Setting up an offshore development center feels like navigating a minefield of vendor pitfalls, cultural barriers, and hidden costs that can torpedo your budget faster than you can say “technical debt.” You’re under pressure to cut development costs while maintaining quality standards, but most implementation guides skip the real challenges that derail ODC projects.
Over 92% of the world’s largest 2,000 companies now leverage IT outsourcing services, with the majority incorporating offshore custom software development as a core component of their technology strategy—yet many still struggle with complexities that prevent them from achieving promised savings. This guide delivers the exact framework successful enterprises use to establish profitable offshore centers while avoiding expensive mistakes.
I’ll walk you through proven strategies that deliver 30-60% cost savings based on independent industry analysis, with real examples from companies that achieved sustainable results through structured implementation.
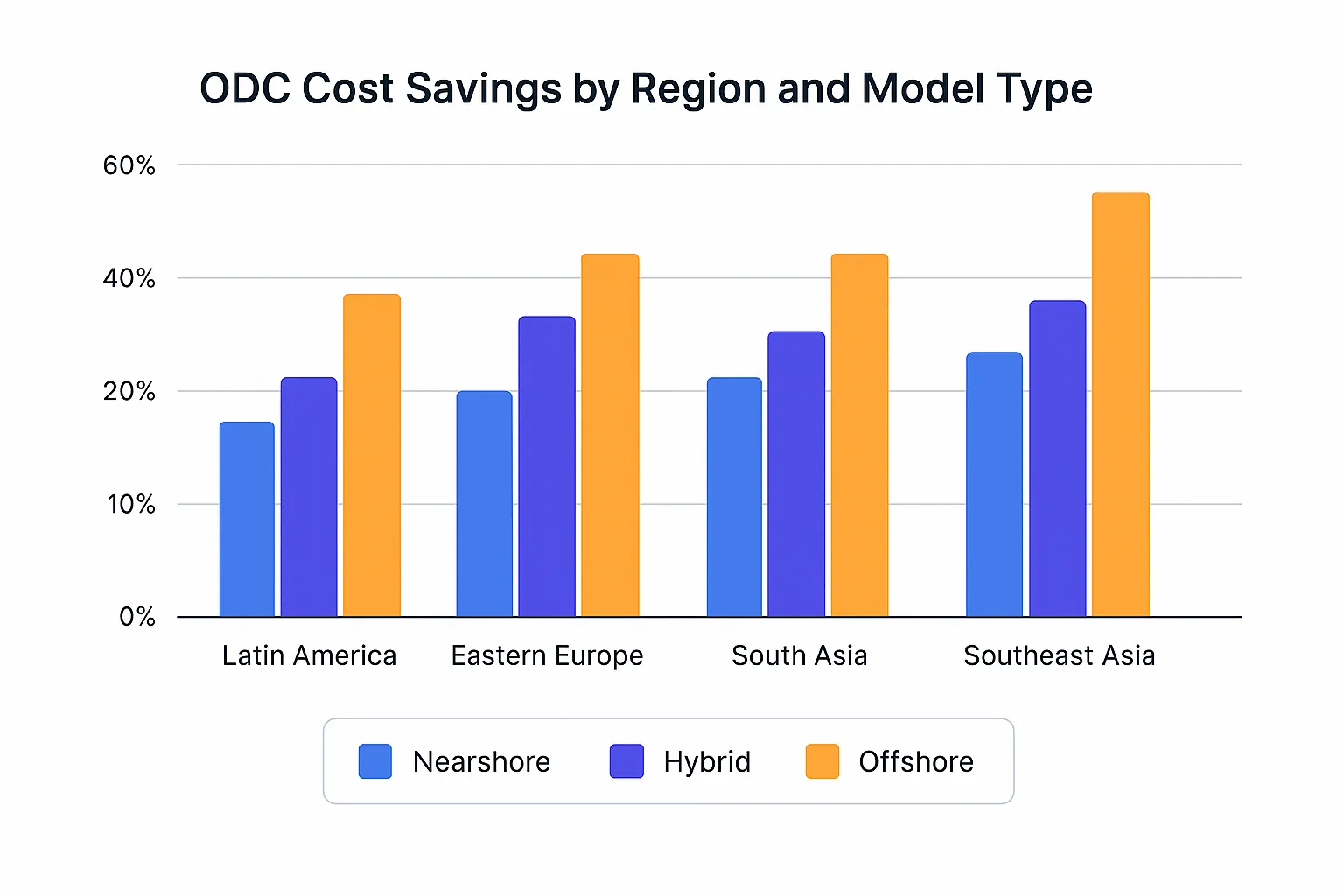
Fig.1 ODC Cost Savings by Region and Model Type
Your 90-Second ODC Blueprint
Setting up an offshore development center requires strategic planning across five critical areas:
- Business case definition: Clear objectives, success metrics, and ROI targets
- Location and vendor selection: Due diligence framework with pilot testing
- Organizational design: Team structure, governance, and communication protocols
- Infrastructure setup: Physical, digital, and security requirements
- Implementation execution: Phased rollout with performance monitoring
Proper implementation delivers 30-60% cost savings while maintaining quality through structured governance and proven risk management.
