With the rapid expansion of digital commerce, IT applications have become the backbone of modern e-commerce businesses. From small startups to established retail giants, businesses now rely on innovative software solutions to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and drive growth. This guide walks through essential IT applications in e-commerce, focusing on practical examples and strategies for business owners and managers in retail.
1. Introduction to E-commerce Applications
E-commerce is reshaping the retail world at an unprecedented pace, opening up opportunities for businesses of all sizes. With the global market continuously growing, companies are investing heavily in mobile and web-based applications to meet the demands of today’s digital-savvy customers.
Statistics about E-commerce in General and E-commerce Apps
The e-commerce industry has experienced explosive growth, with global online sales surpassing $5 billion in 2022. This trend has been fueled by widespread internet access, the growth of mobile commerce, and the increasing demand for convenience and variety. A significant portion of these sales happens through e-commerce applications, which account for around 60% of all online transactions.
Definition and Scope of E-commerce Applications

E-commerce applications are platforms that facilitate the buying and selling of products and services online, ranging from basic online stores to complex multi-vendor marketplaces. These apps encompass mobile and web-based platforms, supporting activities such as browsing, order processing, and customer support.
Importance in Modern Business
In today’s competitive landscape, e-commerce applications are indispensable tools for business owners. They serve as digital storefronts, foster brand loyalty, and streamline business operations. For business owners and managers, embracing e-commerce technology is not just an option but a strategic necessity to stay relevant and competitive.
2. E-commerce Apps Examples That Rock
To understand the impact of IT applications on e-commerce, let’s explore some real-world examples of companies that have successfully leveraged technology to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and drive growth. Each case study highlights unique strategies and features that make these platforms stand out, offering valuable lessons for retailers aiming to optimize their own e-commerce approach.
Amazon: Leading with Innovation and Customer-Centricity

Amazon is widely recognized as a pioneer in e-commerce, constantly pushing the boundaries of technology to enhance the customer experience. The company’s mobile and web apps are designed to offer a seamless shopping journey, blending convenience, personalization, and efficiency.
- Personalization with AI and Machine Learning
Amazon’s recommendation engine is powered by advanced machine-learning algorithms that analyze each customer’s browsing and purchasing history. By leveraging data insights, Amazon’s app delivers personalized product recommendations that account for individual preferences, seasonal trends, and even predicted future purchases. This personalized approach not only drives sales but also keeps customers engaged, making them more likely to return to the platform. - One-Click Purchasing and Streamlined Checkout
Amazon’s one-click purchase feature, which allows users to complete orders instantly, is a prime example of how a simple yet innovative feature can remove friction from the shopping experience. This functionality is integrated across both web and mobile platforms, ensuring convenience for customers on any device. It’s especially effective for repeat customers, reducing the likelihood of cart abandonment. - Supply Chain Optimization and Fulfillment Centers
Amazon’s app also supports its industry-leading logistics and supply chain network. Through real-time inventory tracking and integration with fulfillment centers, Amazon ensures that most products are available for rapid dispatch. This logistics backbone is complemented by the app’s order tracking feature, allowing customers to monitor shipments in real-time—a transparency feature that has set new standards in customer service. - Voice-Activated Shopping with Alexa
Amazon has integrated voice-activated shopping through Alexa, allowing users to browse and purchase items simply by speaking to their device. This innovation caters to customers who prefer hands-free shopping, setting Amazon apart as a brand that consistently finds new ways to meet and anticipate customer needs.
Key Takeaway: Amazon’s approach to e-commerce highlights the importance of personalization, operational efficiency, and innovation. Retailers can learn from Amazon’s data-driven strategies and commitment to seamless user experiences to increase engagement and loyalty.
Alibaba: A Global Giant with Diverse Market Reach

Alibaba is a leading e-commerce player, particularly in Asia, and operates one of the most diverse e-commerce ecosystems in the world. The company caters to both B2B and B2C customers, providing comprehensive solutions that support suppliers, wholesalers, and individual buyers alike. Alibaba’s e-commerce app is a powerful tool for global transactions, integrating AI, cloud computing, and extensive logistics capabilities to connect buyers and sellers across borders.
