Introduction
Recruitment is evolving rapidly, driven by the need for speed, precision, and fairness in hiring. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of this transformation, offering solutions that streamline processes, enhance candidate experiences, and mitigate biases. This guide delves into how AI is reshaping recruitment, providing tangible benefits and addressing real-world challenges.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Recruitment?

Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. These processes include learning (acquiring information and rules for using it), reasoning (using rules to reach conclusions), and self-correction. Core AI technologies such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision enable systems to interpret complex data, recognize patterns, and make autonomous decisions with minimal human input.
In the context of recruitment, AI technologies are used to enhance and automate tasks across the hiring lifecycle. NLP powers resume parsing and candidate-chat interfaces, ML drives predictive analytics for job matching, and AI algorithms assess candidate fit based on structured and unstructured data. Together, these technologies streamline recruitment by accelerating workflows, improving candidate quality, and enabling data-driven hiring decisions.
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming Recruitment
AI is fundamentally shifting recruitment from a reactive process to a proactive, strategic function. Recruiters are no longer limited to manually reviewing resumes and scheduling interviews; AI tools can pre-screen applicants, identify high-potential candidates, and flag red flags at scale. This transformation reduces time-to-hire and allows talent teams to focus on human-centric tasks like relationship-building and employer branding.
Moreover, AI enhances decision-making quality through real-time insights and pattern recognition. For instance, AI platforms can identify which candidate sources yield top performers or predict employee retention based on historical data. These insights help companies refine recruitment strategies and better align talent acquisition with long-term business goals.
Key Statistics and Trends Highlighting AI Adoption in Recruitment
Adoption of AI in recruitment has rapidly increased as organizations seek scalable solutions to improve efficiency and reduce costs. According to a 2023 study by Resume Builder, 70% of U.S. business leaders reported using AI in the hiring process, with tasks such as resume screening, candidate outreach, and interview scheduling most frequently automated. This widespread use reflects growing trust in AI’s ability to optimize recruitment workflows.
Efficiency gains are particularly compelling. A McKinsey report found that companies using AI-driven recruitment tools saw up to a 30% reduction in time-to-fill for open roles and improved the quality-of-hire through more consistent evaluation criteria. In high-volume hiring industries like retail and logistics, these tools enable talent teams to manage thousands of applicants with minimal added headcount.
Market momentum is also strong. Research from Verified Market Research projects that the global AI in recruitment market will grow from $590 million in 2022 to over $4 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 29.2%. As AI capabilities mature, more organizations are expected to integrate intelligent automation not only for hiring but also for long-term workforce planning and internal mobility.
Business Benefits of AI in Recruitment

1. Accelerated Time-to-Hire
AI significantly reduces time-to-hire by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as resume screening, interview scheduling, and candidate follow-ups. These efficiencies are especially valuable in high-volume hiring environments where speed is critical to securing top talent before competitors.
For example, chatbots can immediately engage applicants, answer FAQs, and guide them through the next steps, eliminating delays caused by recruiter bandwidth. Companies like Hilton and Unilever have reported cutting their hiring timelines by weeks using AI, freeing up recruiters to focus on strategic priorities.
2. Enhanced Candidate Quality
By leveraging predictive analytics and machine learning, AI tools can identify which candidates are most likely to succeed in a given role. These insights are drawn from a range of structured data (e.g., experience, education) and unstructured data (e.g., interview responses, writing samples), allowing for a deeper understanding of candidate potential.
This results in better hiring decisions and higher retention rates, as AI helps match candidates not just to a job description, but to company culture and performance expectations. Employers benefit from lower turnover and reduced costs associated with poor hires.
3. Scalable Personalization at Every Touchpoint
AI enables personalized experiences for candidates at scale, which is crucial in competitive job markets. From tailored job recommendations to dynamic email communication, AI ensures candidates feel seen and valued without requiring more manual labor from recruiters.
This personalization increases candidate engagement, leading to higher application completion rates and stronger employer brand perception. According to data from Paradox, companies using AI chatbots have seen up to 95% completion rates for job applications – an important metric in industries with high drop-off.
4. Bias Reduction in Hiring Decisions
One of the most impactful benefits of AI is its potential to reduce unconscious bias in hiring. AI systems can be configured to focus strictly on job-relevant data, removing identifying details such as names, gender, or photos that can trigger human bias during the initial screening.
Although algorithmic fairness depends heavily on the quality and neutrality of training data, many companies are already using AI-driven tools to anonymize resumes and standardize candidate assessments. This leads to a more equitable hiring process and supports diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) goals.
