The fintech (financial technology) industry is vast and ever-evolving, covering a broad range of digital solutions aimed at improving financial services. From personal finance apps that help us track our spending to complex payment processing systems that facilitate international trade, fintech innovations touch nearly every aspect of our financial lives. However, within the larger fintech ecosystem, certain sectors stand out for their focus on providing digital solutions that transform traditional financial services. These sectors—digital payments, lending, personal finance, investment tech, insurtech, and regtech—each have unique impacts and meet distinct needs.
But as innovation takes center stage, which fintech sector stands out as the most digitally focused? We’ll look into the degree of digital adoption across sectors like digital payments, neobanking, insurance technology (insurtech), wealthtech, and lending platforms, and identify the leaders in terms of embracing a fully digital ecosystem.
The Drive Toward Digitalization in Fintech
Before diving into sector comparisons, it’s crucial to understand the driving forces behind fintech’s digitalization. Digitalization in financial technology refers to using software, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain to enhance traditional financial services. These innovations are meant to improve user experience, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and provide new capabilities that were not previously possible.
According to Boston Consulting Group (BCG)’s 2024 report, “Global Fintech: Prudence, Profits, and Growth,” digitalization is not just about delivering convenience to consumers—it’s about creating sustainable business models that yield profitability and growth amid rapid change.
Digital Payments: The Original Fintech Powerhouse
Digital payments were among the earliest adopters of fintech innovation. They have transformed the way we move money—from remittances to peer-to-peer transfers and online shopping payments. With constant innovation in mobile apps, contactless technology, and digital wallets, the payments industry continues to focus heavily on digital transformation.
The extent of digitalization
Digital payments are inherently digital, and their progress reflects their core integration of technology. Payment companies have not only streamlined transactions but also adopted advanced technologies like blockchain to enable secure cross-border payments and biometrics for authentication. The introduction of near-field communication (NFC) and QR code payments has further enhanced convenience, allowing for seamless transactions across a variety of platforms and devices.
Case Study: PayPal’s Transformation
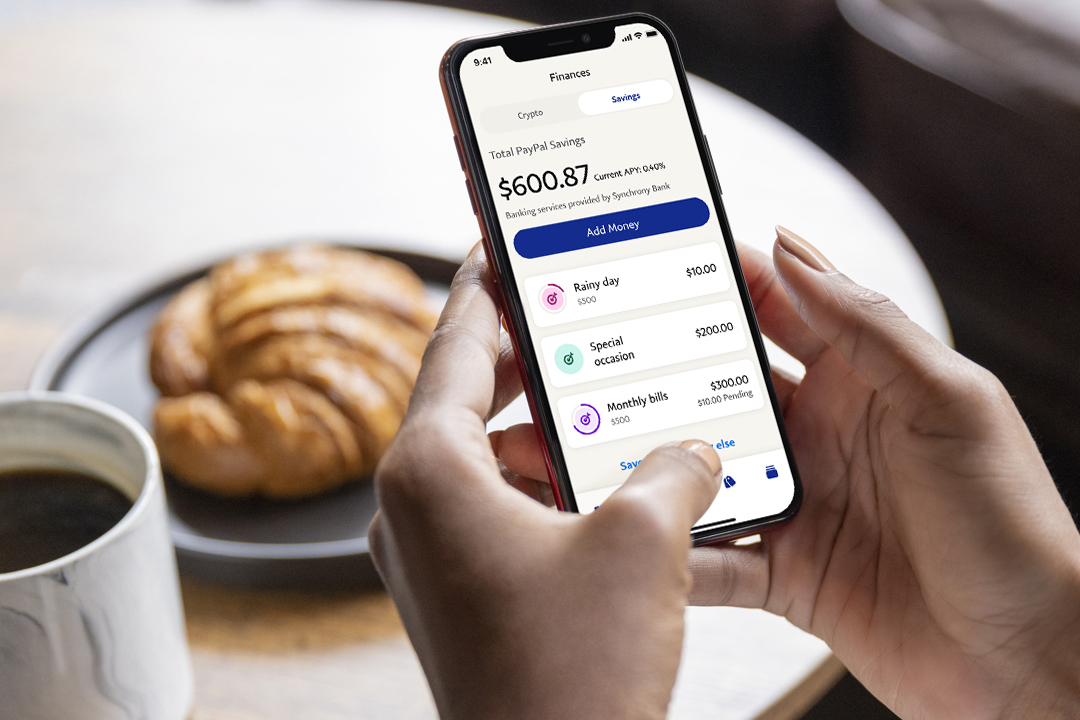
Image 1: PayPal offered a seamless online platform that allowed users to send and receive money instantly, without the need for physical branches or lengthy paperwork.
