Introduction
The modern workplace is evolving rapidly—shaped by hybrid workforces, rising expectations for personalized employee experiences, and a relentless need for productivity. Amid this transformation, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a strategic enabler, automating routine tasks, uncovering actionable insights, and enhancing decision-making across departments.
This guide explores the most impactful AI use cases in the workplace, from HR and operations to IT and internal communications—revealing how businesses are using AI not just to optimize, but to reimagine work itself.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in the Workplace?
 1. Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
1. Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the ability of machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence—such as recognizing patterns, making decisions, and learning from data. Core AI technologies include machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. These technologies are already embedded in tools many businesses use daily, from voice assistants to data analytics dashboards (IBM definition).
In the workplace, AI takes on a very practical role. It automates repetitive processes, predicts business trends, powers virtual assistants, personalizes learning and development, and enhances collaboration through smart tools. From an HR chatbot answering onboarding questions to an IT helpdesk ticket routed by AI, these technologies are quietly—and profoundly—reshaping how work gets done.
Want to explore how AI can transform your sector? Discover real-world strategies for deploying smart technologies in airline systems. Visit How to Integrate AI into Your Business in 2025 to get started today and unlock the full potential of AI for your business!
2. The Growing Role of AI in Transforming the Workplace
AI is being deployed to support hybrid and remote work by optimizing meeting scheduling, summarizing discussions, and recommending follow-ups based on email and chat content. These tools are particularly valuable for distributed teams that need to stay aligned across time zones and platforms.
HR departments are leveraging AI for talent acquisition and retention. From resume parsing to candidate ranking and even cultural fit analysis, AI models help speed up hiring while minimizing human bias. AI also powers employee sentiment analysis, giving managers real-time insights into morale and engagement trends.
Across functions, AI augments decision-making by turning data into actionable recommendations. Marketing teams use it to prioritize leads, IT teams deploy it to detect anomalies in network traffic, and finance departments use AI to spot irregular spending patterns. The result is faster, data-informed decision-making that supports agility and growth.
3. Key Statistics or Trends in AI Adoption
According to PwC, 86% of CEOs say AI is a “mainstream technology” in their offices in 2024, up from 62% in 2020 (PwC Global AI Study). This reflects a growing acceptance of AI not just in IT, but across people management, customer experience, and operations.
IBM’s 2023 Global AI Adoption Index found that 35% of businesses are already using AI in at least one function, and an additional 42% are exploring its use. Key motivators include improving employee productivity, increasing data-driven decisions, and enhancing service delivery (IBM AI Index).
The market for workplace AI solutions is expected to surpass $37 billion by 2030, driven by increased demand for intelligent automation, virtual agents, and AI-enhanced collaboration tools (Fortune Business Insights).
Business Benefits of AI in the Workplace
AI is no longer experimental—it’s delivering real value by addressing long-standing challenges in workforce productivity, communication, and resource planning. Here are five specific benefits where AI is helping businesses rethink the workplace.
 1. Improved Employee Productivity
1. Improved Employee Productivity
AI boosts productivity by handling routine administrative tasks like scheduling, data entry, and status reporting. This frees up employees to focus on higher-value activities, from strategy development to creative problem-solving.
Smart assistants embedded in tools like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace can now draft emails, summarize documents, and even suggest follow-up actions. These time-savers add up across the organization, especially for knowledge workers managing high information volumes.
2. Smarter Talent Management
Recruiting the right talent has always been a challenge. AI is streamlining hiring by automating resume screening, ranking candidates based on skills and experience, and even predicting cultural fit based on behavioral data.
Beyond hiring, AI supports learning and development by recommending personalized training paths based on performance metrics, job role, and future skill demand. This enables companies to continuously reskill their workforce in alignment with evolving business goals.
3. Enhanced Employee Experience
AI is being used to personalize the employee journey—from onboarding to career development. Chatbots assist new hires with FAQ-style queries, while virtual onboarding coaches guide them through tools, policies, and training schedules.
Real-time sentiment analysis via AI scans communication platforms for engagement signals, allowing HR teams to respond proactively to morale dips. These tools help foster more empathetic, responsive workplace cultures.
4. Predictive Operational Efficiency
AI helps identify process inefficiencies and optimize resource allocation. Facilities teams use AI to manage energy usage, cleaning schedules, and desk occupancy based on real-time utilization patterns.