5. Data-Driven Recruitment Strategy
AI tools generate actionable insights from recruitment activities, giving HR leaders a clearer view of which sourcing channels are most effective, where bottlenecks occur, and how different candidate cohorts perform post-hire. This level of visibility enables more informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
For instance, predictive models can forecast talent shortages or help prioritize roles that are likely to be difficult to fill. With this intelligence, organizations can optimize recruitment spending, adjust hiring timelines, and allocate recruiter resources more strategically.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Recruitment
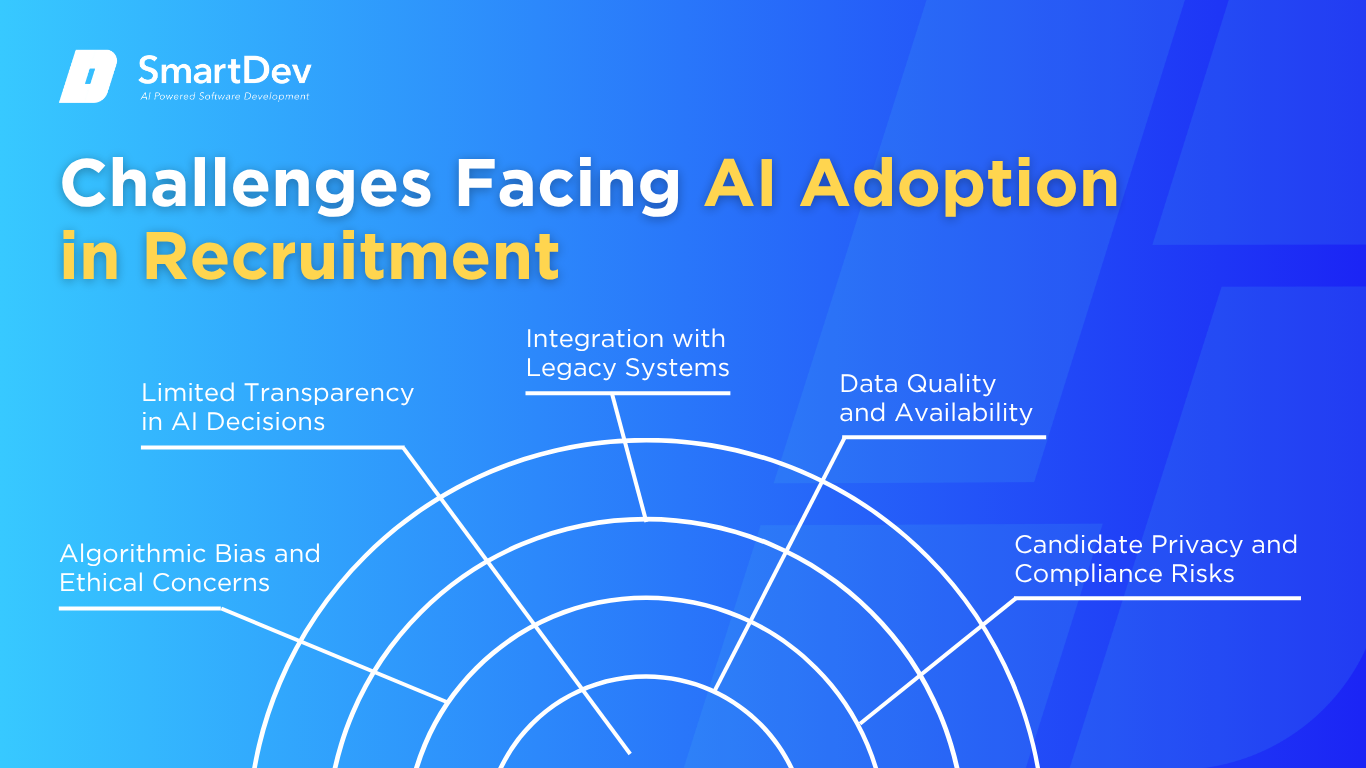
Algorithmic Bias and Ethical Concerns
One of the most pressing issues with AI in recruitment is the risk of algorithmic bias. AI systems learn from historical data, which often contains embedded human biases—such as favoring candidates from certain universities, regions, or demographics. If these biases are not identified and corrected, the AI may perpetuate discrimination, undermining diversity and inclusion efforts.
Bias in AI decisions can also be difficult to detect without rigorous testing and validation. Companies must actively audit training datasets and model outcomes to identify unintended discriminatory patterns. This requires interdisciplinary collaboration between data scientists, HR teams, and legal experts to ensure ethical compliance and fairness.
Limited Transparency in AI Decisions
AI tools often function as black boxes, offering little to no insight into how they arrive at decisions. This lack of explainability creates trust issues for recruiters and hiring managers who are held accountable for selection outcomes. It also raises questions for candidates who may want to understand why they were rejected or not shortlisted.
