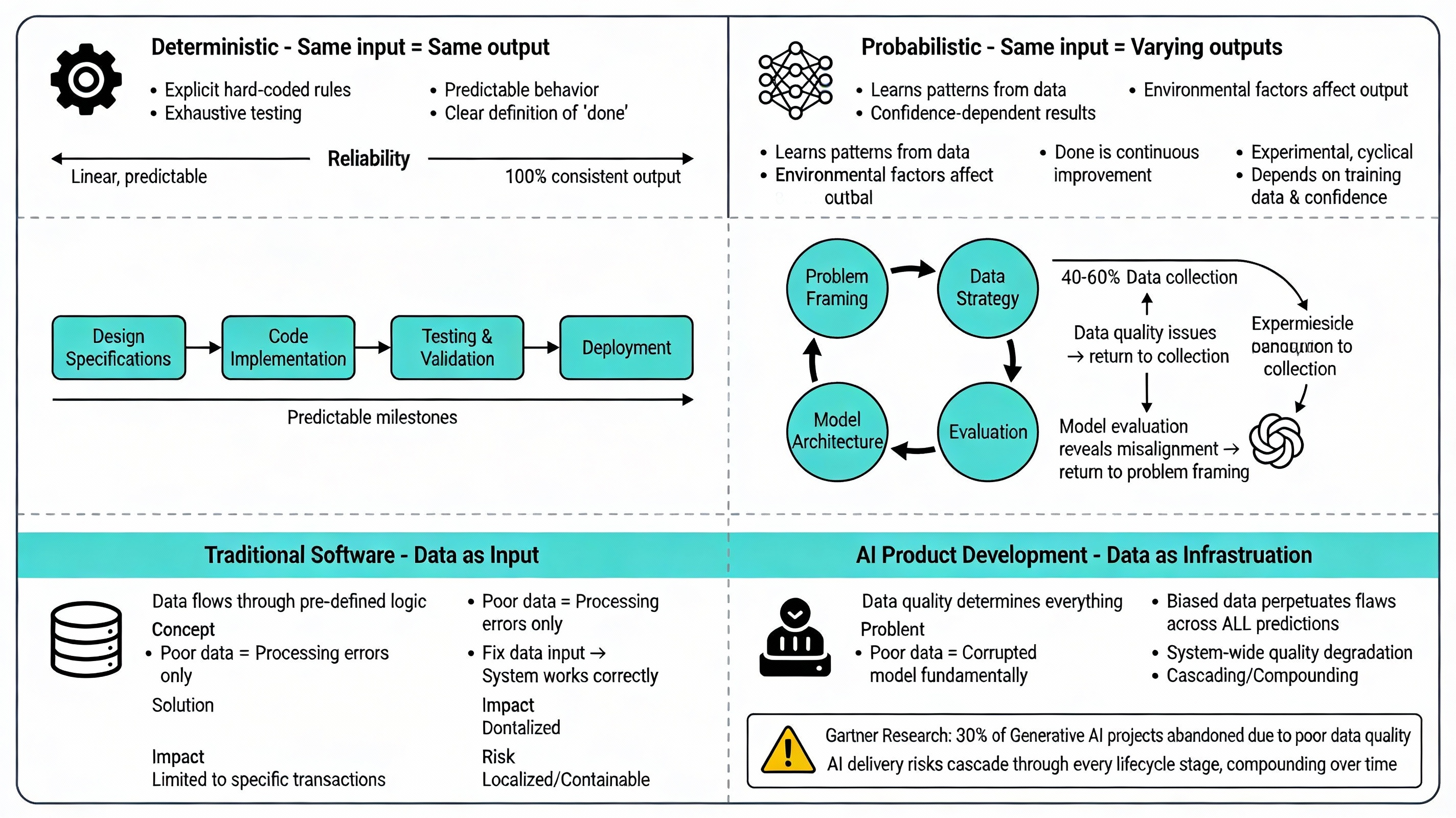
Traditional software development operates on deterministic principles: the same input reliably produces the same output. Engineers write explicit rules, test them exhaustively, and deploy code that behaves predictably in production. This predictability enables precise planning, reliable timelines, and clear definitions of “done.”
AI product development operates on fundamentally different principles. AI systems produce probabilistic outputs where the same input may yield varying results depending on model confidence, training data distribution, and environmental factors. According to NIST’s analysis of how AI risks differ from traditional software risks, this distinction reshapes every aspect of product development-from initial problem framing to post-deployment monitoring.
A recommendation engine doesn’t execute hard-coded rules; it learns patterns from data and makes predictions that improve-or degrade-over time. When SmartDev’s AI development services engage with clients, the first challenge is often shifting mindsets from deterministic software thinking to probabilistic AI reasoning.
Linear Processes vs. Experimental Cycles
Software development follows relatively linear paths: design specifications → code implementation → testing validation → deployment. While Agile methodologies introduced iteration, the fundamental work remains sequential with clear milestones and predictable checkpoints.
The AI product lifecycle operates through experimental cycles where each stage continuously feeds back into earlier phases. Research on AI product development lifecycle shows that problem framing influences data strategy, which determines model architecture, which reveals new problem dimensions, which prompts reframing. This cyclical nature makes traditional project management frameworks fundamentally inadequate.
Consider a typical AI project timeline: data collection consumes 40-60% of project duration, yet data quality issues discovered during model training necessitate returning to the collection phase. Model evaluation might reveal that the original problem definition was misaligned with what AI can realistically solve, forcing teams back to problem framing. This non-linear progression defies traditional Gantt charts and milestone-based planning.
SmartDev’s 3-week AI discovery program specifically addresses this challenge by validating business problems, aligning stakeholders, and defining clear paths forward before development complexity increases exponentially.
Data as Infrastructure, Not Input
In traditional software, data flows through pre-defined logic. Poor data quality creates processing errors, but the application logic remains sound. Fix the data input, and the system functions correctly.
In AI product development, data quality determines everything. Poor data doesn’t just cause processing errors-it fundamentally corrupts the model itself. An AI system trained on biased, incomplete, or outdated data will perpetuate those flaws across every prediction it makes, regardless of how sophisticated the algorithm.
This elevates data from operational input to strategic infrastructure. At least 30% of generative AI projects will be abandoned specifically due to poor data quality, according to Gartner research. The AI delivery risks associated with data dependencies cascade through every stage of the development of lifecycle, compounding rather than diminishing over time.
