Introduction
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are the backbone of modern business operations, integrating functions like finance, supply chain, HR, and customer management into a unified platform. However, traditional ERP systems often struggle with data silos, manual processes, and limited adaptability. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming ERP systems by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and providing predictive insights.
This guide explores how AI-driven use cases are revolutionizing ERP systems, turning them into intelligent platforms that drive efficiency and strategic advantage.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in ERP?

Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
AI encompasses technologies that enable machines to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. Core AI technologies include Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Computer Vision. These technologies allow systems to analyze data, understand human language, and interpret visual information.
In the context of ERP, AI integrates these technologies to automate routine tasks, analyze vast datasets, and provide predictive insights. This integration enhances the ERP system’s ability to adapt to changing business conditions, improve decision-making, and streamline operations. For instance, AI can automate invoice processing, predict inventory needs, and provide real-time financial forecasting.
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming ERP
AI is transforming ERP systems by introducing intelligent automation that eliminates manual and repetitive tasks. Tasks such as invoice approvals, purchase order matching, and data entry can now be handled automatically by AI algorithms, drastically improving operational speed and reducing human error.
Beyond automation, AI enhances ERP systems through predictive analytics, enabling more proactive and data-driven decision-making. By analyzing historical and real-time data, AI tools can forecast inventory needs, customer demand, and financial trends. This level of foresight empowers businesses to plan more accurately, optimize resources, and minimize waste or overstock situations.
Finally, AI elevates the role of ERP systems in strategic management by delivering real-time insights and intelligent recommendations. Whether through AI-powered dashboards or natural language queries, decision-makers now access critical business intelligence faster and with greater clarity. These enhancements transform ERP from a back-office system into a forward-looking, responsive platform that drives business innovation.
Key Statistics and Trends Highlighting AI Adoption in ERP
The integration of AI into ERP systems is accelerating, driven by the need for enhanced efficiency and real-time decision-making. In 2024, the global AI in ERP market was valued at approximately USD 4.5 billion and is projected to reach USD 46.5 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.3%. This substantial growth reflects the increasing demand for intelligent ERP solutions that can automate processes and provide predictive analytics.
A significant number of organizations are recognizing the importance of AI in their ERP systems. According to a survey, more than 65% of organizations believe AI is critical to their ERP systems. This sentiment is echoed by CIOs, with 65% anticipating AI integration into ERP systems in 2024. The adoption of AI is particularly prominent in industries such as manufacturing, retail, and healthcare, where real-time data analysis and process optimization are crucial.
The broader ERP market is also experiencing significant growth, influenced by the integration of AI technologies. The ERP market is projected to expand from USD 81.15 billion in 2024 to USD 238.79 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 14.4%. This growth is attributed to the increasing complexity of business operations and the need for scalable, adaptable, and automated ERP systems. The integration of AI, machine learning, and cloud computing is making ERP systems more efficient and responsive to changing business needs.
Business Benefits of AI in ERP
AI is driving measurable value across the ERP landscape by addressing critical operational pain points, from inefficient workflows to poor forecasting accuracy and siloed decision-making. Below are five core business benefits, each directly tied to pressing challenges that AI helps solve within modern ERP systems.
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
AI streamlines traditionally manual ERP processes such as data entry, invoice matching, and order processing. By automating these repetitive tasks, businesses can dramatically reduce processing times and minimize human errors. This operational speed translates to quicker turnaround times and more responsive service delivery.
More importantly, this level of automation frees up internal resources to focus on strategic priorities rather than routine administration. AI-driven workflows also ensure consistent data input, which improves data reliability across modules like finance, inventory, and procurement. As a result, teams operate with cleaner, more actionable data, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making.
2. Smarter, Faster Decision-Making
ERP systems powered by AI deliver real-time analytics that help leaders make more informed decisions. Machine learning models can detect trends and anomalies in financial data, production levels, or sales pipelines—providing early warnings and strategic insights before issues arise.
This predictive capability transforms decision-making from reactive to proactive. Instead of acting after the fact, businesses can now forecast demand, plan inventory, and adjust budgets with confidence. AI tools embedded in dashboards and reports make this intelligence accessible at every organizational level, ensuring alignment and agility across departments.
