In our initial discussion on embedded finance, we explored its definition and foundational technology—how seamlessly financial services can be integrated into non-financial businesses’ platforms. Continuing from where we left off, this post delves deeper into the multifaceted impact of embedded finance on companies and consumers alike, analyzing both the profound benefits and the significant challenges it presents.
I. Benefits of Embedded Finance
Embedded finance is rapidly transforming how consumers interact with financial services, seamlessly integrating these services into non-financial business platforms. This integration is a convenience and a strategic enhancement that benefits businesses and their customers. Embedded finance has proven to be a powerful tool for businesses seeking to diversify and increase their revenue streams. By incorporating financial services, companies can enhance their core offerings and tap into new sources of income such as transaction fees, interest from lending, or premiums from insurance services.
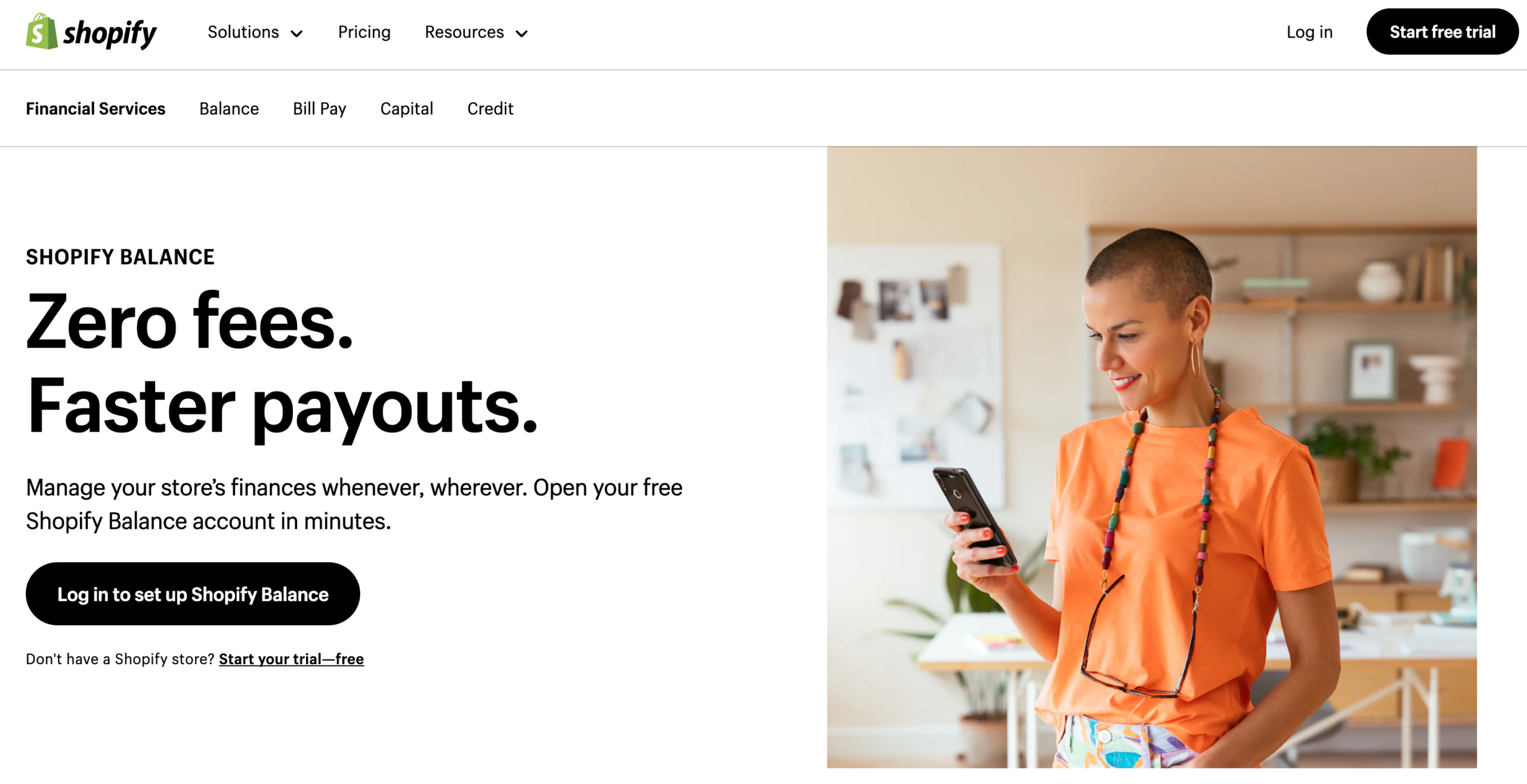 Figure 1: Shopify’s Implementation of Payment Processing
Figure 1: Shopify’s Implementation of Payment Processing
One of the standout examples of embedded finance success is Shopify, which has significantly capitalized on this trend by embedding various financial solutions directly into its platform. In 2020, Shopify launched “Shopify Balance,” a suite of financial services designed specifically for their merchants. This move aimed to simplify business finance management for their users, enabling more accessible access to critical financial tools directly from their Shopify dashboard.