Understanding Offshore Development Centers: Models That Actually Work
An offshore development center is a dedicated software development facility established in a foreign country to access cost advantages, specialized talent, and operational scale while maintaining direct control over your development processes.
Unlike traditional outsourcing where you hand off projects and hope for the best, ODCs function as extensions of your internal team. You get dedicated resources working exclusively on your projects with governance frameworks that align with your company standards.
Companies implementing ODCs achieve 30-40% cost reduction as a conservative baseline, with some reporting savings up to 60% depending on destination and engagement model. But cost isn’t the only benefit – you also gain access to specialized skills, larger talent pools, and 24/7 development cycles through timezone advantages.
Three ODC Models: Picking Your Poison (Strategically)
Captive Centers: Maximum Control, Maximum Investment
Captive centers provide maximum control through wholly-owned subsidiaries. You own everything – the office space, equipment, staff, and processes. This model offers perfect cultural alignment and long-term strategic value, but requires significant upfront investment and operational management expertise.
Best for: Large enterprises with long-term offshore strategies and resources to manage complex international operations.
Build-Operate-Transfer: Training Wheels for ODCs
Hybrid partnerships through build-operate-transfer models combine vendor expertise during setup with eventual ownership transfer. Your vendor handles the messy startup phase – recruiting, training, infrastructure setup, process establishment – then hands you the keys after 18-24 months.
Best for: Companies wanting captive benefits without startup headaches, with plans for eventual full ownership.
Vendor-Managed Teams: Fastest Time to Value
Dedicated team extensions through vendor-managed models provide immediate access to resources with lower setup costs. Your vendor handles HR, infrastructure, and local compliance while you maintain project control and team interaction.
Best for: Companies needing quick scaling without long-term ownership commitments.
Step 1: Define Business Objectives That Drive Real Results
Successful ODC implementation begins with clearly defined business objectives beyond “save money and go faster.” Vague goals create expensive experiments that fail to deliver measurable value.
Establish quantifiable success metrics such as:
- 30-40% cost reduction within 18 months
- 20% faster delivery cycles within 12 months
- 95% quality scores maintained or improved
- Specific revenue impact targets tied to capabilities
These metrics provide objective benchmarks for evaluating ODC performance and making data-driven optimization decisions.
Technology Stack Requirements: Getting Specific About Needs
Define required technology platforms, development tools, security frameworks, and integration capabilities that align with your existing enterprise architecture. Generic technology assessments lead to capability gaps that create expensive retrofitting.
AI-powered development environments are becoming standard, with companies reporting 40% fewer post-release bugs through integrated CI/CD pipelines. Your technology stack should support current needs while enabling future capability expansion.
