In the rapidly evolving world of finance, a transformative shift is underway with the rise of embedded finance. This integration of financial services into non-financial platforms is not just enhancing user experience—it’s revolutionizing the very fabric of the banking industry. This blog post explores the evolution of embedded finance, its impact on traditional banking, and its potential to shape the future of financial services.
I. Understanding Embedded Finance: Definition and Components
Imagine browsing through your favorite online retailer, filling your cart with products. When it’s time to check out, instead of being redirected to a traditional bank or credit card entry form, you’re offered an instant loan right at the checkout to pay for your purchases. You accept, agree to the terms, and complete your purchase—all without leaving the retailer’s website or app. This seamless integration of financial services into everyday shopping experiences is a prime example of embedded finance.
What is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance integrates financial services into environments traditionally not focused on banking or financial transactions. This means you can directly access financial services like loans, insurance, payment processing, and even investment opportunities, where you shop, socialize, or manage your business online.
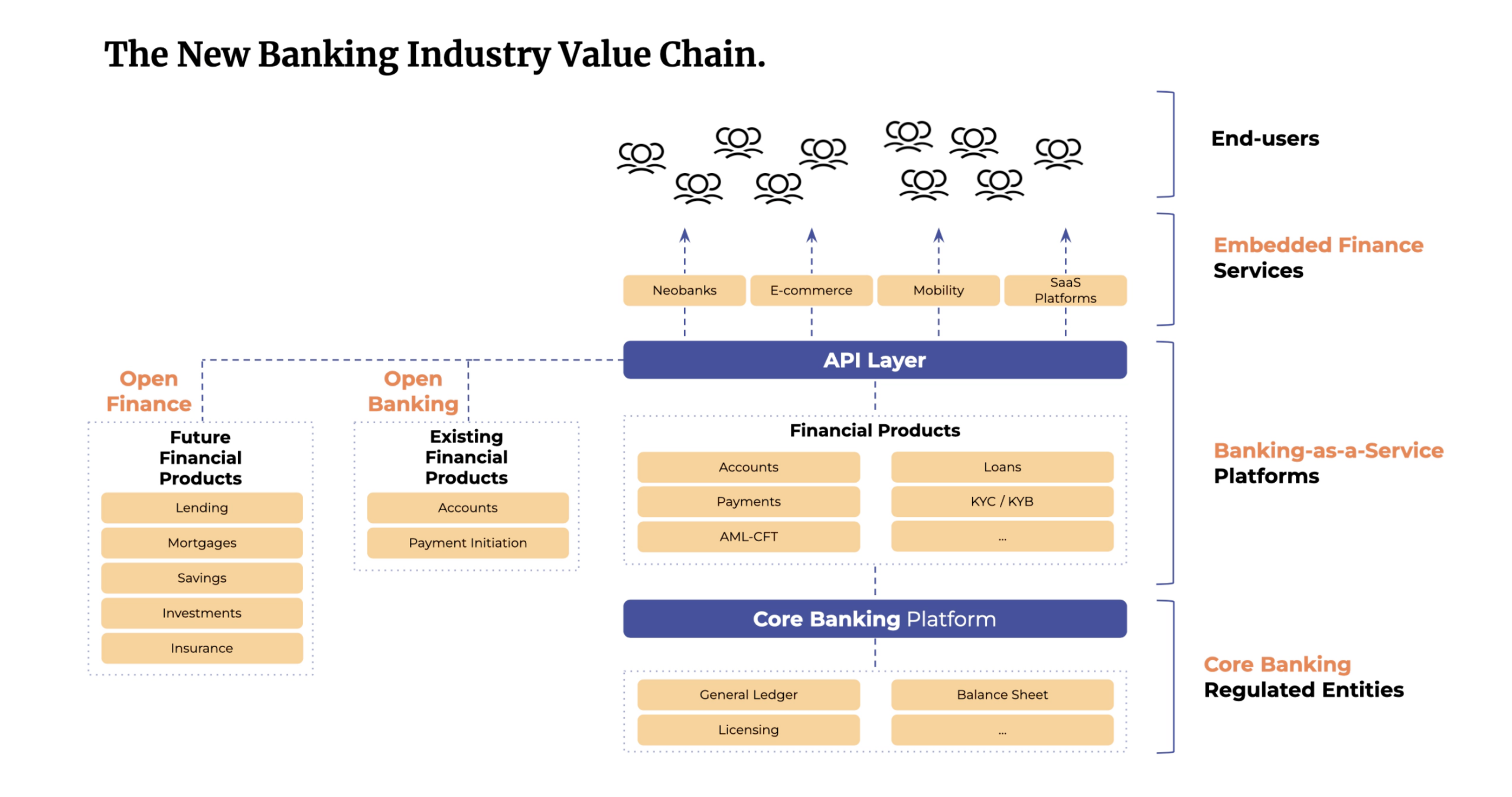 Figure 1: The New Banking Industry Value Chain (Skaleet, 2024)
Figure 1: The New Banking Industry Value Chain (Skaleet, 2024)
The Components Powering Embedded Finance
Embedded finance isn’t just a concept; it’s a sophisticated ecosystem supported by several technological pillars:
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): These are the backbone of embedded finance. APIs allow different software systems to communicate with each other. In embedded finance, APIs enable banking services to be integrated smoothly into retail websites, mobile apps, or social media platforms. For example, an e-commerce site can use APIs to connect to a financial institution’s services to offer instant credit at the point of sale.
