Introduction
Fintech is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). From enhancing customer experiences to fortifying security measures, AI is becoming an indispensable asset in the financial technology sector.
This comprehensive guide delves into the pivotal role of AI in fintech, exploring its applications, benefits, and the challenges that accompany its adoption.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Fintech?
 Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. These processes include learning (acquiring information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. Core technologies underpinning AI include machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision.
In fintech, AI is leveraged to automate and enhance financial services. This includes applications such as fraud detection, customer service automation through chatbots, personalized financial advice, and credit scoring. By processing vast amounts of data efficiently, AI enables fintech companies to offer more accurate, secure, and user-friendly services.
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming Fintech
AI is revolutionizing fintech by enabling real-time data analysis, which is crucial for tasks like fraud detection and risk assessment. For instance, AI algorithms can identify unusual transaction patterns, flagging potentially fraudulent activities instantly, thereby enhancing security measures.
Moreover, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are improving customer service by providing instant responses to queries, handling transactions, and offering personalized financial advice. This not only enhances user experience but also reduces operational costs for fintech companies.
In the realm of credit scoring, AI models analyze a broader range of data points beyond traditional credit histories, enabling more inclusive lending practices. This approach allows fintech firms to assess creditworthiness more accurately, especially for individuals with limited credit histories.
Key Statistics and Trends Highlighting AI Adoption in Fintech
AI is Reshaping Risk Management and Fraud Detection: By 2025, AI is expected to reduce false positives in fraud detection by up to 80%, according to Deloitte. Fintech firms are leveraging machine learning to spot suspicious patterns in real time, helping institutions proactively manage fraud risks and avoid financial losses.
Generative AI is Revolutionizing Financial Services: A recent Gartner survey found that 77% of fintech companies plan to adopt generative AI to develop hyper-personalized financial products and automate customer support. These applications allow firms to deliver tailored experiences and scale customer service efficiently.
AI Use Is Broadening Across Fintech Operations: McKinsey reports that 78% of financial services firms now deploy AI in at least one function – ranging from underwriting to portfolio management. This widespread use shows that AI is no longer experimental; it’s a strategic asset driving decision-making and innovation across the value chain.
AI is Unlocking Cost and Efficiency Gains: According to Accenture, banks and fintechs using AI for front- and back-office operations have achieved up to 30% cost savings while improving customer engagement. These savings stem from AI’s ability to automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and accelerate service delivery.
Want to see how AI is redefining what is possible in fintech? Visit How to Integrate AI into Your Business in 2025 and explore actionable strategies for AI-driven transformation.
Business Benefits of AI in Fintech
AI is driving measurable improvements across fintech: cutting costs, boosting decision quality, and unlocking new revenue models. These benefits go far beyond automation; they represent a strategic shift in how financial services are delivered, scaled, and personalized.

Real-Time Fraud Detection and Prevention
Modern fraud schemes are adaptive and increasingly sophisticated, exploiting vulnerabilities in digital payment systems and transaction workflows. AI enables financial institutions to analyze thousands of variables per second, detecting anomalies in behavioral patterns, device fingerprints, geolocation mismatches, and transaction velocity without delay.
By incorporating machine learning into fraud operations, fintech can identify subtle signs of abuse across payment ecosystems. Unlike traditional models that rely on past data, AI systems provide proactive defense mechanisms, reducing false positives and operational friction. This improves not only security outcomes but also customer experience, by minimizing account disruptions from inaccurate flags.
Hyper-Personalized Financial Products
Customer expectations in fintech have shifted from mass-market offerings to individualized experiences. AI algorithms analyze granular user data, such as transaction history, income cycles, life stage events, and investment behaviors, to dynamically tailor product recommendations, credit options, or savings nudges.
Unlike static segmentation approaches, AI-driven personalization evolves with the user, responding in real-time to behavioral changes. For example, a user’s drop in spending or shift in location can trigger contextual alerts or spending advice. This level of precision creates higher engagement, deeper trust, and more meaningful financial relationships, often outperforming traditional CRM-based marketing strategies.
Enhanced Credit Risk Assessment
Credit assessment has traditionally depended on narrow indicators like income, credit score, and repayment history, leaving millions of potential borrowers underserved. AI expands the lens by ingesting alternative data sources such as utility bill payments, mobile phone usage, gig economy income, and even browsing behaviors. These data points offer a more holistic view of financial behavior, especially for users with little or no credit history.
This redefinition of creditworthiness enables fintech to serve younger, informal, or non-traditional earners with greater confidence. Moreover, AI-powered underwriting models can rapidly adjust based on macroeconomic shifts, detecting early signs of risk and recalibrating exposure. As a result, firms reduce default rates while reaching broader market segments, both high-impact outcomes in a competitive lending environment.
