Introduction
The lending industry faces growing pressures, from fluctuating interest rates to an increasing demand for quicker, more efficient loan approval processes. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is helping to address these challenges, transforming how lenders evaluate creditworthiness, mitigate risk, and engage with customers. This guide explores how AI is already reshaping lending and where it could take the industry in the future.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Lending?

Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
AI refers to computer systems capable of performing tasks that usually require human intelligence, such as learning from data, making decisions, and predicting outcomes. AI is powered by technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and deep learning. In lending, AI helps automate processes, improve decision-making, and provide faster, more personalized services to both lenders and borrowers.
In the lending sector, AI is used to refine credit risk assessments, speed up loan approvals, and detect fraud more effectively. By utilizing vast amounts of data, AI offers more accurate predictions, allowing lenders to make informed decisions quickly. The result is improved operational efficiency, reduced risk, and enhanced customer experiences.
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming Lending
AI is rapidly revolutionizing how lenders assess risk, manage portfolios, and interact with customers. Leading financial institutions leverage AI to analyze a range of data points, from traditional credit scores to alternative data sources such as social media activity, transaction history, and even utility payments. This deeper data analysis enables more accurate and nuanced creditworthiness assessments, allowing lenders to approve loans more confidently and quickly.
Additionally, AI is helping lenders move from a “one-size-fits-all” approach to personalized loan offers. By analyzing individual financial behavior and preferences, AI tailors loan terms such as interest rates and repayment schedules, enhancing customer satisfaction and accessibility. For example, AI-driven credit models can offer lower rates to borrowers with strong repayment histories but limited traditional credit scores, creating opportunities for underserved groups.
In terms of operational efficiency, AI is transforming routine tasks. Virtual assistants and chatbots powered by natural language processing now handle customer inquiries, loan application guidance, and payment reminders, ensuring faster responses and freeing up human staff for higher-value tasks. Loan origination, document verification, and fraud detection are also becoming more automated, reducing approval times and minimizing manual errors.
Key Statistics and Trends in AI Adoption in Lending
AI is transforming lending as financial institutions increasingly integrate it into core processes. McKinsey’s The State of AI in 2024 reports that 78% of organizations across industries have adopted AI in at least one business function, with financial services firms heavily focusing on lending applications like loan origination and credit decisions. Specifically, Fannie Mae’s Mortgage Lender Sentiment Survey 2023 finds that 29% of lenders are deploying or trialing AI in these areas, with expectations of broader adoption by 2025 to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Generative AI is reshaping how lenders engage with customers and streamline operations. According to Wolters Kluwer (2024), 35% of financial institutions are experimenting with generative AI for tasks such as customer communication, document generation, and underwriting. These tools improve borrower experiences through personalized interactions and reduce manual workloads, enabling faster and more efficient loan processing.
Regulatory oversight and measurable benefits highlight AI’s impact in lending. BDO (2024) notes that the U.S. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau emphasizes fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI-driven lending to prevent bias. Accenture’s 2024 Report finds that AI adoption can reduce loan processing costs by up to 50% and improve risk assessment accuracy by 15–25%, resulting in quicker approvals and a better borrower experience.
Business Benefits of AI in Lending
AI is tackling long-standing challenges in the lending industry, such as slow approval times, inaccurate credit assessments, and high operational costs. Here are five key business benefits that AI delivers to lenders seeking a competitive edge:
1. Faster, More Accurate Loan Approvals
AI accelerates the loan approval process by analyzing vast amounts of data, from credit scores to non-traditional factors like spending patterns, social behaviors, and transaction histories. This leads to faster, data-driven decisions, significantly reducing the approval times from days or weeks to mere minutes. The automated process minimizes human error, ensuring that decisions are consistent and reliable across all applicants.
Moreover, AI models can be continually refined with new data, improving credit risk assessments over time. This helps lenders maintain speed while increasing accuracy and reducing the likelihood of defaults. It’s a win-win for both lenders and borrowers, with more efficient processes and better outcomes.
2. Personalized Loan Offerings
AI allows lenders to create personalized loan products by analyzing borrowers’ unique financial behaviors, preferences, and goals. Instead of offering a one-size-fits-all loan, lenders can tailor loan amounts, interest rates, and repayment terms to meet individual customer needs. This approach not only increases the likelihood of loan approval but also enhances customer satisfaction by offering terms that align with their financial situation.
As AI continuously monitors changes in borrowers’ behaviors and credit profiles, it enables lenders to adjust loan offers dynamically. This ensures that loan terms evolve alongside a borrower’s financial circumstances, fostering better customer retention and encouraging repeat business.