1.1 Case Study: Shopify’s Financial Growth Through Embedded Finance
Shopify’s integration of financial services has proven to be highly lucrative. As of the first quarter of 2021, more than 73% of Shopify’s revenue was generated from merchant solutions, most of which came from embedded financial products. This includes their payment processing solutions, where Shopify accepts credit cards and other popular payment methods through an immediately available payment provider. The convenience and variety of payment options offer a smooth checkout experience, appealing to a global audience by accommodating multiple payment methods and local currencies.
Furthermore, Shopify charges transaction fees for payments processed through its system, with card rates starting at 2.9% + 30¢ USD per online transaction. This fee structure contributes significantly to their revenue, as evidenced by their financial reports from Q1 2021, which showed that their Merchant Solutions revenue stream was $668.0 million, marking a growth of 137%. The increase in Gross Merchandise Volume primarily drove this impressive growth.
1.1.1 Enhanced Customer Experience
Shopify excels in enhancing the customer experience through its embedded finance solutions. By integrating payment processing solutions directly into the platform, Shopify ensures that the e-commerce checkout process is as smooth and friction-free as possible. This helps retain customers by reducing checkout abandonment and attracts new users looking for a seamless purchasing experience. Additionally, Shopify provides a mobile-friendly checkout, further enhancing accessibility and convenience for users shopping via mobile devices.
The case of Shopify demonstrates the dual benefits of embedded finance—enhancing the customer experience while driving significant revenue growth. By reducing friction in financial transactions and offering integrated financial management tools, Shopify has simplified commerce for its users and set a benchmark for how businesses can leverage embedded finance to transform their operational and financial landscapes. This strategic adoption of embedded financial services is not just a trend but a forward-looking approach that more businesses are likely to follow, considering its substantial benefits in revenue generation and customer satisfaction. As we continue to witness the evolution of commerce, embedded finance stands out as a key innovator in redefining the industry.
II. Consumer Advantages of Embedded Finance
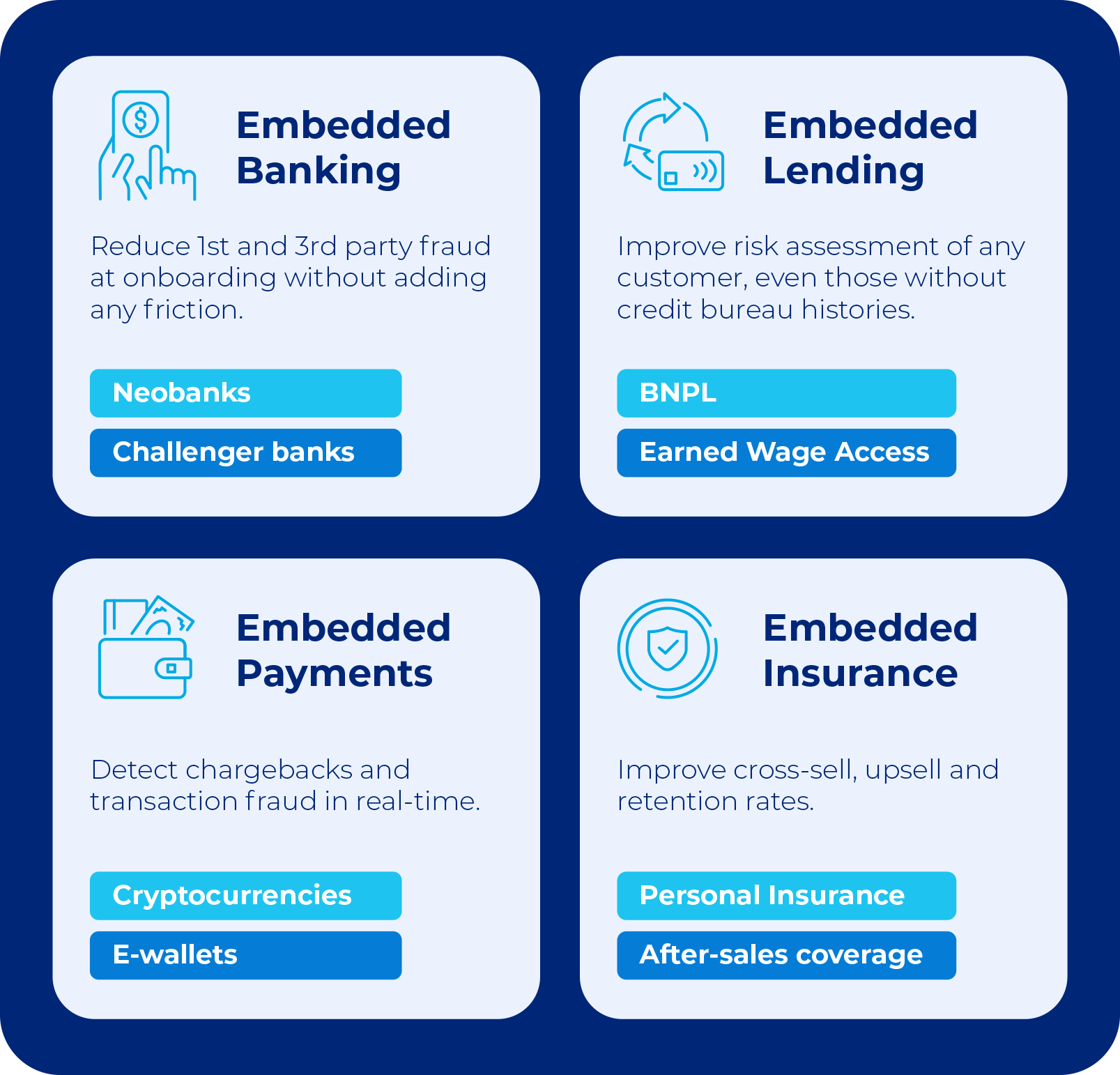 Figure 2: Types of Embedded Finance (Derilova, 2024)
Figure 2: Types of Embedded Finance (Derilova, 2024)
