
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way devices, systems, and applications interact, but its rapid growth has outpaced the development of standardized frameworks. While established industries like Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) have long relied on robust standards, IoT—and particularly Industrial IoT (IIoT)—is still navigating a fragmented landscape.
Emerging technologies such as NB-IoT and LTE CAT-M1 are designed to support wireless IoT communication, yet many deployments remain in early stages. This lack of unified data standards creates challenges in machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, limiting the scalability and efficiency of IoT systems. For IoT to achieve its full potential, consistent frameworks are essential to ensure seamless device integration and interoperability.
This blog explores the importance of unified data standards in IoT, the challenges of achieving interoperability, and how these standards are shaping the future of connected systems.
Introduction
Importance of Unified Data Standards in IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become a driving force behind innovation in industries as diverse as healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture. With billions of devices connected worldwide, IoT has transformed how businesses operate and deliver value. However, this exponential growth has also created a fragmented ecosystem where devices often function in isolation, unable to communicate effectively with one another.
Unified data standards are critical to addressing this challenge. By establishing a common framework for device communication and data exchange, these standards eliminate silos, reduce development complexity, and unlock the full potential of IoT. They streamline processes, enable interoperability, and foster innovation, paving the way for scalable and efficient IoT ecosystems.
For example, in healthcare, standardized protocols allow medical devices to seamlessly share critical patient data, improving diagnostics and treatment outcomes. Similarly, in manufacturing, unified data standards ensure machinery across different suppliers integrates efficiently, optimizing production processes. Without these standards, businesses risk increased costs, operational inefficiencies, and stunted innovation.
Overview of IoT Interoperability Challenges
Despite its promise, IoT’s lack of interoperability remains a persistent obstacle. Devices from various manufacturers are often designed with proprietary protocols, creating barriers to integration. According to FutureIOT [1], this fragmented landscape results in a situation where “devices may not speak the same language, even when they serve the same purpose.” For instance, smart home systems may include devices from different brands—lighting, security cameras, and thermostats—but without a unified standard, their interoperability is limited, requiring separate control systems or middleware to enable communication.
The implications of these challenges are significant. Businesses face increased development costs as they build custom solutions to bridge incompatible devices. Security vulnerabilities emerge as disparate systems struggle to implement cohesive protection measures. Furthermore, this lack of standardization slows innovation, as companies must spend time and resources resolving compatibility issues instead of focusing on creating new products and services.
Unified data standards offer a promising solution by addressing these pain points directly. By enabling seamless device communication, they reduce integration complexity, improve security, and accelerate IoT adoption across industries. As highlighted by FutureIOT [1], the journey toward achieving unified standards is lengthy and requires industry-wide collaboration, but the benefits are undeniable—an interconnected ecosystem where IoT devices can truly realize their transformative potential.
1. Understanding Unified Data Standards
Unified data standards are the backbone of a truly interconnected Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. They define a common framework for how data is formatted, transmitted, and interpreted across devices and systems. By providing a universal language for communication, these standards eliminate the fragmentation that often plagues IoT deployments, ensuring seamless interaction between diverse platforms and technologies.
1.1. Definition and Key Concepts

Unified data standards in IoT refer to a structured set of protocols, data formats, and frameworks that enable seamless communication and data exchange between devices. At its core, these standards act as a universal language, establishing consistency in data structure, communication protocols, and interoperability rules. These standards ensure that devices from different manufacturers can seamlessly communicate without requiring complex, custom integrations. In industries like smart manufacturing or industrial IoT (IIoT), this standardization is critical to enable real-time data sharing across sensors, machines, and cloud platforms.
For example, protocols like MQTT or CoAP are often part of IoT ecosystems, but without unified standards, their integration can vary widely, creating inefficiencies. Unified data standards ensure that regardless of the protocol, data can be seamlessly exchanged and interpreted.
Another application in a smart city setting, sensors monitoring traffic, weather, and energy usage might originate from different vendors and use various data structures. Unified standards allow these devices to integrate their outputs into a cohesive system, supporting data-driven decision-making. According to PortQii [2], unified data standards are essential to bridging the communication gap, enabling systems to operate cohesively and efficiently while simplifying the overall architecture.
1.2. Key benefits of Unified Standards

Unified data standards bring numerous benefits to IoT ecosystems, fostering collaboration, reducing inefficiencies, and driving innovation.