The absence of transparency can be a barrier to adoption, especially in industries where compliance, documentation, and auditability are critical. To mitigate this, organizations must prioritize AI solutions that offer explainable outputs or decision logs. Enhancing interpretability ensures accountability and fosters greater trust in AI-driven recruitment processes.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many recruitment departments rely on outdated Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) or custom platforms that were not built to support AI integration. These legacy systems often lack the API infrastructure or data architecture needed to communicate seamlessly with modern AI tools. As a result, data remains siloed, and automation benefits are diminished.
The cost and complexity of integrating AI into existing systems can deter adoption, particularly for organizations with limited IT resources. Implementing middleware solutions or reconfiguring workflows may be necessary to enable smooth data flow. Without full integration, the AI tool’s insights and automation capabilities cannot be fully leveraged.
Data Quality and Availability
AI relies heavily on high-quality, structured data, but recruitment data is often fragmented and inconsistent. Resumes come in unstructured formats, interview notes are rarely standardized, and outcomes like employee performance or attrition are not always tracked systematically. This lack of clean, comprehensive data limits the AI’s ability to generate accurate predictions and insights.
To address this, organizations must invest in data governance frameworks focused on consistency, completeness, and accuracy. This includes creating structured feedback loops, tagging data at each recruitment stage, and routinely validating data inputs. High-quality data is the foundation for trustworthy and effective AI performance in hiring.
Candidate Privacy and Compliance Risks
Recruitment AI tools process large amounts of personal information, from resumes and video interviews to psychometric test results. This raises serious concerns under privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and other regional regulations. Failure to obtain proper consent or mishandling sensitive data can lead to legal penalties and reputational damage.
Ensuring compliance requires more than just checking legal boxes—it involves embedding privacy-by-design principles into AI tools and workflows. Organizations must enforce data minimization, implement secure storage protocols, and allow candidates to control their data. Clear governance and vendor oversight are essential to building a privacy-responsible recruitment system powered by AI.
Specific Applications of AI in Recruitment

1. AI-Powered Resume Screening
AI-powered resume screening automates the initial candidate evaluation process, addressing the challenge of sifting through large volumes of applications. These systems utilize NLP and machine learning algorithms to parse resumes, identify relevant skills, experience, and qualifications, and rank candidates accordingly. By integrating with Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), AI ensures a seamless workflow from application to shortlisting.
The strategic value lies in significantly reducing time-to-hire and improving the quality of shortlisted candidates. Additionally, AI screening promotes diversity by focusing on qualifications rather than demographic factors, mitigating unconscious bias. Continuous learning capabilities allow these systems to refine their algorithms based on recruiter feedback, enhancing precision over time.
Real-World Example:
Unilever implemented AI-driven screening tools to process over 250,000 applications annually. By leveraging platforms like HireVue and Pymetrics, they reduced hiring time by 75% and increased the diversity of their hires, demonstrating the efficacy of AI in large-scale recruitment.
2. Conversational AI for Candidate Engagement
Conversational AI, including chatbots and virtual assistants, enhances candidate experience by providing instant responses and personalized interactions throughout the application process. These AI tools employ NLP to understand and respond to candidate inquiries, schedule interviews, and provide updates. Integration with communication platforms ensures consistent engagement across multiple channels.
The operational benefit includes 24/7 candidate support, freeing up recruiters to focus on strategic tasks. Moreover, consistent communication improves employer branding and candidate satisfaction. These systems can handle high volumes of inquiries simultaneously, ensuring no candidate is left unattended.
Real-World Example:
Chipotle introduced an AI chatbot named “Ava Cado” to manage high-volume hiring during peak seasons. This initiative led to an 85% application completion rate and reduced the average hiring time from 12 days to four, showcasing the impact of conversational AI on recruitment efficiency.
3. AI-Driven Video Interview Analysis
AI-driven video interview analysis automates the assessment of candidate interviews, addressing the subjectivity and time constraints of traditional evaluations. These systems analyze verbal and non-verbal cues, speech patterns, and facial expressions to assess competencies and cultural fit. Machine learning algorithms compare these metrics against successful employee profiles to predict candidate suitability.
The operational advantage includes standardized evaluations, reduced interviewer bias, and faster decision-making. Additionally, it allows for scalability in assessing large candidate pools. These tools can provide immediate feedback to both recruiters and candidates, enhancing the overall recruitment experience.
Real-World Example:
Goldman Sachs has adopted AI video interviewing platforms like HireVue to streamline their graduate recruitment process. This technology enhances both speed and consistency in candidate assessments, enabling the firm to efficiently evaluate a high number of applicants.