- AI-Driven Product and Supplier Matching
Alibaba uses AI to match suppliers with potential buyers based on preferences, purchasing history, and even geographic location. This feature is invaluable in Alibaba’s B2B marketplace, where buyers are often searching for niche products or bulk orders. By optimizing the matching process, Alibaba’s app saves buyers time and enhances the likelihood of successful transactions. - Robust Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Alibaba’s app is intricately linked to Cainiao, its logistics network, which uses big data to optimize inventory management and shipping routes. For example, during major shopping events like Singles’ Day, the app manages millions of orders seamlessly, ensuring timely deliveries through its intelligent logistics platform. This capability highlights the app’s power in managing massive transaction volumes, a critical asset in the global e-commerce market. - Live Streaming for Customer Engagement
Alibaba has pioneered live streaming within its app, allowing sellers to demonstrate products in real-time to thousands of viewers. Live streaming has been a huge success in markets like China, where it’s become a preferred shopping method for consumers. By integrating this feature, Alibaba enhances engagement, builds trust, and provides an interactive way for consumers to learn about products. - Localized Payment and Currency Options
Given its global reach, Alibaba’s app integrates Alipay, allowing customers to pay in their local currencies and through familiar payment methods. This localization of payment options makes it easier for international customers to complete transactions, increasing the platform’s accessibility and appeal to a global audience.
Key Takeaway: Alibaba’s app demonstrates the potential of technology to create a comprehensive, globally accessible e-commerce ecosystem. For retailers looking to expand internationally, Alibaba’s use of localized payment options, AI-driven matching, and interactive shopping experiences offers inspiration on how to meet diverse customer needs.
3. Types of E-commerce Applications
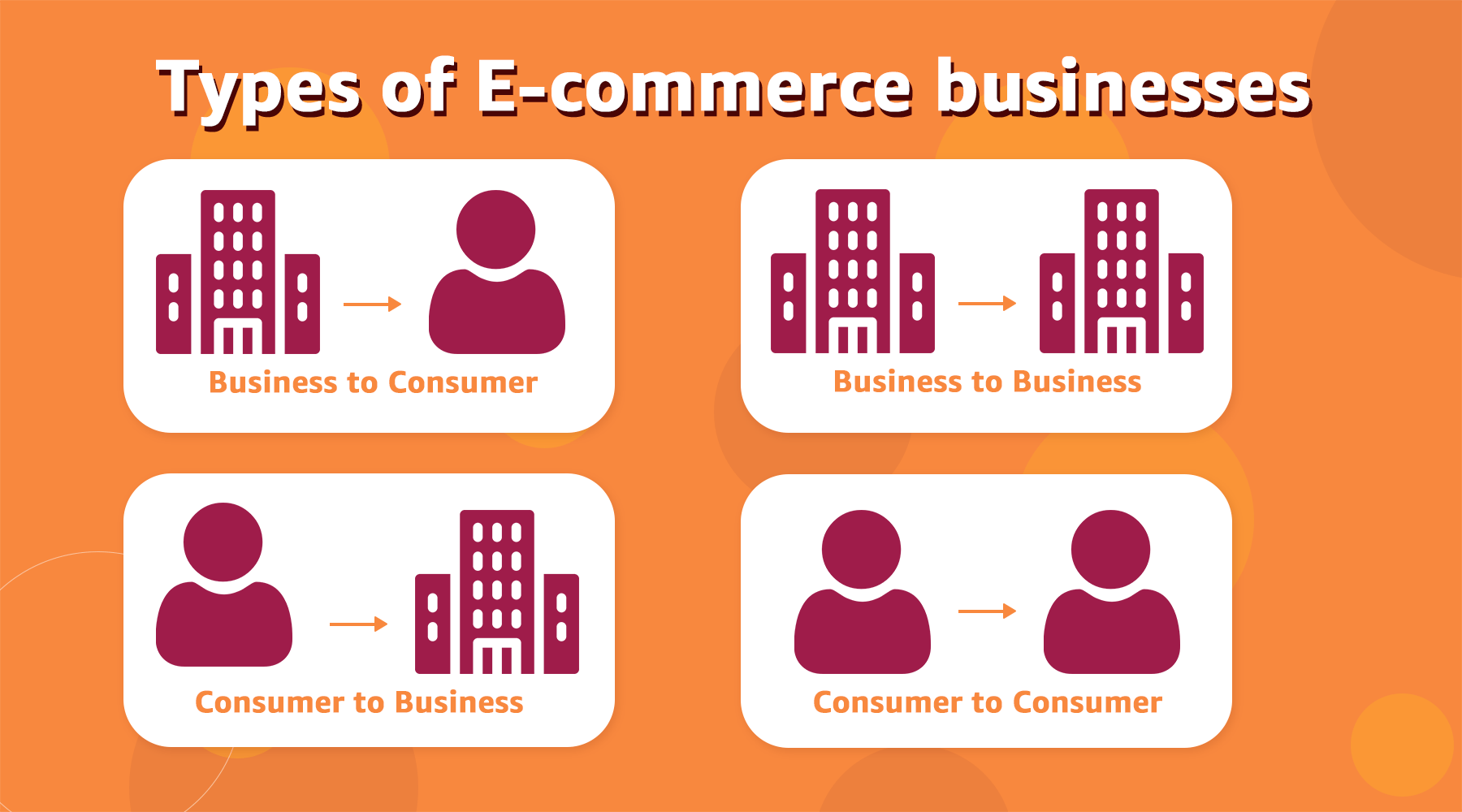
E-commerce applications vary widely, and choosing the right type can directly impact how well you meet customer and market needs. Each type supports different transaction models, from direct-to-consumer to peer-to-peer platforms.