In IT, AI predicts system downtimes and flags anomalies before they become service disruptions. These insights help organizations minimize downtime and reduce response times—driving both cost savings and user satisfaction.
Want to see how predictive maintenance is revolutionizing uptime and cutting costs? Read our deep dive on AI-driven maintenance in manufacturing and discover how you can move from reactive fixes to intelligent foresight.
5. Automated Compliance and Risk Management
Compliance and security are core concerns in today’s data-driven workplace. AI-powered monitoring tools analyze communication logs, access records, and transactions to detect compliance breaches or risky behaviors.
AI also supports data privacy by identifying and redacting personally identifiable information (PII) from unstructured data sources, which is especially critical for GDPR and HIPAA compliance in industries like healthcare and finance.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in the Workplace
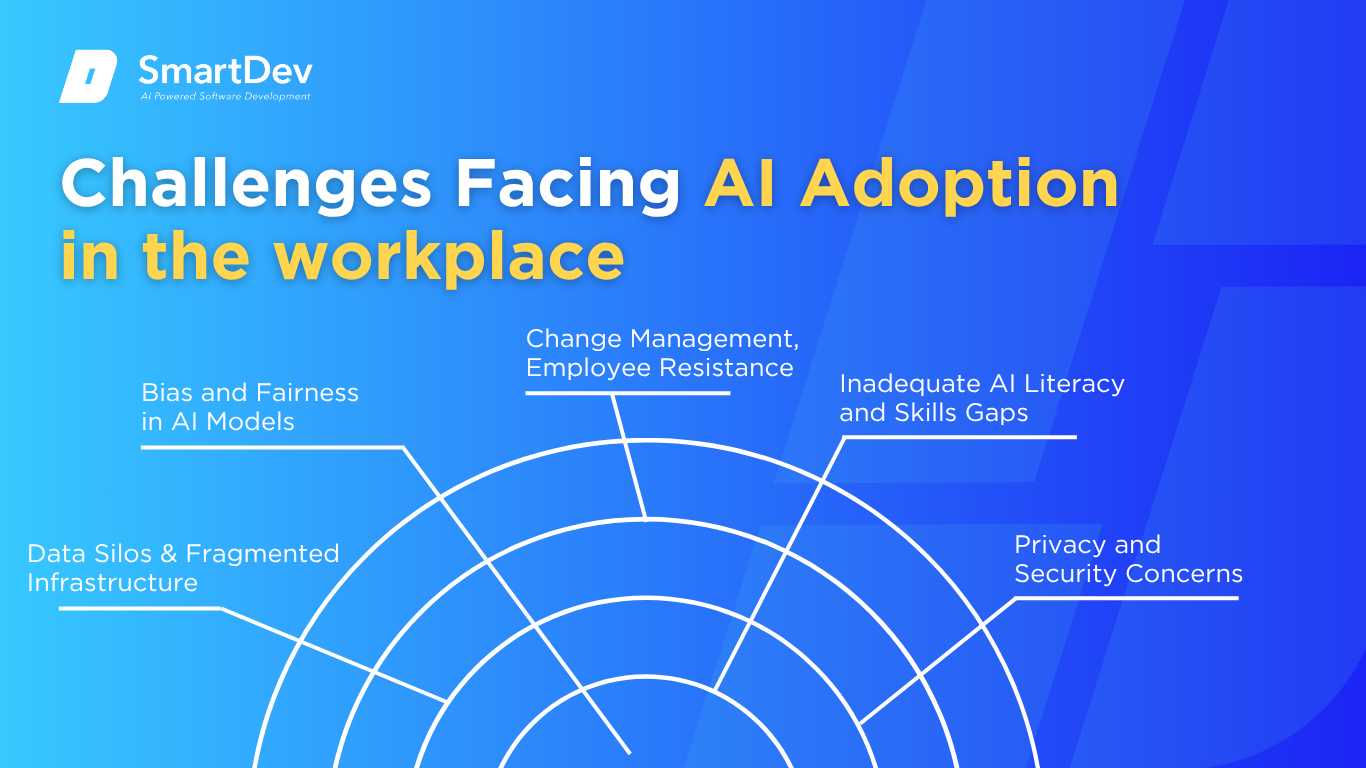
Despite its promise, integrating AI into workplace systems presents a number of organizational and technical hurdles. Below are five key challenges that businesses must address to successfully deploy AI at scale.