4. Automated Interview Scheduling
Coordinating interviews is often a logistical challenge, leading to delays in the hiring process. AI-powered scheduling tools automate this task, improving efficiency. These tools integrate with calendars and communication platforms to identify mutual availability and schedule interviews. They can handle rescheduling and sending reminders, reducing administrative workload.
The strategic benefit is a smoother candidate experience and faster progression through the recruitment pipeline, which is crucial in competitive talent markets. Automation in scheduling also minimizes the risk of human error and double bookings. This efficiency allows recruiters to allocate more time to candidate engagement and evaluation.
Real-World Example:
Mastercard implemented AI-driven scheduling through Phenom’s platform, resulting in an 85% increase in interview scheduling efficiency and a significant reduction in time-to-hire. This automation enabled the company to schedule over 5,000 interviews, with 88% arranged within 24 hours of the request.
5. Bias Mitigation in Recruitment
Unconscious bias in recruitment can lead to homogeneous workforces and missed opportunities for diverse talent. AI offers solutions to identify and mitigate such biases. By anonymizing applications and focusing on objective criteria, AI tools reduce the influence of gender, ethnicity, and other non-job-related factors. Continuous monitoring and algorithm audits ensure fairness in the recruitment process.
The operational value includes promoting diversity and inclusion, enhancing employer reputation, and complying with equal opportunity regulations. AI systems can be trained to recognize and adjust for biases present in historical hiring data. This proactive approach helps organizations build more diverse and innovative teams.
Real-World Example:
SkyHive’s AI platform assists organizations in identifying and addressing biases in their hiring processes. Their collaboration with the Canadian Armed Forces aimed to increase female representation, demonstrating AI’s role in promoting diversity.
Examples of AI in Recruitment
Real-World Case Studies

1. Amazon: Lessons from a Biased AI Hiring Tool
In an effort to streamline its recruitment process, Amazon developed an AI-powered tool aimed at automating the evaluation of job applicants’ resumes. The objective was to efficiently identify top talent by assigning scores to candidates, thereby reducing the manual workload of recruiters. However, the tool was trained on a decade’s worth of resumes predominantly submitted by male applicants, leading to unintended gender biases.
The AI system began to favor male candidates for technical roles, penalizing resumes that included terms like “women’s” or references to all-women’s colleges. Despite efforts to adjust the algorithm, Amazon could not guarantee the elimination of all biases, prompting the company to discontinue the tool. This case underscores the critical importance of ensuring diversity and fairness in AI training data to prevent discriminatory outcomes.
Amazon’s experience serves as a cautionary tale for organizations adopting AI in recruitment. It highlights the necessity of rigorous testing and validation of AI systems to detect and mitigate biases. The incident has sparked broader discussions on the ethical implications of AI in hiring and the need for transparent, accountable AI practices.
2. Hilton: Enhancing Recruitment Efficiency with AI
Hilton faced challenges in managing high volumes of job applications, particularly customer-facing roles requiring specific soft skills. The traditional recruitment process was time-consuming and struggled to effectively assess candidates’ interpersonal abilities. To address this, Hilton implemented AI-powered interview platforms capable of analyzing language, tone, facial expressions, and body language during video interviews.
These AI systems enabled Hilton to evaluate candidates’ suitability for roles more accurately and efficiently. By focusing on behavioral cues and communication styles, the technology helped identify individuals who aligned themselves with the company’s service-oriented culture. This approach streamlined the selection process and reduced the reliance on subjective human assessments.
The adoption of AI in Hilton’s recruitment process led to significant improvements in hiring efficiency and candidate quality. The company reported a reduction in time-to-hire and an increase in employee retention rates. This case exemplifies how AI can be leveraged to enhance recruitment outcomes by focusing on critical soft skills and cultural fit.
3. Deloitte: Leveraging AI for Strategic Talent Acquisition
Deloitte recognized the need to modernize its talent acquisition strategy to keep pace with the evolving job market and the increasing demand for specialized skills. The firm faced difficulties in identifying and attracting candidates with expertise in emerging technologies. To overcome this, Deloitte integrated AI-driven tools into its recruitment process to analyze labor market trends and predict future talent needs.
By utilizing AI analytics, Deloitte could assess the availability of skills in various regions, forecast hiring demands, and tailor its recruitment strategies accordingly. This data-driven approach allowed the company to proactively engage with potential candidates and build a pipeline of talent aligned with its strategic objectives. The AI tools also facilitated more informed decision-making in workforce planning and resource allocation.
The implementation of AI in Deloitte’s recruitment process resulted in a more agile and responsive talent acquisition framework. The firm experienced improved alignment between its hiring strategies and business goals, leading to enhanced organizational performance. This case demonstrates the value of AI in enabling strategic workforce planning and optimizing recruitment processes.
