Embedded finance is revolutionizing the financial services landscape by integrating financial services into non-financial products. This paradigm shift is enabling companies across various sectors to offer financial services directly within their platforms, creating seamless customer experiences and unlocking new revenue streams. The rise of embedded finance is not only reshaping the industry but also blurring the lines between financial and non-financial services. This blog post explores the emergence of embedded finance, its impact on the industry, the role of nonbanks in driving this transformation, and a real-life case study illustrating these changes.
The Concept of Embedded Finance
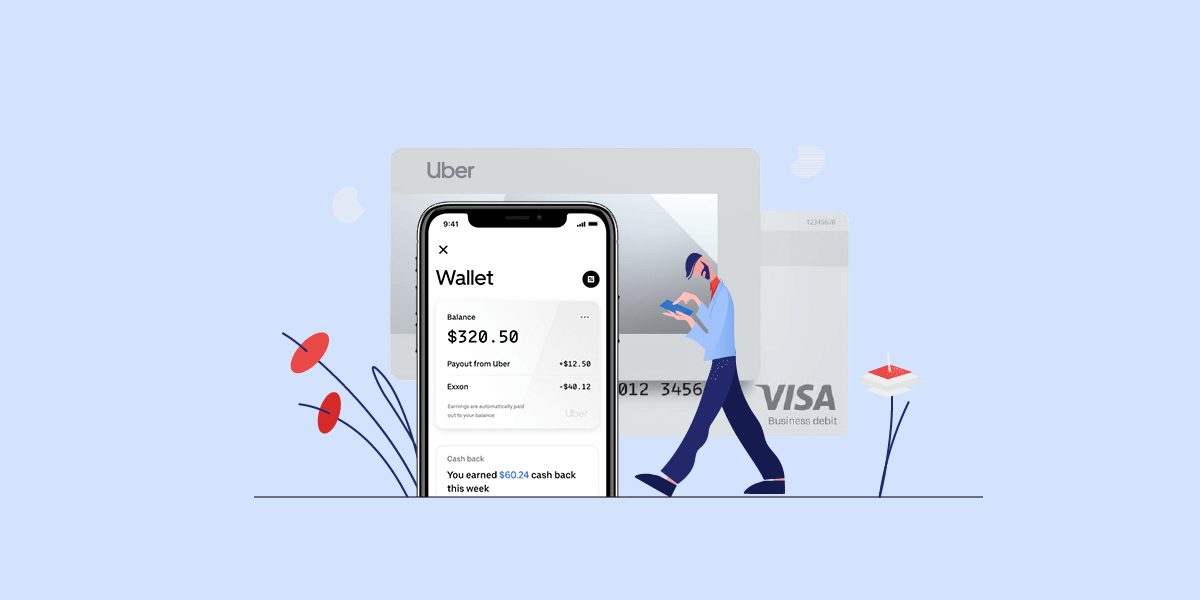
Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial services into the products and services of non-financial companies. This allows businesses to offer payment processing, lending, insurance, and other financial services within their own ecosystems. For example, ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft provide drivers with integrated banking services, while e-commerce platforms like Shopify enable merchants to access capital and manage payments directly within their systems (McKinsey, 2021).
The concept is rooted in the idea of making financial services more accessible and convenient by embedding them in everyday activities. This approach reduces friction for consumers and businesses, creating a more streamlined experience. According to a report by Bain & Company (2022), the embedded finance market is projected to grow to $7 trillion by 2030, driven by increasing demand for integrated financial solutions.
The Role of Nonbanks
Nonbanks, such as technology companies and fintech startups, are at the forefront of the embedded finance revolution. These entities leverage their technological expertise and large customer bases to offer financial services without the need for traditional banking infrastructure. This has led to a surge in innovative financial products and services that cater to specific customer needs.

One prominent example is Stripe, a technology company that provides payment processing services. Stripe’s embedded finance solutions allow businesses to accept payments, manage subscriptions, and access financing seamlessly. By embedding financial services into their platforms, nonbanks like Stripe are able to create new revenue streams and enhance customer loyalty (Financial Times, 2021).
Another significant player is Square, which offers a suite of financial tools for small businesses. Square’s ecosystem includes payment processing, point-of-sale systems, and business financing, all integrated into a single platform. This enables small business owners to manage their financial operations more efficiently and access services that were previously only available through traditional banks (Square, 2021).
Transforming the Customer Experience
Embedded finance is fundamentally changing the way customers interact with financial services. By integrating these services into non-financial platforms, companies can offer a more holistic and convenient experience. For instance, a consumer purchasing a product on an e-commerce site can now access financing options at the point of sale, making it easier to complete the purchase. This not only improves the customer experience but also increases conversion rates for businesses.