3. Improved Forecast Accuracy
One of the most valuable applications of AI in ERP is predictive forecasting. By analyzing historical patterns and real-time data, AI models enhance the precision of forecasts across supply chain, finance, and sales functions. This reduces the risks of overstocking, stockouts, or cash flow mismatches.
For example, AI can assess seasonal trends, vendor lead times, and customer buying behavior to suggest optimal inventory levels. This supports better planning and ensures that operational decisions are based on forward-looking insights rather than guesswork. The result is more stable operations and improved customer satisfaction due to consistent product availability.
4. Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
AI reduces operational costs by minimizing manual labor and improving resource utilization. Automated quality checks, predictive maintenance, and smart scheduling ensure that assets and people are used efficiently, cutting down on waste and unplanned downtime.
In finance, AI-driven ERP can flag anomalies in spending or identify patterns that suggest fraud or inefficiencies. By identifying these issues early, companies can plug revenue leaks and make better use of their budgets. Across departments, AI empowers teams to do more with less, directly contributing to improved margins and ROI.
5. Personalization and User Experience
AI enhances the ERP user experience through personalized dashboards, voice-activated interfaces, and intelligent assistants. These features adapt to individual user roles and behaviors, ensuring each employee sees the data and tools most relevant to their work. This not only improves productivity but also encourages ERP adoption across the organization.
Furthermore, AI-powered chatbots integrated into ERP systems can handle common user queries, from checking inventory levels to pulling up customer records. This reduces the workload on IT and support teams while giving users quicker access to the information they need. In fast-moving industries, this real-time accessibility creates a decisive advantage.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in ERP
Despite the compelling advantages, implementing AI within ERP systems is far from straightforward. Below are five specific challenges that businesses must address to successfully deploy AI in ERP environments.
1. Integration with Legacy Systems
Many companies still operate on legacy ERP platforms that were not designed to support AI technologies. These systems often lack APIs, modern data architectures, or processing capabilities required to run machine learning models or real-time analytics. As a result, integrating AI has become technically complex and resource intensive.
Without proper integration, AI tools may not access the full range of operational data, leading to incomplete insights and reduced effectiveness. Bridging this gap requires either substantial upgrades or migration to AI-ready ERP platforms—both of which demand significant investment and careful change management to avoid disrupting ongoing operations.
2. Inconsistent or Low-Quality Data
AI systems rely heavily on structured, consistent, and high-quality data to produce accurate outputs. Unfortunately, many ERP environments suffer from fragmented or outdated data due to inconsistent data entry, siloed departments, or insufficient data governance. These issues undermine the performance of AI algorithms.
Improving data quality involves cleaning historical records, standardizing formats, and setting up ongoing validation processes. It also requires cross-functional coordination to ensure that all departments use consistent definitions and categories. Without this foundation, even the most sophisticated AI models will generate flawed or misleading results.
3. Skills Gaps and Resource Constraints
Deploying AI-enhanced ERP systems requires new skill sets—ranging from data science and machine learning to AI model governance and change management. Many organizations lack in-house talent with the necessary expertise to configure, train, and maintain these AI systems effectively.
This shortage leads to overreliance on external consultants or third-party vendors, which can be costly and limit knowledge transfer. Additionally, IT and ERP teams may be stretched thin managing core system stability, leaving little capacity to explore or support AI projects. Developing internal capability is critical but takes time and sustains investment.
4. High Costs and Unclear ROI
The upfront costs of AI implementation in ERP can be substantial. Expenses may include software upgrades, cloud infrastructure, consulting services, and employee training. For many organizations, especially mid-sized businesses, these costs pose a significant barrier.
Moreover, the return on investment from AI-enhanced ERP is not always immediate or easily measurable. Some benefits, such as improved decision-making or user experience, are qualitative or realized over time. Without a clear business case or roadmap for value realization, securing buy-in from leadership can be challenging.
5. Data Security and Compliance Risks
ERP systems handle sensitive data across finance, HR, and operations. Introducing AI introduces new vectors for data exposure, especially when third-party tools or cloud platforms are involved. Ensuring data privacy, compliance with regulations like GDPR, and robust cybersecurity becomes even more critical.