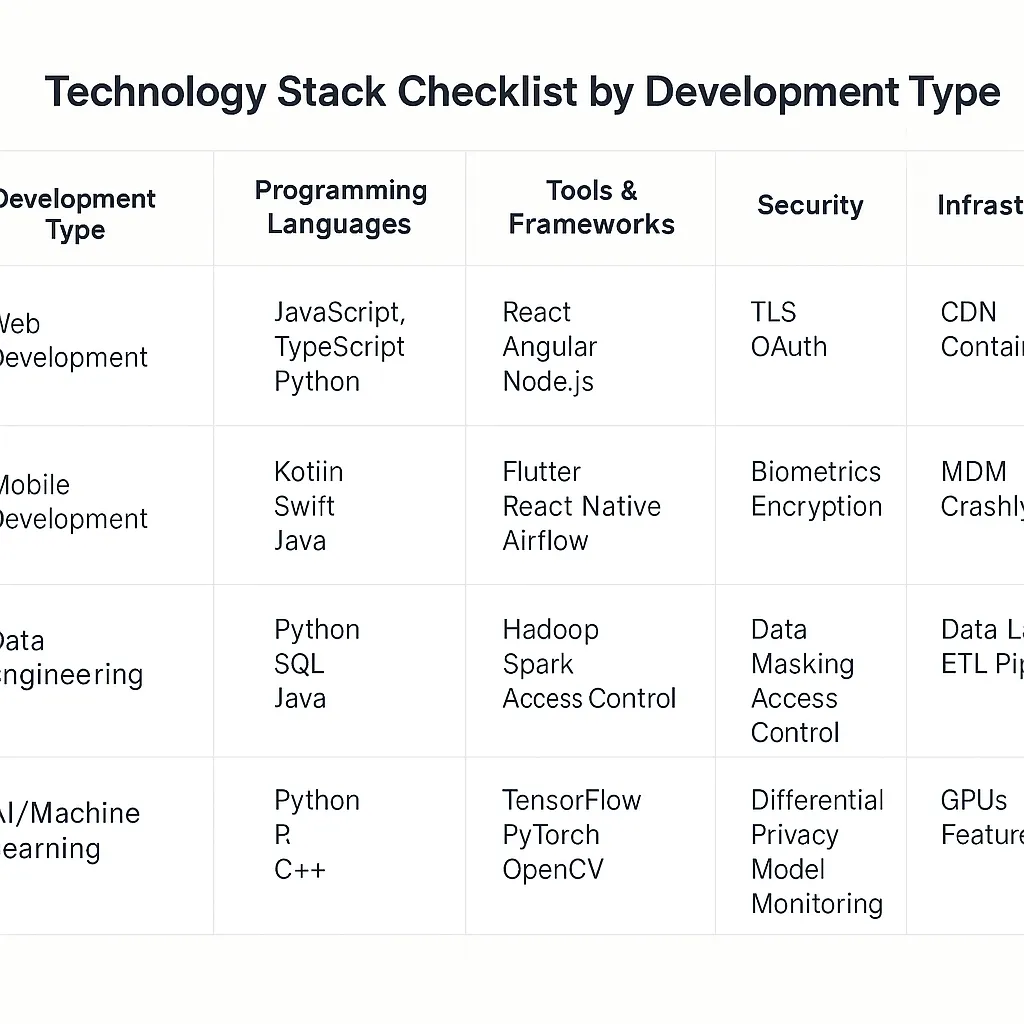
Fig.2 Technology Stack Checklist by Development Type
Infrastructure planning must account for:
- Hardware requirements and cloud platform strategies
- Network connectivity and bandwidth specifications
- Security protocols and compliance frameworks
- Backup systems and disaster recovery capabilities
Modern ODCs require ISO 27001 and SOC 2 compliant security frameworks to meet enterprise standards.
Budget Planning: The Hidden Costs That Kill ODCs
Calculate comprehensive costs including setup expenses, operational overhead, technology infrastructure, legal compliance, and ongoing management requirements over 3-5 year periods.
Hidden costs often account for 20-30% of total ODC investment, making thorough financial modeling essential for accurate ROI projections.
Often-overlooked expenses include:
- Travel costs for team visits and training
- Cultural integration and team building programs
- Knowledge transfer and documentation efforts
- Initial productivity ramp-up periods
- Legal and compliance consulting
- Currency fluctuation buffers
Develop detailed financial models showing expected returns and break-even timelines. Well-implemented ODCs typically achieve break-even within 18 months through systematic approach execution.
Step 2: Location Selection Using Data-Driven Criteria
Assess technical skill availability, English proficiency levels, educational infrastructure, and technology adoption rates in potential destinations. Technical capability varies significantly between regions and impacts your ability to find qualified resources.
Vietnam stands out with strong technical capabilities and cost advantages of up to 40% compared to onshore development, plus over 70% English proficiency rates among technical professionals.
Location Evaluation Framework:
- Political stability and economic conditions
- Legal framework maturity and IP protection
- Government support for technology sectors
- Timezone compatibility with your operations
- Cultural alignment and communication styles
- Infrastructure quality and business environment
- Total cost competitiveness including hidden expenses
Vietnam ranks in the top three globally for ODC setups due to a stable business environment and supportive technology policies.
Vendor Due Diligence: Separating Marketing from Reality
Evaluate vendor expertise in required technologies, industry experience, development methodologies, and quality processes through detailed technical assessments rather than glossy presentations.
Technical Assessment Checklist:
- Demonstrated expertise in your technology stack
- Industry-specific experience and case studies
- Development methodology maturity (Agile, DevOps, etc.)