Moreover, embedded finance enables personalized financial solutions tailored to individual needs. Companies can leverage data from their platforms to offer customized lending, insurance, and investment products. This level of personalization was previously difficult to achieve with traditional financial services. A report by Accenture (2021) highlights that 63% of consumers are more likely to purchase financial products from non-financial brands that they trust, emphasizing the importance of personalized, embedded financial solutions.
Embedded finance also enhances customer loyalty by creating a seamless and integrated experience. For example, travel booking platforms can offer insurance and financing options directly within their booking process, ensuring that customers have all the financial services they need without leaving the platform. This convenience fosters greater customer satisfaction and loyalty, as customers appreciate the ease and efficiency of having all their needs met in one place (Accenture, 2021).
Business Benefits and Revenue Streams
For businesses, embedded finance presents significant opportunities for new revenue streams and improved customer engagement. By integrating financial services into their offerings, companies can monetize their existing customer base in new ways. For example, an online marketplace can offer sellers access to working capital loans based on their sales data, generating additional revenue through interest and fees (Bain & Company, 2022).
Additionally, embedded finance can drive higher customer retention and lifetime value. By offering integrated financial services, businesses can create more stickiness in their ecosystems, making it harder for customers to switch to competitors. This is particularly valuable in highly competitive markets where customer loyalty is crucial for long-term success (McKinsey, 2021).
Regulatory Considerations
While embedded finance offers numerous benefits, it also presents regulatory challenges. The integration of financial services into non-financial platforms raises questions about consumer protection, data privacy, and systemic risk. Regulators are grappling with how to oversee this rapidly evolving landscape and ensure that consumers are adequately protected.
In response, regulatory bodies are beginning to establish frameworks to address the unique challenges posed by embedded finance. For example, the European Union’s Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) aims to enhance consumer protection and promote innovation by opening up payment services to nonbank providers. PSD2 requires banks to open their payment services and customer data to third-party providers through open APIs, fostering competition and innovation in the financial sector (European Commission, 2021).
Similarly, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) in the United States has issued guidance on how fintech companies can obtain banking charters, ensuring that they operate within a regulated framework. The OCC’s guidance aims to strike a balance between encouraging innovation and protecting consumers, providing a clear pathway for fintech companies to offer banking services (OCC, 2021).
Future Outlook
The future of embedded finance looks promising, with continued growth and innovation on the horizon. As technology advances and customer expectations evolve, the demand for integrated financial solutions is expected to increase. Companies across various sectors will continue to explore new ways to embed financial services into their platforms, creating more value for their customers and shareholders.
The rise of embedded finance also presents opportunities for collaboration between traditional financial institutions and nonbanks. By partnering with technology companies and fintech startups, banks can leverage their regulatory expertise and capital resources to develop innovative embedded finance solutions. This collaborative approach can help bridge the gap between traditional and digital financial services, ensuring that consumers benefit from the best of both worlds.
Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in the future of embedded finance. These technologies can enhance the personalization and efficiency of financial services, enabling companies to offer more tailored solutions to their customers. For instance, AI-powered credit scoring models can provide more accurate and inclusive assessments, expanding access to credit for underserved populations (World Economic Forum, 2022).
Case Study: Shopify and Stripe
Shopify, a leading e-commerce platform, provides an excellent case study of how embedded finance can transform a business. In partnership with Stripe, Shopify has integrated a suite of financial services into its platform, enabling merchants to manage payments, access capital, and handle other financial transactions seamlessly.
Payments Integration
Shopify Payments, powered by Stripe, allows merchants to accept payments directly on their websites without needing a third-party payment processor. This integration simplifies the checkout process for customers and reduces transaction fees for merchants. According to Shopify, this seamless payment experience has resulted in higher conversion rates and increased sales for its merchants (Shopify, 2022).