Automation of Back-Office Operations
Behind every fintech interface is a web of manual tasks – document verification, transaction matching, compliance checks – that strain operations at scale. AI automates these with precision, using OCR (optical character recognition), natural language processing, and machine vision to classify documents, extract data, and validate identities across disparate systems.
This automation doesn’t merely reduce headcount; it improves process reliability, auditability, and regulatory alignment. In onboarding, for example, AI can verify identity documents, cross-check sanctions lists, and assess risk profiles within minutes. These capabilities accelerate time to revenue while minimizing errors that could result in compliance violations or user churn.
Smarter Customer Support with Virtual Agents
Customer support is a high-cost, high-volume function where responsiveness directly impacts satisfaction and retention. AI-powered chatbots and voice agents trained on financial-specific language models now resolve routine requests, like balance inquiries, password resets, or transaction disputes, through natural dialogue and contextual memory.
These systems go beyond scripts, handling multi-step workflows and integrating with backend APIs to take real action. When escalation is needed, they provide context to human agents, reducing resolution time and improving first-contact accuracy. The cumulative effect is not just cost savings, but also a scalable, always-on support channel that aligns with the expectations of digital-first customers.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Fintech
While the promise of AI is clear, the path to successful implementation in fintech is anything but straightforward. The complexity of regulated environments, combined with technical and ethical concerns, continues to present formidable obstacles.
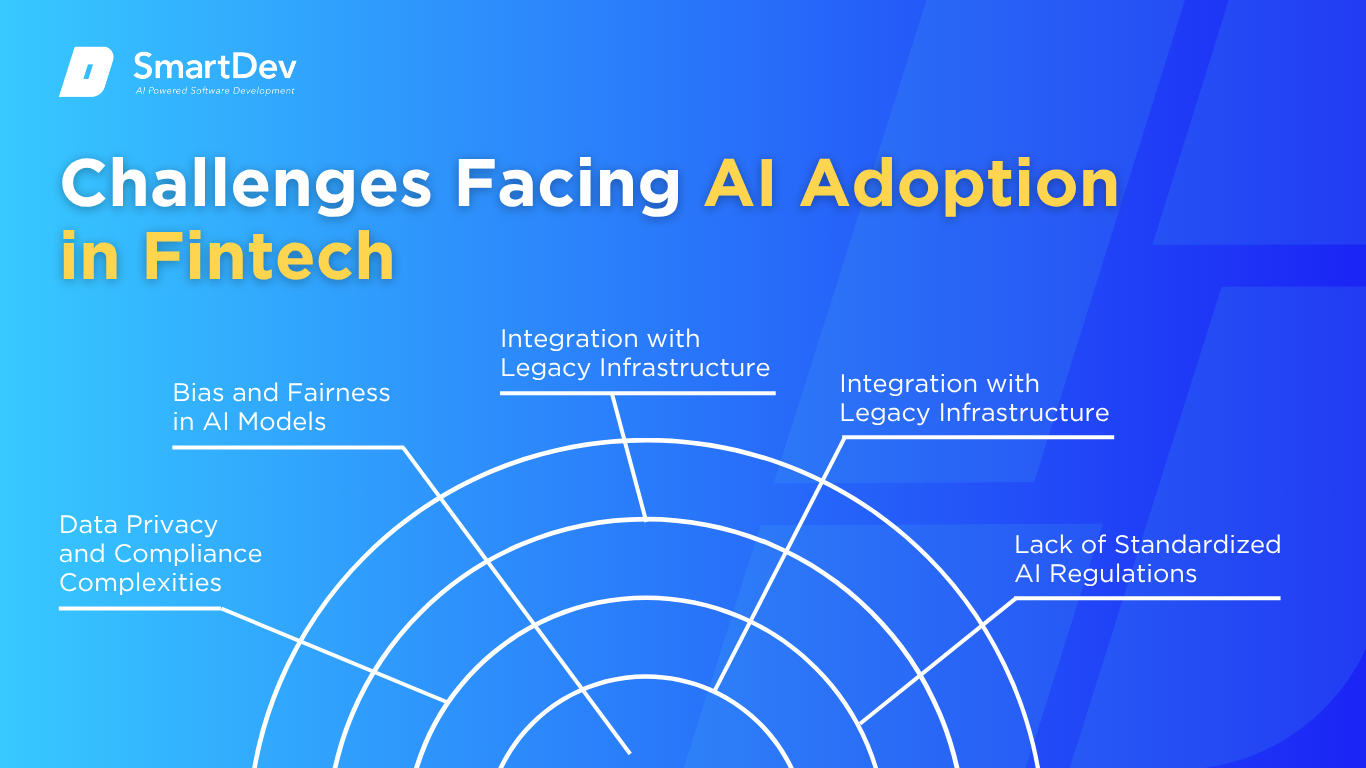
Data Privacy and Compliance Complexities
AI thrives on data, but fintech firms operate in one of the most tightly regulated data environments. Processing personally identifiable information (PII), payment data, and behavioral signals demands strict compliance with global frameworks such as GDPR, CCPA, and PSD2. Every layer of AI deployment like data ingestion, model training, decision execution must be auditable and explainable.