AI models themselves can also introduce risks, such as biased decision-making or unintended data exposure through training sets. Organizations must establish clear governance policies for how AI is trained, validated, and monitored. This includes both technical safeguards and ethical oversight to ensure responsible AI usage within ERP systems.
Specific Applications of AI in ERP
AI is revolutionizing ERP systems by automating complex processes, enhancing decision-making, and improving operational efficiency. Below are six impactful AI applications in ERP, each accompanied by real-world examples demonstrating their effectiveness.

1. Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for inventory management, production planning, and customer satisfaction. AI-powered predictive analytics in ERP systems analyze historical data, market trends, and external factors to forecast demand more accurately.
Machine learning algorithms process vast datasets, identifying patterns and correlations that traditional methods might miss. These insights enable businesses to anticipate market changes, adjust inventory levels, and optimize supply chains proactively.
Implementing predictive analytics reduces stockouts and overstock situations, leading to cost savings and improved customer service. However, the accuracy of predictions depends on data quality and the relevance of input variables.
A leading consumer goods company integrated AI-driven demand forecasting into its ERP system, analyzing seasonal trends and customer behavior. This approach led to a 30% reduction in inventory carrying costs and prevented stockouts during peak periods. The company optimized production schedules based on accurate forecasts, enhancing overall efficiency.
2. Intelligent Automation in Finance & Accounting
Financial processes often involve repetitive tasks prone to human error. AI introduces intelligent automation in finance and accounting within ERP systems, streamlining operations and enhancing accuracy.
NLP and machine learning algorithms automate tasks like invoice processing, expense management, and financial reporting. Automating financial processes reduces manual workload, minimizes errors, and accelerates reporting cycles. It also ensures compliance with regulatory standards by maintaining accurate and timely records.
Omega Healthcare Management Services implemented AI-powered document processing using UiPath’s platform to handle medical billing and insurance claims. This automation saved over 15,000 employee hours per month, reduced documentation time by 40%, and achieved a 99.5% accuracy rate, resulting in a 30% ROI for clients.
3. AI-Enhanced Human Resources Management
Managing human resources involves complex processes like recruitment, performance evaluation, and employee engagement. AI enhances HR management within ERP systems by providing data-driven insights and automating routine tasks.
Machine learning models analyze employee data to identify patterns related to performance, attrition, and training needs. AI-powered chatbots handle employee queries, schedule interviews, and assist in onboarding processes.
Integrating AI in HR improves decision-making, enhances employee experience, and reduces administrative burdens. It also helps in identifying skill gaps and planning workforce development strategies.
Ramco Systems integrated AI into its HR and payroll software, introducing the Self Explaining Payslip (SEP) system. This feature uses AI to address employee payroll queries automatically, improving transparency and reducing HR workload. The system enhances employee satisfaction by providing instant, accurate responses.
4. AI-Driven Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer relationship management is vital for business growth. AI algorithms analyze customer interactions, purchase history, and feedback to predict future behavior and preferences.
AI enhances CRM within ERP systems by providing personalized customer experiences and predictive insights. Chatbots and virtual assistants offer real-time support, handling inquiries and guiding customers through purchasing processes.
Implementing AI in CRM leads to increased customer satisfaction, higher retention rates, and improved sales performance. It enables businesses to tailor marketing strategies and product offerings effectively.
Vodafone leveraged AI to enhance customer service by integrating intelligent chatbots into its ERP system. These chatbots handle common customer inquiries instantly, allowing human representatives to focus on complex issues. This approach improved response times and customer satisfaction levels.
5. Supply Chain Optimization with AI
Efficient supply chain management is essential for meeting customer demands and minimizing costs. AI optimizes supply chains within ERP systems by providing real-time insights and predictive analytics.
AI models analyze data from various sources, including supplier performance, transportation logistics, and market trends, to optimize inventory levels and delivery schedules. They also predict potential disruptions and suggest alternative strategies.
By enhancing visibility and responsiveness, AI-driven supply chain management reduces delays, lowers costs, and improves customer service. It also enables proactive risk management.