3. Enhanced Risk Management
AI improves risk assessment by analyzing data points far beyond traditional credit scores, including transaction history, employment data, and even social behavior patterns. This comprehensive view of a borrower’s financial health provides lenders with a much clearer picture of risk, allowing for more accurate predictions of loan defaults or late payments.
Additionally, AI-powered predictive models help lenders identify high-risk borrowers early, enabling proactive measures such as adjusting loan terms, offering financial counseling, or even denying risky applications before they become problematic. This proactive approach reduces overall portfolio risk and improves profitability.
4. Improved Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI significantly enhances fraud detection by continuously monitoring loan applications for signs of fraudulent activity. Machine learning algorithms can analyze transaction patterns and flag inconsistencies or unusual behaviors that indicate potential fraud. These systems are capable of learning from new fraud tactics, making them increasingly effective at identifying suspicious activity over time.
By leveraging AI, lenders can reduce the risk of fraud, minimize financial losses, and protect customers from identity theft. Real-time fraud detection also improves the overall security and trustworthiness of the lending process, which is crucial for maintaining customer confidence.
5. Streamlined Operations and Cost Reduction
AI automation streamlines routine tasks, such as document verification, loan origination, and customer service inquiries, freeing up human employees to focus on higher-value activities. Virtual assistants, chatbots, and AI-powered customer service platforms handle thousands of borrower queries, significantly reducing operational costs and improving customer satisfaction by providing quick responses 24/7.
Additionally, AI-driven automation reduces manual errors and speeds up processes, resulting in shorter approval cycles and less paperwork. This leads to lower overhead costs and higher efficiency, ultimately allowing lenders to pass on the savings to their customers in the form of lower rates or fees.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Lending
While AI holds great promise for transforming the lending industry, its adoption comes with several challenges that lenders must navigate. Here are five critical hurdles that lenders face when implementing AI effectively:

1. Legacy Systems and Data Fragmentation
Many lenders still rely on outdated legacy systems that were not designed to handle the vast amounts of data AI requires. These systems often operate in silos, making it difficult to aggregate and process data across departments. This fragmentation can prevent AI models from accessing clean, structured, and real-time data, which is essential for making accurate, reliable predictions.
The process of modernizing infrastructure can be costly and complex, requiring substantial investment in both technology and training. Lenders need to ensure their data is centralized and standardized across systems for AI to function optimally. Without this foundational update, AI projects may fail due to incomplete or inconsistent data inputs, undermining the reliability of AI-driven insights.
2. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
As AI relies on large datasets, often containing sensitive financial and personal information, data privacy and security are major concerns for lenders. Regulatory frameworks such as the GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California impose strict rules on how data can be collected, stored, and used. Ensuring compliance with these regulations while using AI to process sensitive customer data is a significant challenge.
Lenders must invest in robust security measures to safeguard customer information and mitigate the risk of data breaches. Furthermore, clear consent protocols must be in place to ensure transparency about how customer data is being utilized by AI systems, which can be a complex and ongoing process.
3. Skills and Expertise Gap
AI adoption in lending requires specialized skills, including data science, machine learning, and AI model development. However, the demand for skilled professionals in these areas often exceeds supply, leading to a talent shortage. Many lenders struggle to recruit or train the necessary staff to build, deploy, and manage AI systems effectively.
Bridging this skills gap may involve investing in employee training programs or partnering with external AI consultants. Lenders who fail to address this talent shortage risk ineffective AI integration or slow adoption, which could lead to missed opportunities in the competitive lending market.
4. Ethical and Bias Concerns
AI systems in lending can unintentionally reinforce existing biases if not properly monitored and managed. For example, biased training data such as historical lending decisions that favor certain demographics can lead to biased loan approvals, ultimately perpetuating inequality in access to credit.
Lenders must implement strategies to ensure their AI models are fair, transparent, and free from bias. Regular audits of AI decision-making processes and the use of “explainable AI” techniques, where algorithms can explain their decisions, can help mitigate these concerns. Failing to address AI bias can result in reputational damage and regulatory scrutiny.
5. Cost and ROI Uncertainty
While AI promises significant efficiency gains and cost savings in the long run, the initial investment in technology, infrastructure, and talent can be substantial. For many lenders, determining the return on investment (ROI) for AI initiatives can be difficult, particularly when benefits like improved customer experience or more accurate risk assessment are harder to quantify.
Lenders must be strategic in their AI adoption, prioritizing use cases that offer clear and measurable outcomes. Clear metrics for success and a phased approach to AI implementation can help mitigate concerns about upfront costs and ensure long-term value.