The Seven Unique Dynamics of AI Product Development
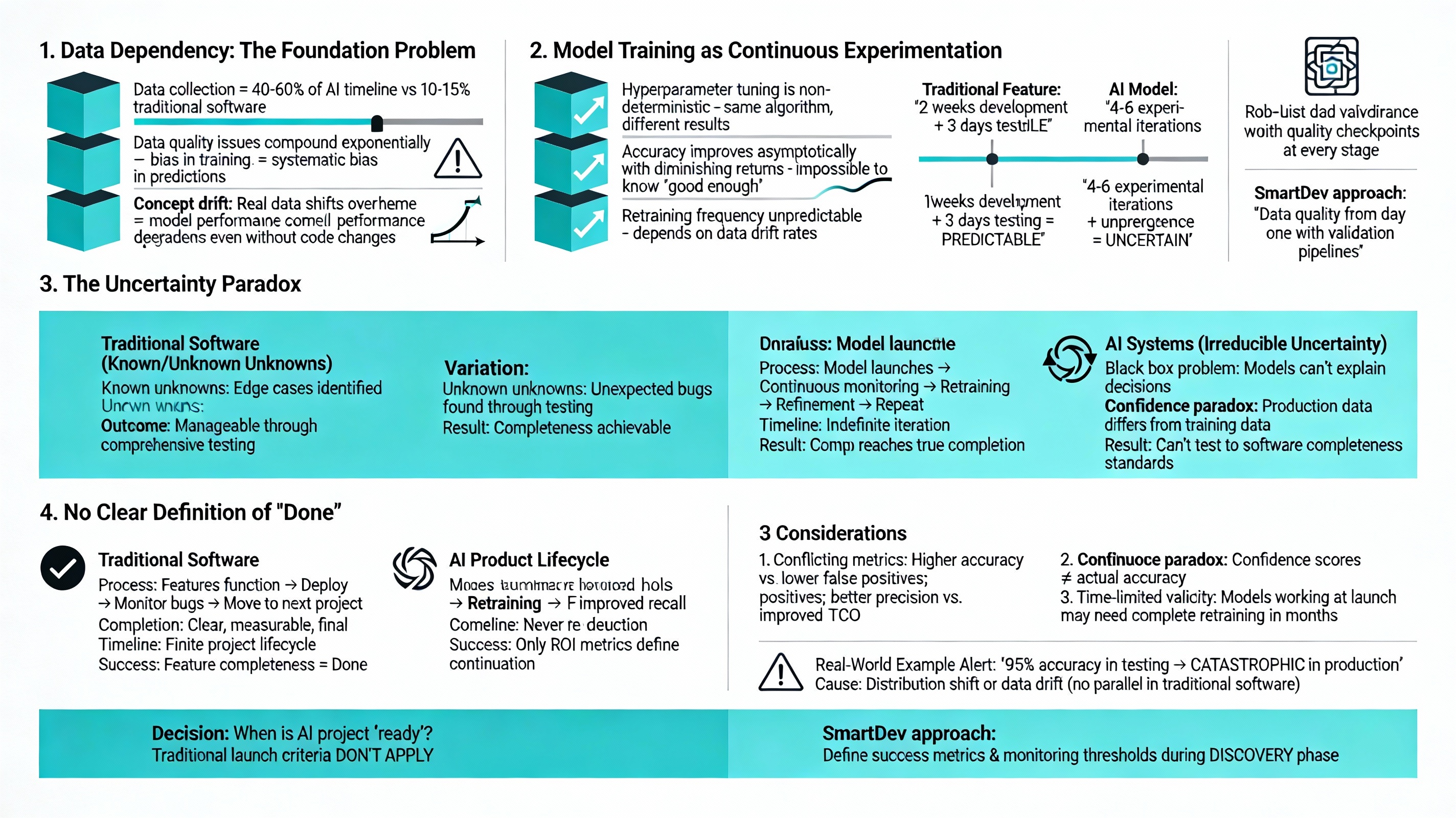
1. Data Dependency: The Foundation Problem
Unlike traditional software where data flows through pre-built logic, AI systems are fundamentally defined by their training data. This creates a dependency that doesn’t exist in conventional development and represents the single largest source of project failure.
Challenge specifics:
- Data collection consumes 40-60% of AI project timelines, compared to 10-15% in traditional software projects
- Data quality issues compound exponentially-bias in training data manifests as systematic bias in predictions that can’t be fixed through code changes
- Real-world data distributions shift over time (concept drift), degrading model performance even when no code changes occur
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) identifies data quality as the primary differentiator between AI and traditional software risks. According to NIST research, “The data used for building an AI system may not be a true or appropriate representation of the context or intended use, and harmful bias and other data quality issues can affect AI system trustworthiness.”
Mitigation approach: Robust data governance frameworks with quality checkpoints at every stage. SmartDev’s AI & Machine Learning solutions prioritize data quality from day one, implementing validation pipelines that catch issues before they cascade downstream.
2. Model Training as Continuous Experimentation
Software testing asks binary questions: Does the feature work? Does it meet specifications? AI vs software development evaluation operates on a spectrum of uncertainty: How well does it work? Under what conditions does performance degrade? What confidence level should trigger human review?
Challenge specifics:
- Hyperparameter tuning is non-deterministic-the same algorithm with different random initialization can produce meaningfully different results
- Model accuracy improves asymptotically with diminishing returns, making it impossible to know when “good enough” has been achieved
- Retraining frequency is unpredictable and depends on data drift rates that vary by domain and deployment context
This experimental nature means AI projects can’t be estimated with the precision that traditional software allows. While a traditional feature might take “2 weeks of development + 3 days of testing,” an AI model might require “4-6 experimental iterations with unpredictable timeline based on model performance convergence.”
3. The Uncertainty Paradox
Software systems contain known unknowns (edge cases we identify) and unknown unknowns (unexpected bugs). Both are manageable through comprehensive testing and defensive programming.
AI systems contain irreducible uncertainty built into their probabilistic nature. Models can’t explain their own decisions with complete transparency (the “black box” problem), confidence scores don’t always correlate with actual accuracy, and edge cases emerge in production unpredictably.
According to research on managing uncertainty in AI product development, “Prediction intervals and confidence intervals give bounds on expected outcomes under specified assumptions, but these assumptions may not hold in deployment environments that differ from training conditions.” This means AI product development fundamentally cannot be tested to the same completeness standards as traditional software.
Real-world example: AI models performing with 95% accuracy in testing environments can experience catastrophic failure on real-world data distributions that differ even slightly from training data. This phenomenon, called distribution shift or data drift, has no direct parallel in traditional software development.