Embedded finance epitomizes convenience by seamlessly integrating financial services into the apps and platforms consumers use daily. This integration means that consumers can access essential financial services—such as payments, lending, and insurance—right where and when they need them, without the cumbersome need to switch between different applications or interfaces. This streamlined approach is achieved by embedding these financial functions directly into non-financial apps and services, allowing users to engage with financial services without leaving their preferred environments. For example, a user can apply for credit, make payments, or insure purchases directly within an e-commerce app, eliminating the need to navigate away to separate banking portals. This saves valuable time and significantly simplifies users’ financial management tasks.
Moreover, consumers appreciate embedded finance’s simplicity, as it removes the need for multiple logins or redirects to external sites. Every transaction happens within a single, familiar platform, enhancing user experience by making financial interactions as straightforward as possible. Embedded finance also caters to a broader audience, including those who may have found traditional banking systems inaccessible or overly complicated. By lowering these barriers, embedded finance enhances convenience and extends financial inclusivity, reaching users who might not typically engage with conventional financial institutions.
2.1 Personalization of Financial Products
Embedded finance revolutionizes how businesses understand and serve their customers by leveraging extensive data insights. By integrating financial services within their platforms, enterprises gain a unique vantage point to collect a wealth of data regarding their customers’ behaviors, preferences, and economic interactions. This rich data allows for the creation of highly personalized financial products that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of individual users.
2.1.1 Data-Driven Customization
Businesses can analyze the data collected from their platforms to understand various factors such as purchasing patterns, frequency of transactions, and the financial health of their customers. This data is then used to create customized financial offers that align with the customer’s unique financial situation and preferences. For example, customers who frequently make large purchases may be offered a premium credit card with higher credit limits and rewards. In contrast, another who makes smaller, more frequent purchases may receive offers for micro-loans or installment payments.
2.1.2 Risk Profile Adaptation
Embedded finance also allows businesses to adjust their offerings based on each customer’s risk profile. Companies can assess each customer’s lending risk by analyzing transaction histories and financial behaviors and adjusting terms and interest rates accordingly. This risk-adjusted approach minimizes defaults and ensures that customers are not overburdened by financial products unsuited to their financial capacity.