Access to Capital
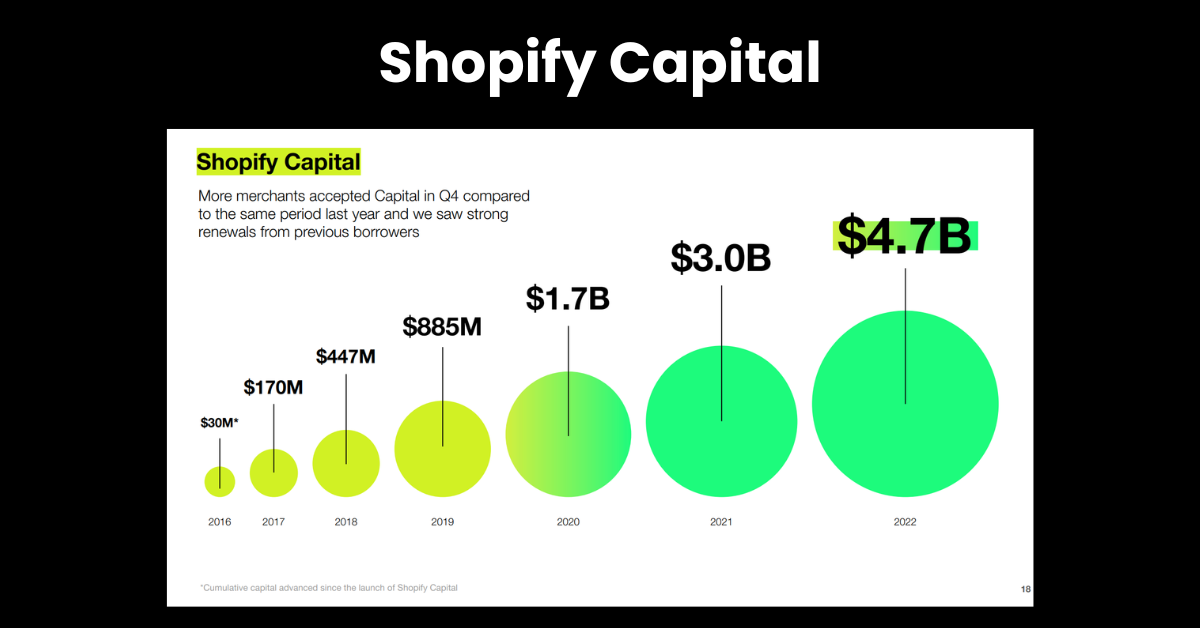
In addition to payment processing, Shopify offers Shopify Capital, a service that provides merchants with access to funding based on their sales data. By analyzing transaction data, Shopify can offer personalized financing options, such as loans and cash advances, tailored to the needs of individual businesses. This access to capital helps merchants grow their operations without the need for traditional bank loans, which can be difficult and time-consuming to obtain (Shopify, 2022).
Enhanced Customer Experience
By embedding financial services into its platform, Shopify has created a more integrated and user-friendly experience for its merchants. This approach reduces the complexity of managing multiple financial services and allows merchants to focus on growing their businesses. The success of Shopify’s embedded finance solutions is reflected in its financial performance, with the company reporting a 96% year-over-year increase in revenue for its Merchant Solutions segment in 2021 (Shopify, 2021).
The rise of embedded finance is transforming the financial services industry by integrating financial solutions into non-financial platforms. Nonbanks are playing a crucial role in driving this transformation, leveraging their technological capabilities to offer innovative and personalized financial services. As the industry continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks will need to adapt to ensure consumer protection and promote sustainable growth. The future of embedded finance holds immense potential, promising to create more seamless and convenient financial experiences for consumers worldwide.
At the forefront of this evolution are companies like SmartDev, which are pioneering the development and integration of embedded finance solutions. By leveraging their technological expertise and deep understanding of the financial landscape, SmartDev is enabling businesses to offer cutting-edge financial services embedded within their platforms. This not only enhances customer experience but also opens up new revenue streams and opportunities for growth. As the industry continues to advance, our company remains committed to driving innovation and delivering solutions that meet the evolving needs of businesses and consumers alike.
If you’re ready to explore how embedded finance can revolutionize your business, SmartDev is here to help. Our team of experts specializes in creating tailored financial solutions that seamlessly integrate into your existing platforms, enhancing both customer experience and business performance.
Contact SmartDev today to learn more about our embedded finance solutions and how we can help you stay ahead in the rapidly evolving financial landscape. Let’s innovate together and drive the future of finance!
References
Accenture, 2021. Embedded Finance: What it Takes to Prosper in the New Value Chain.
Bain & Company, 2022. The $7 Trillion Embedded Finance Market Opportunity.
European Commission, 2021. Payment Services Directive (PSD2) – Directive (EU) 2015/2366.
Financial Times, 2021. How Stripe became Silicon Valley’s most prized asset.
McKinsey & Company, 2021. The Future of Banking: Fintech or Techfin?
Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), 2021. OCC’s Approach to Fintech Charters.
Shopify, 2021. Shopify Announces Fourth-Quarter and Full-Year 2021 Financial Results.
Shopify, 2022. Shopify Capital.
Square, 2021. Square Financial Services.
World Economic Forum, 2022. The Future of Financial Services: How Disruptive Innovations are Reshaping the Industry.