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): The most common model, where retailers sell directly to consumers. Examples include Amazon, Zalando, and Walmart.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Companies sell products or services to other businesses. Alibaba and ThomasNet are prominent B2B platforms, supporting wholesale transactions.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): Peer-to-peer sales platforms where individuals buy and sell among themselves, such as eBay and Facebook Marketplace.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): Here, individuals provide services or products to companies, as seen in influencer partnerships where individuals promote products to their audience.
By understanding these categories, retailers can tailor their e-commerce applications to their business models, enabling efficient operations and stronger market alignment.
4. Key IT Applications in E-commerce
Leveraging key IT applications allows businesses to enhance efficiency, improve customer experience, and stay competitive. From managing customer relationships to analyzing data, these tools are invaluable for e-commerce success. Below, we discuss several critical IT applications for e-commerce businesses
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Personalized Marketing
CRM systems like Salesforce and Zoho are instrumental in managing customer relationships by storing valuable data such as purchase history and behavioral trends. These platforms empower businesses to segment customers, personalize communications, and launch targeted marketing campaigns that drive customer retention. For example, a retailer could leverage CRM data to send a personalized discount offer to frequent buyers during a holiday season, resulting in higher conversion rates and increased loyalty.
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Efficient inventory and supply chain management are vital for e-commerce success. Platforms like NetSuite and TradeGecko streamline stock tracking, supplier coordination, and demand forecasting. By automating these processes, retailers can minimize stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and ensure timely delivery. For instance, a multi-warehouse retailer could use inventory software to automatically reallocate stock based on real-time demand across locations, optimizing logistics and reducing shipping costs.
Data Analytics and AI for Customer Insights
Data analytics platforms, such as Google Analytics, enable e-commerce retailers to analyze website traffic, conversion rates, and customer demographics. More advanced AI tools, like IBM Watson, provide predictive insights, helping businesses anticipate customer needs. A fashion retailer, for example, can use AI to forecast which styles are trending and adjust inventory to match demand, thus increasing relevance and reducing unsold stock.
Mobile and Web App Development for Optimal Customer Experience
A seamless mobile and web app experience is crucial for customer engagement. Frameworks like React Native and Flutter allow developers to create responsive, high-performance applications. For example, a user-friendly checkout process with saved payment information, one-click reordering, and tailored recommendations can significantly boost retention. By adopting a customer-first design approach, retailers ensure smoother navigation, higher user satisfaction, and stronger brand loyalty.
5. Key Considerations for E-commerce App Development
Developing an e-commerce app requires a strategic approach that considers both present and future needs. Here are essential factors to keep in mind when building your app.
Identifying Target Audience and Market Needs
Conducting comprehensive market research is essential. This includes identifying demographics, understanding customer pain points, and assessing demand trends. Retailers can use tools like surveys, social media insights, and competitor analysis to align the app’s features with customer expectations.
Selecting Suitable Technology Platforms
Choosing the right technology platform lays a foundation for success. Platforms like WooCommerce, Magento, and Shopify each offer unique features suited for different business scales. For instance, Magento’s scalability makes it ideal for enterprises, while WooCommerce’s integration with WordPress appeals to smaller retailers.
Planning for Scalability and Future Upgrades
As e-commerce evolves, the ability to scale is crucial. Structuring the app for scalability—using microservices, for example—allows businesses to add new features without overhauling the entire system. Regular updates to incorporate emerging technologies, like AI-driven chatbots, ensure the app remains competitive and adaptable.
Security Strategy and Legal Compliance
Compliance with legal standards, such as GDPR for data privacy, and implementing robust security protocols are vital. Security measures like SSL encryption, multi-factor authentication, and data encryption safeguard customer data, while legal compliance fosters customer trust and avoids regulatory issues.
6. 8 Steps of How to Build an E-commerce App

Creating an e-commerce app can seem complex, but breaking it into clear steps makes the process manageable. These eight steps outline the main stages of app development, from defining your vision to launching the final product.
- Define Objectives and Scope: Establish clear goals, define your target audience, and outline the essential features.
- Market Research: Analyze competitors, assess customer needs, and identify potential obstacles.