SAP integrated AI into its supply chain management, enabling automated supplier scoring, dynamic purchase order adjustments, and intelligent route planning. Organizations using SAP’s AI capabilities achieved faster returns on investment and improved supply chain efficiency.
6. AI-Powered Fraud Detection and Compliance Monitoring
Financial fraud and compliance violations pose significant risks to organizations. AI enhances fraud detection and compliance monitoring within ERP systems by identifying anomalies and ensuring adherence to regulations.
Machine learning algorithms analyze transaction patterns, flagging unusual activities that may indicate fraud. AI also monitors compliance with internal policies and external regulations, providing alerts for potential breaches.
Implementing AI in this context reduces financial losses, protects the company’s reputation, and ensures regulatory compliance. It also streamlines audit processes by maintaining detailed records and reports.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 incorporated AI-driven fraud protection features into its ERP system. These features analyze transactions in real-time, detecting and preventing fraudulent activities. Businesses using this system reported enhanced security and reduced financial risks.
Examples of AI in ERP
Real-World Case Studies
Transitioning from specific applications, it’s essential to explore real-world case studies that demonstrate the tangible benefits of integrating AI into ERP systems. These examples highlight the transformative impact of AI across various industries.

1. Omega Healthcare: Streamlining Operations with AI
Omega Healthcare, a major provider of back-office services to over 350 healthcare organizations, faced significant challenges managing the high volume of medical records and insurance documents. Manual data entry processes were labor-intensive, prone to errors, and inefficient given the scale and complexity of healthcare documentation. Maintaining accuracy while reducing processing time was critical, especially under growing compliance and cost pressures.
To address this, Omega partnered with UiPath to integrate AI and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) into their ERP infrastructure. They implemented natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision tools to automatically extract and classify information from unstructured documents such as medical transcripts and insurance claims. This AI-driven automation streamlined data capture, ensured consistency, and routed information to the appropriate systems without human intervention.
As a result, Omega saved over 15,000 employee hours per month and reduced documentation processing time by 40%. The AI system achieved 99.5% accuracy, significantly improving data integrity and compliance. Clients benefited from a 30% return on investment, demonstrating the efficiency and financial gains made possible through intelligent ERP transformation.
2. Zara: Enhancing Retail Operations through AI
Zara, the global fashion retailer, faced the complex challenge of managing rapid product turnover, shifting consumer demand, and inventory across hundreds of locations. Traditional ERP systems struggled to adapt to the speed and dynamism of fast fashion, leading to inefficiencies in stock management and delayed responses to market trends. The need for data-driven decision-making became more pressing as Zara expanded globally.
To improve operational agility, Zara integrated Odoo, an AI-enabled ERP solution, which allowed for real-time analytics and intelligent inventory forecasting. The system leveraged AI to analyze point-of-sale data, predict demand patterns, and optimize warehouse replenishment. By combining historical sales data with current buying behavior, Zara created a responsive feedback loop between consumer trends and inventory decisions.
This AI integration led to improved stock availability and reduced inventory holding costs. Zara enhanced customer satisfaction by ensuring popular items were restocked quickly, aligning production schedules with actual demand. The company gained a competitive edge by accelerating its supply chain responsiveness and boosting profitability through smarter resource planning.
3. Cleveland Clinic: Optimizing Supply Chain with AI
Cleveland Clinic, one of the leading academic medical centers in the United States, encountered inefficiencies in its supply chain operations. Managing medical inventory, processing purchase orders, and ensuring timely procurement required considerable manual input, which was both time-consuming and error prone. These inefficiencies risked operational delays and increased administrative overhead, especially during times of fluctuating demand.
To resolve this, Cleveland Clinic embedded AI capabilities into its ERP system to automate invoice processing and streamline inventory tracking. AI models provided predictive insights into potential shortages and supplier performance, allowing the clinic to make more informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, automation tools handle routine data entry tasks, freeing up staff to focus on higher-value activities.
The implementation significantly improved agility in supply chain management, ensuring critical supplies were ordered and delivered without delay. The clinic enhanced its ability to respond to changing needs while reducing human error in procurement. As a result, operational efficiency improved, administrative workload decreased, and medical staff gained more time to focus on patient care.