This creates operational overhead and legal risk. For example, training a fraud detection model on transaction data could inadvertently expose private user details if not properly anonymized. Moreover, regulations increasingly demand transparency around algorithmic decisions, requiring fintech to provide “clear reasoning” for AI-driven outcomes like credit denials – something many current systems are not equipped to do.
Bias and Fairness in AI Models
Even the most advanced AI models can carry hidden biases if the training data reflects historical inequities. In fintech, this can manifest in discriminatory lending patterns, unfair interest rates, or unequal fraud detection thresholds. The reputational and legal risks of such outcomes are enormous, especially as regulators begin scrutinizing algorithmic accountability.
Solving bias is not as simple as “cleaning the data.” It requires deliberate inclusion of diverse datasets, frequent fairness audits, and the integration of bias detection metrics into model performance tracking. Few fintech have internal capabilities or governance frameworks to execute these safeguards rigorously, leaving many exposed to ethical and compliance pitfalls.
Integration with Legacy Infrastructure
Despite being tech-driven, many fintech still depend on legacy banking or ERP systems to manage core services like payments, reconciliation, and reporting. These platforms often lack the APIs, data access layers, and real-time processing capacity needed to support modern AI applications.
Integrating AI into such environments typically requires building middleware layers, migrating to cloud infrastructure, or re-architecting data pipelines, each a costly, high-risk endeavor. This slows down time-to-value and limits experimentation, especially for smaller firms with constrained engineering resources.
Scarcity of Specialized Talent
AI in fintech sits at the intersection of data science, machine learning, regulatory knowledge, and financial domain expertise. Hiring professionals who can navigate both AI architecture and sector-specific challenges like AML compliance or credit scoring is increasingly competitive and expensive.
Moreover, retaining this talent is equally difficult, as large tech firms often lure top candidates with higher salaries and broader AI portfolios. Many fintechs are forced to rely on third-party vendors or open-source tools, which can limit control and differentiation in AI strategy.
Lack of Standardized AI Regulations
Regulatory bodies are only beginning to define formal rules for AI usage in financial services. As a result, fintech firms operate in a fragmented legal landscape—where practices acceptable in one jurisdiction may be restricted to another. This lack of clarity hinders product design and go-to-market planning.
For instance, generative AI used in customer interactions may raise legal questions about liability, data ownership, or manipulation risks. Without clear guidelines, firms often self-regulate or delay adoption altogether. The absence of industry-wide standards also makes benchmarking AI performance and safety difficult, especially when working with cross-border customers.
Specific Applications of AI in Fintech
AI is revolutionizing the fintech industry, enabling companies to enhance efficiency, personalize services, and mitigate risks. This section explores the specific applications of AI in fintech, real-world case studies, and innovative solutions shaping the future of financial services.

1. Credit Risk Assessment and Management
AI-driven credit risk assessment is transforming the way financial institutions evaluate borrowers. Traditional credit scoring models often rely on limited data, potentially excluding creditworthy individuals without extensive credit histories. AI models, however, can analyze a broader range of data, including transaction history, social media activity, and alternative financial behaviors, to assess creditworthiness more accurately.
These AI systems utilize machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and predict default risks. By continuously learning from new data, they adapt to changing economic conditions and borrower behaviors. This dynamic approach allows for more inclusive lending practices, enabling institutions to serve a wider customer base while managing risk effectively.
JPMorgan Chase utilizes AI and machine learning to enhance its credit risk assessment processes. By analyzing vast datasets, including transaction histories and market trends, the bank can more accurately predict creditworthiness and potential defaults. This approach not only streamlines loan approvals but also reduces the risk of lending to high-risk borrowers.
2. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Fraud detection is a critical application of AI in fintech, addressing the increasing sophistication of fraudulent activities. Traditional rule-based systems often struggle to detect novel fraud patterns, leading to financial losses and reputational damage.