- Seamless Integration:
Devices across various platforms and protocols can exchange data effortlessly. This integration allows systems to work together, enhancing functionality and user experience. For instance, smart home devices—from thermostats to security systems—can interoperate through standardized protocols, creating a unified system for homeowners. - Cost Efficiency:
The absence of unified standards often necessitates the development of custom middleware to connect disparate systems, increasing costs. Unified data standards eliminate this need, streamlining development and reducing both time and financial investment. As PortQii [2] notes, businesses adopting standardized frameworks can achieve significant cost savings by minimizing redundant development efforts. - Improved Security:
Security is a critical concern in IoT, with vulnerabilities often arising from inconsistent or proprietary communication protocols. Unified standards typically incorporate robust security measures, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of breaches. A standardized approach also simplifies the implementation of security best practices across the ecosystem. - Scalability:
Unified standards make it easier to scale IoT systems by simplifying the integration of new devices or systems. Whether it’s expanding a factory’s IoT-enabled machinery or adding devices to a smart building, standardized protocols enable growth without re-engineering existing systems. - Accelerated Innovation:
Interoperability fosters collaboration between manufacturers, developers, and other stakeholders. By reducing compatibility issues, unified data standards free up resources that can be redirected toward innovation. As a result, businesses can focus on developing advanced features and services rather than solving integration challenges.
Unified data standards are more than a technical necessity; they are a catalyst for the growth and maturation of IoT. By enabling seamless communication and collaboration, they drive progress and open doors to new possibilities in industries ranging from application engineering to industrial automation. The adoption of these standards is essential to achieving an interconnected IoT future where devices, systems, and stakeholders can truly work in harmony.
2. Current IoT Standards and Protocols
2.1. Overview of Existing Standards
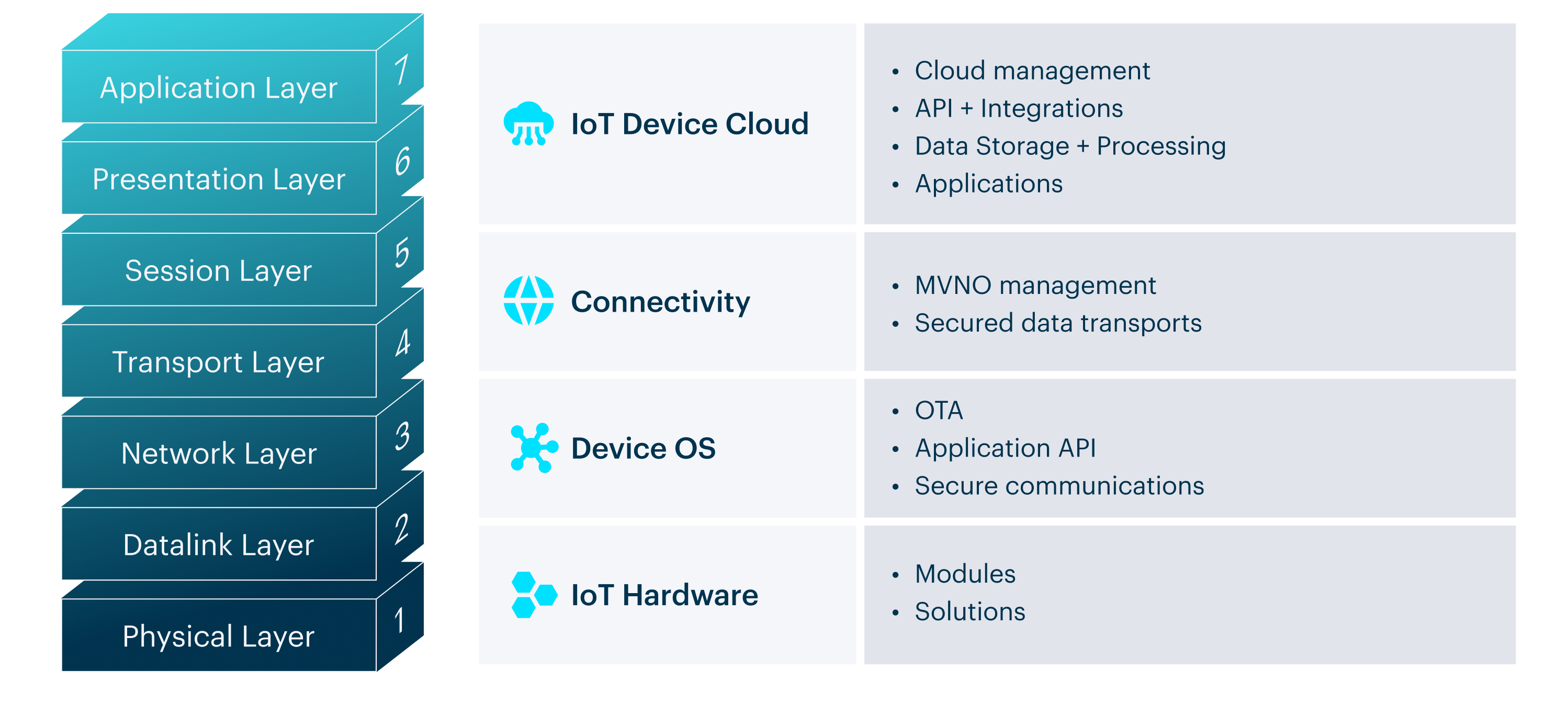
The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem relies on several widely adopted standards and protocols to facilitate communication between devices. Each protocol is designed with specific goals in mind, tailored to meet the diverse needs of IoT applications. However, while these standards have enabled remarkable advancements, their coexistence also presents unique challenges.