Innovative AI Solutions
Emerging AI technologies are continually transforming ERP systems, making them more intelligent and responsive. Innovations like Generative Business Process AI Agents (GBPAs) are redefining how businesses approach process automation.
GBPAs integrate generative AI with business process modeling, enabling ERP systems to interpret user intent and synthesize workflows in real-time. This approach allows for dynamic optimization of tasks such as budget planning and financial reporting.
The adoption of self-adaptive ERP frameworks that leverage NLP is also on the rise. These systems automate customization by transforming business processes into adaptable models, improving efficiency, and reducing reliance on manual adjustments.
As AI continues to evolve, ERP systems will become more autonomous, capable of making decisions, and adapting to changing business environments. This evolution promises increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced strategic planning capabilities for organizations across various industries.
AI-Driven Innovations Transforming ERP
Emerging Technologies in AI for ERP
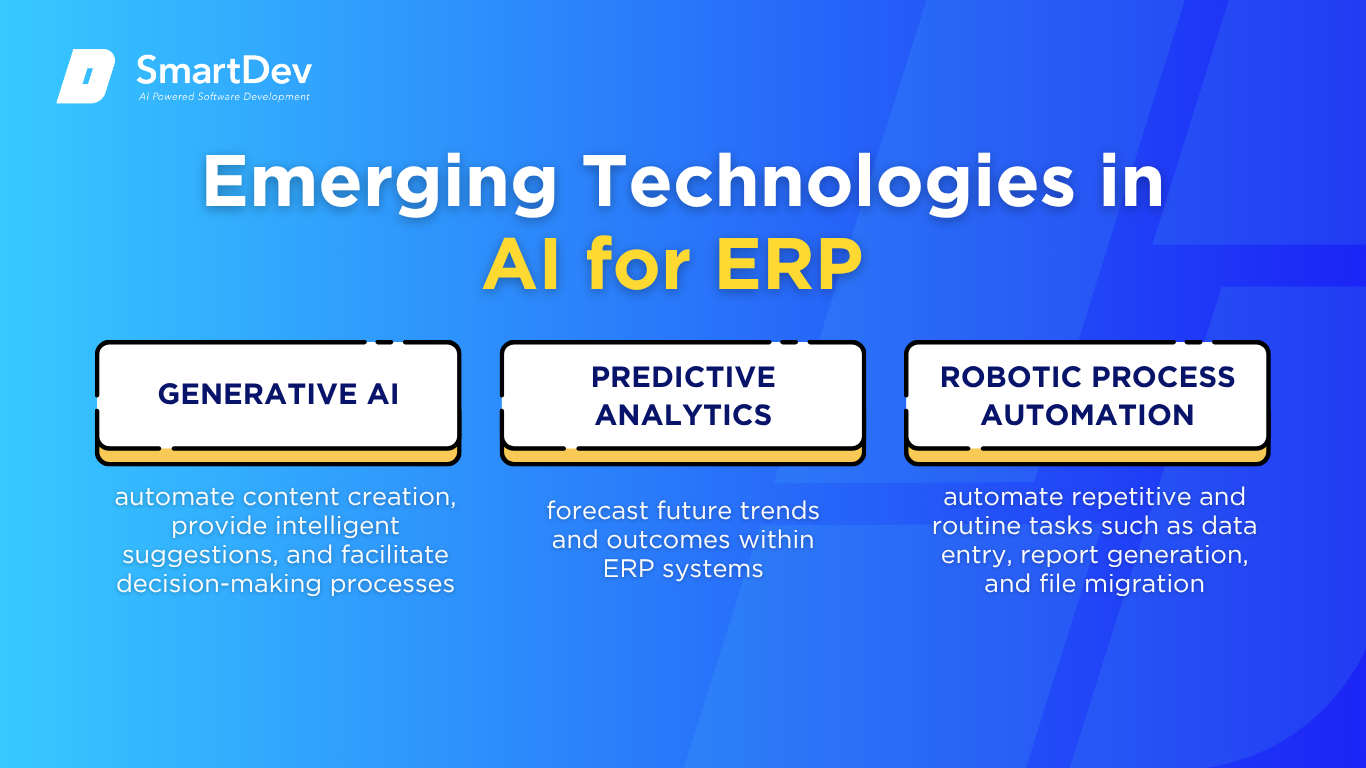
Generative AI is revolutionizing ERP systems by enabling them to automate content creation, provide intelligent suggestions, and facilitate decision-making processes. For instance, SAP’s AI co-pilot, Joule, assists users by generating reports, drafting communications, and offering insights across various ERP modules, thereby streamlining operations and enhancing user experiences.