Before digitalization, payment services were primarily reliant on physical cash, checks, or bank transfers, all of which involved considerable time and effort for both consumers and businesses. PayPal revolutionized the payment industry by providing a fully digital platform that allowed users to make transactions instantly without the need for a traditional bank. By adopting a digital-first strategy, PayPal eliminated the dependency on physical infrastructure, dramatically reducing the costs and time associated with financial transactions.
After digitalization, PayPal’s impact became evident not only in consumer convenience but also in global reach. The adoption of technologies like one-touch payments, integration with e-commerce platforms, and partnerships with financial institutions led to a significant increase in user adoption. PayPal’s ability to offer cross-border payments seamlessly has opened up international markets for small businesses and freelancers, fostering a truly global economy. The company’s integration of advanced security features such as multi-factor authentication has further instilled confidence among users, driving higher transaction volumes and expanding its footprint in the digital payments space.
The Challenges
Despite their progress, digital payment companies still rely heavily on traditional banking infrastructure, such as card networks and banking partners, limiting complete independence. Additionally, the rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) may present both opportunities and challenges as the sector evolves. As CBDCs gain traction, digital payment firms may need to adapt their models to integrate or support these new forms of currency, which could mean rethinking infrastructure and compliance.
The Opportunities
The global shift towards cashless societies offers a promising future for the digital payments sector. By expanding into underbanked regions and leveraging technologies like blockchain for transparency and security, digital payments can continue to be a leader in fintech digitalization.
Neobanking: Fully digital financial services
Neobanks allow customers to perform all banking activities—from account creation to applying for loans—directly through their smartphones, making banking more accessible and convenient for tech-savvy users.
Case Study: Monzo’s Impact on Digital Banking

Image 2: By putting the needs of its customers first and leveraging the power of technology, Monzo has emerged as a beacon of innovation in the banking industry, inspiring change and driving progress for the benefit of all.
Monzo, a UK-based neobank, provides a compelling case study of how fully digital banking can change the industry. Before neobanks like Monzo, traditional banks controlled the market with physical branches, manual processes, and complicated service offerings that often lacked transparency and user engagement. Accessing basic financial services, such as opening an account, tracking spending, or applying for loans, involved in-person visits and paperwork, making banking difficult for many customers.
Monzo changed this by offering a digital-first banking experience that is accessible and user-centric. With Monzo’s app-based model, customers can open accounts in minutes from their phones, eliminating the need for branch visits. Features like real-time spending notifications, budgeting tools, and fee-free international transactions have made managing personal finances easier than ever. Monzo’s focus on transparency and user experience has resulted in high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty. By actively engaging with users through community forums, Monzo continuously improves its services, demonstrating how a digital bank can effectively prioritize customer needs.
The extent of digitalization
Neobanks have embraced a digital-first philosophy, leveraging cloud-based infrastructure to eliminate legacy IT problems. This allows them to be agile, provide fast and convenient services, and cater to customer needs in a personalized manner. Neobanks are leading in areas like real-time transaction updates, cost-effective international transfers, and seamless in-app customer support. The ability to offer instant account setup, integrated spending analytics, and virtual cards has positioned neobanks as strong contenders in the digital banking space.