- UI/UX Design: Prioritize a user-friendly, intuitive design that aligns with your brand.
- Choose a Tech Stack: Select a platform that fits your business size, budget, and growth plans.
- Develop Core Features: Build critical functionalities like shopping cart, checkout, and payment processing.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Conduct rigorous testing to identify bugs and optimize performance.
- Launch: Deploy the app to app stores and market it to your target audience.
- Gather Feedback and Iterate: Collect user feedback and continually refine the app for a better user experience.
7. E-commerce App MVP Features
Starting with an MVP allows businesses to enter the market quickly and refine their product based on user feedback. MVPs focus on essential features, providing a foundation that can be expanded over time. Here’s what to include in an MVP for an e-commerce app.
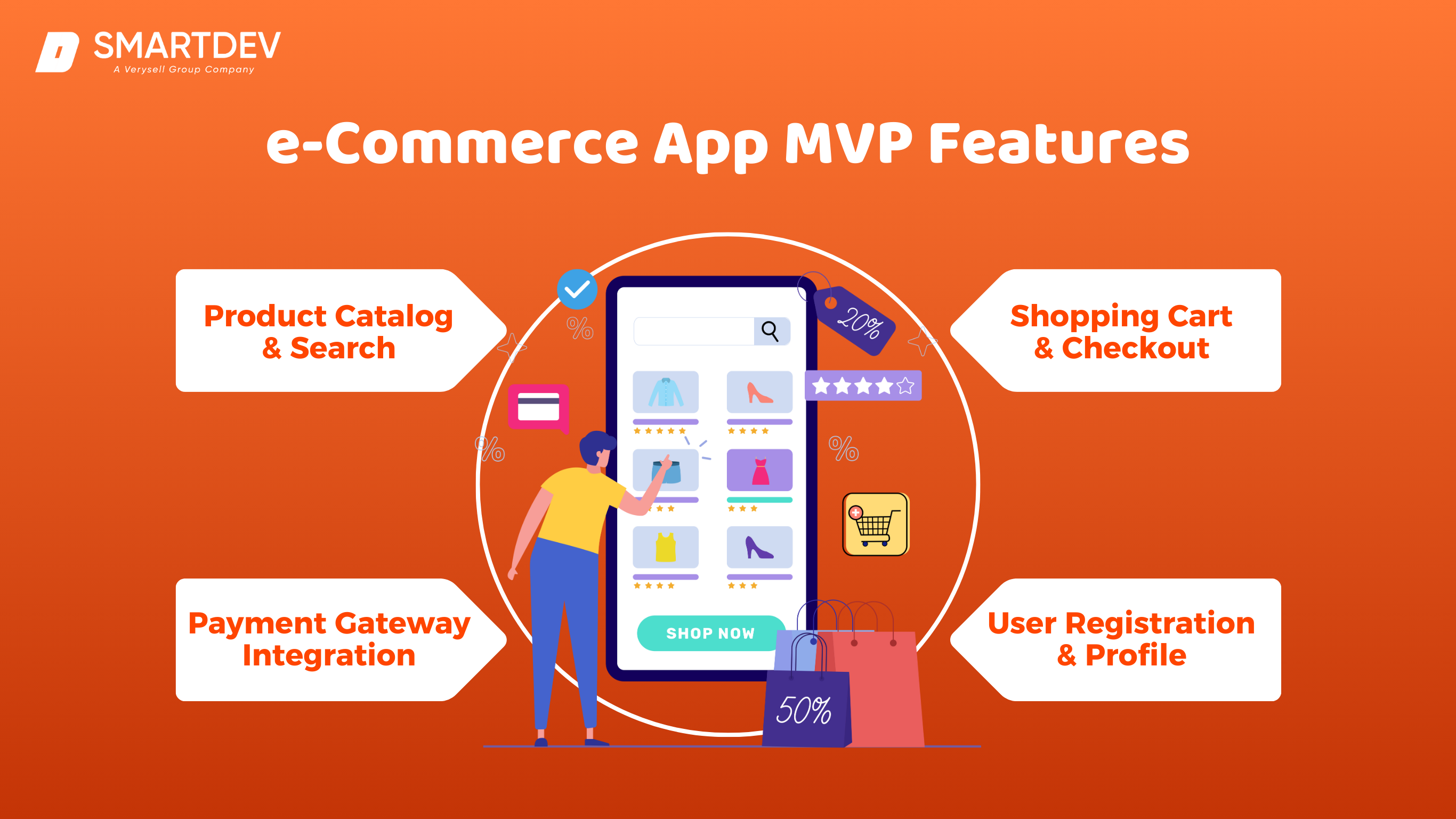
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach focuses on essential features, allowing retailers to launch faster and on budget. Core MVP features include:
- Product Catalog and Search: Enables customers to browse products and find specific items.
