Introduction
Finance and accounting are at a pivotal juncture. With mounting pressure to enhance accuracy, reduce costs, and adapt swiftly to regulatory changes, traditional methods often fall short. Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerges as a transformative force, automating routine tasks, uncovering insights from vast data sets, and bolstering compliance measures. This guide delves into how AI-driven solutions are revolutionizing finance and accounting, turning challenges into strategic opportunities.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Finance and Accounting?

Definition of AI and its core technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision-making. Core technologies under the AI umbrella include machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. These technologies enable machines to process and analyze large volumes of data, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions.
In the context of finance and accounting, AI refers to the application of these technologies to automate processes like data entry, financial analysis, and compliance checks. By leveraging AI, organizations can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making capabilities in their financial operations.
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming Finance and Accounting
AI is reshaping financial operations by automating routine tasks, allowing professionals to focus on strategic activities. For instance, AI-powered tools can process invoices, reconcile accounts, and generate financial reports with minimal human intervention, significantly reducing processing time and errors.
In accounting, AI enhances audit processes by analyzing entire data sets to identify anomalies and potential fraud, which might be overlooked in traditional sampling methods. This comprehensive approach not only improves accuracy but also builds trust in financial reporting.
Financial institutions are also leveraging AI for risk assessment and management. By analyzing historical data and market trends, AI models can predict potential risks and suggest mitigation strategies, enabling proactive decision-making.
Key Statistics and Trends Highlighting AI Adoption in Finance and Accounting
The adoption of AI in finance and accounting is accelerating. According to a Gartner survey, 58% of organizations were using AI in finance functions in 2024, up from 37% the previous year.
Private companies are leading the way, with 81% piloting or using AI in accounting and similar numbers in financial planning. Public companies are also embracing AI, with 75% implementing it in accounting functions.
The accounting sector is projected to experience a 30% annual growth rate in AI adoption from 2023 to 2028, highlighting the industry’s recognition of AI’s transformative potential.
To explore which fintech sectors are leading in digital transformation and AI adoption, check out our blogpost on fintech sectors driving digital solutions.
Business Benefits of AI in Finance and Accounting
AI is providing measurable value in finance and accounting by tackling critical challenges like inefficiencies, high costs, and gaps in decision-making. Below are five key benefits businesses can gain from implementing AI in these sectors.

1. Enhanced Productivity
AI automates repetitive tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and account reconciliation, freeing up professionals to focus on strategic initiatives. This automation not only accelerates workflows but also reduces the likelihood of human errors.
AI-driven platforms can process large volumes of transactions swiftly, enabling real-time financial reporting and faster decision-making. This efficiency is crucial for organizations aiming to stay competitive in dynamic markets.
2. Improved Accuracy and Compliance
AI enhances accuracy in financial reporting by identifying discrepancies and anomalies that might be missed by human reviewers. In auditing, AI tools analyze entire data sets to detect irregularities, strengthening the integrity of financial statements.
Moreover, AI assists in compliance by continuously monitoring transactions against regulatory requirements, promptly flagging potential issues for review. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties.
3. Predictive Analytics for Strategic Decision-Making
AI leverages historical data to forecast financial trends, enabling organizations to make informed strategic decisions. Predictive analytics can anticipate cash flow fluctuations, market shifts, and customer behaviors, allowing for proactive planning.
By identifying patterns and trends, AI supports budgeting, investment strategies, and resource allocation, aligning financial planning with organizational goals.
4. Fraud Detection and Risk Management
AI enhances fraud detection by analyzing transaction patterns to identify unusual activities indicative of fraudulent behavior. Machine learning algorithms can adapt to new fraud tactics, improving detection over time.
In risk management, AI assesses various risk factors, such as credit scores and market volatility, to evaluate potential threats. This comprehensive analysis aids in developing robust risk mitigation strategies.
To dive deeper into how AI enhances fraud detection and risk mitigation, read our article on AI-Driven Fraud Detection.