- Open Banking Initiatives: Open banking is a system where banks open up their APIs to third parties to allow them to build applications and services around the financial institution. This transparency and accessibility fuel innovation in embedded finance by enabling third-party developers to create financial solutions that can be directly integrated into various platforms. For instance, through open banking, a fintech app can access your banking data (with your permission) to provide personalized financial advice or budgeting help.
- Ubiquitous Internet Connectivity: The global spread of Internet access has been a crucial enabler of embedded finance. With more people online than ever, businesses have the opportunity to offer financial services on a vast scale. Internet connectivity ensures these services can be delivered in real time, enhancing user convenience and satisfaction. Whether applying for a loan or making an investment, these actions can now be performed instantly as part of a more significant, integrated digital experience.
II. Real-Time Financial Transactions
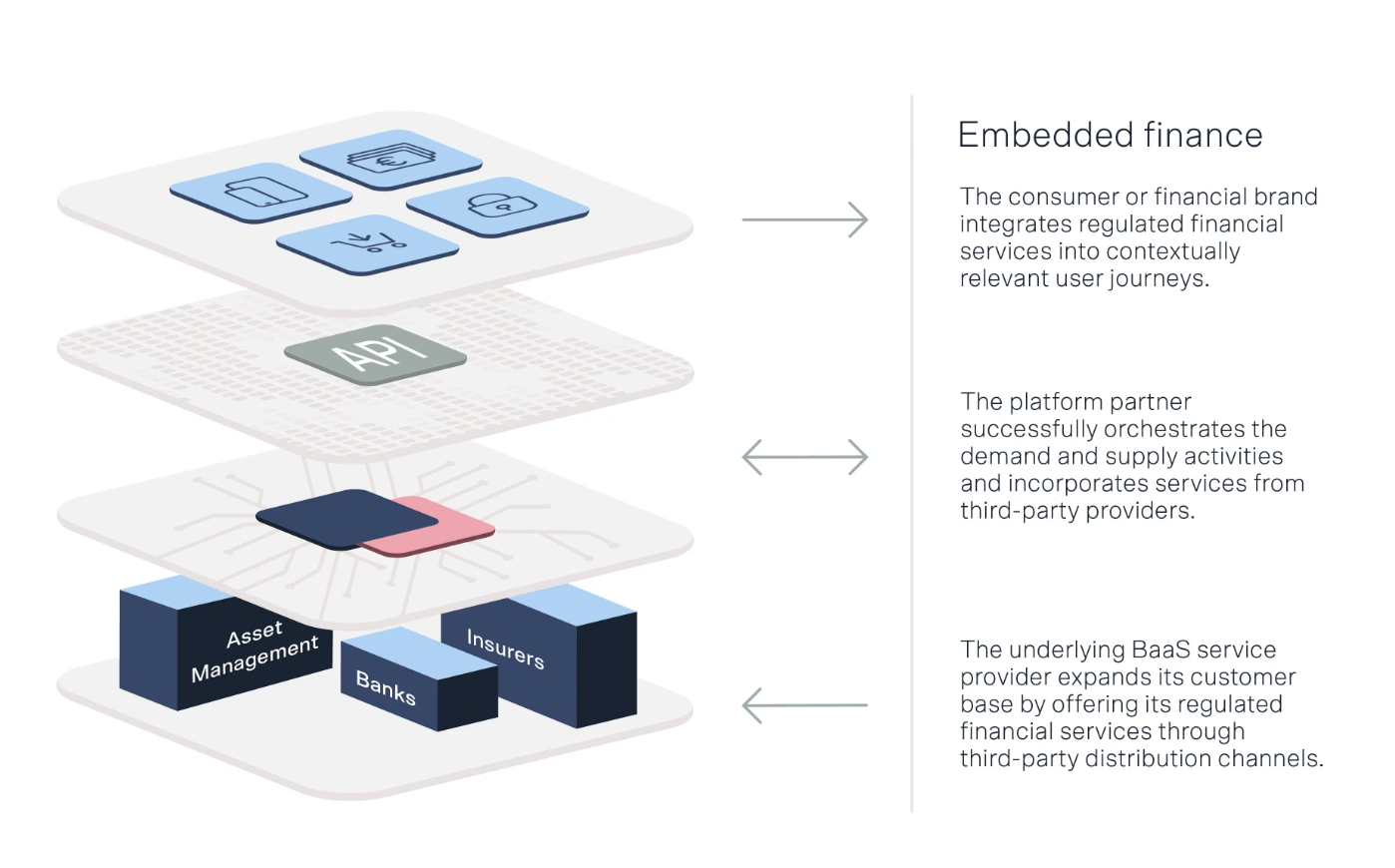
Figure 2: The different layers of embedded finance (Holtmann, 2022)
The real magic of embedded finance lies in its ability to make financial services part of the consumer’s everyday online activities. When you use a ride-sharing app and choose to pay later or split the payment for a new appliance on an e-commerce platform through an embedded lending service, you participate in a real-time financial transaction enabled by embedded finance.