AI-powered fraud detection systems employ machine learning and anomaly detection techniques to identify unusual transaction patterns in real-time. By analyzing vast amounts of data, including transaction history, user behavior, and device information, these systems can detect and prevent fraudulent activities more effectively.
Mastercard has integrated AI into its fraud detection systems, notably through its Decision Intelligence platform. This system analyzes transaction data in real-time, assessing factors like purchase history and user behavior to assign risk scores. By doing so, Mastercard can identify and prevent fraudulent activities within milliseconds, enhancing security for both merchants and consumers.
3. Personalized Financial Services
Personalization in financial services enhances customer engagement and satisfaction. AI enables fintech companies to offer tailored financial advice, product recommendations, and budgeting tools based on individual customer data.
By leveraging natural language processing and machine learning, AI systems can analyze customer interactions, spending habits, and financial goals to provide personalized insights. The operational value of AI-driven personalization includes increased customer retention, higher product uptake, and improved financial well-being for users.
Bank of America’s virtual assistant, Erica, leverages AI to provide personalized financial guidance to customers. Erica can assist with tasks such as checking balances, providing spending insights, and offering budgeting advice. With over 42 million users and more than 2 billion interactions, Erica exemplifies how AI can enhance customer engagement and satisfaction in banking.
4. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are transforming customer service in fintech by providing instant, 24/7 support. These tools handle routine inquiries, assist with transactions, and offer financial advice, improving customer experience and operational efficiency.
Natural language processing enables chatbots to understand and respond to customer queries conversationally. Machine learning allows them to learn from interactions and improve over time, offering increasingly accurate and helpful responses. The strategic benefits include reduced customer service costs, faster response times, and enhanced user satisfaction.
CBA has implemented AI-powered chatbots to handle customer inquiries, processing approximately 50,000 daily interactions. These virtual assistants provide context-aware responses, improving efficiency, and allowing human staff to focus on more complex issues. The integration of AI in customer service has significantly enhanced the bank’s operational capabilities.
5. Algorithmic Trading and Portfolio Management
AI is revolutionizing trading and investment management through algorithmic trading and robo-advisors. These systems analyze market data, news, and trends to make informed investment decisions and manage portfolios efficiently.
Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and predict market movements, enabling high-frequency trading strategies. Robo-advisors use AI to assess individual risk profiles and financial goals, providing personalized investment recommendations. The operational advantages include increased trading speed, reduced human error, and accessible investment services for a broader audience.
AQR Capital Management, a leading quantitative hedge fund managing $136 billion, has increasingly adopted AI and machine learning in its trading strategies. By analyzing vast amounts of market data, AQR’s AI systems can identify patterns and execute trades with improved accuracy and speed. This shift has contributed to enhanced performance and competitiveness in the financial markets.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Regulatory compliance is a complex and resource-intensive aspect of financial services. AI streamlines compliance processes by automating data analysis, monitoring transactions, and generating reports, reducing the burden on compliance teams.
AI systems can detect suspicious activities, ensure adherence to regulations, and adapt to changing compliance requirements. Natural language processing aids in analyzing legal documents and extracting relevant information for compliance purposes. The strategic value includes reduced compliance costs, improved accuracy, and timely reporting.
Germany’s financial regulator, BaFin, employs AI to detect market abuse and monitor trading activities. The AI system enhances the accuracy of identifying suspicious patterns, thereby increasing the likelihood of catching offenders. This implementation underscores the role of AI in strengthening regulatory compliance and maintaining market integrity.
Examples of AI in Fintech
Real-World Case Studies
Real-world AI applications in fintech demonstrate tangible outcomes and operational advantages. These examples provide actionable insights into how leading companies are using AI to reshape financial services.

1. American Express: Leveraging AI for Customer Insights and Fraud Control
American Express (Amex) faced increasing pressure to both improve customer personalization and enhance fraud detection in a rapidly digitizing environment. As transaction volumes grew and customer expectations for tailored services intensified, legacy systems proved insufficient for real-time insights and proactive fraud prevention. Amex needed a more dynamic system that could interpret massive volumes of customer data efficiently and securely.
To meet this challenge, Amex integrated deep learning models capable of analyzing billions of transaction records, customer behavior patterns, and geolocation data in real-time. These models allowed Amex to deliver highly personalized offers and alerts to customers while simultaneously identifying anomalies that could indicate fraudulent behavior. Additionally, AI was used to dynamically segment customers and predict spending behaviors, enabling targeted marketing campaigns with greater ROI.