5. Cost Reduction
Implementing AI reduces operational costs by streamlining processes and minimizing errors that could lead to financial losses. Automated systems require less manual intervention, decreasing labor costs and increasing efficiency.
Additionally, AI-driven insights can identify cost-saving opportunities, such as optimizing supply chains or renegotiating contracts, contributing to overall financial health.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Finance and Accounting
Although AI holds transformative potential for finance and accounting, its successful adoption requires careful planning and execution. Organizations must strategically manage the integration of these technologies to optimize efficiency and fully leverage their benefits.

1. Data Quality and Integration
AI systems rely on high-quality data to function effectively. Inconsistent, incomplete, or siloed data can hinder AI performance, leading to inaccurate analyses and decisions.
Integrating AI with existing systems requires careful planning to ensure seamless data flow and compatibility, which can be resource intensive.
2. Talent and Skill Gaps
The successful deployment of AI necessitates professionals with expertise in data science, machine learning, and AI technologies. A shortage of skilled personnel can impede AI initiatives and limit their effectiveness.
Organizations must invest in training and development programs to build internal capabilities and attract top talent in the field.
3. Ethical and Regulatory Concerns
AI applications in finance and accounting raise ethical questions, particularly regarding data privacy and decision-making transparency. Ensuring that AI systems operate within ethical boundaries and comply with regulations is paramount.
Organizations must establish governance frameworks to oversee AI use, addressing issues such as bias, accountability, and compliance with laws like GDPR.
4. Change Management and Organizational Resistance
Introducing AI can disrupt established workflows and face resistance from employees concerned about job security or changes in responsibilities. Effective change management strategies are essential to facilitate adoption.
Engaging stakeholders, communicating benefits, and providing training can help ease the transition and foster a culture receptive to innovation.
5. Cost and Resource Constraints
Implementing AI solutions can be costly, involving expenses related to technology acquisition, infrastructure upgrades, and personnel training. For some organizations, especially smaller ones, these costs may be prohibitive.
Careful cost-benefit analysis and phased implementation plans can help manage expenses and demonstrate the value of AI investments over time.
Specific Applications of AI in Finance and Accounting

1. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Fraud detection is crucial in finance, as timely identification of fraudulent activities can prevent significant financial loss. AI analyzes transaction data in real-time, spotting patterns of suspicious behavior using machine learning models. These models can detect anomalies by assessing both structured and unstructured data, improving the speed and accuracy of fraud detection.
AI systems learn from previous data, enabling them to adapt and recognize evolving fraud tactics. This allows financial institutions to react swiftly and prevent fraud in real time, reducing the need for manual oversight. The ability to continually refine detection models helps stay ahead of emerging threats. The main benefit is AI’s ability to scale, reduce false positives, and react faster than human analysts. AI’s continuous learning means it gets better over time, and its integration into existing workflows makes fraud detection more efficient. This leads to stronger security and less fraud-related loss.
Real-World Example: Mastercard uses AI to monitor over 75 billion transactions annually. Its machine learning models detect fraud by analyzing transaction patterns and flagging suspicious activities instantly. This has reduced fraud-related chargebacks by 50%, improving transaction security.
2. Predictive Analytics for Financial Forecasting
AI enhances financial forecasting by analyzing past data to predict future trends, such as cash flow and market performance. Machine learning models analyze both structured (financial records) and unstructured (news, social media) data to improve prediction accuracy. This allows businesses to better prepare for future market changes and trends.
AI models use regression and time-series analysis to identify patterns and predict outcomes, adjusting in real-time as new data emerges. This helps forecast key financial metrics more accurately and enables proactive planning. Continuous data input and model updates improve prediction reliability over time.
The advantage of AI in forecasting is its ability to process large amounts of data quickly and provide real-time insights. It reduces risks by providing data-driven predictions and helps in making well-informed business decisions. This results in better financial planning and resource management. For a deeper look at how AI-powered financial modeling supports faster, data-driven decisions, explore our post on AI in financial modeling and forecasting.