Predictive analytics leverage historical data to forecast future trends and outcomes within ERP systems. By analyzing past behaviors and organizational inputs, ERP platforms can predict consumer behavior or market dynamics, allowing business leaders to make data-driven decisions quickly and proactively manage resources.
RPA integrates with ERP systems to automate repetitive and routine tasks such as data entry, report generation, and file migration. By deploying software bots to handle these processes, organizations can reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and increase operational efficiency, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
AI’s integration into ERP systems is also playing a pivotal role in promoting sustainability within organizations. Predictive analytics powered by AI can forecast demand more accurately, leading to optimized inventory levels and reduced waste. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze historical sales data and market trends to predict future demand, allowing companies to adjust their procurement and production schedules accordingly.
Moreover, AI-driven ERP systems can optimize energy consumption by analyzing usage patterns and identifying areas where energy efficiency can be improved. Smart systems can automatically adjust heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy and usage, leading to significant energy savings. These sustainability efforts not only contribute to environmental conservation but also result in cost savings for businesses.
How to Implement AI in ERP
Step 1. Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Before deploying AI in ERP, businesses must evaluate where it can add the most value, be it in finance, logistics, or customer service. This means reviewing current workflows, spotting inefficiencies, and mapping out where automation or insights could make a clear impact.
Just as important is assessing whether your IT infrastructure can support AI. From data availability to system integration, having executive buy-in and a shared vision across departments is key to a successful transformation.
Step 2. Building a Strong Data Foundation
Clean, structured, and accessible data is essential for any AI-enabled ERP system to function effectively. Without reliable data, AI models can’t produce meaningful insights or automate tasks accurately.
Businesses should also integrate data from different systems to create a unified, real-time view. Equipping employees with data literacy skills and promoting strong governance helps maintain long-term AI success.
Step 3. Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Not all AI tools are created equal, especially when it comes to ERP. Choose platforms that align with your system architecture, scale to your business size, and offer capabilities tailored to your use cases.
Partnering with experienced vendors who offer ongoing support and industry-specific features can reduce risk and speed up adoption. Look for proven success in ERP AI deployment, not just promises.
Step 4. Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Starting small with a well-defined pilot helps uncover early issues and measure AI’s real-world impact. For instance, testing AI in procurement or inventory tracking lets you assess cost savings before expanding.
Once validated, a phased rollout with close performance tracking ensures the broader implementation aligns with your goals. Feedback loops during this phase are critical for refinement and scaling.
Step 5. Training Teams for Successful Implementation
AI is only as effective as the people who use it. That’s why upskilling your workforce in both technical tools and strategic thinking is crucial to long-term success.
Fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration helps your teams adapt and thrive. Internal champions and cross-functional training can further accelerate adoption and value creation.
Measuring the ROI of AI in ERP
Key Metrics to Track Success
Evaluating the return on investment (ROI) of AI integration into ERP systems involves tracking various performance metrics. Productivity improvements can be measured by assessing the reduction in time spent on manual tasks, such as data entry or report generation. For instance, Omega Healthcare Management Services reported saving over 15,000 employee hours per month by automating tasks like medical billing and documentation.
Cost savings achieved through automation are another critical metric. By reducing errors and streamlining processes, AI can lead to significant financial benefits. Additionally, improvements in decision-making speed and accuracy, customer satisfaction, and compliance rates can serve as indicators of AI’s impact on business performance.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Real-world examples underscore the tangible benefits of integrating AI into ERP systems. Omega Healthcare Management Services, for instance, implemented AI-powered automation in its revenue cycle management processes. By partnering with UiPath, the company automated tasks such as medical billing and insurance claims processing, resulting in a 30% ROI for clients and a 50% reduction in turnaround time.