4. No Clear Definition of “Done”
Software projects reach completion when specified features function according to requirements. Teams deploy, monitor for bugs, and move to the next project.
AI product lifecycle never reaches true completion, iteration continues indefinitely, and only ROI metrics define whether to continue investment. Feature completeness doesn’t equal business value because model performance degrades over time, requiring continuous retraining, monitoring, and refinement.
Challenge specifics:
- Performance metrics can conflict with each other (higher accuracy vs. lower false positive rate; better precision vs. improved recall)
- Continuous retraining becomes operational overhead that must be factored into total cost of ownership
- Models that work well at launch may require complete retraining within months as data distributions shift
Decision implication: When do you declare an AI project “ready”? Traditional launch criteria don’t apply because AI product lifecycle systems evolve continuously post-deployment. SmartDev’s approach to AI in product development emphasizes defining success metrics and monitoring thresholds during the discovery phase, before development begins.
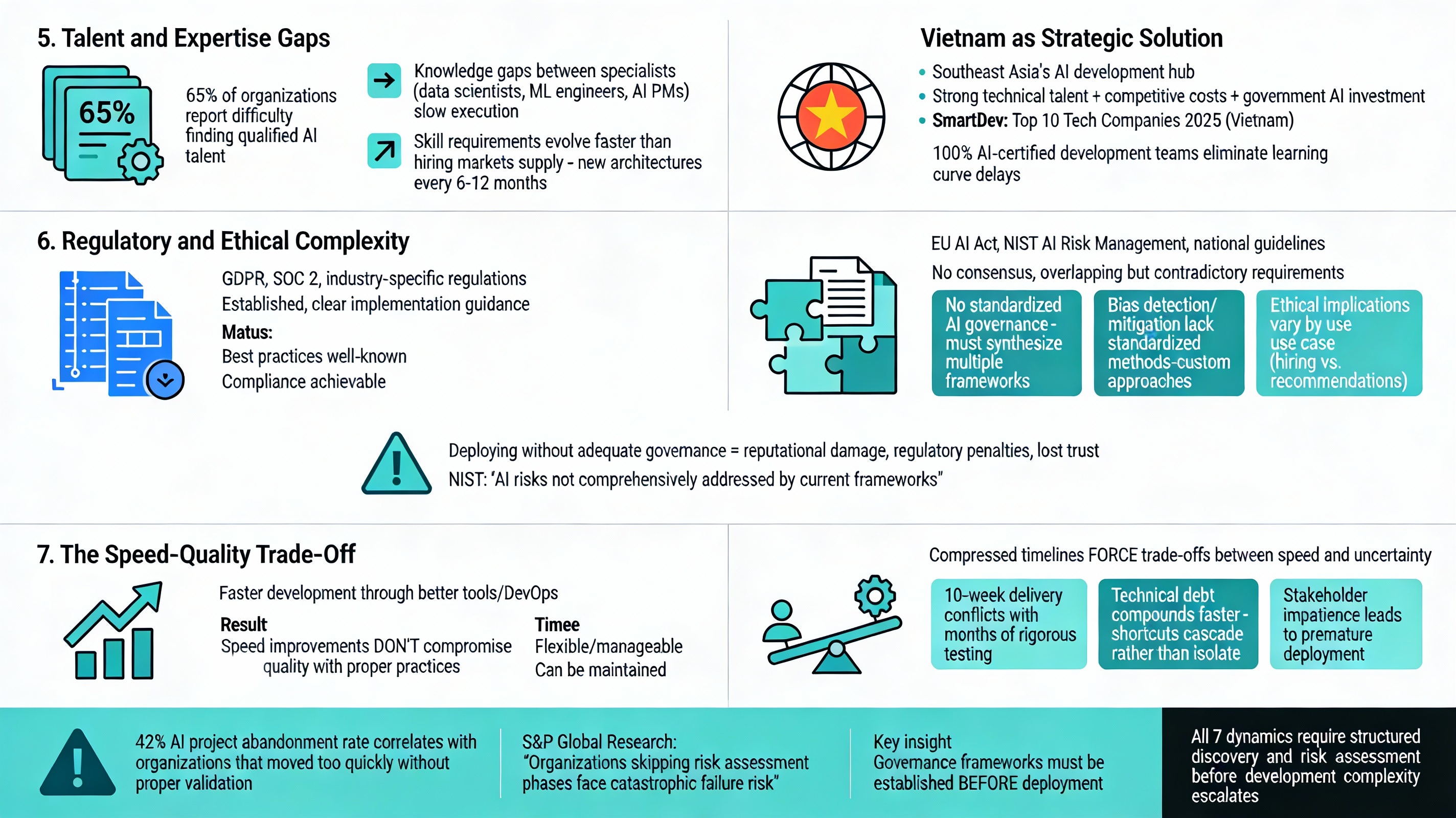
5. Talent and Expertise Gaps
Traditional software development benefits from a large, globally distributed talent pool with relatively standardized skill frameworks. Hiring developers, QA engineers, and product managers follows well-established patterns.
AI product development requires specialized expertise that remains in severe shortage: data scientists who understand statistical modeling, ML engineers who can optimize model training pipelines, AI product managers who can translate business problems into ML-appropriate use cases.
Challenge specifics:
- 65% of organizations report difficulty finding qualified AI talent
- Knowledge gaps between specialist roles (data scientists, ML engineers, AI product managers) slow execution because effective AI development requires cross-functional collaboration that traditional software teams don’t need
- Skill requirements evolve faster than hiring markets can supply, as new architectures (transformers, diffusion models, agentic AI) emerge every 6-12 months
Vietnam has emerged as a strategic solution to this talent challenge. According to industry analysis, Vietnam is becoming Southeast Asia’s AI development hub due to its combination of strong technical talent, competitive costs, and government investment in AI education. SmartDev, recognized among Vietnam’s Top 10 Tech Companies 2025, addresses this gap through 100% AI-certified development teams that eliminate learning curve delays.
6. Regulatory and Ethical Complexity
Traditional software operates within mature compliance frameworks (GDPR for data privacy, SOC 2 for security, industry-specific regulations). While complex, these frameworks provide clear implementation guidance with established best practices.
AI introduces emerging and fragmented regulatory landscapes where consensus hasn’t formed. The EU AI Act, NIST AI Risk Management Framework, and various national guidelines provide overlapping but not fully aligned requirements.