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport):
This lightweight messaging protocol is highly efficient, making it ideal for IoT devices with constrained bandwidth or processing power. MQTT’s publish/subscribe architecture allows devices to communicate asynchronously, enabling seamless data flow in use cases like remote monitoring and real-time alerts. It’s particularly popular in industrial IoT and energy management. - CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol):
Designed for low-power and low-bandwidth environments, CoAP is optimized for IoT devices that operate on limited resources, such as sensors in smart agriculture or wearable health monitors. Its RESTful architecture supports HTTP-like interactions, making it easy for developers to implement. - LwM2M (Lightweight Machine-to-Machine):
This protocol specializes in device management and monitoring, offering features like remote configuration and firmware updates. LwM2M is a favorite in industrial applications, where efficient management of large device fleets is critical.
Each protocol addresses specific aspects of IoT communication, from data transfer efficiency to device management. However, their specialized nature often means that businesses must deploy multiple protocols simultaneously, leading to a fragmented landscape that complicates integration and increases costs. As highlighted by ByteSnap [3], the diversity of IoT standards reflects the wide range of IoT applications, but also underscores the pressing need for harmonization.
2.2. Limitations of Diverse Protocols
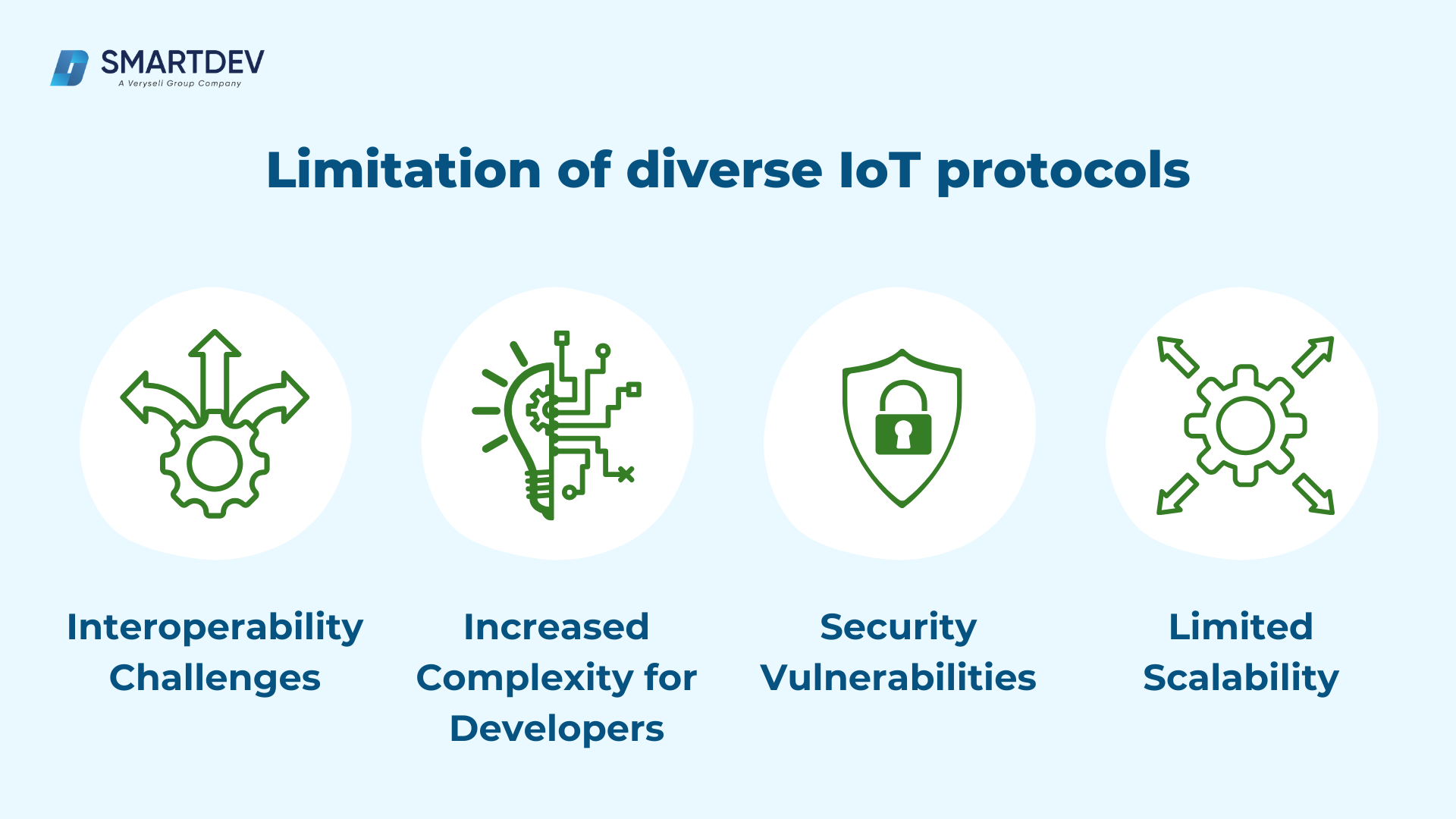
Despite their strengths, the coexistence of multiple protocols often creates fragmentation in IoT ecosystems. Here’s how this impacts IoT deployments:
- Interoperability Challenges:
Devices using different protocols often struggle to communicate seamlessly, requiring costly middleware or custom integrations. This limits the ability to create scalable, unified IoT systems. - Increased Complexity for Developers:
Developers must account for protocol-specific requirements, adding to development time and complexity. Without unified standards, ensuring compatibility across protocols becomes a daunting task. - Security Vulnerabilities:
Each protocol comes with its own security framework, and inconsistencies between protocols can leave IoT systems exposed to potential threats. For instance, a robust MQTT implementation may not align well with a CoAP-based system, creating security gaps. - Limited Scalability:
As IoT ecosystems grow, managing diverse protocols across thousands of devices becomes increasingly impractical. This can stifle the adoption of IoT in industries like smart cities or connected healthcare, where uniform communication is critical.