Specific Applications of AI in Lending
From loan approvals to fraud prevention, AI is streamlining processes, enhancing customer experiences, and improving efficiency. The implementation of machine learning, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making is helping lenders make smarter decisions faster. Here’s how AI is being applied across various lending functions:
1. Automated Loan Approval and Risk Assessment
AI is drastically changing the way loans are approved and how lenders assess credit risk. Traditionally, creditworthiness assessments have relied heavily on FICO scores and basic financial data, which can overlook other important risk factors. With AI, lenders can leverage more advanced algorithms that consider a broader range of data points, such as employment history, transaction patterns, and even social media activity.
By analyzing vast datasets, AI can make more accurate predictions regarding a borrower’s likelihood of repayment, reducing human error and bias. Additionally, AI models can process applications in real time, improving loan processing times and making faster, more efficient decisions.
Upstart is an AI-driven lending platform that uses machine learning to assess creditworthiness. Instead of relying only on traditional FICO scores, Upstart analyzes over 1,000 data points, such as education, work history, and income, to predict loan default risk. This allows Upstart to approve loans for individuals with less conventional credit histories, expanding access to credit for underserved populations.
2. Personalized Loan Offerings
AI allows lenders to offer more personalized loan products based on an applicant’s financial situation, preferences, and behavior. Traditional loans often follow a one-size-fits-all model, where the same terms are applied to all applicants. AI, however, can tailor loan offers to better match an individual’s needs, such as adjusting interest rates, loan amounts, and repayment schedules based on an applicant’s risk profile.
Using machine learning algorithms, lenders can analyze customers’ spending habits, income stability, and financial goals to provide personalized offers that have a higher chance of being accepted. This leads to better customer satisfaction and increased loan acceptance rates, as customers feel they are being offered products suited to their specific financial situation.
Kiva, a global micro-lending platform, utilizes AI to match borrowers with lenders by analyzing customer profiles, repayment history, and financial needs. This personalized approach helps Kiva offer microloans at lower interest rates to underserved borrowers, particularly in developing economies, expanding access to credit in places where traditional financial institutions are less active.
3. Fraud Prevention and Detection
AI is increasingly being used for fraud detection in the lending process. Traditional methods often rely on basic checks and manual verification, but these can be slow and prone to error. AI, on the other hand, can analyze large volumes of data in real time to detect suspicious patterns and anomalies that could indicate fraudulent activity, such as fake identities or unauthorized transactions.
By utilizing machine learning algorithms trained on historical fraud data, AI systems can identify new types of fraud and improve over time as they learn from new examples. This allows lenders to act faster and more effectively in preventing fraud, reducing potential losses, and ensuring the security of the lending process.
Zest AI uses machine learning to detect fraud in lending by analyzing patterns in loan applications. It looks for discrepancies in applicants’ personal data or unusual transaction behaviors that may suggest fraudulent activity. This helps reduce the risk of approving loans for fraudulent borrowers and ensures a safer lending environment for everyone.
4. Loan Default Prediction and Early Intervention
AI models can predict loan defaults before they happen by analyzing a borrower’s financial behavior and identifying early warning signs. By using predictive analytics, lenders can proactively intervene with at-risk borrowers, offering solutions such as restructuring loans, providing financial counseling, or offering temporary forbearance.
These models are trained on vast amounts of data, including past borrower behaviors, economic trends, and payment history, to anticipate the likelihood of default. By addressing potential defaults early, lenders can reduce losses and maintain healthier portfolios.
FICO, a leader in predictive analytics, uses AI to assess the likelihood of loan default by analyzing customer behavior, payment history, and broader economic conditions. Lenders using FICO’s AI models can identify borrowers at risk of default and take preventative measures, such as offering alternative payment options, reducing the chances of delinquency, and minimizing financial losses.
5. Customer Engagement and Retention
AI enhances customer engagement by providing more personalized interactions through chatbots and virtual assistants. Instead of relying solely on human customer service representatives, AI systems can engage borrowers with real-time responses, answer questions about loan status, or guide them through the application process. This creates a seamless experience and reduces wait times for customers.
Additionally, AI can predict a customer’s needs and proactively offer relevant financial products, such as new loan offers or refinancing options, increasing customer satisfaction and retention. By analyzing a borrower’s financial journey, AI systems can provide recommendations tailored to their evolving needs.
Cleo, a financial assistant powered by AI, uses natural language processing to engage with users and provide financial insights. By analyzing spending patterns and saving habits, Cleo offers personalized suggestions for loans, savings plans, and budgeting tips. This AI-driven engagement not only improves user experience but also helps borrowers make informed financial decisions.