Challenge specifics:
- No consensus on AI governance standards-organizations must synthesize guidance from multiple frameworks with sometimes contradictory requirements
- Bias detection and mitigation lack standardized methods, leaving organizations to develop custom approaches that may not scale
- Ethical implications vary dramatically by use case: AI in hiring faces different scrutiny than AI in content recommendation, requiring use-case-specific governance
Real-world risk: Deploying AI without adequate governance leads to reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and loss of stakeholder trust. As NIST emphasizes, “AI systems bring a set of risks that are not comprehensively addressed by current risk frameworks.”
7. The Speed-Quality Trade-Off
Traditional software development has achieved speed improvements through better tools, frameworks, and DevOps practices. Faster development doesn’t inherently compromise quality when proper practices are followed.
In AI product development, compressed timelines often force trade-offs between speed and uncertainty management. The experimental nature of model development means that rushing through validation phases leaves critical AI delivery risks undetected.
Challenge specifics:
- 10-week delivery timelines conflict with rigorous testing requirements that can take months for comprehensive validation
- Technical debt accumulates faster in compressed AI timelines because shortcuts taken during model development compound rather than remaining isolated
- Stakeholder impatience leads to premature deployment before uncertainty is properly managed and governance frameworks established
Risk: Launching AI products before governance frameworks are established and model limitations are understood. According to S&P Global research, the 42% AI project abandonment rate correlates directly with organizations that moved too quickly through validation phases without proper risk assessment.
Is your AI product destined to join the 42% that fail in production?
Most organizations discover critical governance gaps and data quality issues only after expensive failures. SmartDev helps enterprises validate AI opportunities, build governance frameworks before development, and implement risk management strategies that prevent costly project abandonment.
De-risk your AI lifecycle, align teams on success metrics, and build AI products with clarity using SmartDev's proven 3-week AI discovery and governance expertise.
Talk to an AI Strategy ExpertCritical Risks in AI Product Development Lifecycle
High-Impact, High-Probability Risks
Data Quality Degradation: Impact (High) × Probability (High)
The most common and consequential risk in AI product development. Training data that seemed adequate during development proves insufficient in production. Data distributions shift over time, introducing samples the model never encountered during training.
Solution: Robust data validation pipelines and automated drift detection systems alert teams before model performance degrades significantly. Regular data audits and quality monitoring are non-negotiable operational requirements.
Model Accuracy Degradation Over Time (Drift): Impact (High) × Probability (High)
Models trained on historical data gradually lose relevance as the world changes. This “concept drift” is inevitable and requires continuous monitoring to detect and address.
According to research on drift monitoring, “When drift is detected, a drift monitoring system will trigger alerts and update existing models. This process takes place as part of the MLOps pipeline.” Organizations without automated drift detection experience silent model failures that degrade business value without triggering alerts.
Solution: Implement MLOps platforms that automatically monitor production data distributions, compare them to training distributions, and trigger retraining when drift exceeds thresholds.
Stakeholder Misalignment on Success Metrics: Impact (High) × Probability (High)
Technical teams optimize for model accuracy while business stakeholders care about ROI and business impact. Without aligned success metrics, technically successful projects fail to deliver business value.
Solution: KPI alignment workshops during problem framing phase; clear governance structures that bridge technical and business decision-making. SmartDev’s AI discovery process specifically addresses this through stakeholder alignment in Week 1, before any technical work begins.

High-Impact, Medium-Probability Risks
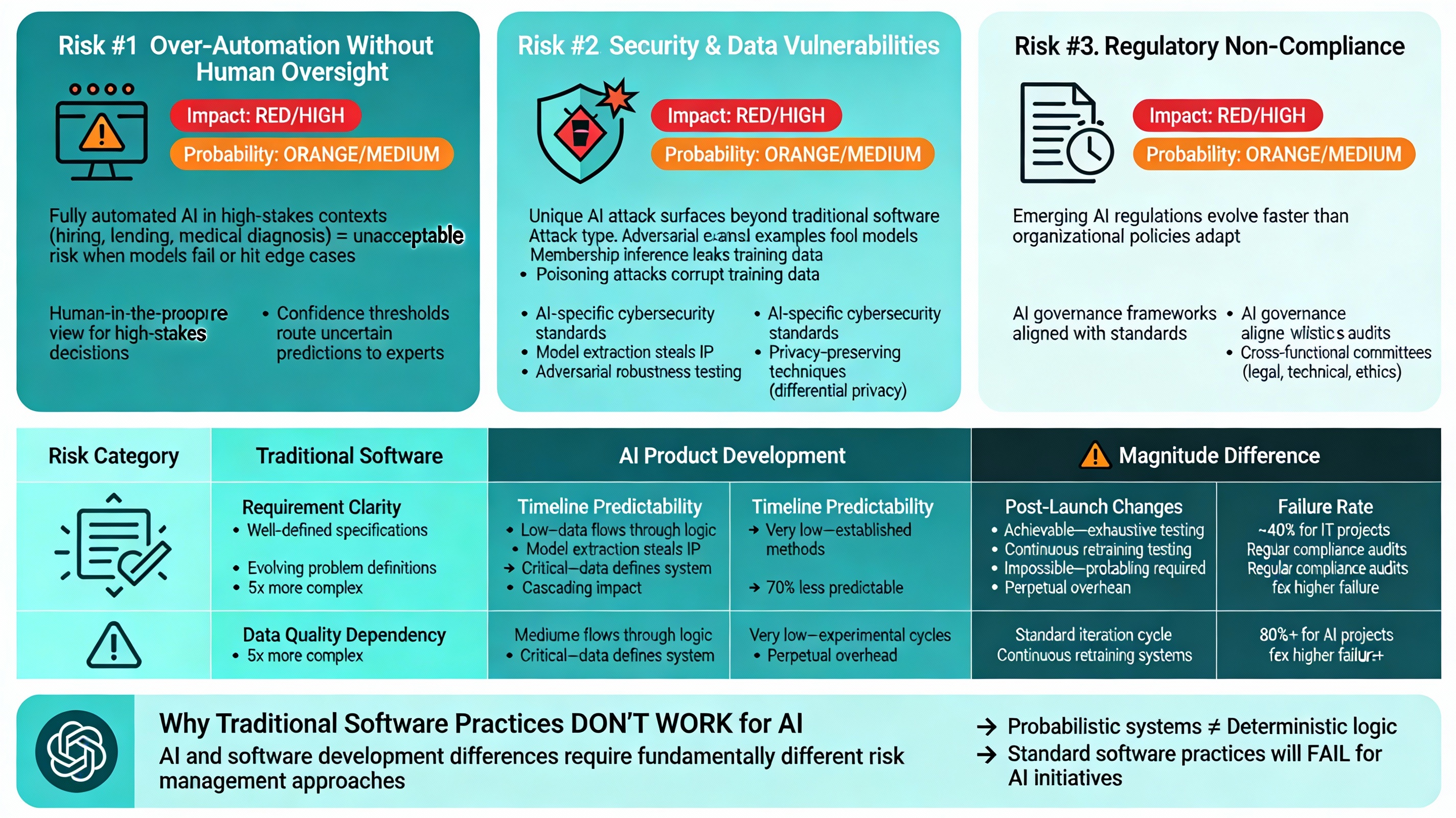
Over-Automation Without Human Oversight: Impact (High) × Probability (Medium)
Fully automated AI decision-making in high-stakes contexts (hiring, lending, medical diagnosis) creates unacceptable risks when models fail or encounter edge cases they weren’t trained for.