The result was a significant increase in fraud detection rates without a rise in false positives, enhancing both security and customer satisfaction. Amex also reported improved marketing conversion rates, thanks to AI-driven personalization efforts that better matched offers to individual preferences. This dual implementation of AI for both fraud detection and personalization illustrates Amex’s leadership in deploying intelligent systems that improve operational efficiency and deepen customer loyalty.
2. Bank of America: Transforming Customer Service with Erica
Bank of America recognized the need to enhance customer service efficiency and personalization in the face of increasing customer inquiries and the demand for instant support. Traditional customer service channels were insufficient to meet these evolving expectations.
In response, the bank launched Erica, an AI-powered virtual assistant that utilizes natural language processing and machine learning to interact with customers. Erica assists users with tasks such as checking balances, providing budgeting tips, and alerting them to unusual charges, all through a conversational interface.
Since its launch, Erica has engaged in over 2 billion interactions with more than 42 million clients, significantly improving customer engagement and satisfaction. The virtual assistant has become a cornerstone of Bank of America’s digital strategy, streamlining customer service operations and providing personalized financial guidance at scale.
3. Klarna: Revolutionizing Customer Support with AI Chatbots
Klarna faced challenges in scaling its customer support operations to handle a growing volume of inquiries across multiple languages and regions. The reliance on human agents led to increased operational costs and longer response times.
To overcome this, Klarna implemented an AI-powered chatbot developed in collaboration with OpenAI. This chatbot manages two-thirds of customer service inquiries, effectively performing the work equivalent to 700 full-time agents. It supports customer service in 35 languages across 23 countries, handling queries in under two minutes.
The deployment of the AI chatbot has led to a $40 million profit improvement, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction while maintaining the quality of service. Klarna’s move highlights AI’s significant impact on operational scalability and the ability to deliver prompt support globally.
Innovative AI Solutions
Generative AI is enabling hyper-personalized banking by creating tailored financial advice, investment content, and educational tools. Banks are deploying this technology to build deeper customer relationships, increase digital engagement, and support financial literacy initiatives.
AI-enhanced document processing automates the extraction, classification, and analysis of financial documents such as loan applications and tax forms. This reduces manual labor, shortens processing times, and minimizes human error, especially in underwriting and compliance workflows.
In regulatory technology (RegTech), AI systems monitor transactions and scan regulatory updates in real time to ensure compliance. These tools alert compliance officers to potential violations, allowing proactive risk management and reducing penalties. As regulatory complexity increases, AI is becoming indispensable in maintaining compliance integrity.