 1. Data Silos and Fragmented Infrastructure
1. Data Silos and Fragmented Infrastructure
Many organizations store data in disconnected systems—HR tools, CRM platforms, Slack, emails—making it difficult for AI to gain a unified view. This fragmentation limits the effectiveness of AI models, especially those reliant on contextual understanding.
Solving this issue requires robust integration layers and a unified data governance strategy. Investing in middleware and cross-platform APIs is a practical first step toward creating a data environment AI can learn from.
Building responsible AI starts with awareness. Learn how to tackle real-world bias in our guide on AI fairness and ethical strategies.
2. Bias and Fairness in AI Models
AI is only as unbiased as the data it’s trained on. When historical hiring, promotion, or communication data reflects bias, AI models can perpetuate those inequities. This is a critical concern for HR applications, where fairness is paramount.
To mitigate risk, organizations must adopt explainable AI models, continuously monitor outcomes, and train models with diverse and representative data sets. Involving legal and ethics teams in AI development is also essential for trustworthy implementation.
For those navigating these complex waters, a business-oriented guide to responsible AI and ethics offers practical insights on deploying AI responsibly and transparently, especially when public trust is at stake.
3. Change Management and Employee Resistance
Introducing AI into workplace routines can trigger anxiety about job displacement or loss of autonomy. Employees may view AI as a surveillance tool rather than a productivity enhancer.
Addressing this challenge requires clear communication about AI’s role as an augmenting—not replacing—force. Engaging employees early, offering training, and demonstrating value in everyday workflows can build trust and support adoption.
4. Inadequate AI Literacy and Skills Gaps
AI systems can only deliver value when users understand how to work with them. Many teams lack the analytical or technical skills required to interpret AI-generated insights or monitor performance effectively.
Upskilling programs, AI literacy workshops, and collaborative interfaces can help bridge this gap. Business leaders must also invest in building cross-functional teams where technical and domain expertise can collaborate effectively.
5. Privacy and Security Concerns
Using AI to monitor employee performance or analyze communications raises sensitive privacy issues. Without clear boundaries, such systems risk violating employee trust or running afoul of data protection regulations.
To address this, businesses must implement transparent usage policies, anonymize data wherever possible, and prioritize security in all AI deployments. Partnering with privacy officers and external counsel can help balance innovation with responsibility.
Specific Applications of AI in the Workplace
AI is rapidly transforming work environments by automating routine tasks, enhancing collaboration, and improving productivity. These six applications illustrate the most impactful ways businesses are leveraging machine intelligence today.
 1. Automated Talent Sourcing & Screening
1. Automated Talent Sourcing & Screening
Automated talent sourcing and screening use AI-powered tools to parse resumes, evaluate candidate profiles, and identify top matches based on skills and job requirements. These systems solve the industry-wide problem of sifting through thousands of applicants manually—a process that is time-consuming and prone to bias. By using machine learning algorithms trained on historical hiring data, these platforms can identify patterns that correlate with successful hires, recommending candidates who may not have traditional resumes but possess the right skills.
These tools work by harvesting resumes and job descriptions into data lakes, then applying NLP models to classify skills, experiences, and cultural fit. The AI integrates into applicant tracking systems (ATS), flagging high-potential candidates for recruiters to evaluate further. Human reviewers then assess shortlists, ensuring qualitative judgment complements quantitative filtering. Technical considerations include ensuring algorithmic fairness, while data security protocols prevent leakage of candidate personal data.
The strategic impact lies in drastically reducing cost-per-hire and time-to-fill metrics, while improving candidate quality. Automated screening helps overcome anecdotal limitations in human judgment and opens pipelines to more diverse talent pools. However, organizations must maintain transparency, audit model behavior for bias, and ensure compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Real-World Example:
Unilever deployed Pymetrics’ AI-powered platform to screen candidates via gamified challenges and predictive analytics. They complemented it with HireVue’s video-interview AI tools that analyze communication skills. This approach cut time-to-hire by 75% and doubled the number of interviews processed per recruiter.
2. Intelligent Virtual Assistants for Internal Support
Intelligent virtual assistants (IVAs) are conversational AI tools embedded into digital work platforms to support employees with requests ranging from IT help to HR queries. They solve bottlenecks in ticket-based systems and email trails by providing instant answers and automated workflows. By enhancing responsiveness and standardizing internal support, these tools reduce friction across teams and enable staff to focus on value-added tasks.