3. The Role of Unified Standards in IoT
3.1. Enhancing Device Communication and Integration
3.1. Enhancing Device Communication and Integration
Unified data standards serve as the backbone of IoT integration, bridging the gap between disparate devices and systems. This capability is particularly vital in complex IoT ecosystems such as smart cities, where various systems—traffic management, public safety, and energy grids—must operate cohesively.
For instance, in a smart traffic system, sensors, cameras, and signals from different manufacturers must collaborate to optimize traffic flow. Unified standards ensure that data from these devices can be shared and interpreted without additional middleware, reducing latency and enhancing system efficiency. According to AVSystem [4], such standards eliminate communication barriers by creating a universal framework that supports real-time, device-to-device data exchange.
Key Business Implications:
- Faster Deployments: Simplified integration accelerates project timelines.
- Reduced Costs: Minimizes the need for middleware and custom development.
- Scalable Growth: Supports large-scale IoT systems, such as smart factories or connected healthcare networks.
3.2. Promoting Seamless Interoperability
Interoperability lies at the heart of IoT’s success, and unified data standards make this possible by ensuring that devices from different vendors can communicate without compatibility issues.
Despite their strengths, the coexistence of multiple protocols often creates fragmentation in IoT ecosystems. Here’s how this impacts IoT deployments:
- Interoperability Challenges:
Devices using different protocols often struggle to communicate seamlessly, requiring costly middleware or custom integrations. This limits the ability to create scalable, unified IoT systems. - Increased Complexity for Developers:
Developers must account for protocol-specific requirements, adding to development time and complexity. Without unified standards, ensuring compatibility across protocols becomes a daunting task. - Security Vulnerabilities:
Each protocol comes with its own security framework, and inconsistencies between protocols can leave IoT systems exposed to potential threats. For instance, a robust MQTT implementation may not align well with a CoAP-based system, creating security gaps. - Limited Scalability:
As IoT ecosystems grow, managing diverse protocols across thousands of devices becomes increasingly impractical. This can stifle the adoption of IoT in industries like smart cities or connected healthcare, where uniform communication is critical.