Similarly, SAP’s integration of its AI co-pilot, Joule, into its ERP suite has enhanced productivity and decision-making capabilities for its clients. By leveraging AI to automate routine tasks and provide intelligent insights, businesses have experienced improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
Another success story comes from Deloitte, which worked with UiPath and ServiceNow to automate repetitive processes for government agencies through a Digital Labor PM. One automation handled 2,000 transactions in under 11 hours, a task that previously took over 500 hours, leading to a 300% productivity boost and significant ROI.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While the integration of AI into ERP systems offers numerous benefits, organizations must be mindful of potential pitfalls. One common challenge is the lack of high-quality, structured data necessary for effective AI analysis. To address this, companies should prioritize data cleansing and establish robust data governance practices.
Another issue is employee resistance to adopting new technologies. Overcoming this requires clear communication about the benefits of AI, involving employees in the implementation process, and providing adequate training. Additionally, organizations should be cautious of over-automation, ensuring that AI complements human decision-making rather than replacing it entirely.
Future Trends of AI in ERP

Predictions for the Next Decade
Looking ahead, AI is poised to become an integral component of ERP systems, driving further automation and intelligence. We can anticipate the emergence of more sophisticated AI capabilities, such as advanced predictive analytics, real-time decision-making support, and enhanced natural language processing interfaces.
The integration of AI with other emerging technologies, like the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain, will further enhance ERP functionalities. For example, combining AI with IoT can enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance in manufacturing processes, while blockchain can enhance data security and transparency in supply chain management.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To remain competitive in this evolving landscape, businesses should proactively embrace AI integration into their ERP systems. This involves staying informed about technological advancements, investing in employee training, and fostering a culture of innovation.
Collaborating with technology partners and participating in industry forums can provide valuable insights and facilitate knowledge sharing. Moreover, organizations should continuously evaluate and refine their AI strategies to align with changing business needs and technological developments.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI is redefining what’s possible in ERP systems, moving them from rigid, transactional platforms to intelligent, adaptive business engines. By incorporating technologies like generative AI, predictive analytics, and computer vision, companies can streamline operations, reduce waste, and make faster, more informed decisions across finance, supply chain, HR, and more.
However, unlocking these benefits doesn’t happen by accident. It requires the right foundation: clean, integrated data; carefully selected tools; strategic pilot programs; and, most importantly, a workforce that’s prepared to evolve alongside the technology. When done right, AI doesn’t just improve ERP; it transforms the entire organization.
Moving Forward: A Path to Progress
There’s never been a better moment to rethink what your ERP system can do. As AI continues to evolve at breakneck speed, businesses that integrate it early are already transforming how they operate – cutting costs, improving decision-making, and gaining the agility to respond faster to market changes. If your ERP still relies heavily on manual processes or siloed data, now is the time to step forward.
At SmartDev, we help companies bridge the gap between potential and performance through intelligent AI integration tailored to ERP environments. From automating workflows and enhancing reporting to deploying AI copilots that assist your teams in real-time, we’ve helped enterprises across industries turn technology into tangible value. Whether you’re just beginning or ready to scale, our team is here to guide the journey with a custom pilot that fits your goals and infrastructure.
Let’s unlock what AI can do for your ERP – partner with SmartDev and build smarter, faster, and more resilient operations today.
—
References:
- AI in ERP Market | Market.us
- AI-Powered ERP Systems: Review and Applications | IJCSPTH
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software Market | Fortune Business Insights
- AI Integration in ERP Systems: Opportunities and Challenges | Preprints.org
- Omega Healthcare and UiPath Use AI to Process Health Transactions | Business Insider
- AI-Powered Payroll Automation Tool and Self-Explaining Payslip | Ramco
- Vodafone Uses Microsoft Azure AI to Improve Customer Experience | Microsoft
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fraud Protection | Microsoft Learn
- AI-Powered Fashion: How Tech is Reshaping Zara’s Fashion Empire | Michigan Journal of Economics
- How Cleveland Clinic is Innovating in Healthcare with Data and AI | Forbes