IVAs rely on NLP and dialog management engines that convert employee questions into intents and entities. They pull from knowledge bases—such as policy documents, troubleshooting guides, or SaaS APIs—to offer real-time guidance or automatically open service tickets. When unresolved queries arise, requests are escalated to human agents, with full context passed along to improve case resolution speed. Privacy is critical, so data encryption, access controls, and audit logs are essential to maintain compliance.
These systems improve efficiency by deflecting low-value queries and reducing resolution times by up to 60%, according to industry benchmarks. They provide consistent support regardless of shift or location, helping distributed teams stay productive. For successful adoption, companies must ensure the VA is regularly updated with evolving document libraries and supported by robust governance to build trust with users.
Real-World Example:
Siemens integrated IBM Watson Assistant into its internal service systems to handle IT, HR, and facilities inquiries. The assistant resolved roughly 55% of employee questions without human intervention. Siemens achieved a 40% reduction in support tickets and saw a 30% uplift in user satisfaction.
3. Predictive Workforce Planning
Predictive workforce planning uses AI to forecast staffing needs, talent gaps, and workforce attrition by analyzing historical data, market trends, and business objectives. It solves a critical problem for HR and operations leaders who struggle to align workforce supply with future demand—particularly in industries affected by seasonal variation or volatile project pipelines. With accurate forecasts, organizations can make informed decisions on hiring, training, and succession planning before problems arise.
AI models for workforce planning use time-series forecasting, regression models, and classification algorithms trained on employee tenure, performance, exit interviews, and project data. These models predict churn, estimate ramp-up times, and assess internal mobility patterns. Integrated into HRIS or ERP platforms, AI gives managers proactive dashboards to guide workforce allocation and scenario planning.
Strategically, predictive workforce planning supports agility and cost control. It enables leaders to shift from reactive headcount adjustments to proactive talent strategies that reduce turnover and ensure skill readiness. Key considerations include ensuring data privacy, handling sensitive workforce information ethically, and avoiding algorithmic assumptions that penalize non-linear career paths.
Real-World Example:
Royal Dutch Shell implemented AI models using Workday Prism and custom analytics to forecast skills gaps across its global workforce. The company used predictions to adjust its hiring roadmap and upskilling initiatives. Shell saw a 16% improvement in project staffing efficiency and reduced short-term contractor spend by 12%.
4. AI-Powered Employee Sentiment Analysis
Employee sentiment analysis leverages AI to monitor morale, engagement, and emerging workplace issues through analysis of communication platforms, survey responses, and pulse checks. It addresses the challenge of blind spots in leadership awareness and the delayed response to cultural or productivity issues. By analyzing tone, keyword frequency, and behavioral signals, AI helps HR teams act on concerns before they become crises.
These models use NLP and sentiment classification algorithms trained on annotated corpora to extract emotional cues and satisfaction markers. Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and internal forums are scanned (with user consent and anonymization) for patterns indicating burnout, dissatisfaction, or disengagement. Results feed into dashboards accessible to HR and team leaders, often segmented by department, region, or tenure group.
The operational value lies in enabling faster, more targeted interventions—whether it’s leadership check-ins, training refreshers, or policy reviews. Sentiment data complements traditional performance indicators and helps create a more responsive, transparent culture. Ethical use requires employee awareness, data minimization, and governance policies that balance insight with privacy.
Real-World Example:
Cisco deployed AI-powered sentiment analysis via its internal “People Insights” platform, built on Qualtrics and NLP layers. It helped identify burnout signals and engagement dips during the shift to remote work. As a result, the company improved its well-being initiatives and saw a 14% increase in employee satisfaction over two quarters.
5. Personalized Learning & Development (L&D)
Personalized L&D platforms use AI to recommend training programs tailored to an employee’s role, skills, learning style, and career goals. Traditional L&D programs often fail to engage learners because they rely on generic content and rigid pathways. AI solves this by delivering targeted content that adapts over time—boosting both engagement and effectiveness.
Recommendation engines are at the core of these platforms. They apply collaborative filtering, skill-matching, and behavioral analytics to suggest content from internal libraries or third-party MOOCs (e.g., Coursera, Udemy). As employees complete modules, the system refines future suggestions based on success metrics, knowledge gaps, and user feedback. L&D administrators receive cohort-wide insights to improve program design and ROI.