AI-Driven Innovations Transforming Fintech
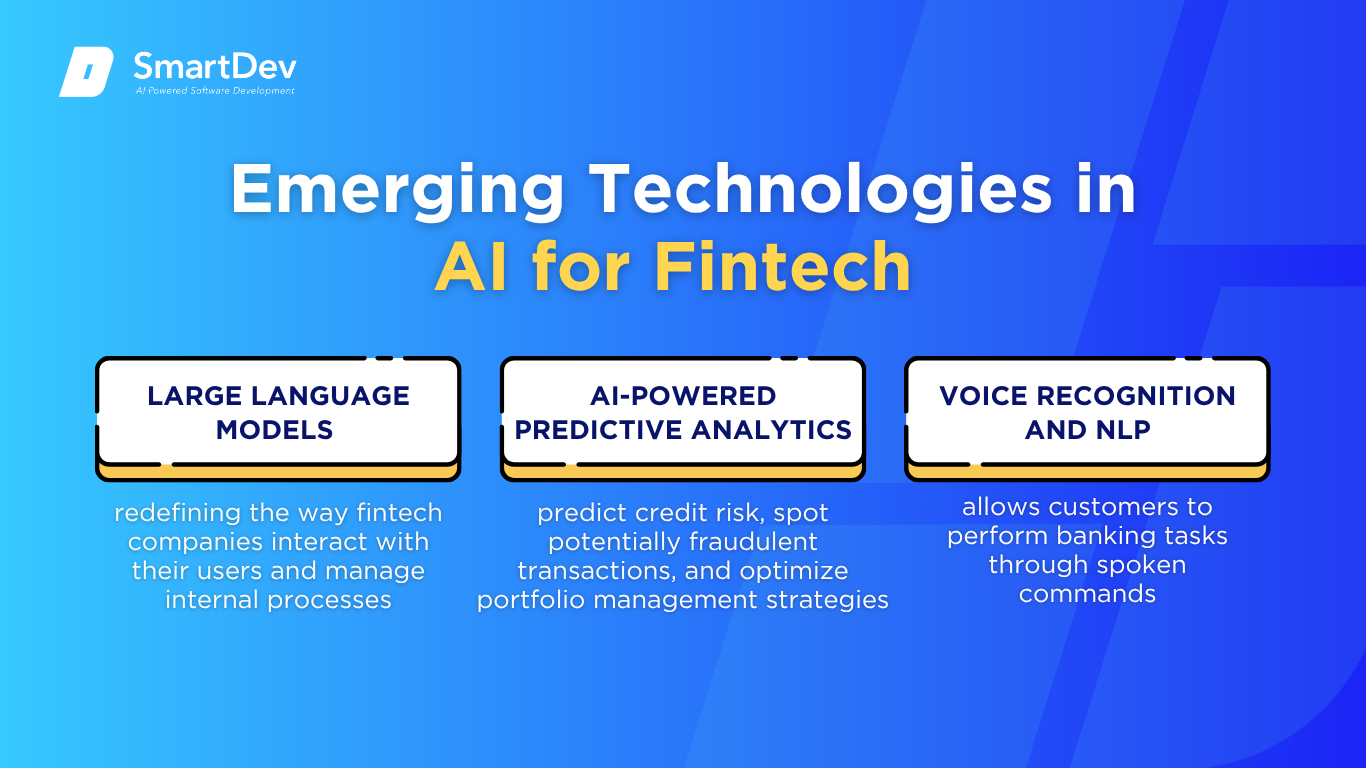
Emerging Technologies in AI for Fintech
Large Language Models (LLMs) are rapidly redefining the way fintech companies interact with their users and manage internal processes. Tools like OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Anthropic’s Claude can understand, generate, and contextualize human language with impressive accuracy. In fintech, this translates to more responsive and personalized customer service chatbots, faster document processing, and smarter virtual assistants.
AI-Powered Predictive Analytics is another breakthrough transforming how fintech companies anticipate and react to market trends and customer behavior. By analyzing historical data, transaction patterns, and real-time activity, AI systems can predict credit risk, spot potentially fraudulent transactions, and optimize portfolio management strategies. This foresight enables companies to make more informed decisions, reduce financial losses, and offer better, more tailored services to customers.
Voice Recognition and NLP are also reshaping user interaction on fintech platforms. This technology allows customers to perform banking tasks through spoken commands, enhancing accessibility and convenience. More importantly, it combines biometric voice identification to ensure security and prevent fraud. Fintech apps now let users check balances, transfer funds, or get investment updates simply by speaking with no typing required.
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
AI contributes significantly to sustainability in fintech by reducing waste through predictive analytics. By analyzing transaction data and customer behavior, AI can forecast demand, optimize resource allocation, and minimize unnecessary expenditures. This predictive capability leads to more sustainable financial practices and reduced environmental impact.
Moreover, AI optimizes energy consumption within fintech operations. Smart systems powered by AI monitored and managed energy usage in data centers and offices, leading to significant energy savings. These systems adjust energy consumption based on real-time needs, promoting eco-friendly practices, and reducing operational costs.
How to Implement AI in Fintech
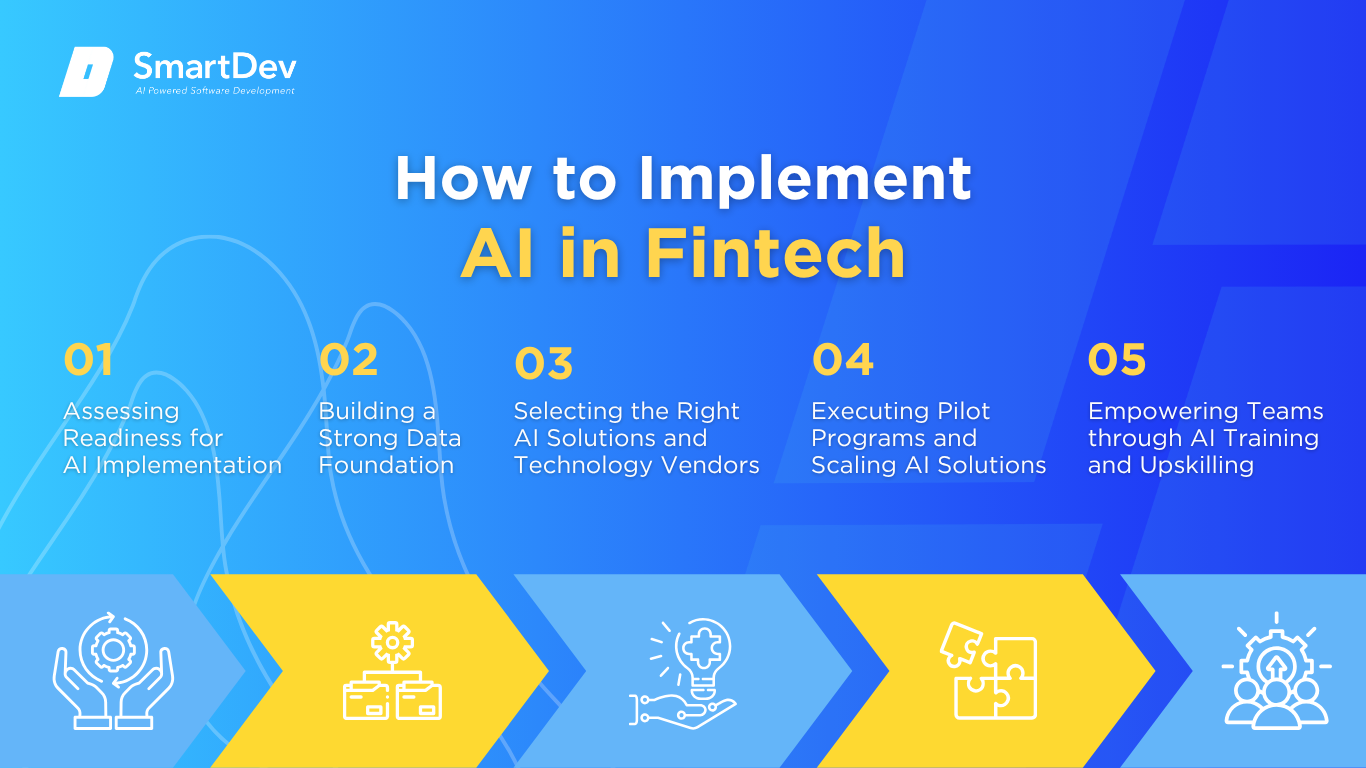
Step 1: Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Before integrating AI, fintech companies must assess their readiness by identifying business areas suitable for AI integration. This involves evaluating processes that can benefit from automation, such as customer service, fraud detection, and risk assessment. Understanding the specific needs and challenges of these areas ensures a targeted and effective AI implementation.
Additionally, companies should evaluate their technological infrastructure and workforce capabilities. Ensuring that the existing systems can support AI technologies and that employees are prepared for the transition is crucial. This assessment helps in developing a comprehensive AI adoption strategy that aligns with the company’s goals.
Step 2: Building a Strong Data Foundation