- Shopping Cart and Checkout: Streamlines the purchasing process.
- Payment Gateway Integration: Ensures secure, seamless transactions.
- User Registration and Profile: Allows customers to create accounts for personalized experiences.
By prioritizing these core features, businesses can test their app in the market, collect user feedback, and implement improvements over time.
Why Focus on an MVP First
Launching an MVP provides critical insights into user preferences and app performance, allowing businesses to iterate effectively. This approach minimizes risk and helps refine the product based on real-world usage.
8. How to Build an E-commerce App Without Coding
For small to medium-sized businesses, building an e-commerce app without coding can be an efficient and budget-friendly solution. Here’s a detailed look into how no-code platforms can support e-commerce development:
Using No-code Platforms: Shopify, WooCommerce, Wix, and Beyond
Platforms like Shopify and Wix allow businesses to build e-commerce apps with little to no coding knowledge. Each platform offers a range of customizable templates, drag-and-drop editors, and integrations to enhance functionality.
- Shopify
Shopify allows business owners to set up fully functional e-commerce stores in a matter of hours. With its user-friendly dashboard, drag-and-drop editor, and over 6,000 apps in its App Store, Shopify provides extensive customization options even without coding. Retailers can easily integrate payment gateways, manage inventory, and personalize the storefront to match their brand identity. - WooCommerce
As a WordPress plugin, WooCommerce enables businesses to transform their websites into robust e-commerce stores. WooCommerce supports numerous third-party plugins for additional functionality, such as payment processing, inventory management, and SEO optimization. This flexibility makes it a powerful option for retailers already familiar with WordPress. - Wix
Known for its drag-and-drop builder, Wix provides an accessible platform for creating visually appealing e-commerce sites. Wix’s ADI (Artificial Design Intelligence) feature can generate customized website templates, making it an ideal choice for beginners. Its built-in tools for SEO, product management, and payment processing make Wix a solid no-code option.
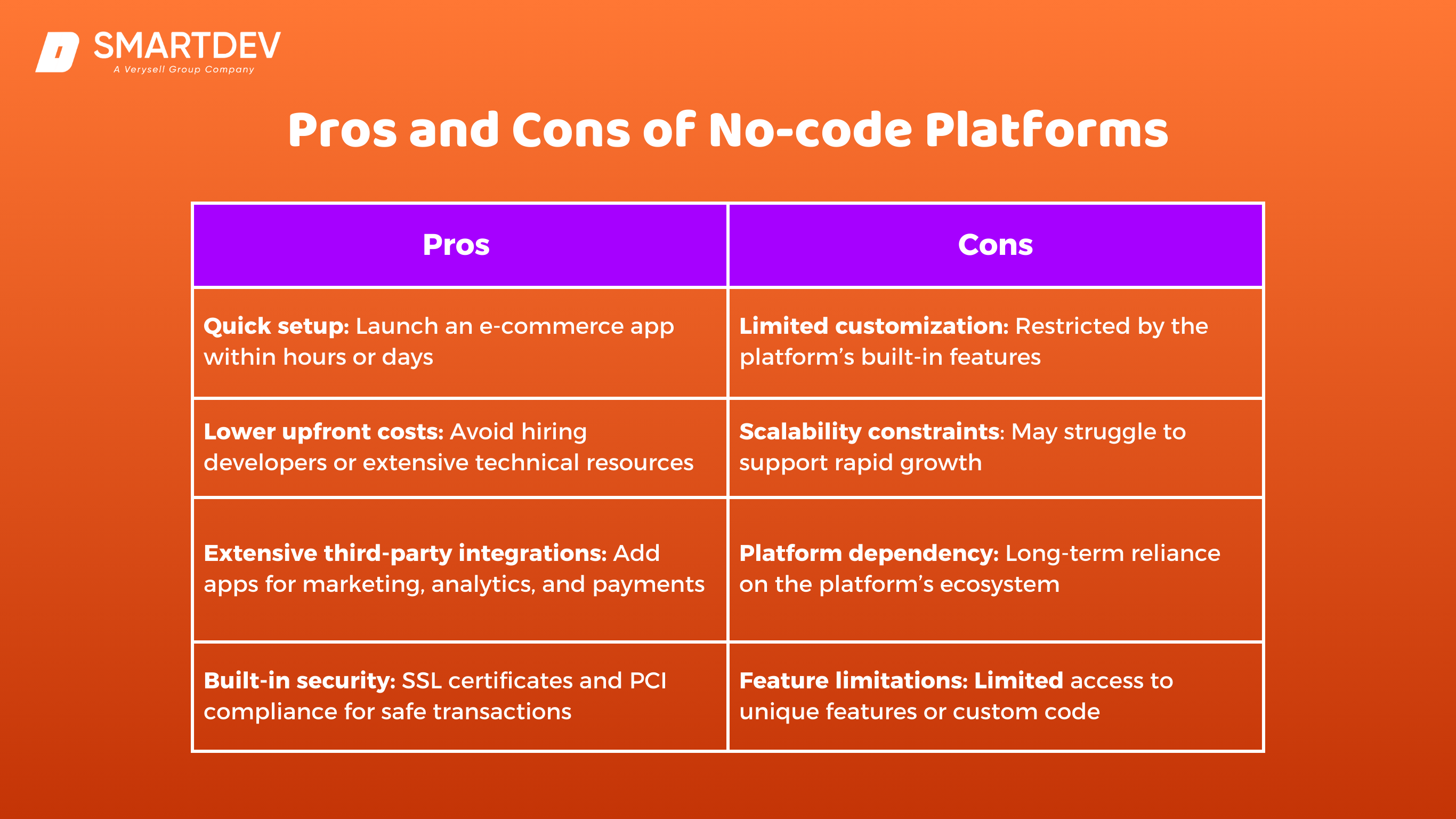
Pros and Cons of No-code Platforms