6. Automated Document Verification
In the lending industry, the verification of documents (e.g., income statements, tax returns, identity verification) has traditionally been a time-consuming and error-prone process. AI automates document verification by using optical character recognition (OCR) and NLP to extract and validate data from submitted documents in real-time.
This reduces manual work, enhances accuracy, and accelerates the loan approval process. AI can also identify forged or altered documents by cross-referencing submitted data with external databases, improving the overall security and integrity of the lending process.
DocuSign utilizes AI to automate document verification in the lending process. By using AI-powered OCR and NLP technologies, DocuSign extracts data from submitted documents, verifies their authenticity, and cross-references them with external databases to ensure that the borrower’s information is accurate, reducing fraud and speeding up loan approvals.
Need Expert Help Turning Ideas Into Scalable Products?
Partner with SmartDev to accelerate your software development journey — from MVPs to enterprise systems.
Book a free consultation with our tech experts today.
Let’s Build TogetherExamples of AI in Lending
AI has become a game-changer in the lending industry, transforming how financial institutions interact with customers, process loans, and mitigate risks. Here are four more examples that showcase the different ways AI is being applied in lending:
Real-World Case Studies

1. Square Capital: AI for Small Business Lending
Square Capital, the lending arm of Square, leverages AI to provide financing options for small businesses that may not have access to traditional credit. Square’s AI-driven model assesses the financial health of a business by analyzing transaction data from the Square point-of-sale system, including sales volume, transaction history, and business trends. This enables Square to offer loans to small businesses based on real-time performance data rather than relying solely on traditional credit scores.
AI algorithms continuously assess risk by analyzing patterns in sales and payment history, allowing Square Capital to offer flexible and timely financing options tailored to each business’s needs. This data-driven approach minimizes risk and accelerates the loan approval process, making it easier for small businesses to get the funding they need without complex paperwork.
Square Capital has used AI to lend over $7 billion to small businesses, providing fast and personalized loan offers. The platform’s AI models evaluate transaction data from millions of businesses and generate tailored loan offers that are processed quickly, helping small businesses maintain cash flow and grow.
2. SoFi: AI for Personalized Student Loans
SoFi, a digital lender known for its student loan refinancing, uses AI to offer more personalized loan terms based on a borrower’s financial behavior. Traditional student loan lenders often offer a one-size-fits-all approach, but SoFi’s machine learning algorithms assess factors such as income potential, employment history, and spending patterns to create customized repayment plans for each borrower.
SoFi’s AI-driven platform can predict the likelihood of loan repayment success and offer flexible terms, including lower interest rates, to borrowers based on their individual financial profiles. This helps borrowers save money on interest while making it easier to manage repayment, especially for those just entering the workforce.
SoFi’s AI algorithms have helped reduce the interest rates on student loan refinancing for borrowers with strong earning potential. By considering factors like income growth and employment stability, SoFi is able to offer personalized loan terms that benefit borrowers in their early careers, boosting their chances of successful repayment.
3. OakNorth: AI for Commercial Lending Risk Analysis
OakNorth, a UK-based commercial lender, uses AI to perform sophisticated risk assessments for commercial loans. Unlike traditional banks, OakNorth’s AI platform, OakNorth Analytical Intelligence (ONAI), leverages big data and machine learning to predict a borrower’s ability to repay a loan by analyzing large datasets, including financial statements, market trends, and sector-specific data.
ONAI’s algorithms provide a more granular, accurate analysis of risk compared to traditional models, enabling OakNorth to assess loan applications faster and with more precision. This helps the bank identify the right businesses to lend to and mitigate potential defaults, all while offering more favorable loan terms to low-risk businesses.
OakNorth used its AI platform to help The Restaurant Group secure a tailored loan, offering flexible repayment options that took into account their cash flow patterns, expansion plans, and market conditions. The AI-driven platform provided risk insights that helped both the bank and the borrower make informed decisions.
4. American Express: AI for Credit Card and Loan Offer Personalization
American Express (Amex) is leveraging AI to offer personalized credit card and loan products based on customer spending behaviors, credit scores, and preferences. By analyzing millions of customer transactions and interactions, Amex’s AI-powered system identifies patterns in how customers manage their finances, offering personalized credit limits and tailored loan offers based on individual financial habits.
Amex uses predictive analytics to forecast a customer’s future spending patterns and adjust credit limits accordingly. This ensures that customers are offered products that fit their unique financial needs, whether they need more credit for everyday purchases or a personal loan for larger expenses.