2.2 Case Study: Amazon Lending – Personalization of Financial Products Through Embedded Finance
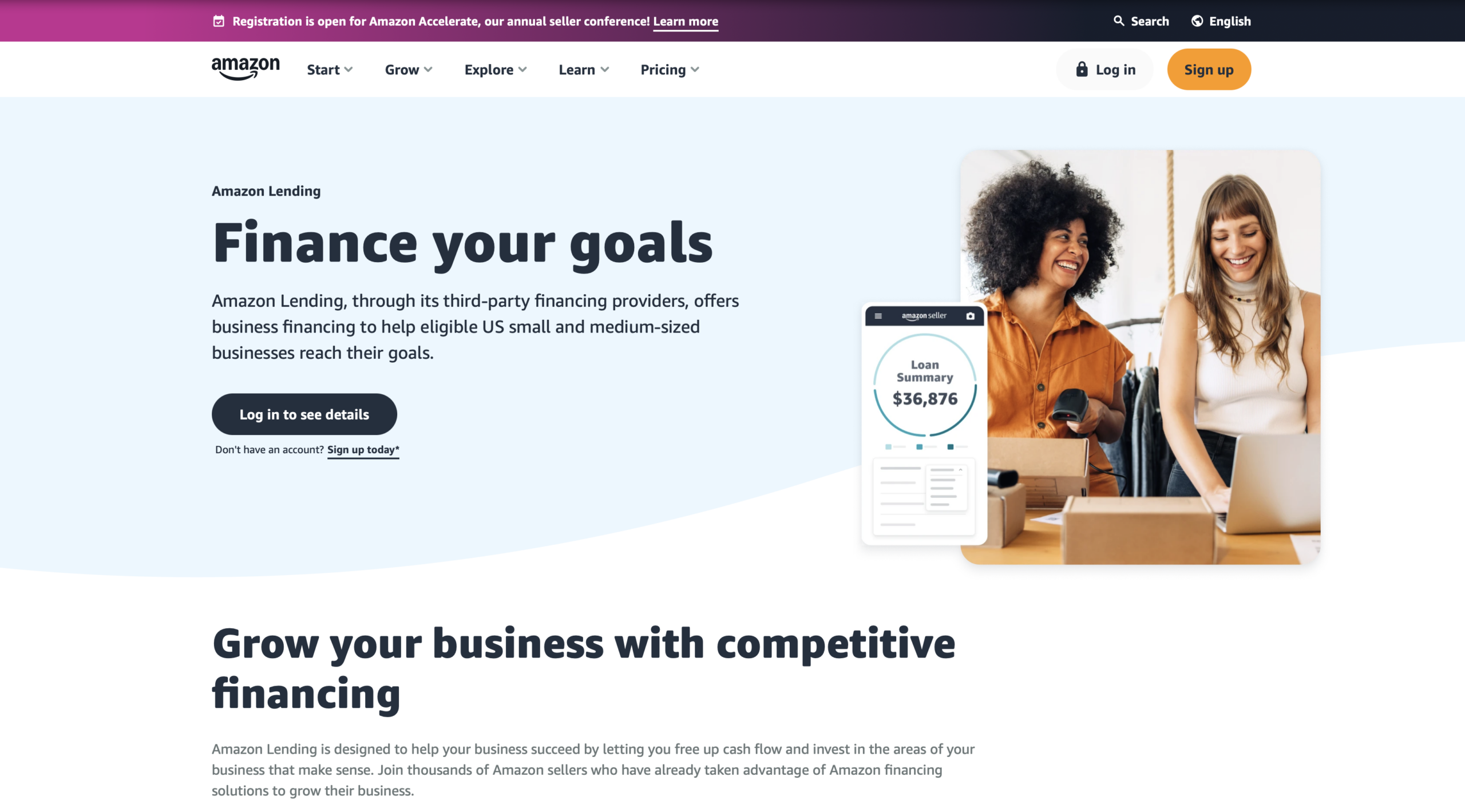
Figure 3: Amazon Lending official webpage
Amazon Lending exemplifies how embedded finance can be leveraged to offer highly personalized financial products intricately aligned with users’ needs. As an integral part of Amazon’s suite of services to its sellers, Amazon Lending utilizes the vast amount of data generated on its platform to tailor financial solutions that support the growth and sustainability of its sellers’ businesses. Amazon Lending is a financial assistance program for qualified sellers on its platform. By providing business financing solutions directly through Amazon Lending and third-party partners, Amazon caters to the unique needs of small and medium-sized businesses within its ecosystem. This approach simplifies sellers’ financing process and integrates financial services seamlessly into their operational workflow on Amazon.