A robust data foundation is essential for successful AI implementation. Fintech companies must focus on data collection, ensuring that they gather relevant and high-quality data from various sources. This data serves as the backbone for AI algorithms, enabling accurate predictions and insights.
Data cleaning and management are equally important. Implementing best practices for data governance ensures that the data used is consistent, accurate, and secure. Proper data management facilitates efficient AI operations and compliance with data protection regulations.
Step 3: Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Selecting appropriate AI tools and vendors is critical. Fintech companies should evaluate AI platforms based on their compatibility with existing systems, scalability, and the specific needs of the business. Tailored solutions that address unique challenges in the fintech sector are more likely to yield positive results.
Collaborating with reputable vendors who have experience in the fintech industry can provide valuable insights and support. These partnerships ensure that the AI solutions implemented are reliable, efficient, and aligned with industry standards.
Step 4: Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Implementing AI should begin with pilot testing in selected areas to evaluate performance and identify potential issues. This approach allows fintech companies to make necessary adjustments before a full-scale deployment, reducing risks and ensuring a smoother transition.
Once the pilot tests yield satisfactory results, scaling up involves expanding AI applications across various departments. Continuous monitoring and evaluation during this phase are essential to maintain effectiveness and adapt to evolving business needs.
Step 5: Training Teams for Successful Implementation
Employee training is vital for the successful integration of AI. Fintech companies should invest in upskilling programs that equip employees with the knowledge and skills to work alongside AI technologies. This includes understanding AI functionalities, interpreting AI-generated insights, and managing AI tools effectively.
Creating a culture that embraces innovation, and continuous learning fosters a positive environment for AI adoption. Encouraging collaboration between AI systems and human expertise leads to enhanced productivity and job satisfaction.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Fintech
Key Metrics to Track Success
To truly evaluate AI’s ROI in fintech, companies must focus on metrics that connect directly to performance gains. One of the clearest is productivity improvement. AI enables faster, automated workflows in areas like loan processing, customer service, and compliance. This allows employees to shift toward more strategic tasks, improving overall organizational agility and output.
Cost savings through automation is another core indicator. Machine learning models streamline processes by reducing manual effort, optimizing resource allocation, and minimizing errors. In fraud detection, for instance, AI reduces false positives and operational overhead. These efficiencies directly lower operational costs and accelerate decision-making, impacting profitability.