American Express’s AI models have enabled them to offer targeted credit card promotions and loan offers to customers based on their spending behavior and creditworthiness. By personalizing the customer experience, Amex has improved customer loyalty and provided more relevant financial products to its users.
Innovative AI Solutions
AI-Driven Innovations Transforming Lending
Emerging Technologies in AI for Lending
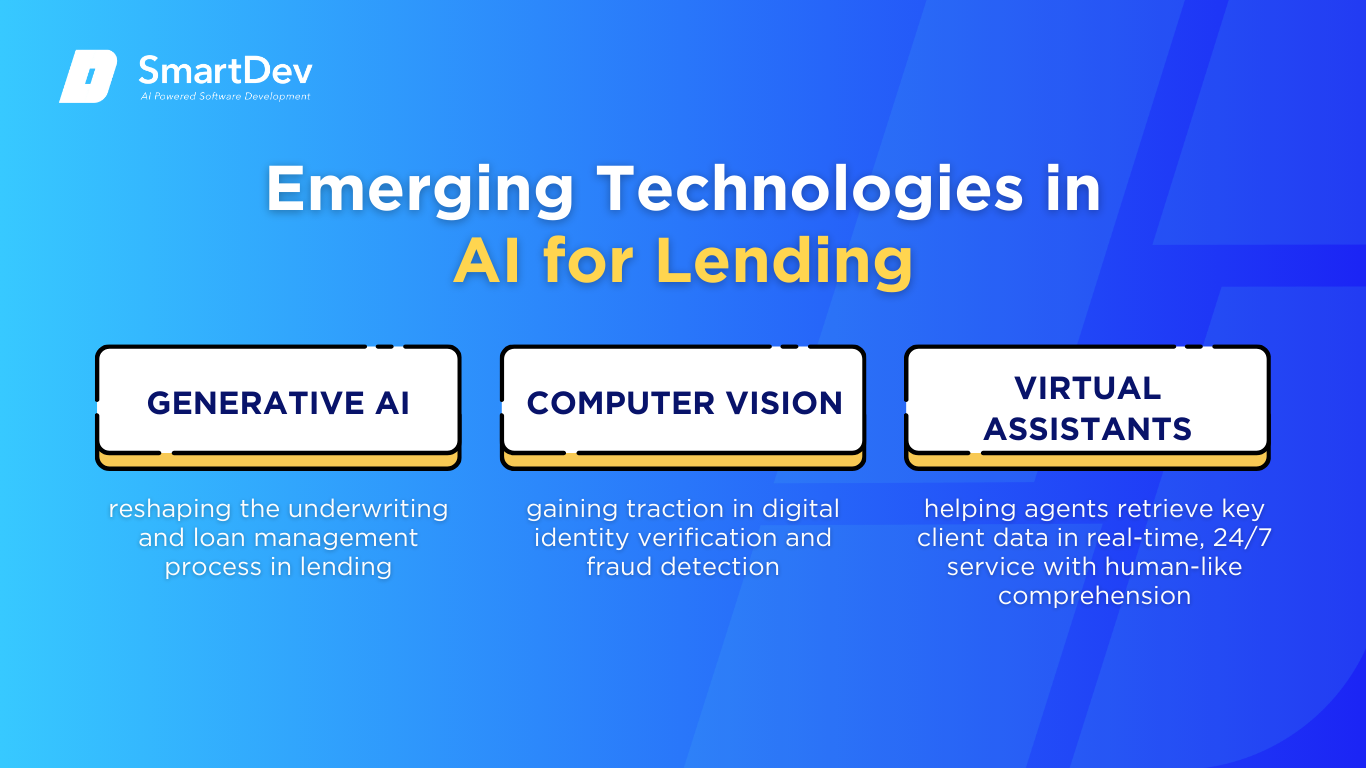
Generative AI is reshaping the underwriting and loan management process in lending. Lenders can now automate document processing, generate personalized loan offers, and simulate risk scenarios using synthetic datasets. This capability accelerates decision-making for underwriters while enhancing customer experience through faster, more tailored loan offers.
Computer vision is gaining traction in digital identity verification and fraud detection. AI can now process video evidence from loan applications, detect inconsistencies in submitted documents, and even verify facial recognition during onboarding. This reduces fraud, streamlines approval processes, and minimizes the need for in-person meetings—offering both operational savings and improved customer convenience.