Eligibility for Amazon Lending is determined through carefully analyzing a seller’s performance on the platform. Amazon evaluates potential borrowers based on their sales history, their ability to increase sales, and their level of customer satisfaction. This ensures that the financial products offered are not only suited to the financial capabilities of the sellers but are also likely to contribute positively to their business operations. Sellers are required to have at least three months of trading history on Amazon, ensuring that there is sufficient data to make an informed lending decision.
Impact of Tailored Loans on Business Growth
The personalized loan offers provided by Amazon Lending are specifically designed to meet the individual financial needs of each seller. This customization allows sellers to use the funds in various ways that directly benefit their business, such as expanding marketing efforts, broadening product lines, increasing the workforce, or enhancing infrastructure. This flexibility is crucial for small businesses that need tailored financial solutions to address specific challenges or opportunities.
Enhanced Seller Experience and Outcomes
Amazon reports that sellers participating in Amazon Lending often experience a noticeable increase in sales, although exact figures vary. This boost is attributed to the additional capital that allows sellers to invest in areas of their business that can lead to greater product visibility and improved customer reach. The success of the loans in driving business growth further cements the trust and loyalty of sellers towards Amazon, as they perceive these financial products as tools that genuinely support their business expansion.
Building Trust and Loyalty
The personalized nature of the loans, combined with the supportive approach taken by Amazon, fosters a strong sense of trust and loyalty among sellers. They feel supported by Amazon as a marketplace for their products and as a partner interested in their business success. This relationship is vital for Amazon’s long-term strategy to nurture a thriving marketplace where sellers are motivated and equipped to offer their customers the best products and services.
Amazon Lending is a prominent example of how embedded finance can transform traditional business financing models. By using data-driven insights to offer personalized financial products, Amazon not only enhances the operational capacity of its sellers but also deepens their engagement with the platform. This case study underscores the significant benefits of embedded finance, particularly its ability to foster tailored, impactful financial interactions within existing ecosystems. Embedded finance, while transformative, presents substantial challenges that businesses must carefully navigate to ensure compliance and security. These challenges stem primarily from the complex regulatory landscape and financial data management risks.
III. Challenges of Embedded Finance
The financial sector is among the most heavily regulated industries globally. As companies embed financial services into their platforms, they face diverse and intricate financial regulations that can vary widely from one jurisdiction to another. This complexity poses a significant compliance challenge, particularly for businesses operating internationally.
3.1 Compliance with the EU’s PSD2

Figure 4: PSD2 (Recurly, 2022)
The European Union’s Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) is an example of these regulatory challenges. PSD2 is designed to increase competition and participation in the payments industry, including from non-banking entities, and to enhance the security and transparency of payment services across Europe. The directive imposes rigorous requirements on payment service providers, such as improved customer authentication processes and the mandate to provide third-party access to their APIs. Navigating these regulations requires substantial legal and technical expertise, and failure to comply can lead to severe penalties.
Alongside the regulatory complexities, security issues represent a significant hurdle for companies engaging in embedded finance. Financial transactions involve sensitive personal data, making them a prime target for cybercriminals. Ensuring the security of these transactions is paramount.
Data Security and Privacy Regulations
To safeguard user data, companies must comply with stringent data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US. The GDPR, for instance, sets strict guidelines on processing personal data and grants individuals greater control over their information. Businesses are required to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to secure this data.
3.2 Mitigation Strategies
To address these security challenges, businesses can adopt some robust mitigation strategies:
- Encryption: Implementing robust encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit is crucial to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Secure Access Protocols: Utilizing secure access protocols, such as multi-factor authentication, helps to safeguard user accounts from unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing is essential to identifying and mitigating system vulnerabilities.
- Data Minimization: Adopting data minimization principles ensures that only necessary data is collected and stored, reducing the potential impact of a data breach.
Additionally, businesses must remain vigilant about emerging threats and continuously update their security practices to address new vulnerabilities.
Navigating the challenges of embedded finance requires a proactive approach to regulatory compliance and data security. By understanding and addressing these challenges, businesses can effectively harness the benefits of embedded finance while minimizing risks, ultimately fostering trust and ensuring a secure environment for their users.