Solution: Human-in-the-loop review processes for high-stakes decisions; confidence thresholds that route uncertain predictions to human experts for verification and judgment.
Security & Data Vulnerabilities: Impact (High) × Probability (Medium)
AI systems face unique attack surfaces beyond traditional software: adversarial examples that fool models, model extraction attacks that steal intellectual property, membership inference that leaks training data, and poisoning attacks that corrupt training data.
Solution: AI-specific cybersecurity standards, adversarial robustness testing, and privacy-preserving techniques like differential privacy.
Regulatory Non-Compliance: Impact (High) × Probability (Medium)
Emerging AI regulations create compliance requirements that evolve faster than organizational policies and infrastructure can adapt.
Solution: Establish AI governance frameworks aligned with recognized standards; regular compliance audits; cross-functional governance committees with legal, technical, and ethics representation.
Comparative Risk Assessment: AI vs. Traditional Software
| Risk Category | Traditional Software | AI Product Development | Magnitude Difference |
| Requirement Clarity | Well-defined specifications | Evolving problem definitions | 5x more complex |
| Data Quality Dependency | Low-data flows through logic | Critical data defines the system | Cascading impact |
| Timeline Predictability | Medium-established methods | Very Low-experimental cycles | 70% less predictable |
| Post-Launch Changes | Standard iteration cycle | Continuous retraining required | Perpetual operational overhead |
| Testing Completeness | Achievable-exhaustive testing | Impossible-probabilistic systems | Fundamentally uncertain |
| Failure Rate | ~40% for IT projects | 80%+ for AI projects | 2x higher failure rate |
This comparative analysis reveals why organizations can’t simply apply traditional software development practices to AI initiatives. The differences between AI and software development require fundamentally different risk management approaches that account for probabilistic systems rather than deterministic logic.
Managing Uncertainty in AI Product Development
Build a Robust Risk Management Framework
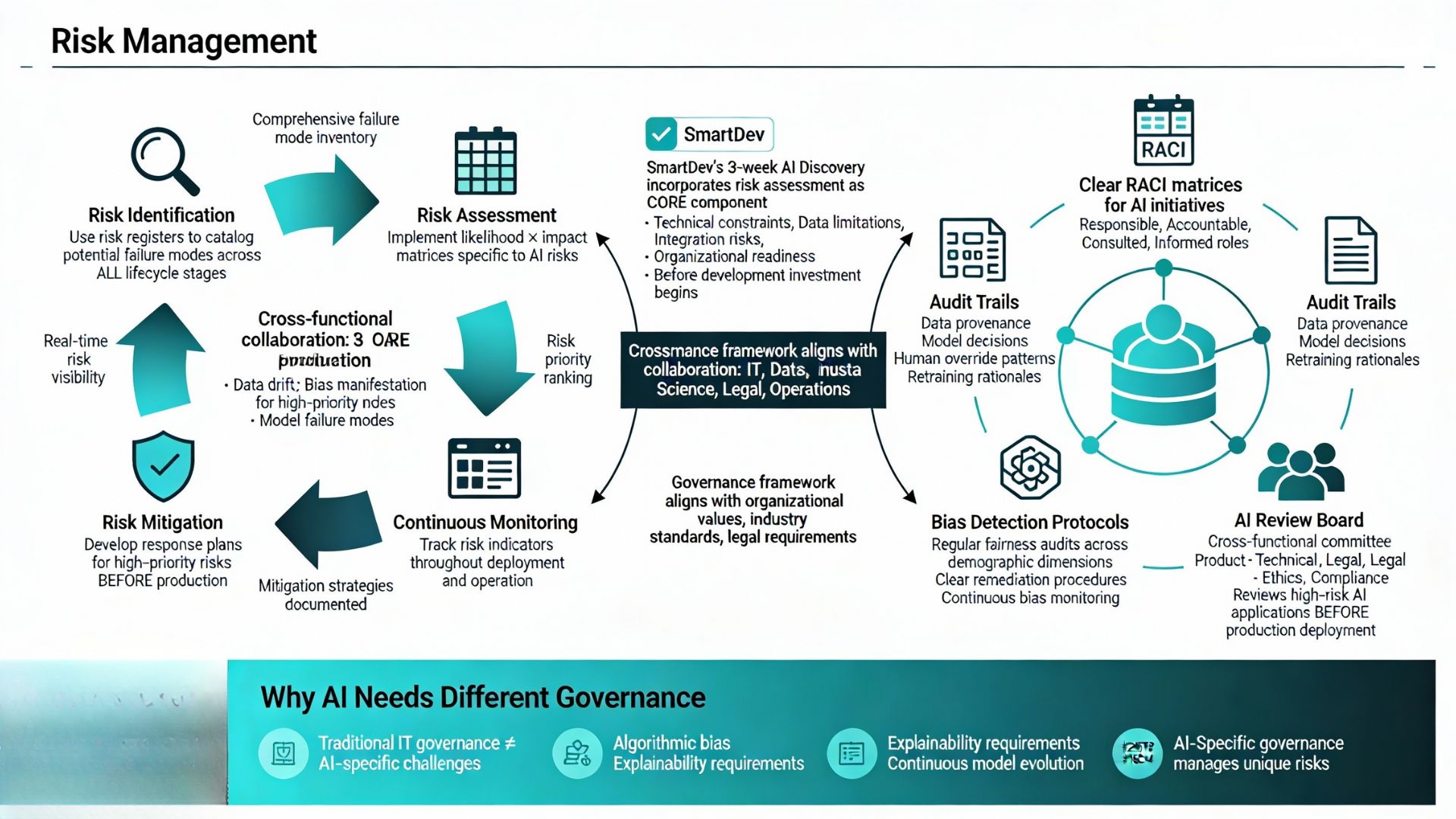
According to research on navigating AI unpredictability, organizations must implement “cross-functional approaches to managing uncertainty in AI product development, fostering collaboration between IT, data science, legal, and operations teams.”