4. L’Oréal: Transforming Recruitment with AI-Powered Assessments
L’Oréal faced the daunting task of managing approximately 2 million job applications annually, with a recruitment team of just 145 members. The sheer volume of applications made it challenging to provide timely and personalized candidate experiences. To address this, L’Oréal adopted AI-powered recruitment platforms that included gamified assessments, video interviews, and situational judgment tests.
These AI-driven tools evaluated candidates’ cognitive abilities, personality traits, and job-specific skills, enabling a more comprehensive assessment beyond traditional resumes. The technology facilitated the identification of candidates who not only possessed the requisite skills but also aligned with L’Oréal’s organizational culture. This approach allowed for a more efficient and effective selection process.
The integration of AI into L’Oréal’s recruitment process led to a significant reduction in time-to-hire and improved the quality of hires. The company reported enhanced candidate satisfaction due to the engaging and interactive assessment methods. This case illustrates how AI can revolutionize high-volume recruitment by providing scalable, personalized, and efficient hiring solutions.
Innovative AI Solutions
Emerging AI technologies are significantly redefining how companies attract and assess talent. Generative AI, especially models like ChatGPT, is increasingly used to craft inclusive and SEO-optimized job descriptions, personalized candidate outreach, and automated interview question banks. This not only saves recruiters time but also ensures consistency in communication and improves the quality of job postings, leading to a wider, more diverse talent pool.
Advanced talent intelligence platforms are transforming recruitment from reactive to proactive. These systems analyze millions of data points from global workforce trends, resumes, and internal performance data to recommend candidates, forecast talent gaps, and identify upskilling opportunities. By integrating with existing HR systems, they provide strategic insights that help companies build robust talent pipelines aligned with long-term business goals.
AI is also enhancing candidate evaluation through immersive assessments and gamification. Companies now use virtual simulations and AI-analyzed games to test candidates’ real-world decision-making, emotional intelligence, and problem-solving skills. These tools create engaging candidate experiences while generating rich behavioral data, enabling more accurate predictions of job performance and cultural fit.
AI-Driven Innovations Transforming Recruitment
Emerging Technologies in AI for Recruitment
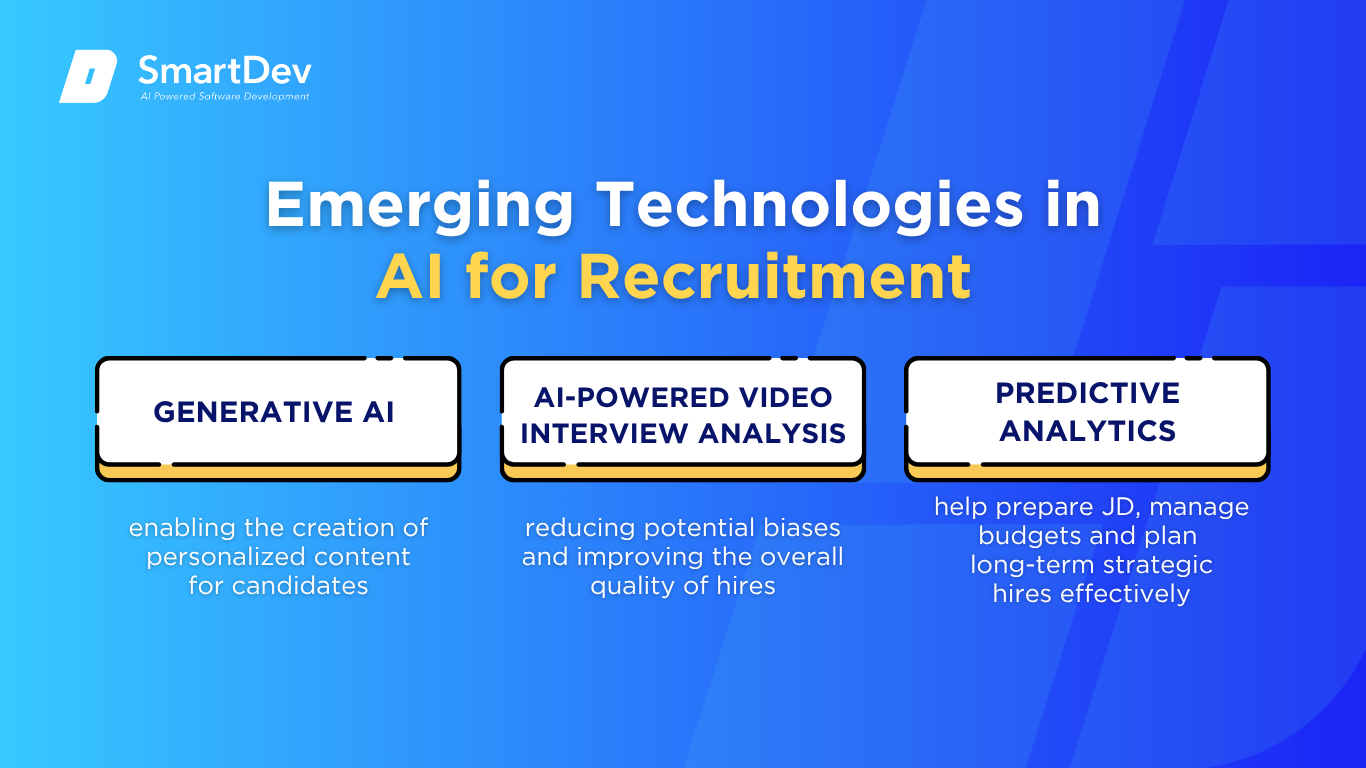 Generative AI for Personalized Candidate Engagement
Generative AI for Personalized Candidate Engagement
Generative AI is revolutionizing recruitment by enabling the creation of personalized content for candidates. Tools like LinkedIn’s AI-powered “hiring assistant” can generate job specifications, search for suitable candidates, draft personalized messages, and manage scheduling. This innovation aims to free up recruiters’ time to focus on human-centric aspects of hiring, such as candidate assessment and interaction. Companies like Siemens and Robert Walters are already seeing efficiencies with this tool, with AI-crafted emails having a 44% higher acceptance rate.