The strategic benefit is scalable workforce development that aligns with individual aspirations and organizational needs. By automating training curation and sequencing, HR teams can close skills gaps faster and at a lower cost. Considerations include ensuring equal access, content quality control, and integration with performance review systems.
Real-World Example:
Accenture uses its internal platform, “MyLearning,” powered by AI and integrated with Workday, to deliver personalized training paths. The system analyzes project assignments, career goals, and feedback to adapt content dynamically. The company reported a 24% increase in training completion rates and a 30% improvement in internal mobility.
6. Intelligent Document Management & Knowledge Retrieval
AI-enabled document management systems transform how employees find, access, and extract value from internal documentation. The traditional problem is information sprawl—documents buried in intranets, cloud drives, and email threads, slowing decision-making and collaboration. AI solves this by indexing content, summarizing key points, and surfacing relevant documents contextually.
These platforms use NLP, semantic search, and deep learning-based summarization to tag and retrieve information based on intent rather than keyword matches. For example, an employee looking for “latest expense policy” would receive the updated PDF, a TL;DR summary, and related Slack conversations. AI integrates with Microsoft SharePoint, Confluence, and Google Workspace to offer cross-platform relevance.
This capability enhances operational speed, reduces duplication, and improves knowledge transfer across distributed teams. It also supports compliance by ensuring staff always access the latest documents and policies. However, care must be taken to secure sensitive documents and validate AI-generated summaries for accuracy.
Real-World Example:
Deloitte implemented an AI-powered document intelligence platform based on Microsoft Syntex and Azure Cognitive Search. It helped employees surface the right policies and client files in seconds, rather than minutes. Deloitte estimated a 22% reduction in time spent on information retrieval across key business functions.
Need Expert Help Turning Ideas Into Scalable Products?
Partner with SmartDev to accelerate your software development journey — from MVPs to enterprise systems.
Book a free consultation with our tech experts today.
Let’s Build TogetherExamples of AI in the Workplace
The previous section explored key AI applications in theory and execution. Now we turn to real-world examples—demonstrating how leading organizations are successfully using AI in the workplace to generate measurable results and competitive advantage.
Real-World Case Studies
 1. IBM: AI for HR and Retention Forecasting
1. IBM: AI for HR and Retention Forecasting
IBM has long been a pioneer in deploying AI for human capital management. It implemented a proprietary AI system to predict which employees are likely to quit, analyzing factors like manager feedback, role changes, and commute length. By alerting managers proactively, IBM improved talent retention and aligned HR interventions with predictive outcomes.
The results were striking: IBM reported that the AI model was 95% accurate in forecasting employee turnover. This led to significant savings—estimated at $300 million—through reduced attrition and better internal mobility. The model is now embedded into IBM’s talent management platform as a strategic decision-support tool for people leaders.
2. Deloitte: Knowledge Management with AI Search
Deloitte faced a major challenge in surfacing client information and policy documentation quickly across a vast internal knowledge base. To solve this, they deployed AI-powered search tools using Microsoft Syntex and Azure Cognitive Services. The platform could semantically understand queries and return relevant documents, summaries, and recommendations in seconds.
The impact was measurable: Deloitte reduced information search time by 22% across advisory, audit, and consulting teams. Employees reported higher satisfaction with internal systems, and client-facing teams improved turnaround times on deliverables. This AI implementation not only increased operational efficiency but reinforced Deloitte’s reputation for digital fluency.
3. Walmart: Voice AI for Frontline Productivity
Walmart introduced “Ask Sam,” an AI-powered voice assistant for its retail associates. The tool enables employees to ask questions about store policies, product availability, and price checks—reducing reliance on managers or lengthy manuals. The assistant uses natural language understanding and connects to Walmart’s internal knowledge systems for real-time answers.
Since launch, Walmart reported that store employees saved thousands of hours weekly in reduced information retrieval. Store efficiency improved, and employee satisfaction rose due to faster responses and less dependency on hierarchical communication. “Ask Sam” is now a core element of Walmart’s digital workplace transformation strategy.
Innovative AI Solutions
As companies expand their use of AI, new tools are emerging that go beyond automation—bringing contextual awareness, personalization, and deeper collaboration into everyday workflows.