AI-powered virtual assistants are transforming how lenders interact with customers and agents. From guiding applicants through loan applications to helping agents retrieve key client data in real-time, NLP-driven bots offer 24/7 service with human-like comprehension. AI makes loan servicing more intuitive, data-rich, and frictionless, allowing agents to focus more on relationship-building than administrative tasks.
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
AI is helping lenders build more sustainable, resource-efficient operations by predicting loan default risks, optimizing loan pricing, and minimizing manual data entry. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns that flag at-risk borrowers, allowing lenders to intervene early with personalized offers or outreach. This reduces loan losses, preserves revenue, and cuts down on repetitive processing and administrative waste.
Firms are also using AI to clean and maintain vast datasets, ensuring more accurate records, better segmentation, and less duplication. This enhances data sustainability while providing more precise insights for lending decisions. Additionally, predictive analytics is guiding smarter portfolio management, helping lenders align long-term growth strategies with sustainability and compliance goals.
How to Implement AI in Lending
A step-by-step guide for adopting AI in lending: assessing readiness, preparing data, choosing vendors, piloting, and training.
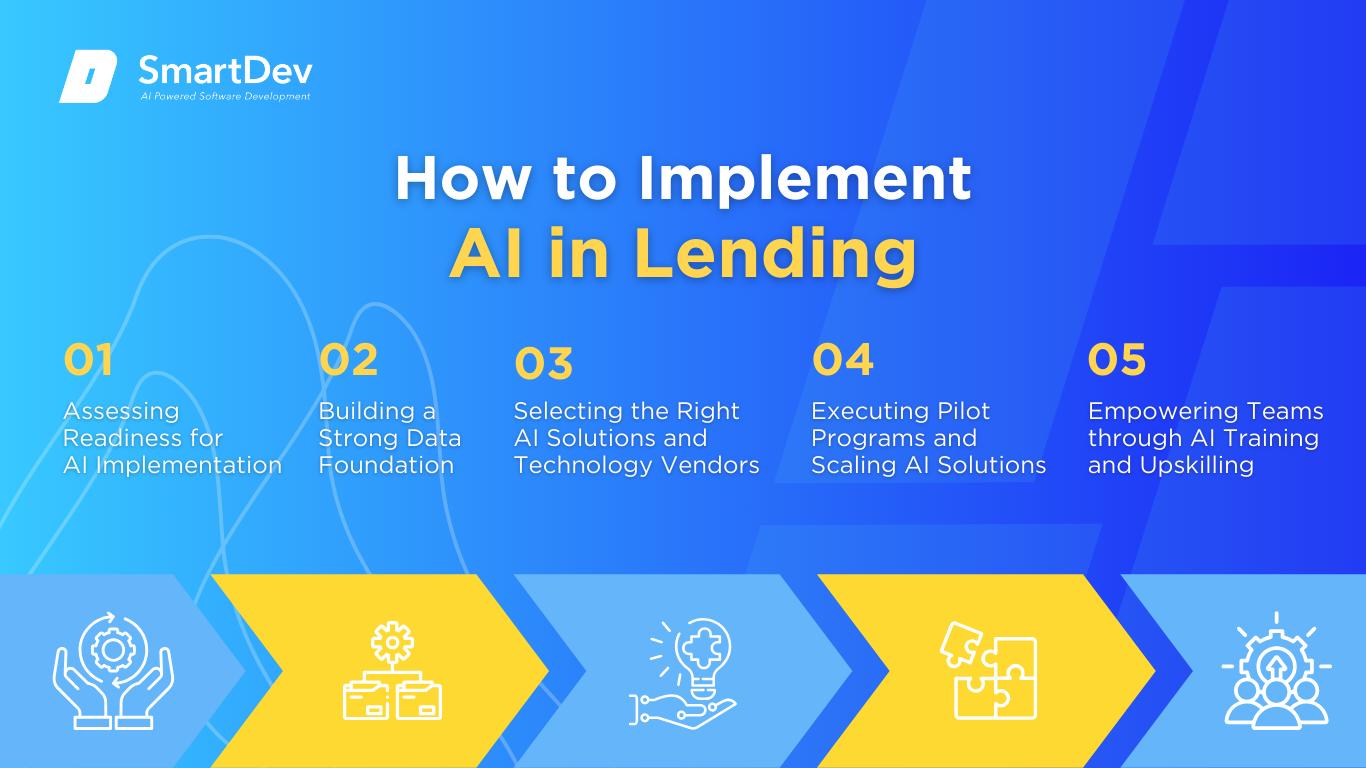
Step 1: Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Before diving into AI adoption, lending institutions need to identify areas where AI can bring the most value. Common entry points include credit scoring, fraud detection, loan underwriting automation, and personalized loan offerings. If your teams are overwhelmed by manual processes, dealing with high fraud rates, or struggling to personalize loan products for individual customers, these are key areas where AI can have an immediate impact.