Framework components:
- Risk identification phase: Use risk registers to catalog potential failure modes across all lifecycle stages
- Risk assessment: Implement likelihood × impact matrices specific to AI risks (data drift, bias manifestation, model failure modes)
- Risk mitigation: Develop response plans for high-priority risks before they manifest in production
- Continuous monitoring: Track risk indicators throughout deployment and ongoing operation
SmartDev’s 3-week AI discovery incorporates risk assessment as a core component, identifying technical constraints, data limitations, integration risks, and organizational readiness factors before development investment begins.
Establish AI-Specific Governance
Traditional IT governance frameworks don’t adequately address AI-specific challenges like algorithmic bias, explainability requirements, and continuous model evolution that characterize AI systems.
Governance model components:
- Decision ownership: Clear RACI matrices defining who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed for AI initiatives and deployment decisions
- Audit trails: Documentation of data provenance, model decisions, human override patterns, and retraining rationales
- Bias detection protocols: Regular fairness audits across demographic dimensions with clear remediation procedures
- AI Review Board: Cross-functional committee (product, technical, legal, ethics, compliance) that reviews high-risk AI applications before production deployment
According to guidance on implementing AI governance, “Establish an AI governance framework by defining specific governing principles for AI that align with organizational values, industry standards, and legal requirements.”
Implement Continuous Monitoring & Feedback Loops
Unlike traditional software where monitoring focuses on uptime and error rates, AI systems require monitoring of data quality, model performance, drift, and fairness metrics across multiple dimensions.
Monitoring components:
- Production performance metrics: Real-time tracking of accuracy, precision, recall, and business-relevant KPIs that actually matter to end users
- Real-time anomaly detection: Automated systems that flag unusual patterns in input data or model predictions indicating potential problems
- Automated retraining triggers: Thresholds that initiate model retraining when drift exceeds acceptable levels or performance degrades below targets
Tool recommendations: MLOps platforms like Weights & Biases, Databricks MLflow, Google Cloud Model Monitoring, and AWS SageMaker Model Monitor provide infrastructure for continuous AI system oversight and management.
Create Safety Valves in the Deployment Pipeline
Deployment strategies:
- A/B testing for model changes: Deploy new model versions to small user segments before full rollout to detect issues early
- Canary deployments: Gradual rollout that monitors performance in production before expanding exposure to all users
- Fallback mechanisms: Rules-based backup systems that activate when model confidence drops below thresholds
- Human-in-the-loop review: Routing high-uncertainty predictions to human experts for verification and final decision-making
Real-world example: Banking AI systems route high-value lending decisions above certain thresholds to human underwriters, ensuring that edge cases receive human judgment even as most routine applications are automated.
Invest in Data Quality from Day One
Given that poor data quality causes 30% of GenAI project abandonment and data issues are the highest-probability, highest-impact risk in AI delivery risks, upfront data investment provides the highest ROI in risk mitigation.
Data governance framework:
- Quality metrics and SLAs: Define acceptable ranges for completeness, accuracy, consistency, and timeliness
- Regular data audits: Periodic review of data quality, bias, and representativeness with documented findings
- Data lineage tracking: Documentation of data sources, transformations, and quality checks throughout the system
Cost-benefit analysis: Organizations that invest 40-60% of AI product lifecycle project timeline in data quality prevent downstream crises that force project restarts or complete abandonment of initiatives.
Build Redundancy for Critical Decisions
Approaches:
- Ensemble models: Combining predictions from multiple models reduces individual model failure risk