One of the most promising frontiers is generative AI in workplace communication. Tools like Google Workspace’s “Help Me Write” and Microsoft Copilot generate emails, meeting summaries, and reports based on past content and shared files. These tools reduce cognitive load for professionals who process hundreds of messages per day, freeing time for strategic thinking and collaboration.
Conversational analytics platforms are also gaining traction. Tools like Moveworks and Aisera analyze employee intent across support channels—chat, email, ticketing—to proactively resolve issues and improve digital employee experience (DEX). These systems learn from organizational language and context, getting more precise over time without requiring pre-programmed scripts.
Another transformative technology is AI-based behavioral coaching, where platforms like Humu and BetterUp use nudge theory and data science to recommend leadership habits and team development tips. These solutions personalize manager guidance based on team sentiment and performance, supporting culture development at scale.
These examples reflect the value of working with technology partners who understand both the technical and policy implications. If you’re considering a similar digital transformation, don’t hesitate to connect with AI implementation experts to explore what’s possible in your context.
AI‑Driven Innovations Transforming the Workplace
You’re navigating an era where employee expectations, productivity demands, and digital collaboration collide—and AI is emerging as the game changer. From automating routine workflows to unraveling hidden data insights, AI is transforming the way you manage people, processes, and performance.
Innovative tools like chatbots, voice AI, intelligent assistants, and predictive engines are reshaping every function—from HR and facilities to IT and leadership. These AI use cases in the workplace are not just buzzwords—they’re reshaping how work gets done, who does it, and where they excel.
1. Emerging Technologies in AI for the Workplace
Generative AI is shifting from novelty to necessity in your daily toolkit. Platforms like Microsoft Copilot and Google Workspace’s “Help Me Write” help you craft emails, summaries, and even draft proposals in seconds. These assistants act like a second you—freeing you to think bigger and deeper, rather than typing every line.
Computer vision is quietly boosting efficiency in your physical spaces. Smart cameras monitor store shelves, identify empty desks, or scan manufacturing lines—all without human oversight. This visual data helps facilities managers spot issues early, reduce waste, and streamline workflows with precision.
Together, these technologies enhance your operational speed and intelligence across the board. As they integrate into your tools—CRMs, HR systems, even meeting apps—they blend seamlessly into everyday work, delivering productivity gains you can see and measure.
2. AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
Sustainability isn’t just ethical—it’s strategic. Predictive analytics powered by AI can help you identify inefficient energy use, unnecessary waste, or equipment idle time. One global retailer used AI-powered sensors to reduce store-level power use by 15%, saving energy and cost within a single quarter.
Smart energy systems elevate those gains even further. AI can optimize HVAC settings or lighting schedules based on occupancy patterns. In one case, a corporate office cut annual energy consumption by 20% while improving thermal comfort—fueling both ESG results and employee satisfaction.
By weaving AI into sustainability strategy, your company gains purpose and brand value—all while reducing expenses. That’s the kind of impact that resonates across boardrooms and shareholders alike.
How to Implement AI in the Workplace
You’ve seen the possibilities. Here’s exactly how to implement AI in your organization—from readiness to rollout:
 1. Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
1. Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Begin with a readiness assessment focusing on where AI can drive the most value. Are you drowning in support tickets? HR overwhelm? Manual scheduling? Spotting these “pain hotspots” is step one.
Now, evaluate your data ecosystem. What systems do you already use—HRIS, ticket systems, CRM? How clean is your data? Clean, integrated data is the lifeblood of accurate AI predictions and performance, so a data audit should always follow immediately after identifying use opportunities.
2. Building a Strong Data Foundation
Once your key systems and use cases are defined, it’s time to centralize and clean your data. Consolidate siloed records—chat logs, ticket data, HR info—into a secure data pipeline. Consistency is essential: remove duplicates, standardize formats, and tag contextual metadata so AI doesn’t misinterpret entries.
Next, implement governance and privacy protocols. With AI analyzing sensitive workplace data, you’ll need encryption, access control, and data lineage maps. Clear policy and compliance vaults ensure trust and guard against missteps.
3. Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
The AI vendor landscape can feel overwhelming—but the key is alignment. Are you optimizing support tickets? Consider conversational AI from providers like Moveworks or Aisera that embed in your chat platforms. Need L&D automation? Platforms like BetterUp or Degreed may fit.