Real-World Example: JP Morgan Chase uses AI for forecasting stock prices and optimizing trading strategies. Their models analyze market trends and data in real time to make quick, data-driven decisions. This has improved portfolio performance and helped minimize risk.
3. Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading uses AI to execute trades at optimal times based on market data. AI analyzes vast data points, such as price movements and news sentiment, to make high-frequency trading decisions. Machine learning continuously adjusts these strategies, making trading more adaptive to changing market conditions.
AI’s ability to process data faster than humans allows it to execute trades in fractions of a second, identifying opportunities that human traders might miss. This efficiency increases both trading volume and profitability. AI models also reduce human error and emotional bias in trading decisions.
The value of AI here is in its speed and precision, which enable high-frequency trading strategies and real-time adjustments. This increases profitability while reducing risks and mistakes. AI’s continuous learning ensures strategies are optimized as market conditions evolve.
Real-World Example: Goldman Sachs uses AI for high-frequency trading, executing trades faster and more accurately based on real-time data. Their algorithms analyze market conditions to make precise trades. This strategy has enhanced the firm’s trading performance and reduced error rates.
4. Tax Compliance and Optimization
AI automates tax compliance by analyzing financial data and ensuring that businesses adhere to tax regulations. It can identify tax deductions, credits, and optimize strategies by simulating different financial scenarios. This reduces the complexity and human error associated with tax filing and reporting.
Machine learning algorithms continuously learn from past data, improving their ability to suggest strategies that minimize tax liabilities. AI tools also keep up with ever-changing tax laws and regulations, making sure companies remain compliant. This helps businesses stay ahead of compliance deadlines and avoid penalties.
AI-driven tax systems streamline the tax filing process and ensure more accurate filings. This reduces the time and costs associated with tax compliance while providing businesses with actionable insights to optimize tax strategies. This leads to better financial planning and fewer regulatory concerns.
Real-World Example: Deloitte uses AI to optimize tax compliance and strategy, analyzing financial transactions and tax laws to ensure accuracy. The system helps reduce errors and saves time in the filing process. As a result, clients experience reduced tax preparation time and improved compliance.
5. Customer Credit Scoring
AI improves customer credit scoring by incorporating alternative data like social media activity, spending behavior, and employment history. This offers a more holistic assessment of creditworthiness, particularly for those with little to no traditional credit history. By using a wider range of data, AI can better predict risk and approve loans for underserved individuals.
Machine learning models learn from vast amounts of data, continuously refining their credit predictions. These models can adapt to new information, ensuring that credit scoring remains relevant and accurate. This leads to more personalized and inclusive lending decisions.
AI-based credit scoring enables financial institutions to expand access to credit while minimizing risk. It helps lenders approve loans for people traditionally excluded from credit systems while ensuring accuracy and reducing defaults. This results in more inclusive and effective lending practices.
Real-World Example: Upstart uses AI to evaluate creditworthiness by analyzing data points such as education and spending habits. This allows the company to provide loans to individuals with little credit history while maintaining low default rates. Upstart has expanded access to credit for underserved populations while improving its loan portfolio’s performance.
6. Financial Reconciliation
Financial reconciliation ensures that a company’s financial records match up with external documents like bank statements. AI automates this process by extracting and matching transactions, flagging discrepancies. Machine learning and natural language processing help AI understand and resolve inconsistencies, speeding up reconciliation.
AI systems can learn from past reconciliation tasks, improving accuracy over time. They automatically detect errors and anomalies, allowing for faster identification and resolution of discrepancies. This reduces manual effort and accelerates the financial closing process.
The value of AI in reconciliation is in its ability to handle large volumes of data quickly and accurately, reducing human error. Automation leads to more efficient financial closing, saving time and resources. AI also ensures that reconciliations are completed in real time, providing up-to-date and accurate financial data.