- Quality management systems and certifications
- Innovation capabilities and emerging technology adoption
Assess vendor infrastructure, security protocols, compliance certifications, and operational maturity through site visits and reference checks. Look for vendors with proven track records in enterprise environments and relevant certifications (ISO 27001, SOC 2, CMMI Level 3+).
Cultural fit analysis is equally important as technical capabilities for long-term ODC success. Evaluate communication styles, work culture alignment, and change management capabilities through pilot projects and stakeholder interviews.
Legal Framework: Protecting Your Investment
Understand local labor laws, tax obligations, intellectual property regulations, and industry-specific compliance requirements in your chosen destination. Legal compliance failures expose companies to significant financial and operational risks.
Develop comprehensive agreements covering:
- Service level expectations and performance metrics
- Intellectual property rights and ownership
- Data protection and privacy requirements
- Termination clauses and transition procedures
- Dispute resolution mechanisms and governing law
Implement legal protections including IP safeguards, non-disclosure agreements, and data localization compliance. These protections become increasingly important as ODCs handle more sensitive business data and processes.
Ready to learn exactly how to set up an Offshore Development Center (ODC) that delivers 30–60% cost savings without sacrificing engineering quality?
This step-by-step guide walks you through team structure, legal setup, budgeting, and operational best practices.
Discover how leading tech companies build high-performing offshore teams using proven ODC frameworks—covering vendor selection, infrastructure setup, compliance, cost modeling, and long-term scalability.
Explore the Complete ODC Setup Guide (30–60% Savings)Step 3: Organizational Design for Sustainable Operations
Establish clear reporting hierarchies, decision-making authorities, and communication protocols between onshore leadership and offshore teams. Ambiguous reporting structures create confusion and reduce effectiveness.
Organizational Structure Elements:
- Clear role definitions and responsibilities
- Decision-making authority levels and escalation paths
- Career progression frameworks aligned with global standards
- Performance evaluation and feedback mechanisms
- Cross-functional collaboration protocols
SmartDev’s structured approach to team development maintains retention rates above 85% through clear growth opportunities and comprehensive development programs.
Recruitment Standards That Prevent Expensive Hiring Mistakes
Develop comprehensive recruitment standards covering technical skills, soft skills, cultural fit, and growth potential aligned with long-term organizational needs. Poor hiring decisions create cascading problems that are expensive to fix.
Recruitment Framework:
- Technical competency assessments and certifications
- Communication skills and English proficiency testing
- Cultural alignment and work style compatibility
- Problem-solving capabilities and learning agility
- Leadership potential and growth mindset evaluation
Create structured onboarding processes including:
- Technical training and certification programs
- Cultural orientation and company values integration
- Mentorship programs with experienced team members
- Regular check-ins and feedback during initial months
Implement competitive compensation packages, career development opportunities, and recognition programs to maintain low attrition rates. High turnover destroys ODC value propositions and increases operational costs significantly.
Skills Development: Building Capabilities That Scale
Establish continuous learning programs covering emerging technologies, industry best practices, and specialized skill development aligned with business needs rather than generic training catalogs.
Training Program Components:
- Technology certifications and hands-on workshops
- Industry best practices and methodology training
- Communication and cross-cultural collaboration skills
- Leadership development and career advancement programs
- Innovation workshops and emerging technology exploration
SmartDev organizes monthly AI workshops that increased offshore team productivity by 20% through practical application of automation tools and intelligent development practices.
Implement systematic knowledge transfer processes, documentation standards, and mentorship programs to reduce dependency on key individuals and ensure operational continuity.
Step 4: Infrastructure Setup for Enterprise-Grade Operations
Establish appropriate office space, workstations, meeting rooms, and support facilities that meet local standards while reflecting company culture and professional expectations.
Physical environment impacts team morale and productivity significantly in offshore settings. Invest in quality workspace design that supports collaboration, focus, and professional growth.
Physical Infrastructure Checklist:
- Modern office space with flexible work areas
- High-quality workstations and development equipment
- Reliable internet connectivity and backup systems
- Meeting rooms with video conferencing capabilities
- Break areas and amenities that support team culture
Implement robust IT systems including hardware, software licenses, development tools, and testing environments that integrate seamlessly with global systems.
Digital Infrastructure: Tools That Enable Success
Choose integrated communication platforms supporting video conferencing, instant messaging, project collaboration, and document sharing that work effectively across timezones.