Additionally, evaluate your technological and organizational readiness. Are your systems capable of integrating with AI tools or cloud platforms? Do your teams have the analytical expertise to trust AI-driven recommendations? Ensuring both technical infrastructure and a culture open to AI adoption is crucial for success. A strategic readiness assessment allows AI to transition from a trend to a core business enabler.
Step 2: Building a Strong Data Foundation
The power of AI in lending is only as good as the data it processes. Establishing a centralized, clean data architecture that captures customer financial behavior, transaction history, credit data, and other relevant inputs is essential. A strong data foundation allows AI models to operate with the highest accuracy, resulting in more reliable loan decisions and reduced risk.
Consistency and quality of data are paramount. This involves cleaning data, ensuring it’s structured properly, and eliminating duplicate or missing information. A clean, comprehensive dataset fuels AI models and enhances decision-making, from evaluating creditworthiness to detecting fraud patterns.
Step 3: Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Choosing the right AI tools for lending involves selecting platforms that address specific business challenges. Whether it’s predictive lending software, automated credit scoring systems, or fraud detection tools, ensure that the platforms you choose are tailored for financial services and lending.
It’s also essential to evaluate potential vendors for their expertise in regulatory compliance and AI transparency. The lending industry is heavily regulated, so your vendor should provide explainable AI models and be able to integrate smoothly with your existing systems. A partner with a proven track record in the financial sector can help ensure that your AI systems comply with legal requirements and help you build a trust-based relationship with customers.
Step 4: Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Start with small-scale pilot programs to test AI tools and their effectiveness. For example, implement AI-based credit scoring on a subset of loan applications or use automated underwriting for low-risk borrowers. These pilot projects will allow you to measure the AI’s performance, assess its impact on decision speed, and understand its effect on customer experience.
Once pilot testing proves successful, such as faster processing times, higher loan approval accuracy, or improved fraud detection, then it’s time to scale up. Expand AI adoption across different loan types, geographies, or departments. This gradual approach minimizes risk, ensures lessons learned from initial trials are integrated, and allows teams to adjust to the new technology before a full-scale rollout.
Step 5: Training Teams for Successful Implementation
AI in lending isn’t just about technology; it’s about empowering your teams to work alongside AI tools effectively. Training is critical to ensuring that employees understand how AI models work, how to interpret their recommendations, and when to apply human oversight. Staff should be trained to recognize where AI excels (e.g., in risk assessment or fraud detection) and where human expertise is still essential (e.g., in evaluating nuanced borrower situations).
Cross-functional collaboration is key to successful implementation. Encourage teamwork between departments like underwriting, risk management, compliance, and IT. When employees see AI as a collaborative tool rather than a replacement, they are more likely to engage with the technology and maximize its potential. Framing AI as an enhancement to human judgment ensures a more effective, future-proof lending operation.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Lending
Key Metrics to Track Success
Measuring the return on investment (ROI) for AI in lending begins with assessing the operational impact. One of the most noticeable metrics is loan approval speed. AI-driven credit scoring and automated underwriting platforms have shown the ability to reduce decision times from several days or weeks to just hours or minutes. This acceleration not only boosts throughput but also enables lenders to close loans faster, increasing revenue generation and improving customer satisfaction.
Cost savings is another key metric. By automating manual processes like data entry, document verification, and risk assessment, lenders can lower administrative overhead and redirect human resources to higher-value tasks. Additionally, AI-powered fraud detection reduces financial leakage by flagging potential fraudulent applications early, leading to fewer losses and improving overall portfolio performance.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
A prime example of AI-driven ROI in lending is the work done by American Express. By leveraging AI for credit card fraud detection, they’ve reduced fraud losses by 40%. AI models can spot suspicious transactions and patterns with far more accuracy than manual reviews, leading to both cost savings and improved customer trust. As a result, American Express saw a significant decrease in chargebacks, which translated directly into higher net revenue.
Another success story comes from LendingClub, where the implementation of AI-driven credit scoring improved the approval process for personal loans. AI models incorporated a wider variety of data points such as behavioral and transactional data, allowing LendingClub to extend credit to more borrowers while maintaining low default rates. This approach increased both customer acquisition and retention, driving stronger revenue growth.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Despite the potential for high ROI, there are several pitfalls that can hinder the success of AI in lending. One of the most common is poor data quality. Lenders often rely on outdated or fragmented datasets, which can lead to inaccurate credit scoring or poor loan recommendations. When inaccurate data is fed into AI models, it results in wrong decisions and undermines the trustworthiness of the entire system. To mitigate this, lenders must invest in robust data governance and data-cleaning strategies to ensure that the data being used is reliable and up-to-date.