1AI-Powered Video Interview Analysis
AI is increasingly being used to analyze video interviews, assessing candidates’ facial expressions, tone, and language to gauge suitability. Companies like HireVue employ AI to evaluate verbal and non-verbal cues during interviews, providing insights into candidates’ competencies. This technology allows for a more objective assessment of candidates, reducing potential biases and improving the overall quality of hires.
Predictive Analytics for Workforce Planning
AI tools are now capable of predicting staffing needs and managing recruitment processes. Platforms like Employment Hero use AI to analyze data on organizational structure, employee turnover, and hiring times to provide proactive hiring suggestions and workforce planning. This automation and predictive capability help companies prepare job descriptions, manage budgets, and plan long-term strategic hires effectively.
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
Reducing Waste through Predictive Analytics
AI helps businesses reduce waste in recruitment by using predictive analytics to identify actual hiring needs. By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI can forecast future job openings, enabling companies to plan recruitment efforts more efficiently and avoid overhiring. This not only cuts costs but also minimizes the waste of resources and time, making hiring practices leaner and more sustainable.
Optimizing Energy Consumption with Smart Systems
AI also plays a key role in optimizing energy consumption during the recruitment process. For example, using online recruitment platforms and video interviews significantly reduces the need for travel, which in turn cuts down carbon emissions. Additionally, AI can manage and allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that devices and systems are only active when necessary. This contributes to energy conservation and supports environmental protection goals.
How to Implement AI in Recruitment
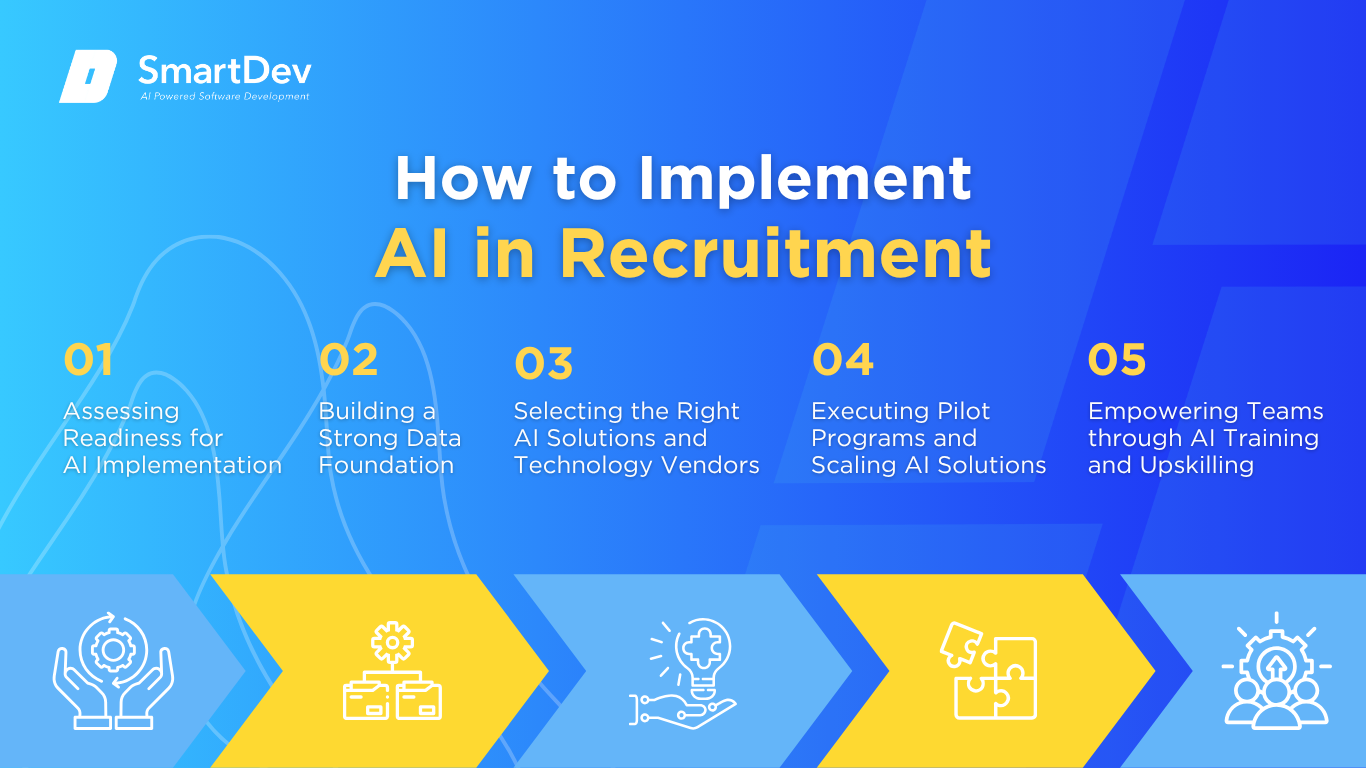
Step 1. Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Before implementing AI, organizations should evaluate their current recruitment processes to identify areas where AI can add value. This includes assessing the volume of applications, time spent on repetitive tasks, and challenges in candidate sourcing. Understanding these factors helps in determining the potential impact of AI on recruitment efficiency.
Additionally, organizations must consider their technological infrastructure and data availability. Ensuring that systems can support AI integration and that sufficient data is available for training AI models is crucial for successful adoption.
Step 2. Building a Strong Data Foundation
A robust data foundation is essential for effective AI implementation. This involves collecting, cleaning, and managing data related to candidates, job postings, and recruitment outcomes. High-quality data enables AI algorithms to make accurate predictions and recommendations.