Real-World Example: BlackLine offers AI-powered reconciliation software that automates the entire reconciliation process. It uses machine learning to improve accuracy and efficiency, cutting reconciliation time by 50%. This leads to faster financial closing and enhanced operational efficiency for businesses.
7. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for Financial Operations
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages AI to automate repetitive tasks like invoice processing and payroll management in financial operations. AI-enhanced RPA systems can learn from previous workflows, improving their performance over time. These systems reduce manual effort and improve overall efficiency in back-office financial operations.
AI-driven RPA can handle multiple tasks across various systems, allowing finance teams to focus on strategic activities. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA reduces human error and accelerates processes, leading to faster decision-making. This scalability is especially valuable for organizations with high transaction volumes.
The strategic benefit of AI in RPA is in reducing operational costs, increasing speed, and improving accuracy in financial operations. AI allows businesses to automate a wide range of tasks, optimizing workflows and enhancing overall productivity. This enables companies to reduce costs while maintaining high-quality standards in their financial processes.
Real-World Example: UiPath provides AI-powered RPA solutions used by financial institutions to automate tasks like accounts payable and reconciliation. Their bots reduce manual work and improve operational efficiency. This has helped firms cut operational costs while streamlining financial processes.
To see how AI can be applied in real-world financial operations, check out our case study on A Bank-Agnostic Supply Chain Finance Platform.
Examples of AI in Finance and Accounting
Real-World Case Studies
AI is becoming a key driver in finance and accounting, helping businesses streamline operations and improve customer experiences. From automating complex processes to providing valuable insights, AI is reshaping the way the industry operates, offering significant benefits across the board.

1. Citibank: AI in Credit Risk Assessment
Citibank uses AI-powered tools for credit risk assessment, helping the bank identify high-risk clients and predict the likelihood of loan defaults. With machine learning algorithms, Citibank evaluates a wide range of customer data, such as spending patterns, payment history, and financial habits, to determine creditworthiness. This enables more accurate risk management decisions, reducing the occurrence of bad loans and enhancing profitability.
The integration of AI has allowed Citibank to reduce manual credit scoring time by 70%, while also increasing the accuracy of its risk assessments. The bank’s ability to predict loan defaults has significantly improved, leading to better financial outcomes and minimizing the risk associated with lending.
2. Ernst & Young (EY): AI in Financial Audits
Ernst & Young (EY) uses AI to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of financial audits. The company leverages machine learning and natural language processing to analyze vast amounts of financial data, identifying anomalies and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. By automating data extraction and document review processes, EY’s AI tools reduce the time needed for audits and improve the accuracy of their findings.
As a result, EY has cut down audit completion times by 40%, while also increasing the accuracy of identifying discrepancies in financial records. This application of AI has helped EY streamline operations, reduced costs, and provide better insights to their clients.
3. Intuit: AI in Tax Preparation
Intuit, the developer behind TurboTax, has integrated AI to enhance its tax preparation software. The AI algorithms help individuals and businesses optimize their tax filings by analyzing user data and recommending deductions and credits. TurboTax’s AI-powered chatbot provides users with real-time assistance, ensuring they file their taxes accurately and efficiently.
The integration of AI has led to a more user-friendly experience, allowing TurboTax to handle over 40 million returns annually. This AI application has saved users an estimated 200 million hours, making tax filing simpler, faster, and more accurate.
Innovative AI Solutions
Emerging AI technologies are transforming finance and accounting, driving efficiency and intelligence in operations. Innovations like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and AI integration with blockchain are reshaping financial services, improving processes, and enhancing security.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is automating back-end tasks like data entry and reconciliation, reducing human intervention and errors. Powered by AI, RPA increases processing speed and efficiency, enabling businesses to focus on strategic services and client-facing roles.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps financial analysts process unstructured data, like market reports and news, to extract key insights and sentiments. This enables more informed investment decisions. Meanwhile, AI integrated with blockchain enhances security and transparency in financial transactions, improving fraud prevention and cross-border payments.