While no-code platforms offer speed and simplicity, they may have limitations in terms of customization and scalability. Weigh the pros and cons to determine if this approach aligns with your business needs.
Tools for Management and Optimization on No-code Platforms
After setting up a no-code e-commerce platform, leveraging management tools can enhance efficiency:
- Analytics: Google Analytics integrates with no-code platforms to provide insights into customer behavior, conversion rates, and site performance.
- Marketing Automation: MailChimp and Klaviyo allow automated email campaigns tailored to customer segments, driving engagement without manual intervention.
- Customer Support: Chatbots, such as Tidio and Zendesk, offer real-time support options, helping businesses address customer queries promptly.
- Inventory and Order Management: Tools like TradeGecko integrate with platforms like Shopify to automate inventory tracking, replenishment, and order processing.
These tools enable retailers to run optimized, data-driven operations without needing complex, custom-built software.
9. Cost Breakdown of Developing an E-commerce App
Understanding the cost structure of e-commerce app development helps businesses budget effectively and make informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of key cost factors and estimated costs for different app types.
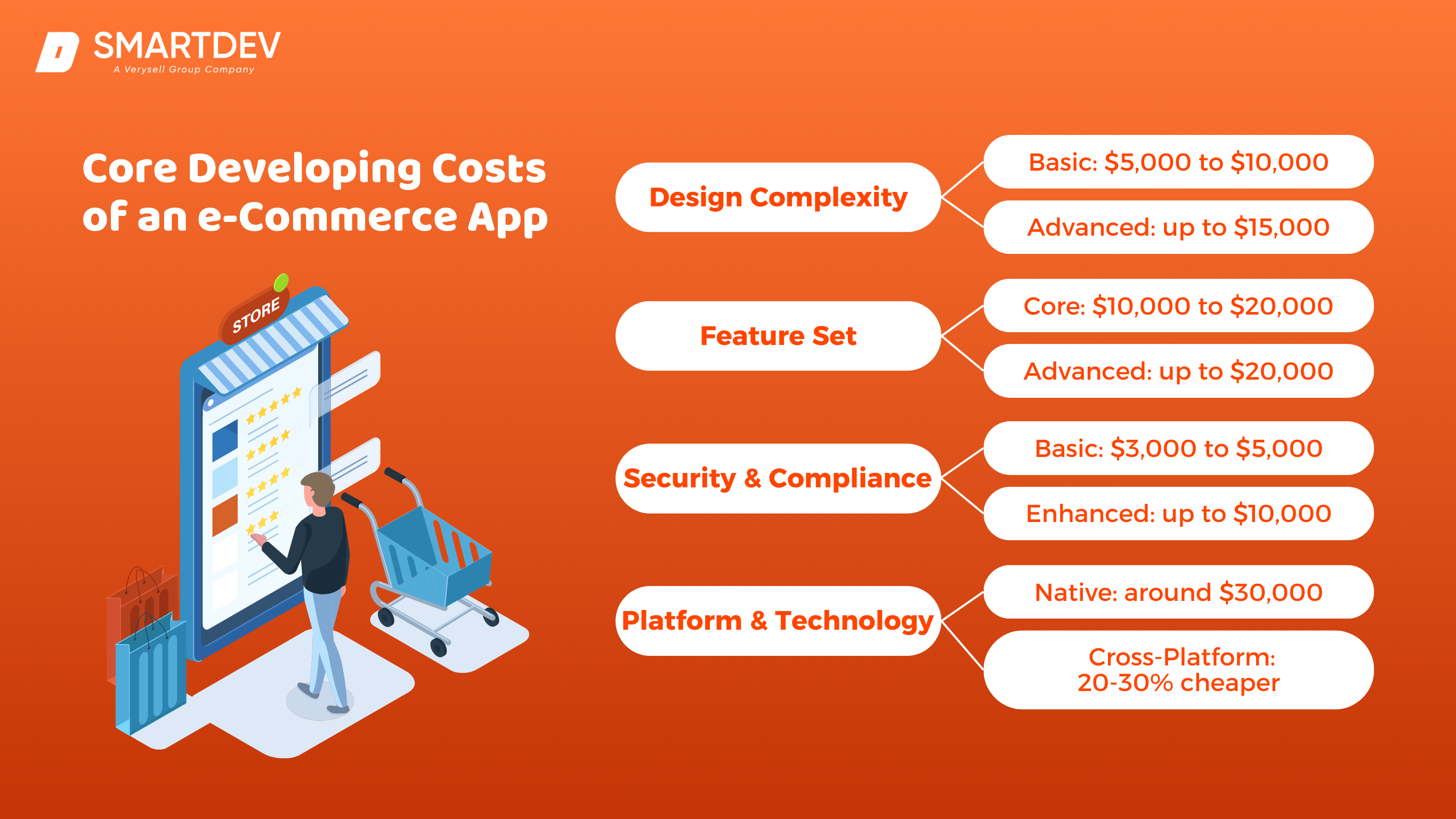
Factors Impacting Development Cost
- Design Complexity
- Basic UI/UX: A simple, minimalist design with basic customization can range from $5,000 to $10,000.
- Advanced UI/UX: A more intricate, branded design with animations or interactive elements can cost upwards of $15,000.
- Feature Set
- Core Features: Basic e-commerce functionalities, like product listings, search, and checkout, generally cost between $10,000 and $20,000.
- Advanced Features: Features like AR try-ons, voice search, and personalized recommendations can increase costs by $20,000 or more due to their complexity.
- Security and Compliance
- Basic Security: SSL certificates, basic encryption, and data compliance can cost around $3,000 to $5,000.
- Enhanced Security: Multi-factor authentication, advanced data encryption, and compliance with standards like PCI DSS can add $10,000 or more to the budget.
- Platform and Technology Costs
- Native vs. Cross-Platform Development: Native apps for iOS and Android cost more (starting around $30,000) due to separate codebases. Cross-platform apps using React Native or Flutter are generally 20-30% cheaper.