In parallel, fintechs track customer experience metrics—from satisfaction (CSAT) and retention to error rates and net promoter scores (NPS). AI-driven personalization and proactive service significantly enhance user engagement. Combined with financial indicators like revenue growth or cost per acquisition, these metrics paint a full picture of AI’s business impact.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Klarna’s AI assistant exemplifies what automation can deliver. Resolving two-thirds of all customer chats—around 2.3 million a month—it performs the work of 700 agents in under two minutes per interaction. The result? A projected $40 million profit boost in 2024 thanks to higher service efficiency, lower costs, and better customer outcomes.
DBS Bank in Singapore has also seen impressive ROI from AI. Its chatbots manage common queries around the clock, freeing agents for more complex issues. Behind the scenes, AI models analyze customer data to deliver targeted offers and detect fraud. These changes improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction, reinforcing DBS’s leadership in digital banking.
In the U.S., Upstart uses AI to enhance lending. Instead of relying on traditional credit scores, its algorithms analyze alternative data like education and work history. This enables more accurate risk assessments, higher loan approval rates, and reduced defaults. As a result, Upstart has expanded financial access while maintaining strong financial returns.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Despite the advantages, AI implementation in fintech can encounter challenges. Common pitfalls include inadequate data quality, lack of clear objectives, and resistance to change among employees. To mitigate these issues, companies should establish clear goals, ensure data integrity, and foster an organizational culture that supports innovation.
Engaging stakeholders throughout the AI adoption process and providing continuous training can also alleviate concerns and promote successful integration. Regularly reviewing and updating AI strategies ensures alignment with evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Future Trends of AI in Fintech

Predictions for the Next Decade
The next decade is poised to witness significant advancements in AI applications within fintech. Emerging trends include the development of more sophisticated AI algorithms for personalized financial services, enhanced fraud detection systems, and the integration of AI with blockchain technologies for secure transactions.
Moreover, the adoption of AI is expected to expand into areas like wealth management, insurance, and regulatory compliance, offering more comprehensive and efficient financial solutions. These developments will likely lead to increased competition and innovation within the fintech industry.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To remain competitive, fintech companies must stay abreast of technological advancements and continuously adapt their strategies. Investing in research and development, fostering partnerships with tech innovators, and maintaining a customer-centric approach are essential.
Additionally, embracing a proactive stance on regulatory compliance and ethical AI practices is crucial. By prioritizing transparency, data privacy, and inclusivity, fintech companies can build trust and ensure sustainable growth in an increasingly AI-driven landscape.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI is transforming fintech at every level, reshaping customer service, risk management, fraud detection, and decision-making. Generative AI, predictive analytics, computer vision, and voice technologies drive faster, more accurate, and personalized financial services. The result is improved efficiency, reduced operational costs, and better customer outcomes across the board.
However, to fully capitalize on these benefits, successful AI implementation requires a strategic approach. That means building a solid data foundation, ensuring system readiness, and selecting the right tools tailored to fintech use cases. Continuous evaluation of outcomes along with a commitment to upskilling teams ensures that AI not only delivers ROI but evolves with the organization’s needs.
Moving Forward: A Path to Progress
There’s never been a more pivotal moment to rethink what AI can do for your fintech operations. As AI technologies advance at an unprecedented pace, early adopters are already gaining competitive advantages: cutting costs, accelerating compliance, and transforming customer engagement. If your systems still rely heavily on manual processes or outdated data flows, now is the time to act.
At SmartDev, we help fintech innovators turn AI potential into real-world performance. Whether it’s automating fraud detection, deploying conversational AI for customer support, or integrating predictive models into your core offerings, our tailored solutions are built around your business goals. From pilot programs to full-scale deployments, we’re here to guide your AI journey with precision and impact.
Let’s unlock the future of fintech together, partner with SmartDev and power smarter, faster, and more secure financial services today.
—
References:
- AI to Fight Insurance Fraud | Deloitte
- The State of AI: How Organizations Are Rewiring to Capture Value | McKinsey
- Gartner Hype Cycle Shows Generative AI in Finance Is at the Peak of Inflated Expectations | Gartner
- Banking Top 10 Trends 2024 | Accenture
- AI for Payments: Efficiency and Fraud Reduction | JPMorgan
- Mastercard Uses AI for Credit Card Fraud Detection | Business Insider
- Erica: AI-Powered Digital Banking Assistant | Bank of America
- Reimagining Banking with AI | Commonwealth Bank of Australia
- AQR Capital Management Embraces AI for Trading Decisions | The Outpost
- GenAI Conversations in Financial Innovation | American Express Ventures