To explore how RPA and machine learning combine to enable intelligent automation in financial services, read our guide on AI-enhanced RPA solutions.
AI-Driven Innovations Transforming Finance and Accounting
Emerging Technologies in AI for Finance and Accounting
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the finance and accounting sectors by automating complex tasks and improving decision-making. Generative AI is used to streamline financial reporting, create audit documents, and simulate financial scenarios. This reduces manual work, boosts accuracy, and allows professionals to focus on more strategic activities.
Computer vision is another breakthrough technology revolutionizing finance and accounting. It processes visual data such as invoices and receipts, automating data extraction and reducing human error. This accelerates accounts payable and receivable processes while simplifying compliance and auditing tasks.
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are enhancing customer service in finance. These tools handle inquiries, guide clients, and assist internal teams with tasks like expense reporting. By automating these processes, they free up human resources for more complex work and increase efficiency across operations.
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
AI is playing a crucial role in promoting sustainability within finance and accounting. By utilizing predictive analytics, AI helps organizations forecast trends related to energy consumption, waste reduction, and sustainable investments. This technology enables more informed decision-making and allows businesses to optimize operations with a focus on reducing environmental impact.
AI-driven tools also assist in ensuring compliance with environmental regulations by automating data collection and analysis. This not only simplifies reporting but enhances transparency and accountability. As sustainability becomes more critical, AI is proving to be an asset for organizations striving to meet their environmental goals.
As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, AI continues to play a pivotal role in driving these efforts. By integrating AI into financial operations, companies can align their practices with global sustainability standards and improve their overall environmental footprint.
How to Implement AI in Finance and Accounting
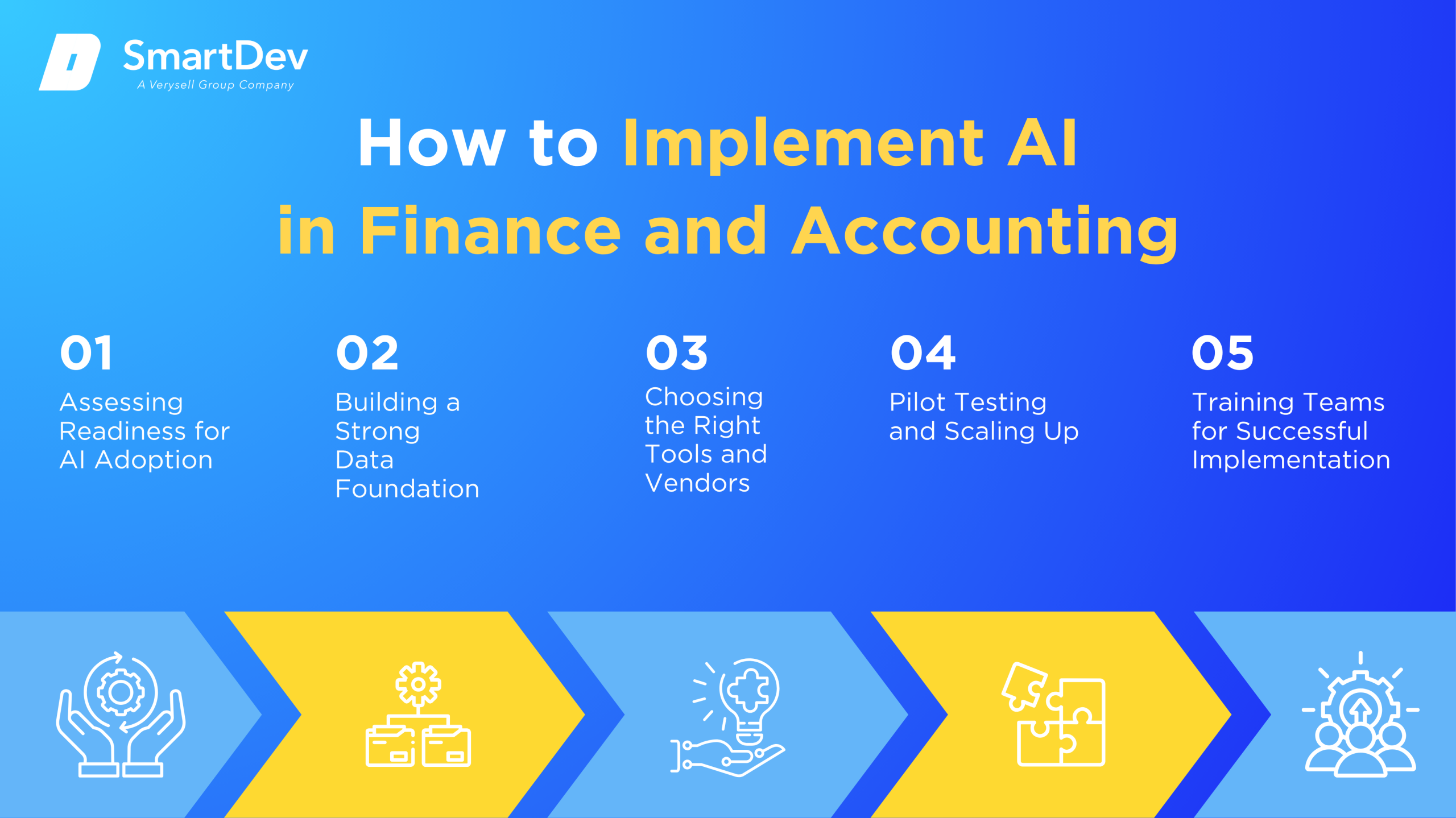
Step 1. Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
The first step in implementing AI in finance and accounting is assessing an organization’s readiness for AI adoption. This involves evaluating current processes to identify areas where AI can add value, such as automating repetitive tasks or improving data analysis. Understanding the existing infrastructure and data quality is essential for determining whether AI can be integrated successfully without significant disruptions.