3.3. Overcoming barriers for adoption
Challenges still remain in achieving widespread adoption, including:
- Vendor Lock-In: Businesses tied to proprietary systems may face resistance to switching to open standards.
- Legacy Systems: Integrating older devices with new standards requires careful planning and investment.
- Coordination Across Stakeholders: Unified standards require collaboration between governments, industry bodies, and technology providers, which can be slow and complex.
4. Industry Applications
4.1. Smart Manufacturing & Smart Cities
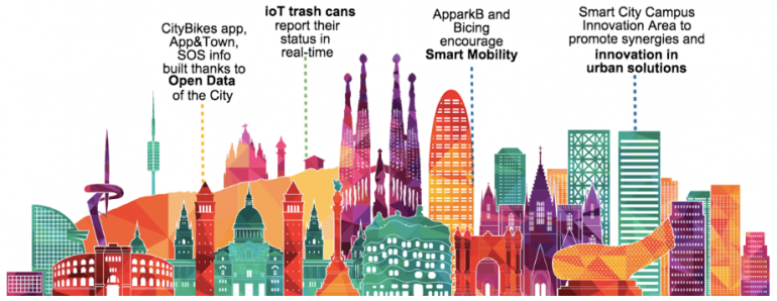
In the context of smart cities, unified data standards are critical for managing diverse systems, such as traffic control, energy distribution, and public safety. A prime example is the Barcelona Smart City Project, where unified IoT protocols facilitate communication between thousands of sensors and devices across the city.
Key Outcomes:
- Traffic Management: Sensors integrated through standardized protocols optimize traffic flow by monitoring congestion and dynamically adjusting traffic signals.
- Energy Efficiency: Unified standards enable real-time data exchange between solar panels, smart grids, and public lighting, reducing energy waste.
- Public Safety: Emergency response systems leverage interoperable devices to provide faster, more coordinated responses to incidents.
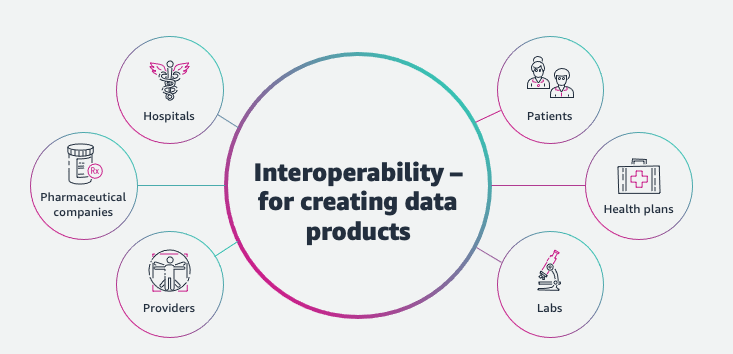
4.2. Healthcare: Interoperable Medical Devices for Better Care
The Mayo Clinic has implemented unified data standards to integrate various medical devices and electronic health records (EHR). This integration has resulted in:
- Seamless Data Flow: Patient data from different devices is consolidated into a single EHR system, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
- Remote Monitoring: Patients use standardized wearable devices to transmit real-time health data to healthcare providers, enabling proactive care.
- Improved Compliance: Standardized data formats ensure adherence to HIPAA regulations, safeguarding patient information.
4.3. Industrial IoT: Streamlining Manufacturing Operations
Siemens has adopted unified data standards in its manufacturing processes, leading to:
- Optimized Production: Machines and sensors communicate in real-time, reducing downtime by 30% through predictive maintenance.
- Cross-Platform Communication: Equipment from different vendors operates cohesively, streamlining workflows and increasing productivity.
- Enhanced Safety: Interoperable sensors detect hazardous conditions, automatically shutting down equipment to prevent accidents.

4.4. Logistics: Optimizing Supply Chain Management
Unified standards are the backbone of smart city initiatives, where thousands of interconnected devices monitor and manage traffic, utilities, and public safety. These standards enable data sharing across platforms, improving urban efficiency and quality of life for citizens.
4.5. Retail and E-Commerce: Personalized Customer Experiences
Walmart has utilized unified data standards to enhance its IoT infrastructure, resulting in:
- Inventory Management: Smart shelves provide real-time inventory data, reducing stockouts by 15%.