Look for solutions that integrate natively with your infrastructure—Slack, Microsoft Teams, Workday, Zoom—so your teams don’t need to learn another interface. Always assess vendor support, compliance readiness, and track record within your industry.
4. Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Start small to win big. Choose one use case—like chatbot support or sentiment analysis—and establish KPIs around time saved, satisfaction uplift, or ticket volume reduction. Run a four-to-six-week pilot with robust metrics and stakeholder feedback loops.
Once validated, expand thoughtfully. Rather than launching everywhere overnight, tier rollout across departments or geographies. This mitigates risk, ensures refinement, and builds adoption momentum.
5. Training Teams for Successful Implementation
Don’t forget the human side of AI. Organize interactive workshops for teams using the tools—help them understand what AI can do, how it works, and where they fit in. Provide ongoing training and documentation.
Leaders should champion the transformation by showcasing early successes. When frontline staff hear how AI tooling eased workloads and improved their day, adoption grows organically.
Whether you’re exploring your first pilot or scaling an enterprise-wide solution, our team is here to help. Get in touch with SmartDev and let’s turn your supply chain challenges into opportunities.
Measuring the ROI of AI in the Workplace
You need proof—and these strategies help you build it.
1. Key Metrics to Track Success
Measure both quantitative and qualitative outcomes. Track reductions in ticket volumes, time saved per task, improved HR efficiency, and energy savings. Combine these with survey scores like NPS or employee satisfaction.
Tie AI metrics directly to business goals—like cost reduction, faster onboarding, or better retention. That way, your ROI story resonates with execs and secures future investment.
2. Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
One global tech company used AI chatbots in IT support and saw ticket volume drop by nearly 50% in three months. This freed analysts to tackle more strategic work and lowered annual support cost by over 30%. Employee feedback also showed a 25% increase in satisfaction with helpdesk responsiveness.
A major manufacturer applied AI-based predictive energy controls in its facilities. By analyzing equipment usage patterns, they cut HVAC and lighting energy consumption by 18% across three sites. This translated to hundreds of thousands in annual energy savings.
Another fast-growing firm implemented personalized L&D using AI-driven training recommendations. Within six months, training completion rates rose 40%, internal promotions increased by 22%, and employee survey results flagged a significant boost in growth mindset culture.
3. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
One trap is treating AI like a magic plug-in—without aligning on metrics, training, or cultural change. Always start small, define success, and prepare teams for adoption. Another challenge is data readiness. If your systems are noisy or disjointed, AI performance will suffer. Clean data governance acts as functional insurance. Finally, lack of transparency can lead to mistrust. Using explainable AI models and communicating how conclusions were made builds confidence faster than silent automation.
Future Trends of AI in the Workplace
 1. Predictions for the Next Decade
1. Predictions for the Next Decade
In the next ten years, AI will evolve from task automation to workforce orchestration—helping manage team dynamics, predict burnout, and support human decision-making. Imagine AI-powered digital assistants collaborating in meetings, synthesizing action points, and even surfacing missing context based on collective data.
Personalized adaptive coaching will become standard, with AI nudging leaders to offer recognition or ask better questions based on subtle tone shifts in team messaging. Augmented reality (AR)-enabled, AI-driven workflows will bring immersive training to remote workers. These trends will redefine the employee experience in rich, human-centered ways.
2. How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To stay ahead, view AI as a capability, not a project. Invest in modular, interoperable tools that can grow with your business and stick to open standards where possible. Build internal talent, champion cross-functional teams, and maintain ecosystems of experimentation and data literacy.
Encourage innovation through “AI readiness sprints”—one-week pilots to test hypotheses and surface quick wins. Share early successes transparently across the organization to build momentum.
Conclusion
1. Summary of Key Takeaways on AI Use Cases in the Workplace
Whether it’s smart chatbots, predictive retention models, energy optimization, or AI-triggered learning paths, AI use cases in the workplace are delivering real, measurable impact. These tools don’t replace your teams—they empower them—reducing busy work and elevating strategic contribution.
Overcoming data, adoption, and transparency hurdles is achievable with good planning—and delivers powerful returns in cost, efficiency, culture, and innovation.
2. Call‑to‑Action for Businesses Considering AI Adoption
You don’t need to wait to lead the AI-powered workplace revolution. Start by auditing where AI can make the biggest difference in your operations. Choose one high-impact pilot, install the right tools, and measure results. Then scale smart, and let success guide your roadmap.