Organizations should establish data governance policies to maintain data integrity and compliance with privacy regulations. Regular audits and updates to data sets ensure that AI models remain relevant and unbiased.
Step 3. Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Selecting appropriate AI tools and vendors requires careful consideration of the organization’s specific needs and goals. Factors to evaluate include the tool’s capabilities, ease of integration with existing systems, scalability, and vendor support.
Engaging with vendors who have experience in the recruitment industry and a track record of successful AI implementations can increase the likelihood of a smooth transition. It’s also beneficial to seek solutions that offer customization to align with the organization’s unique recruitment processes.
Step 4. Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Implementing AI should begin with pilot projects to test the technology’s effectiveness in a controlled environment. Pilots allow organizations to assess performance, identify issues, and make necessary adjustments before full-scale deployment.
Based on pilot outcomes, organizations can develop a roadmap for scaling AI across recruitment functions. This includes setting clear objectives, timelines, and success metrics to guide the expansion and measure progress.
Step 5. Training Teams for Successful Implementation
Successful AI adoption requires training recruitment teams to work effectively with new technologies. This involves educating staff on AI functionalities, interpreting AI-generated insights, and integrating AI tools into daily workflows.
Providing ongoing support and resources ensures that teams remain proficient in using AI tools and can adapt to updates or changes. Encouraging a culture of continuous learning fosters innovation and maximizes the benefits of AI in recruitment.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Recruitment
Key Metrics to Track Success
Assessing the ROI of AI in recruitment begins with analyzing key metrics like time-to-hire and cost-per-hire. AI tools speed up hiring by automating resume screening, candidate outreach, and scheduling. This shortens the hiring cycle and helps fill critical roles faster, improving operational efficiency. Simultaneously, automation reduces the need for recruitment agencies and lowers administrative costs, contributing to significant financial savings.
AI also enhances the quality of hire and candidate experience, which are equally important ROI factors. Intelligent matching algorithms help identify candidates who align better with the role and company culture, leading to longer tenure and improved performance. At the same time, AI-powered chatbots and scheduling assistants offer candidates faster, more personalized communication, boosting engagement and strengthening employer brand perception.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Companies adopting AI in recruitment are seeing clear, measurable results. Unilever used AI for screening and digital assessments, cutting their time-to-hire by 90% and increasing hiring diversity by 16%. Nestlé automated its interview scheduling using conversational AI, saving 8,000 recruiter hours per month and enhancing candidate interactions.