Estimated Total Costs for Different Levels of Development
- Basic E-commerce App: $15,000 – $30,000
- Mid-range App with Custom Features: $40,000 – $70,000
- Advanced, Fully Customized App: $80,000 – $200,000+
Budget-Friendly Options: Outsourcing vs. In-house Development
- Outsourcing: Engaging third-party developers in regions with lower labor costs (e.g., Eastern Europe or Asia) can help keep budgets lean while maintaining quality. Outsourcing offers access to specialized skills at a reduced cost.
- In-house Development: In-house teams are often preferred for businesses seeking full control over app features, design, and updates. However, the costs are generally higher, especially when factoring in salaries, benefits, and technology expenses.
Retailers should weigh these options against their long-term goals, considering both the budget and level of control they wish to maintain.
10. Future Trends in E-commerce Applications
E-commerce is continually evolving, with new technologies shaping the future of online shopping. Trends like AI, VR, blockchain, and EFT are transforming how businesses interact with customers. Here’s a look at what the future holds for e-commerce apps.
AI for Personalized Experiences
AI is revolutionizing the personalization of e-commerce. Machine learning algorithms can predict customer preferences, offer tailored recommendations, and optimize marketing strategies. For example, a clothing retailer can leverage AI to analyze browsing patterns and suggest outfits based on individual tastes, improving customer satisfaction and sales.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Online Shopping
VR and AR technologies enable customers to virtually “try on” products. For example, IKEA’s AR app lets users visualize furniture in their homes, bridging the gap between online and in-store experiences. Implementing AR requires specialized development and is still a premium feature, but it can be a game-changer for brands aiming to enhance customer engagement.
Blockchain for Transparent and Secure Transactions
Blockchain is gaining traction in e-commerce for its potential to streamline payment processes and ensure transparency. For high-value products or complex supply chains, blockchain offers a way to verify the authenticity of goods and maintain secure transaction records. Although costly, integrating blockchain can appeal to security-conscious customers and brands prioritizing transparency.