IV. Case Studies with Successful Implementation
4.1 Company Profile: Apple and Apple Pay

Figure 5: Apple Pay
Apple Pay is a quintessential example of embedded finance, integrating payment capabilities directly into Apple devices. This integration significantly enhances the user experience by simplifying transactions and bolstering security. Utilizing Near Field Communication (NFC) technology alongside Apple’s robust hardware suite, Apple Pay offers a secure and private payment method, setting a benchmark in the mobile payments industry.
4.1.1 Success Factors
Seamless Integration: Apple Pay is intricately woven into the fabric of Apple devices, allowing users to execute payments directly from their iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches. This deep integration ensures that users can authorize payments with a single touch without needing to open an app or awaken their device, thanks to advanced technologies like Touch ID and Face ID.
Stringent Security Measures: A strong emphasis on security is at the core of Apple Pay’s design. It employs a sophisticated tokenization system where a unique Device Account Number is assigned, encrypted, and securely stored. Each transaction is authorized with a one-time unique dynamic security code, ensuring that actual card numbers are neither stored on the device nor on Apple servers nor shared with merchants.
Privacy Focus: Apple prioritizes privacy, reassuring users that their purchase history is neither stored nor monitored. This commitment to privacy has played a crucial role in building trust among users, particularly those hesitant to share financial details.
4.2 Lessons Learned
Challenges Overcome
Initially, Apple Pay encountered skepticism concerning user adoption, driven by security concerns and the novelty of the technology. Apple addressed these challenges by:
- Educating Users and Merchants: Apple made significant investments in educating both consumers and merchants about the benefits and operations of Apple Pay, which facilitated smoother adoption.
- Enhancing User Experience: Apple ensured that Apple Pay was secure and incredibly user-friendly, focusing on simplicity and efficiency in transactions to encourage adoption over traditional payment methods.
Apple Pay’s journey highlights several critical insights
- User-Centric Design: Apple Pay’s design is an example of user-centric development. By understanding and prioritizing the needs and concerns of end-users, Apple crafted a product that quickly gained acceptance in the market.
- Importance of Security: The robust security measures implemented in Apple Pay underscore the importance of security in successfully deploying embedded financial services. These measures protect users and build the trust necessary for widespread adoption.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: The key to Apple Pay’s success was its partnerships with central banks, credit card companies, and retailers. These alliances ensured Apple Pay had the support and infrastructure for a successful rollout, enhancing its functionality and reach.
Apple Pay’s case study is a powerful example for other companies looking to implement embedded financial services. It underscores the necessity of a user-centric approach, the critical role of security, and the benefits of strategic partnerships in overcoming initial market challenges. By focusing on these areas, businesses can enhance user experience and ensure the successful integration and acceptance of new financial technologies.
V. Overview
Embedded finance has reshaped how businesses integrate financial services, enhancing operational efficiency and consumer interaction. Companies like Shopify have demonstrated significant revenue growth and improved customer engagement by embedding services like payment processing directly into platforms. For consumers, embedded finance simplifies access to financial services, as seen with Apple Pay, providing secure and seamless transactions directly from personal devices. This accessibility not only improves user experience but also expands financial inclusivity.
Despite its benefits, embedded finance faces regulatory and security challenges. The evolution of Apple Pay illustrates effective strategies to overcome these hurdles, including thorough user education and robust security measures. As the landscape of commerce and financial services continues to evolve, embedded finance stands as a transformative force, redefining industry standards and consumer expectations. Its continued development will likely prompt further innovations and challenges, shaping the future of how financial services are delivered and experienced.
VI. About SmartDev
At SmartDev, we are committed to driving innovation in the financial sector through our comprehensive fintech solutions. By integrating secure mobile applications, cutting-edge blockchain technology, and advanced Robotic Process Automation (RPA), we ensure that our services meet the highest quality and performance standards. Our fintech expertise helps financial institutions enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving economic landscape.
We invite businesses, innovators, and technology enthusiasts to collaborate with us and discover how our expertise in fintech can transform your operations. Let’s work together to leverage these cutting-edge practices, creating solutions that are not only innovative but also highly reliable and scalable. Contact SmartDev today to explore how we can help you achieve your strategic goals with our fintech services. Together, we will advance the capabilities of digital finance and set new benchmarks in the industry.
Visit our Fintech Services Page now to learn more.