- Personalized Marketing: Customer behavior data is integrated to deliver targeted promotions, increasing sales by 10%.
- Operational Efficiency: Standardized protocols simplify the integration of new IoT devices across stores.

4.6. Agriculture: Precision Farming with IoT
John Deere has implemented unified data standards in its precision agriculture solutions, leading to:
- Improved Water Efficiency: Sensors and irrigation systems communicate to optimize water usage, reducing consumption by 25%.
- Enhanced Productivity: Real-time data on soil and weather conditions inform planting decisions, increasing crop yields by 20%.
- Scalability: Standardized protocols allow for easy integration of additional sensors and equipment.

5. Case studies: Redifining Healthcare approach with an All-in-one Healthcare application

Our Client’s Product is a digitalized healthcare application in France, designed for two main purposes: monitoring patients in real time, through NFC bracelets; and managing children in school settings through their digital profile. The mobile app provides secure data storage and supports multi-platform use, ensuring safety and providing instant updates to caregivers. SmartDev has successfully applied comprehensive NFC features, and met their security and multi-tenancy requirements.
5.1. Challenge
Our client needed an application integrating NFC device interactions with low latency recognition to ensure seamless user experience, especially for non-tech savvy users. Additionally, the app must function completely offline, have high security requirements, and ability to adapt to each hospital’s regulation, with multi-tenancy.
5.2. SmartDev's solution
- Comprehensive security solutions: SmartDev developed a cross-platform app with secure storage, leveraging RSA 256 encryption to meet the requirements.
- Automated operations & Multi-tenancy: We employed React Native with New Architecture to maximize codebase-sharing between platforms and integrate continuous and automated reporting to streamline the process.
- Enhanced user experience: user-friendly design, improved NFC features, and Minew BLE for Low-energy devices are added to enhance device interaction, available for both Android & IOS.
5.3. Their key outcomes
- Enhanced customer trust: The core application & NFC service is executed securely and efficiently, ensuring optimization for healtcare providers, safety and reassurance for patients and their families. Our client has achieved 300+ usage by families, with the highest percentage of patient acceptance of 95%.
- Cost-efficiency & Scalability: A cross-platform app streamlines development and maintenance efforts, as code can be shared across both platforms. This reduces development time and costs, while ensuring consistency across the user experience.
- Strong data storage & security: By integrating RSA-256 and industry-standard security solution, the client was able to ensure accurate identity check, secured data privacy and personalized care. This allowed them to deliver excellent service and gain a competitive advantage.