Enhanced Personalization and User Experience Optimization
Improving UX is essential as customers increasingly expect smooth, intuitive shopping journeys. Personalized landing pages, dynamic pricing, and user-driven product recommendations all contribute to a customized shopping experience that retains customer loyalty.
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)
EFT continues to evolve, supporting faster, more secure digital payments. Retailers can reduce reliance on credit cards by integrating EFT, thereby lowering transaction fees. EFT also simplifies international payments, making it ideal for businesses with global customer bases.
11. Conclusion
As e-commerce continues to evolve, leveraging IT applications is essential for business owners aiming to thrive in this dynamic sector. From CRM systems that drive customer loyalty to no-code platforms that offer budget-friendly app solutions, the range of technology available is vast and adaptable. Advanced IT applications not only empower businesses to streamline operations but also enhance customer satisfaction through personalized, secure, and interactive experiences.
Are you ready to integrate these powerful IT applications into your e-commerce strategy? Contact SmartDev to discover how we can help you build a future-ready e-commerce app tailored to your business goals.
FAQ:
1. What are popular names and synonyms for an e-commerce app?
E-commerce apps are also commonly referred to as online shopping apps, digital storefronts, m-commerce apps (mobile commerce), and retail apps.
Other synonyms include mobile retail applications, online marketplace apps, and digital retail platforms. Each term generally describes applications that facilitate online shopping, sales, and customer engagement through digital platforms.
2. What does an e-commerce app do?
An e-commerce app enables businesses to sell products or services online by providing a digital storefront accessible via mobile devices or web browsers. It allows customers to browse products, make purchases, view order statuses, and access customer support.
Additionally, e-commerce apps support backend operations for the retailer, such as inventory management, payment processing, and data analytics for tracking sales and customer behavior.
3. How can businesses improve their e-commerce strategies?
Businesses can enhance their e-commerce strategies by focusing on personalization, investing in user-friendly designs, and optimizing for mobile users. Utilizing data analytics to understand customer preferences, implementing SEO to boost online visibility, and integrating social media marketing can also drive growth.
Ensuring a seamless, responsive shopping experience and offering secure payment options are essential in building customer loyalty and improving conversion rates.
4. Why is mobile e-commerce app development considered the future?
Mobile e-commerce apps are pivotal to the future of retail because they align with consumer trends, particularly the shift towards mobile shopping.
With smartphones being the primary device for online activity, mobile apps allow for more personalized, on-the-go shopping experiences. They also offer features such as push notifications, location-based marketing, and streamlined payment options, all of which enhance convenience and engagement.
5. How can I ensure my e-commerce app meets future business needs?
To ensure your e-commerce app remains relevant, focus on scalability, security, and flexibility. Building on a modular architecture, such as microservices, will allow you to easily add features as your business grows.
Additionally, staying updated with industry trends, integrating AI and data analytics, and ensuring your app meets evolving compliance standards will support future needs and enhance customer trust.
6. What should business owners consider when they want to build an e-commerce app?
When developing an e-commerce app, business owners should consider their target audience, the app’s core functionality, and the technology platform.
Selecting the right development platform (e.g., native, hybrid, or no-code) is crucial, as is planning for scalability. Budgeting for security measures, understanding regulatory requirements, and focusing on a user-friendly design are also essential for building a successful app.
7. What are the essential features my e-commerce mobile application should possess?
An effective e-commerce app should include a visually appealing product catalog, a secure and simple checkout process, and robust payment options. Key features also include user account creation, order tracking, a wish list or cart functionality, customer reviews, and personalized product recommendations.
To build customer loyalty, consider adding loyalty programs, push notifications, and efficient customer support, such as live chat.
8. How do I budget for e-commerce app development?
Budgeting for an e-commerce app requires considering factors like design complexity, desired features, and platform type (native or hybrid). For basic functionality, costs may start around $15,000, but complex apps can exceed $100,000.
Planning for ongoing maintenance, future upgrades, and security also impacts the budget. To control costs, consider using no-code solutions for simple apps, or outsourcing development to a reliable third-party vendor.
References
-
- Ecommerce App Development: 10 Proven Steps + Benefits | Distillery
- E-commerce App Development: Steps, Key Features, Trends | Uptech
- Ecommerce Statistics [Data and Stats Updated Monthly] | Ecommerce Guide
- The 21 Best No-Code App Builders for Any Situation | Knack
- E-commerce Mobile App Development Cost Breakdown | GoMage
- Case Study: How Alibaba Uses AI Chatbots to Serve a Billion Customers
- Amazon Success Story: How it Became the E-commerce Giant