This integration creates a more frictionless consumer experience and new business revenue channels. It also allows traditional financial institutions to reach customers in new and engaging ways directly in their preferred environments. This increases convenience and drives financial inclusion, bringing banking services to underserved populations who may not have easy access to traditional banking facilities.
In conclusion, embedded finance transforms how we think about financial transactions, moving them from the periphery of our digital experiences to become a natural and integrated part of them. The power of APIs, open banking, and internet connectivity offers a more connected, immediate, and personalized financial experience. As this trend continues to evolve, it promises to redefine the finance and global commerce landscape.
III. Historical Context
3.1 Early Beginnings and Technological Advances
The concept of embedded finance isn’t novel. It started with simple mechanisms like store credits and branded credit cards, which allowed customers to access financial services where they shopped. The fundamental transformation began with the advent of the internet and escalated with the proliferation of smartphones and APIs, facilitating sophisticated financial integrations. Early pioneers like PayPal integrated payment processing into online shopping, setting the stage for more complex embedded financial services.
3.2 Key Milestones in the Evolution of Embedded Finance
Initially, embedded finance focused primarily on payments. Over time, it expanded to include more complex services like investments and insurance, woven directly into user interfaces of various consumer platforms. The introduction of open banking regulations, especially in Europe with PSD2, was a critical milestone. It required banks to open their APIs to third parties, catalyzing the growth of embedded finance by enabling fintechs to offer layered financial services directly to end-users.
Platforms like Shopify and Stripe have marked recent trends. These platforms not only process payments but also offer financial products like loans directly within their platforms. This illustrates the growing scope and sophistication of embedded finance.
3.3 Impact on Traditional Banking Models
Embedded finance has disrupted traditional banking by decentralizing financial services. Banks, once the sole providers, now find themselves part of a broader ecosystem, necessitating adaptation to stay relevant. Many traditional banks have begun partnering with fintech companies, using their vast infrastructures to power embedded finance solutions on non-financial platforms. An example of such a partnership is between Apple and Goldman Sachs to offer the Apple Card, integrating credit services within the Apple ecosystem.
IV. Examples of Embedded Finance in Action
![]()
Real-World Applications: A prominent example of embedded finance is the rise of buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services like Klarna and Affirm, which are integrated directly into e-commerce checkouts and offer instant credit options. Another example is Uber, which directly integrates financial operations for drivers and customers within its app, enhancing the user experience and streamlining operations.
Advantages and Potential Obstacles: Embedded finance offers significant benefits. It brings unparalleled convenience and customization for consumers, making financial services accessible directly within the digital platforms they frequent. Keeping financial transactions in-house enhances customer engagement and opens new revenue streams for businesses.
However, embedded finance also presents challenges, particularly in regulatory compliance and data security. As non-financial companies delve deeper into financial activities, they must navigate complex regulatory landscapes and ensure stringent security measures to protect consumer data.
V. Conclusion
Embedded finance signifies a paradigm shift from traditional, standalone banking services to a more integrated approach, embedding financial functionalities into user-centric platforms. This evolution is set to continue, driven by technological advancements and a push towards greater financial inclusion.
As embedded finance blurs the lines between different sectors, it offers a promising future where financial services are no longer the exclusive domain of banks but are accessible wherever consumers need them. This integration promises to make financial operations more intuitive and embedded into our digital lives, heralding a new era in banking that focuses on accessibility, user engagement, and seamless service delivery.
VI. About SmartDev
At SmartDev, we are committed to driving innovation in the financial sector through our comprehensive fintech solutions. By integrating secure mobile applications, cutting-edge blockchain technology, and advanced Robotic Process Automation (RPA), we ensure that our services meet the highest quality and performance standards. Our fintech expertise helps financial institutions enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving economic landscape.
We invite businesses, innovators, and technology enthusiasts to collaborate with us and discover how our expertise in fintech can transform your operations. Let’s work together to leverage these cutting-edge practices, creating solutions that are not only innovative but also highly reliable and scalable. Contact SmartDev today to explore how we can help you achieve your strategic goals with our fintech services. Together, we will advance the capabilities of digital finance and set new benchmarks in the industry.
Visit our Fintech Services Page now to learn more.