6. Challenges in Implementing Unified Standards
6.1. Technical and Organizational Barriers
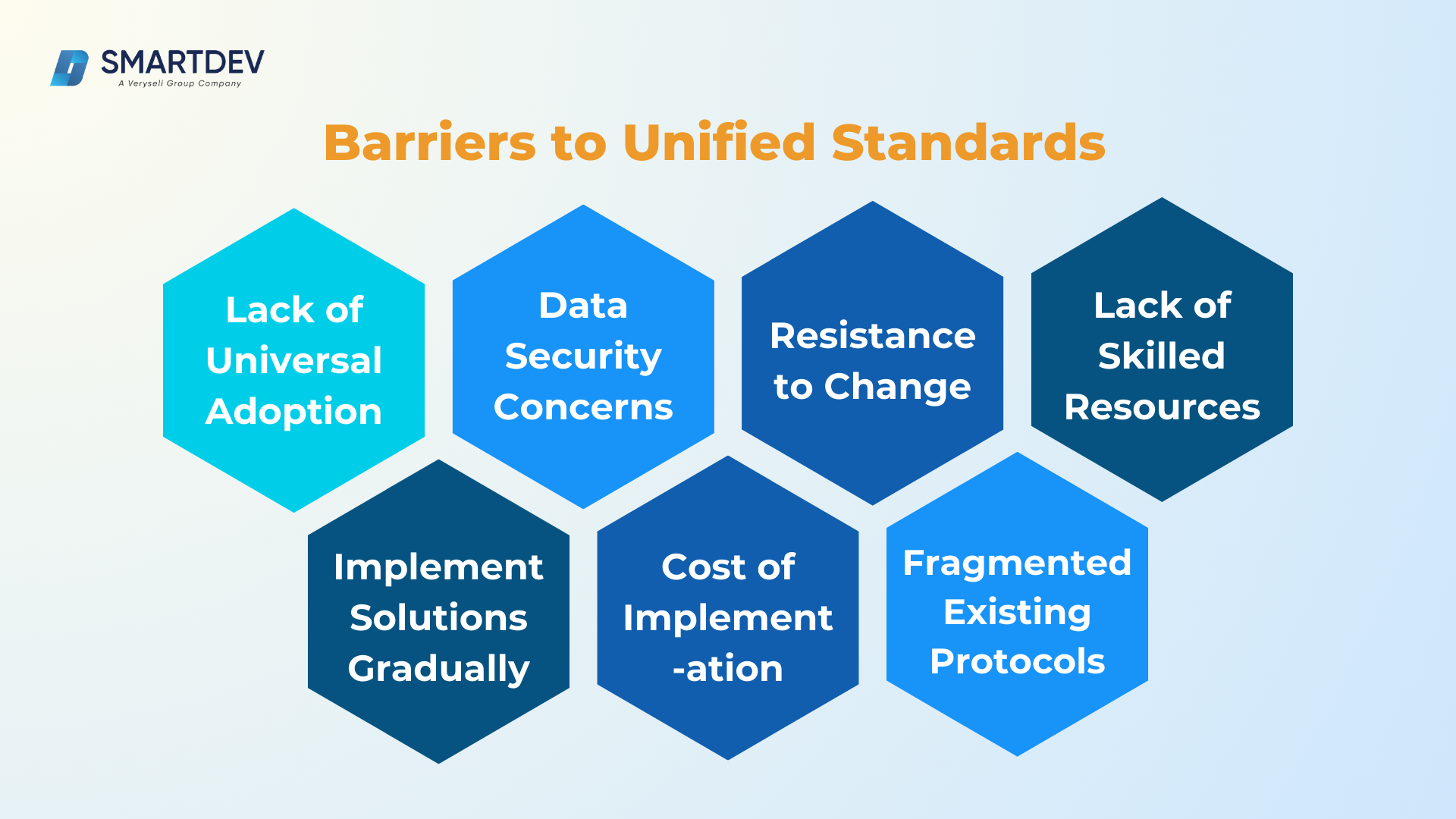
Organizational Barriers to Unified Standards
- Resistance to Change:
Organizations often hesitate to transition from proprietary systems to standardized ones due to concerns about cost, time, and potential disruptions. - Lack of Skilled Resources:
Implementing unified standards requires expertise in IoT architecture, protocol integration, and data management, which many organizations lack. - Cost of Implementation:
The upfront investment in updating systems to comply with unified standards can be a deterrent for smaller businesses or industries with tight budgets.
Technical Barriers to Unified Standards
- Fragmentation in Existing Protocols:
With protocols like MQTT, CoAP, and LwM2M widely used, achieving interoperability between them requires significant effort. Integrating legacy systems with modern IoT devices often demands custom middleware, increasing development complexity. - Lack of Universal Adoption:
Even as standards are developed, not all manufacturers and developers adopt them consistently. This results in fragmented ecosystems where devices struggle to communicate effectively. - Data Security Concerns:
Standardized frameworks must prioritize robust encryption and authentication mechanisms to safeguard sensitive IoT data. Without uniform security protocols, networks are vulnerable to breaches.
6.2. Solutions to Overcome Adoption Hurdles

a. Embrace Open-Source Standards
Open-source frameworks, such as MQTT, CoAP, and LwM2M, provide businesses with accessible, cost-effective solutions for IoT integration. These frameworks foster collaboration and innovation within the developer community, ensuring continual improvement and support.
- Open standards eliminate vendor lock-in, reduce costs, and allow businesses to customize solutions to their specific needs. For instance, adopting MQTT for lightweight messaging or LwM2M for device management ensures compatibility and scalability in IoT ecosystems.
- Platforms like SmartDev IoT Services simplify the integration of open-source protocols by providing tailored solutions, ensuring faster deployment and lower risk.
b. Invest in Training and Skill Development
The successful adoption of unified standards hinges on a workforce equipped with the right skills. Organizations must prioritize training to ensure teams can implement and manage IoT frameworks effectively.
- Key Training Areas:
- IoT protocols (e.g., MQTT, CoAP)
- Data standardization practices
- IoT security measures to address vulnerabilities in interoperable systems
- Practical Implementation:
- Organize workshops and certifications in IoT integration.
- Collaborate with industry associations to provide ongoing training.
c. Implement Scalable Solutions Gradually
A phased approach to adopting unified standards allows businesses to minimize disruption and demonstrate the tangible benefits of standardization.