Step 2. Building a Strong Data Foundation
A solid data foundation is crucial for the successful deployment of AI in finance and accounting. Organizations need to focus on cleaning, organizing, and securing data to ensure that AI tools can operate efficiently and generate accurate insights. Investing in data management systems is key to maintaining data integrity and ensuring that AI applications deliver reliable results.
Step 3. Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Selecting the right AI tools and vendors is critical. Companies must evaluate AI platforms based on scalability, integration capabilities, and specific features tailored to their needs. Partnering with trusted vendors ensures adequate support and minimizes the risks associated with AI adoption.
Step 4. Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Before fully implementing AI, organizations should conduct pilot tests to assess the technology’s effectiveness in small-scale operations. These tests provide valuable insights into performance, help identify potential challenges, and offer opportunities for adjustments. Once successful, AI applications can be scaled up across the business for wider adoption.
Step 5. Training Teams for Successful Implementation
Training is essential for successful AI adoption in finance and accounting. Employees need to be equipped with the necessary skills to understand and leverage AI tools effectively. Continuous learning programs will ensure that teams can work alongside AI technologies to optimize efficiency and performance.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Finance and Accounting
Key Metrics to Track Success
To evaluate the return on investment (ROI) of AI initiatives in finance and accounting, organizations should monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost savings, process efficiency, accuracy improvements, and employee productivity. Tracking these metrics provides insights into the effectiveness of AI applications and informs decision-making for future investments.
Additionally, assessing the impact on customer satisfaction, compliance rates, and revenue growth can offer a comprehensive view of AI’s value. Regularly reviewing and analyzing these metrics ensures that AI initiatives remain aligned with organizational objectives and deliver tangible benefits.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Several organizations have successfully implemented AI in finance and accounting, realizing significant ROI. For example, a multinational corporation integrated AI-powered automation into its accounts payable process, reducing invoice processing time and achieving substantial cost savings. Another company utilized AI for financial forecasting, resulting in more accurate predictions and improved strategic planning.