Communication Technology Stack:
- Video conferencing with screen sharing and recording
- Instant messaging for real-time collaboration
- Project management and task tracking tools
- Document collaboration and version control systems
- Time tracking and productivity monitoring tools
Establish standardized communication protocols including:
- Regular meeting schedules and agenda formats
- Status reporting templates and frequencies
- Escalation procedures and contact hierarchies
- Emergency communication procedures
Deploy comprehensive security measures including access controls, data encryption, network security monitoring, and incident response protocols that meet enterprise security standards.
Step 5: Implementation Through Pilot Projects
Choose pilot projects that demonstrate capabilities while managing risk, typically involving non-critical applications with clear success criteria and measurable outcomes.
Pilot Project Selection Criteria:
- Well-defined scope and requirements
- Manageable complexity and timeline
- Clear success metrics and evaluation criteria
- Non-critical business impact if issues occur
- Representative of future work complexity
Define specific pilot project metrics including delivery timelines, quality scores, client satisfaction ratings, and cost targets to validate ODC model effectiveness.
Team Ramping Strategy: Quality Over Speed
Implement phased team growth allowing for proper integration, training, and culture assimilation before adding complexity or additional resources.
Phased Ramp-Up Approach:
- Phase 1: Core team setup (2-4 senior resources)
- Phase 2: Skill validation and process refinement
- Phase 3: Gradual team expansion based on performance
- Phase 4: Full operational capability with quality metrics
Create comprehensive documentation covering processes, technical specifications, client requirements, and institutional knowledge to ensure continuity and scalability.
Establish formal mentorship relationships between experienced onshore team members and new offshore resources to accelerate competency development and cultural integration.
Step 6: Performance Monitoring and Continuous Optimization
Track cost savings achievement, revenue per employee, profit margins, and ROI realization against established targets with monthly and quarterly reporting.
Financial KPIs:
- Cost per development hour vs. onshore rates
- Total project cost reduction percentages
- Revenue impact from increased development capacity
- ROI timeline and break-even achievement
- Hidden cost tracking and management
Monitor delivery timelines, quality scores, client satisfaction ratings, team productivity, and process efficiency metrics for continuous improvement identification.
Operational KPIs:
- Sprint completion rates and velocity trends
- Defect rates and post-release bug counts
- Client satisfaction scores and feedback
- Team productivity and utilization rates
- Process efficiency and cycle time improvements
Quality Management: Maintaining Standards at Scale
Implement comprehensive quality management systems including regular audits, certification maintenance, and continuous process improvement initiatives.
Quality Framework Components:
- Code review processes and quality gates
- Automated testing and continuous integration
- Performance monitoring and optimization
- Security scanning and vulnerability management
- Documentation standards and knowledge sharing
Maintain systematic client feedback collection and relationship building activities to ensure high satisfaction and retention rates through proactive communication and issue resolution.
Common Challenges: What Actually Goes Wrong (And How to Fix It)
Address cultural differences through awareness training, cultural bridge programs, and inclusive management practices that respect diversity while building unified teams.
Cultural Integration Strategies:
- Cross-cultural awareness training for all team members
- Regular cultural exchange activities and celebrations
- Clear communication guidelines and expectations
- Conflict resolution procedures that respect cultural differences
- Leadership training on managing global teams
Overcome language barriers and communication challenges through training programs, standardized processes, and technology tools that facilitate clear interaction.
Quality Control: Preventing Problems Before They Happen
Address quality inconsistencies through robust process documentation, training programs, quality checkpoints, and continuous monitoring systems.
Quality Control Measures:
- Standardized development processes and coding standards
- Regular code reviews and peer feedback sessions
- Automated testing and quality metrics tracking
- Regular training updates and skill assessments
- Client feedback integration and improvement cycles
Proactively identify and address skill gaps through targeted training, strategic recruitment, knowledge transfer programs, and external education partnerships.
Risk Management: Planning for What Could Go Wrong
Prepare for potential disruptions through business continuity planning, alternative resource arrangements, and crisis communication protocols.
Risk Mitigation Framework:
- Business continuity and disaster recovery plans
- Alternative vendor and resource arrangements
- Insurance and legal protection strategies
- Crisis communication and escalation procedures
- Regular risk assessment and mitigation updates
Build flexibility into operations through modular design, scalable processes, and contingency planning that enables rapid response to changing conditions.
Ready to implement your offshore development center? SmartDev’s proven implementation framework has helped companies achieve 30-60% cost savings while maintaining enterprise quality standards through systematic approaches that address real-world challenges.