Another challenge is the over-reliance on black-box AI models, where the decision-making process is not transparent. To avoid this, lenders must ensure that their AI systems are transparent, interpretable, and that human oversight is integrated into the decision-making process. When AI outputs are explainable and transparent, it builds trust with both borrowers and regulators.
Future Trends of AI in Lending

Predictions for the Next Decade
Over the next decade, AI will become essential to how lenders assess credit risk, serve customers, and design financial products. One of the most significant changes will come from dynamic, real-time credit scoring. Rather than relying on a single, static credit score, AI will continuously analyze data to update credit scores and loan terms in real time. This will allow lenders to offer hyper-personalized loans that evolve with the borrower’s financial situation, creating a much more responsive and customer-centric lending experience.
Generative AI will also revolutionize how loan products are designed and marketed. Lenders will be able to use advanced AI models to create personalized loan documents, offers, and repayment plans based on each borrower’s unique financial profile. AI-driven chatbots and conversational agents will help both borrowers and loan officers by streamlining communication, clarifying loan terms, and providing recommendations for the next steps—ultimately making the lending process more intuitive and user-friendly.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To remain competitive in this AI-driven future, lenders must make AI a core part of their innovation strategies, rather than an afterthought. The first step is to invest in scalable, flexible data infrastructure that connects customer data, credit scoring, loan servicing, and risk management into a unified AI-ready ecosystem. Lenders that can break down data silos and turn fragmented customer information into actionable insights will be better positioned to create more personalized, efficient, and accurate lending solutions.
Lenders should also form cross-functional AI teams that bring together data scientists, underwriters, risk managers, and customer service teams to explore emerging AI technologies like predictive analytics, alternative data sources, or autonomous loan approval systems. Experimentation will be key. The lenders that build “AI sandboxes” today will be the ones who can scale these innovations successfully in the future.
Finally, staying ahead means fostering a culture that embraces AI as a tool for continual improvement. Lenders should prioritize AI literacy across all teams, ensuring that staff members understand how AI models work, how they improve over time, and how to use these tools to drive better customer outcomes. Lenders that view AI not as a challenge but as an opportunity to evolve their business models and enhance customer experiences will be the ones that lead the market in the next decade.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI is fundamentally transforming lending, from real-time credit scoring and dynamic loan underwriting to personalized borrower experiences and advanced fraud detection. With technologies like generative AI, machine learning, and computer vision, lenders are reducing operational bottlenecks, speeding up loan decisions, and providing more tailored, data-driven solutions for their customers.
What’s more, AI is driving both sustainability and scalability in lending. By optimizing processes, cleaning large datasets, and enabling proactive risk management, AI not only enhances operational efficiency but also creates a more responsive, sustainable lending model. Success stories show that AI is already delivering measurable ROI in faster loan processing, reduced fraud, and improved customer satisfaction.
Moving Forward: A Strategic Approach to AI in Lending
AI is no longer a luxury for lenders; it’s a business imperative. To fully harness its potential, financial institutions must focus on building a robust data infrastructure, fostering cross-functional collaboration, and continuously upskilling teams. Integrating AI into credit assessment, loan servicing, and fraud detection workflows helps lenders stay adaptable, competitive, and customer-centric in an ever-changing market.
At SmartDev, we help lenders implement intelligent AI solutions, from predictive credit modeling and automated underwriting to AI-powered fraud prevention and customer service agents. Whether you’re just beginning your AI journey or scaling solutions across your organization, we partner with you to build ethical, secure, and scalable systems that deliver lasting success.
Connect with us today to learn how AI can revolutionize your lending operations, enhance customer relationships, and position your business for future growth.
—
References:
- The State of AI | McKinsey
- Mortgage Lender Sentiment Survey | Fannie Mae
- How AI and Digital Lending Are Transforming the Industry | Wolters Kluwer
- Fair Lending in the Era of AI | BDO
- Upstart Using Machine Learning to Transform the Personal Loan Experience | Harvard Business Review
- Behavioral Fraud Detection in Lending | Zest AI
- Square’s Afterpay Expands Lending Offerings for Small Businesses | The Financial Brand
- Strategies for Lowering Student Loan Interest Rates | SoFi
- Supporting Generative AI Innovation | American Express Ventures