These case studies highlight the potential of AI to transform finance and accounting functions, delivering measurable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and financial performance. Learning from these examples, organizations can identify best practices and tailor AI solutions to their specific needs.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While AI offers numerous benefits, organizations may encounter challenges during implementation. Common pitfalls include inadequate data quality, lack of clear objectives, insufficient training, and resistance to change. To avoid these issues, it’s essential to establish a solid data foundation, set measurable goals, invest in comprehensive training programs, and foster a culture of innovation and adaptability.
Engaging stakeholders throughout the process and maintaining open communication can also mitigate resistance and ensure a smoother transition. By proactively addressing potential obstacles, organizations can maximize the success of their AI initiatives in finance and accounting.
Future Trends of AI in Finance and Accounting
Predictions for the Next Decade

Over the next decade, AI is expected to become increasingly integrated into finance and accounting, driving significant transformations. Advancements in machine learning and data analytics will enable more sophisticated financial modeling, risk assessment, and decision-making. AI-powered tools will likely become standard in areas such as auditing, compliance, and financial reporting, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
Furthermore, the adoption of AI is anticipated to promote greater transparency and real-time insights, facilitating more agile and informed financial strategies. As AI technologies continue to evolve, organizations that embrace these innovations will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To remain competitive in the evolving landscape of finance and accounting, businesses must proactively adopt and integrate AI technologies. This involves staying informed about emerging trends, investing in relevant tools and training, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Collaborating with technology partners and participating in industry forums can also provide valuable insights and opportunities for growth.
By embracing AI and adapting to technological advancements, organizations can enhance their financial operations, drive strategic decision-making, and achieve long-term success in a rapidly changing environment.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI is transforming finance and accounting by automating processes, enhancing decision-making, and promoting sustainability. Implementing AI requires a strategic approach, including assessing readiness, building a strong data foundation, selecting appropriate tools, conducting pilot tests, and training teams. Measuring ROI through key metrics and learning from successful case studies can guide organizations in maximizing the benefits of AI.
Looking ahead, staying informed and adaptable will be crucial for leveraging AI to its full potential in finance and accounting.
Moving Forward: A Path to Progress
As AI continues to reshape the finance and accounting sectors, the key to success lies in adopting these transformative technologies and continuously evolving with them. Businesses must prioritize building a strong data foundation, selecting the right AI tools, and empowering their teams through training. By embracing AI-driven automation and predictive analytics, companies can optimize financial operations, improve accuracy, and drive better decision-making.
At SmartDev, we specialize in providing AI solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve financial performance across industries. Our expert team works with businesses to implement AI-powered strategies that streamline accounting processes and enable smarter financial decision-making.
Contact us today to learn how AI can revolutionize your finance and accounting practices. Let us help you unlock new opportunities, improve compliance, and achieve sustainable growth through cutting-edge AI technologies.
—
References:
- More organizations are turning to AI in the finance function | Journal of Accountancy
- AI Adoption Across US Finance Functions Reaches Highest Levels, with ROI Exceeding Expectations | KPMG
- The Transformative Impact of AI on Accounting | Illinois CPA Society
- At Mastercard, AI is helping to power fraud-detection systems | Business Insider
- AI fraud detection in banking | IBM
- The Role of AI in Financial Modeling and Forecasting | Coherent Solutions
- How large tax and accounting firms can use AI | Thomson Reuters
- How AI Can Transform Fintech, Credit Scoring | Forbes
- AI In Financial Services: Transforming Stock Trading | Forbes
- Exploring the Impact of Blockchain, AI, and ML on Financial Accounting Efficiency and Transformation | International Conference on Multi-Strategy Learning Environment