The Challenges
Despite their technological advancements, neobanks often depend on traditional banks for services like deposit holding and regulatory compliance. Their digital-first model also requires them to navigate complex regulatory landscapes, as many countries still have strict requirements regarding banking licenses and customer protections. Additionally, earning customer trust remains a challenge, as many people still have reservations about the lack of physical branches and the perceived risks of fully digital banking.
The Opportunities
By focusing on user experience, neobanks can differentiate themselves from traditional banks. Providing features such as budgeting tools, real-time notifications, and flexible savings options helps foster greater user engagement. Moreover, partnerships with established financial institutions can enable neobanks to overcome regulatory challenges while maintaining their competitive edge.
Lending Platforms: The Rise of Digital Borrowing
Lending is another financial service where fintech has made significant progress, enabling faster access to loans with more convenient digital processes. Platforms like LendingClub, Upstart, and SoFi are using technology to offer an alternative to traditional bank loans, focusing on providing a fully digital lending experience.
Case Study: Upstart’s Innovative Approach to Credit Scoring

Image 3: Upstart’s platform includes personal loans, automotive retail and refinance loans, home equity lines of credit, and small dollar “relief” loans.
Upstart represents a fresh approach to lending that prioritizes digital innovation. Before Upstart, traditional credit scoring relied heavily on FICO scores, which could overlook individuals with limited credit histories or those from underserved communities. The reliance on traditional metrics often resulted in missed opportunities for borrowers who were otherwise creditworthy.
Upstart introduced an alternative model that evaluates a borrower’s creditworthiness using a broader range of data points, such as education, employment history, and job performance. This digital-first approach has led to faster approvals and a more inclusive lending process. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, Upstart can provide a more accurate assessment of risk, resulting in lower default rates and better loan performance.
The extent of digitalization
Digital lending platforms use AI, big data, and alternative data sources to create sophisticated credit scoring models, making loans accessible to those with limited credit histories. These platforms go beyond traditional credit scores, incorporating data points like social media activity, education, and employment history to assess creditworthiness. The lending process—from application to approval and fund disbursal—is highly automated, providing a much smoother experience than traditional lending methods. Borrowers can get loan offers within minutes, making digital lenders a popular choice for personal and business loans.
The Challenges
However, the overreliance on AI models can be problematic if those models do not account for broader economic shifts, potentially resulting in higher loan defaults. The transparency of AI decision-making is also a concern, as customers may not fully understand how their creditworthiness is evaluated. Regulatory scrutiny is a major hurdle, as lending platforms need to navigate complex rules regarding borrower protections and fair lending practices. Compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations also adds to operational challenges.
The Opportunities
Digital lending has the potential to bridge the credit gap for underbanked individuals and small businesses. By refining AI models to consider a wider range of economic indicators and adopting a more transparent approach to credit assessment, digital lenders can expand their reach. Collaborations with traditional banks can also help improve credibility and compliance, making digital lending platforms more robust.
Digitalization Leads, But the Journey Is Different for Each Sector

Image 4: Each sector of fintech caters to different demographics, needs, and preferences, shaping their approach to digitalization.
Digitalization is a critical element of the fintech revolution, but its adoption varies across sectors. Digital payments and neobanking are leading the charge with their focus on convenience and user experience, appealing primarily to tech-savvy consumers and younger generations. Meanwhile, insurtech, wealthtech, and lending platforms are carving their niches by addressing specific needs, from personalized insurance to accessible investment options.
In the end, the fintech sector’s race for digitalization is not just about technology; it’s about how effectively that technology can be implemented to provide accessible, efficient, and secure financial services.
If you’re ready to elevate your fintech solutions through digitalization, contact us at SmartDev. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you navigate the complexities of the digital landscape. Together, we can unlock new opportunities and drive growth in your business. Have a look at our success case studies here!