- Human oversight for high-stakes decisions: AI augments rather than replaces human judgment in consequential contexts
- Explainability layers: Making AI decisions transparent through attention visualization, SHAP values, or simplified surrogate models
According to research on managing uncertainty in AI product development, “When uncertainty is high, route decisions to human experts rather than making fully automated choices. Design workflows that allow humans to see uncertainty, apply judgment, and correct the system when necessary.”
The 10-Week AI Product Factory Reality
SmartDev’s data-driven analysis shows that AI-first development delivers 30% faster product launches with 40% fewer post-release bugs. Yet these results require careful balance between speed and risk management.
Speed vs. Rigor Trade-Off
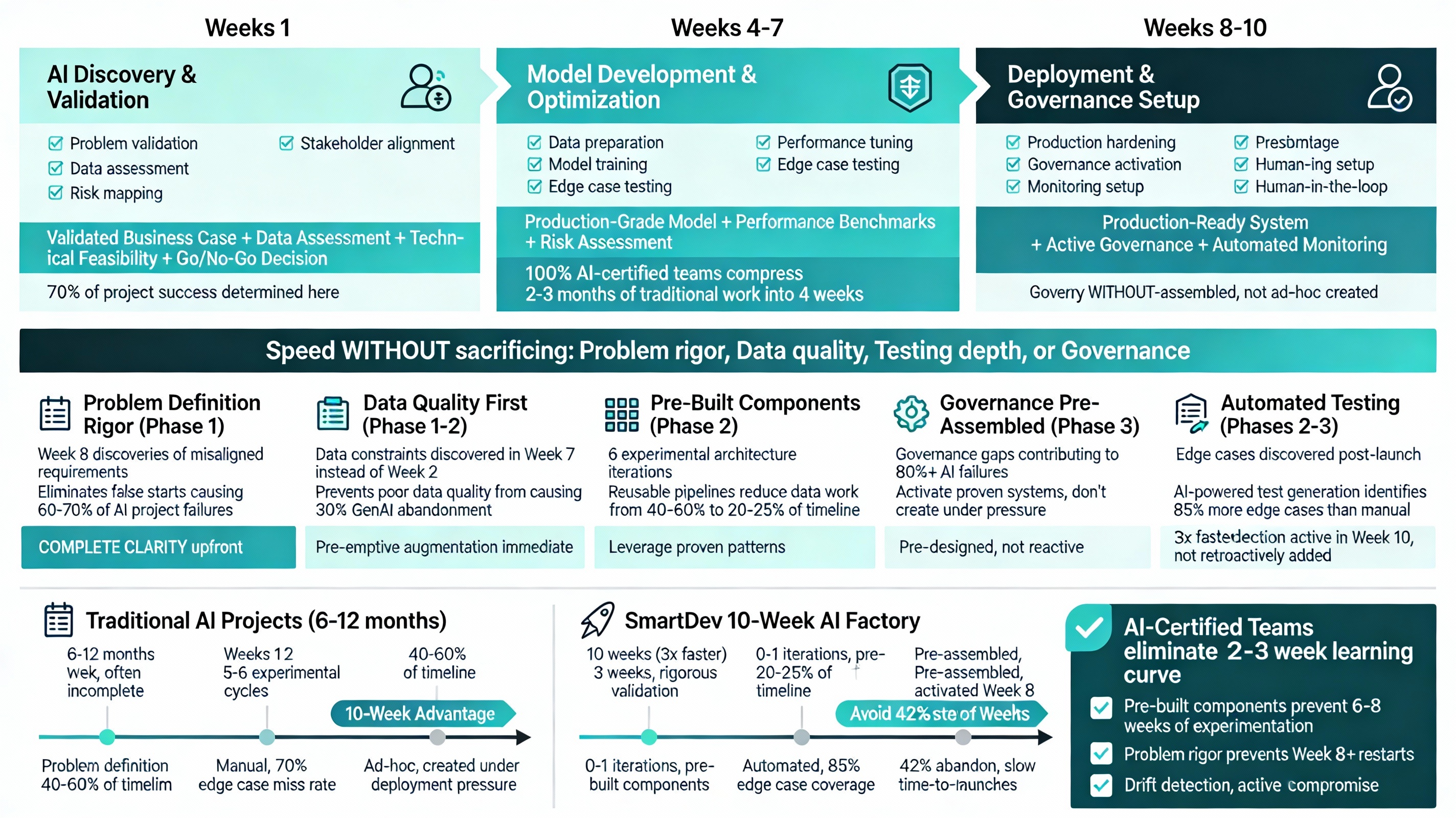
Traditional AI product lifecycle projects with rigorous governance span 6-12 months. But SmartDev’s 3-week AI discovery + development cycles compress this with a structured 10-week delivery model in three critical phases:
The 10-Week AI Product Factory: Three-Phase Breakdown
Phase 1: AI Discovery & Validation (Weeks 1-3)
Foundation phase where 70% of project success is determined:
- Problem Validation: Confirm AI is the right solution
- Data Assessment: Identify 80% of risks early
- Stakeholder Alignment: Align objectives and success metrics across teams
- Risk Mapping: Identify technical, data, regulatory, and integration risks
SmartDev’s discovery delivers validated business case, data quality assessment, technical feasibility analysis, and clear go/no-go decision criteria.
Why critical: Misaligned problem definitions discovered in Week 8 force complete restarts, contributing to the 42% AI project abandonment rate.
Phase 2: Model Development & Optimization (Weeks 4-7)
Development accelerates with foundations from Phase 1:
- Data Preparation: Using pre-built pipelines, not building from scratch
- Model Training: Leverage pre-trained models and reusable architectures
- Performance Tuning: Iterate with automated optimization frameworks
- Edge Case Testing: Identify failure modes early
Key enabler: 100% AI-certified development teams using SmartDev’s AI & Machine Learning solutions with pre-built components eliminate the 3-4 week learning curve typical in organizations without AI specialization.
Result: What takes 2-3 months in traditional projects (experimentation and discovery) happens in 4 weeks using proven patterns from previous projects.
Phase 3: Deployment & Governance Setup (Weeks 8-10)
Production readiness and operational sustainability:
- Production Hardening: Convert research code into production-grade systems
- Governance Activation: Implement AI Review Boards and bias monitoring
- Monitoring Setup: Deploy drift detection and automated performance tracking
- Human-in-the-Loop: Configure confidence thresholds and review workflows for high-stakes decisions
Critical distinction: Governance frameworks are pre-designed and activated in Phase 3, not ad-hoc created during deployment chaos.
Why 10 Weeks Works Without Sacrificing Quality
The critical question: What gets sacrificed in compressed timelines?
Traditional approaches sacrifice managing uncertainty in AI product development, testing depth, and governance rigor,leading to 42% AI project abandonment.
SmartDev’s 10-week model achieves speed without sacrificing these elements:
- Problem Definition Rigor (Phase 1): Complete clarity prevents Week 8 discoveries of misaligned requirements.Eliminatesfalse starts that cause 60-70% of AI project failures.
- Data Quality First (Phase 1-2): Data constraintsidentifiedin Week 2, not Week 7. Pre-emptive augmentation happens immediately. Prevents poor data quality from causing 30% GenAI abandonment.
- Pre-Built Components (Phase 2): Reusable pipelines reduce data collection from 40-60% of timeline to 20-25%. Pre-trained models eliminate 6 experimental architecture iterations.
- Governance Pre-Assembled (Phase 3): Activate proven systems,don’tcreate them under pressure. Prevents governance gaps contributing to 80%+ AI failures.
- Automated Testing (Phases 2-3): AI-powered test generationidentifies85% more edge cases than manual testing. Automated drift detection activates in Week 10, not retroactively added in Month 6.
- AI-Certified Teams (All phases): Specialist knowledge embedded, notacquired. Eliminates 2-3 week learningcurve typical in non-specialized organizations.