- Start Small:
Focus on high-impact areas, such as inventory management in retail or energy monitoring in manufacturing, to validate the value of IoT integration. - Build Modularly:
Introduce standardized solutions in phases, integrating new systems while maintaining compatibility with legacy infrastructure.
d. Collaborate with IoT Experts
Partnering with experienced IoT solution providers can help organizations navigate the complexities of adopting unified standards. Providers like SmartDev bring expertise in designing scalable, secure, and tailored IoT solutions.
- Benefits of Collaboration:
- Expert guidance in choosing the most suitable IoT standards for specific use cases.
- Seamless integration of IoT devices and systems, reducing time-to-market.
- Access to best practices and advanced tools for managing unified standards.
- SmartDev’s Value:
SmartDev’s proven expertise ensures that businesses adopt standards efficiently, overcoming technical and organizational challenges while minimizing risks.
e. Prioritize Security and Compliance
Unified standards often include robust security protocols, but businesses must prioritize implementing these measures effectively to mitigate risks.
Best Practices:
- Use end-to-end encryption and authentication to secure device communication.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities in the IoT ecosystem.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, depending on the industry.
7. Future Trends and Innovations
7.1. Emerging Standards and Frameworks

- Matter Protocol for Smart Homes:
The Matter protocol, backed by tech giants like Google, Apple, and Amazon, is a major step toward standardizing smart home devices. Designed to work across ecosystems, Matter ensures that devices communicate seamlessly, regardless of brand. This protocol sets a precedent for future IoT standardization in consumer-focused applications. - 5G Integration in IoT:
The rollout of 5G networks is enabling low-latency, high-speed connectivity for IoT devices. Standards like NB-IoT and LTE-M, tailored for IoT, are evolving to fully leverage 5G capabilities. This advancement is critical for industries like smart cities and industrial IoT (IIoT), where real-time communication is essential. - AI-Driven Standards:
Emerging frameworks are incorporating AI and machine learning to optimize IoT data handling. These standards aim to enable autonomous interoperability, where devices learn to adapt and communicate without manual intervention. - Zero Trust Security Frameworks:
With increasing cybersecurity threats, unified standards are incorporating Zero Trust models to enhance security. These frameworks ensure continuous authentication, safeguarding IoT ecosystems from vulnerabilities.
7.2. The Path Toward Universal Interoperability

- Cross-Industry Collaboration:
Achieving universal interoperability requires collaboration across industries. Initiatives like the IoT Connectivity Alliance and Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) are bringing together stakeholders to create unified protocols that cater to diverse applications. - Adoption of Open Standards:
The adoption of open-source standards, such as MQTT, CoAP, and OPC UA, is accelerating. These frameworks allow developers to build scalable, future-ready systems while reducing compatibility issues. SmartDev’s expertise in integrating open standards ensures seamless IoT implementations. - Edge Computing Integration:
The rise of edge computing is influencing IoT standardization. Frameworks are being designed to support decentralized data processing, enabling faster decision-making and reducing network dependency. - Focus on Sustainability:
Future IoT standards are increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency and sustainability. By standardizing power-efficient protocols, such as Bluetooth LE and Zigbee, the industry is aligning with global sustainability goals.
8. Conclusion

Unified data standards are the foundation upon which the future of IoT is being built. By enabling seamless communication between devices, reducing integration complexities, and fostering innovation, these standards empower businesses to unlock the full potential of their IoT ecosystems. In an increasingly connected world, prioritizing interoperability is not just an option but a necessity to stay competitive and agile in rapidly evolving markets.
Businesses that embrace unified data standards position themselves for operational excellence, improved scalability, and enhanced customer satisfaction. These standards pave the way for smarter, more efficient systems across industries, enabling organizations to innovate faster and deliver better outcomes.
Join the Movement Toward a Unified IoT Future
The future of IoT depends on collective action. Businesses, developers, and policymakers must collaborate to accelerate the adoption of unified standards. By investing in open-source frameworks, leveraging expert guidance, and aligning with industry-wide initiatives, stakeholders can drive IoT toward universal interoperability.
Ready to take the next step? SmartDev is here to help. With a proven track record in building scalable, interoperable IoT solutions, SmartDev empowers businesses to overcome challenges and embrace the future of IoT.
Contact us today to discover how we can elevate your IoT strategy and help you lead in a connected world.