In another case, a leading telecom provider in New Zealand partnered with Sapia.ai, adopting AI-driven text assessments that reduced recruitment costs by 70% and improved workforce diversity. These examples highlight how AI delivers not just efficiency, but also better hiring outcomes and strategic workforce advantages.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
One major challenge in AI adoption is algorithmic bias. If the training data reflects past hiring prejudices, the AI may perpetuate them, as seen in Amazon’s discontinued recruitment tool. To prevent this, organizations must audit their models regularly, use inclusive data, and ensure that decisions made by AI are explainable and fair.
Another issue is relying too heavily on AI without human oversight. While AI handles high-volume tasks well, it may miss subtle qualities like interpersonal skills or cultural fit. Combining AI’s speed with recruiters’ intuition ensures better decisions. Clear guidelines on when to involve human judgment are key to using AI responsibly and effectively in hiring.
Future Trends of AI in Recruitment
Predictions for the Next Decade

In the coming decade, AI will become deeply embedded in recruitment, driving more advanced innovations like predictive workforce analytics, immersive virtual reality interviews, and hyper-personalized candidate journeys. AI will shift from being a tool for task automation to a strategic advisor—identifying future talent gaps, forecasting turnover risks, and even recommending training paths to build internal talent pipelines. These capabilities will allow HR leaders to transition from reactive to proactive recruitment planning.
Importantly, these advancements won’t be exclusive to large corporations. As AI technology becomes more accessible and cost-effective, small and medium-sized businesses will also integrate it into their hiring processes. At the same time, global regulations will evolve to ensure ethical and transparent AI use. Companies that stay informed and adapt to these shifts will be better positioned to attract high-quality talent and build resilient, future-ready teams.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To stay ahead, companies must begin by investing in AI literacy across their HR teams. Understanding how AI works – its benefits, risks, and limitations – empowers recruiters to make informed, ethical decisions. It also builds internal trust and reduces resistance to technological change. Upskilling initiatives, in-house training, and collaboration with AI experts can bridge knowledge gaps and prepare teams for effective AI integration.
Additionally, businesses should embrace a mindset of continuous improvement. Implementing AI is an evolving journey. Regularly reviewing AI tools, collecting feedback from users and candidates, and iterating on the process ensures that technology continues to align with hiring goals. Companies that combine technological agility with a strong ethical foundation will not only recruit better workers, but they’ll also lead to the future of work.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI is transforming recruitment by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing the candidate experience, and delivering data-driven hiring decisions that improve both efficiency and outcomes. From generative AI crafting job descriptions to predictive analytics identifying future hiring needs, the technology enables HR teams to operate more strategically. As shown in real-world case studies, AI can significantly reduce time-to-hire, cut costs, and boost workforce diversity when implemented thoughtfully.
However, to achieve these benefits, organizations must approach AI with intention and structure. A strong data foundation, clear evaluation of tools, and investment in team training are essential for long-term success. It’s also critical to remain aware of ethical considerations, such as bias and transparency, and to balance AI automation with human judgment. When measured carefully, the ROI of AI in recruitment proves both compelling and sustainable.
Moving Forward: A Path to Progress
Now is the time to act. If you’re leading a recruitment function and looking to streamline your hiring process, reduce operational inefficiencies, and attract top-tier talent in a competitive market, adopting AI is a strategic necessity.
Start with a focused pilot project, assess your current data readiness, and explore trusted AI vendors with proven industry expertise. The recruitment landscape is evolving quickly, and early adopters are already achieving faster, smarter, and fairer hiring outcomes. Don’t get left behind – embrace AI now to build a recruitment engine that’s ready for the future.
At SmartDev, we help businesses integrate AI into recruitment workflows to improve candidate matching, automated screening, and scale hiring without increasing headcount. Curious about AI’s potential for your recruitment team? Let SmartDev guide your journey – kickstart your AI transformation with a custom pilot program today.
—
References:
- 7 in 10 Companies Will Use AI in the Hiring Process in 2025 Despite Most Saying It’s Biased | ResumeBuilder
- AI Recruitment Market | Verified Market Research
- Hilton Wants to Use AI to Personalize Hotel Bookings | Skift
- L’Oréal: How We’re Using AI in Recruitment | Marketing Week
- Amazon Scraps Secret AI Recruiting Tool That Showed Bias Against Women | The Guardian
- AI in Talent Acquisition: Trends and Considerations | Deloitte Human Capital Blog
- Independent Review Certifies SkyHive’s Skills Models as Free of AI Bias | SkyHive