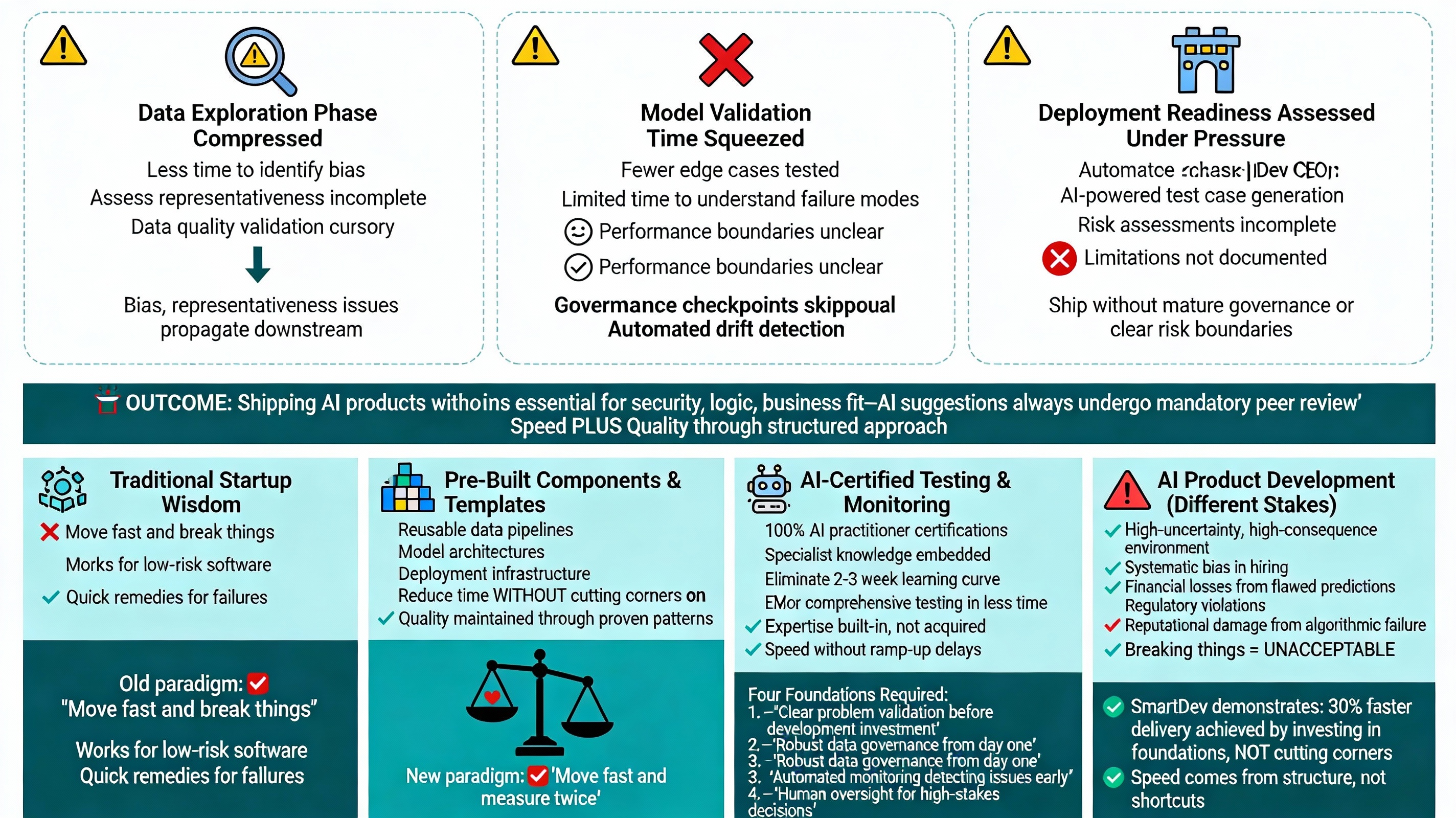
Compressed Timeline Implications
Risk concentration:
- Data exploration phase compressed: Less time to identify bias, assess representativeness, or validate data quality thoroughly
- Model validation time squeezed: Fewer edge cases tested; less time to understand failure modes and performance boundaries
- Deployment readiness assessed under pressure: Teams skip governance checkpoints and risk assessments to meet deadlines
Outcome: Shipping AI products without mature governance, adequate testing, or clear understanding of limitations and failure modes.
Strategies for Fast Delivery Without Compromising Quality
SmartDev’s approach demonstrates that speed and quality aren’t mutually exclusive when proper foundations exist:
Enabling factors:
- Pre-built components and templates: Reusable data pipelines, model architectures, and deployment infrastructure reduce time without cutting corners on quality
- AI-certified development teams: 100% of SmartDev’s developers hold AI practitioner certifications, eliminating learning curve delays
- Automated testing and monitoring: AI-powered test case generation covers 85% more edge cases than manual testing approaches
- Established governance checkpoints: Lightweight but mandatory risk assessments at key decision points throughout development
- SmartDev’s CEO emphasizes: “Human validation remains essential for security, logic, and business fit-AI suggestions always undergo mandatory peer review.” This human-in-the-loop approach maintains quality while leveraging AI for acceleration.
The Paradox: Moving Fast in High-Uncertainty Environments
Traditional startup wisdom: “Move fast and break things.” This works for low-risk software where failures have limited consequences and can be quickly remedied.
AI product development operates in high-stakes environments where “breaking things” can mean systematic bias in hiring, financial losses from flawed predictions, regulatory violations, or reputational damage from algorithmic failures.
The new paradigm: Move fast and measure twice. Speed requires foundations:
- Clear problem validation before development investment
- Robust data governance from day one of the project
- Automated monitoring that detects issues early in production
- Human oversight for high-stakes decisions that affect people
SmartDev’s AI product factory model demonstrates that organizations can achieve 30% faster delivery when they invest in these foundations rather than cutting corners.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does typical AI product development take?
6-12 months with proper governance and rigorous testing throughout all stages. SmartDev’s compressed cycles require pre-existing expertise, reusable components, and established governance frameworks. Organizations attempting rapid AI development without these foundations contribute to the 42% project abandonment rate.
What’s the biggest risk in AI product development?
A: Data quality issues cascade through every stage of the AI product lifecycle. According to Gartner, poor data quality will cause at least 30% of GenAI project abandonment. Unlike traditional software where bad data causes processing errors, AI systems trained on flawed data perpetuate those flaws across every prediction.
Can traditional software practices apply to AI?
A: Partially. DevOps, version control, and testing principles transfer, but AI requires additional practices for drift detection and continuous retraining. The failure to adapt traditional practices to AI-specific needs drives the 80%+ failure rate for AI projects.
How do you manage uncertainty in AI projects?
A: Through robust risk frameworks, continuous monitoring, human oversight for critical decisions, and governance structures that bridge technical and business stakeholders. Research emphasizes: “Capture and report uncertainty with appropriate methods, communicate it clearly to users and stakeholders, and use it to steer safer, more robust decisions.” SmartDev’s AI discovery program builds uncertainty management into the foundation before development begins.
Why do AI products fail more often than software?
A: Higher inherent uncertainty, complex dependencies on data quality, misalignment between technical capabilities and business expectations, and inadequate risk management frameworks. The 80%+ AI failure rate (twice that of traditional IT) reflects organizations applying software development practices to fundamentally different technology with unique dynamics.
Conclusion
Ready to navigate AI product development challenges with expert guidance? SmartDev’s AI development services Combining 100% AI-certified teams, proven governance frameworks, and data-driven delivery approaches that reduce risk while accelerating time-to-market. Explore SmartDev’s AI & Machine Learning solutions or learn about practical AI transformation strategies to start your AI initiative with confidence.
Why do competitors deliver AI products 30% faster while maintaining superior governance?