Ready to accelerate your workplace transformation? Our team specializes in designing, implementing, and scaling AI solutions tailored to your culture, systems, and objectives. Let’s talk—book your custom readiness assessment today.
References
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-the-workplace
- https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work
- https://www.officespacesoftware.com/blog/ai-in-the-workplace-ai/
- https://peopleinsight.co.uk/pros-cons-ai-workplace/
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/artificial-intelligence-business-use-cases
- https://aisera.com/blog/ai-in-workplace/




 1. Data Silos and Fragmented Infrastructure
1. Data Silos and Fragmented Infrastructure 1. Automated Talent Sourcing & Screening
1. Automated Talent Sourcing & Screening 1. IBM: AI for HR and Retention Forecasting
1. IBM: AI for HR and Retention Forecasting 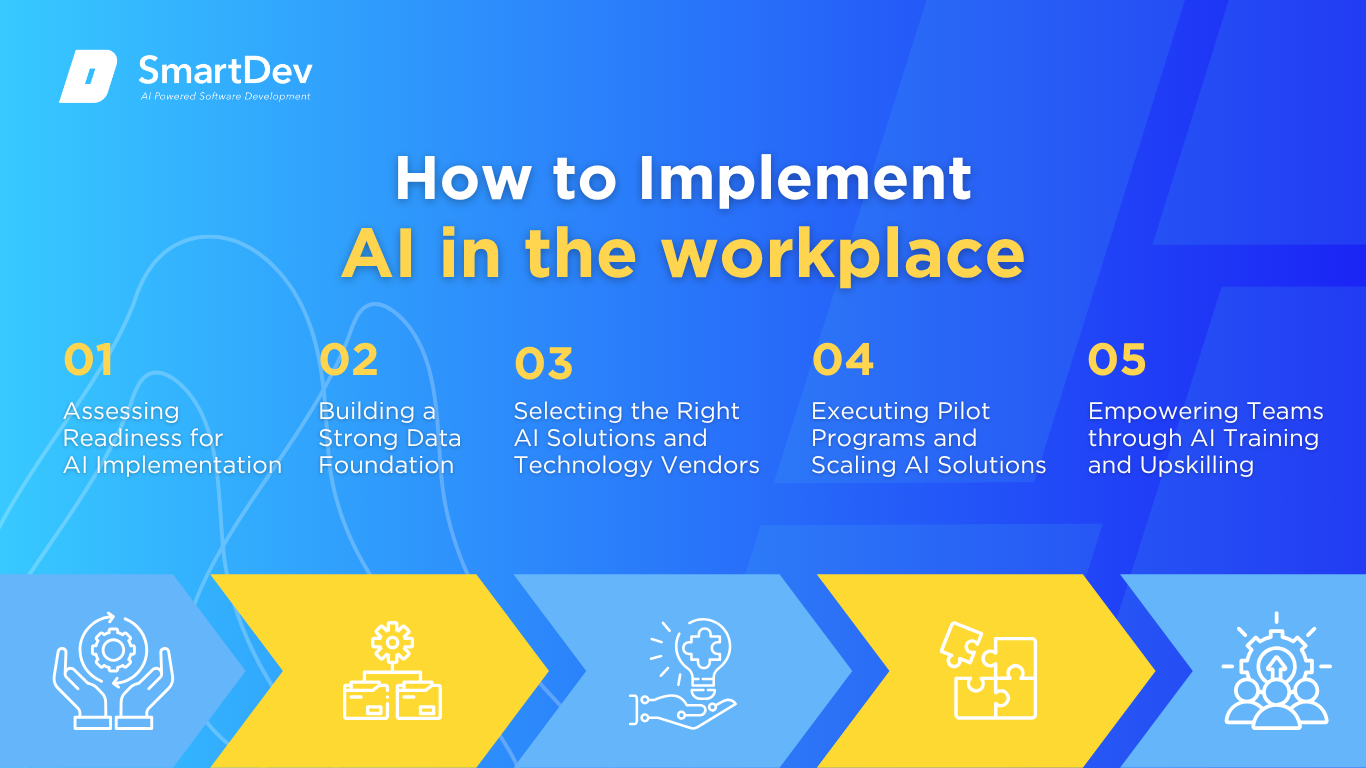 1. Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
1. Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption 1. Predictions for the Next Decade
1. Predictions for the Next Decade




