The BFSI sector faces one of the most aggressive cyber threat landscapes due to its high-value data, digital transactions and expanding cloud infrastructure. Financial institutions are prime targets for ransomware, API attacks and credential breaches, while regulatory frameworks such as PCI DSS and GDPR require continuous monitoring and audit-ready security controls. The cost of data breaches in financial services remains among the highest across industries, making robust security testing a strategic necessity rather than an operational choice. Implementing best practices automated security testing bfsi strategies helps organizations proactively identify vulnerabilities and maintain regulatory compliance.
Manual security testing alone cannot keep up with rapid DevSecOps cycles and increasingly complex architectures. Automated security testing integrates directly into CI/CD pipelines, enabling continuous vulnerability detection, faster remediation and scalable protection. When enhanced with AI and machine learning, modern solutions can detect anomalies, simulate attack paths and prioritize risks intelligently. For BFSI organizations, AI-driven automation strengthens resilience, reduces operational risk and supports secure digital transformation.

Understanding the Security Landscape in BFSI
The Banking, Financial Services and Insurance industry operates in one of the most complex and high-risk cybersecurity environments. Rapid digital transformation, strict compliance requirements and sophisticated cybercriminal tactics create a uniquely challenging security landscape. To implement best practices automated security testing bfsi strategies effectively, organizations must first understand the specific threats and structural risks inherent to this sector.
1. Unique Security Challenges in Banking, Financial Services and Insurance
High-Value Data and Transaction Systems
BFSI organizations store and process highly sensitive information, including:
- Customer personally identifiable information
- Credit card and payment data
- Investment portfolios and trading records
- Loan and mortgage documentation
- Insurance claims data
This data has direct monetary value on underground markets. In addition, real-time transaction systems handle millions of financial operations daily. Any vulnerability can lead to fraud, financial theft or large-scale service disruption. Attackers target both data repositories and transactional APIs to exploit weaknesses quickly before detection.
Complex Legacy Infrastructure
Many banks and insurers still rely on legacy core banking systems built decades ago. These systems often:
- Run on outdated architectures
- Lack modern encryption standards
- Are difficult to integrate with modern security tools
- Require manual patching processes
When digital channels such as mobile apps and fintech integrations are layered on top of legacy systems, the attack surface increases significantly. Security testing becomes more complex because vulnerabilities may exist both in old core systems and new cloud-native components. Automated security testing helps continuously scan across hybrid environments without disrupting operations.
Third-Party and API Risks
Open banking initiatives and fintech partnerships have increased API usage across BFSI ecosystems. While APIs enable innovation and seamless customer experiences, they also introduce risks such as:
- Weak authentication mechanisms
- Misconfigured API gateways
- Excessive data exposure
- Insecure third-party integrations
Third-party vendors, cloud providers and SaaS platforms can also create supply chain vulnerabilities. If a vendor’s security posture is weak, attackers may use it as an entry point into the primary institution. Automated API security testing and continuous monitoring are critical to managing these risks effectively.
Digital Banking Expansion and Cloud Migration
The shift toward digital banking, mobile platforms and cloud infrastructure improves scalability and customer convenience. However, it also introduces:
- Misconfigured cloud storage
- Insecure DevOps pipelines
- Increased identity and access management complexity
- Multi-cloud visibility gaps
As BFSI institutions accelerate cloud adoption, manual testing approaches struggle to keep pace. Automated, AI-enhanced security testing provides continuous visibility across distributed environments and reduces configuration-related vulnerabilities.
 2. Common Vulnerabilities in BFSI Applications
2. Common Vulnerabilities in BFSI Applications
Understanding common weaknesses helps organizations prioritize testing efforts.
OWASP Top 10 in Financial Applications
Many financial applications are vulnerable to risks identified in the OWASP Top 10, including:
- Injection attacks
- Broken authentication
- Sensitive data exposure
- Security misconfiguration
- Cross-site scripting
These vulnerabilities can lead to account takeovers, data leaks and unauthorized transactions. Integrating static and dynamic automated testing tools helps detect such issues early in the development lifecycle.
API Exploitation and Credential Attacks
APIs are a frequent target in BFSI systems. Common threats include:
- Credential stuffing attacks using stolen login data
- Brute-force authentication attempts
- Token manipulation
- Rate-limit bypass techniques
Without automated API testing and anomaly detection, these attacks may go unnoticed until financial damage occurs. Continuous security validation ensures APIs remain protected against evolving exploitation methods.
Insider Threats and Privilege Escalation
Not all threats originate externally. Employees, contractors or partners with legitimate access may intentionally or unintentionally expose systems to risk. Insider threats often involve:
- Excessive access privileges
- Weak identity governance
- Lack of monitoring for suspicious behavior
- Inadequate segregation of duties
Privilege escalation vulnerabilities can allow attackers to gain administrative control after initial access. Automated monitoring combined with behavior-based analytics strengthens internal threat detection.
AI-Powered Attack Techniques
Cybercriminals increasingly use artificial intelligence to automate reconnaissance, generate phishing campaigns and identify exploitable vulnerabilities. AI-driven malware can adapt to defensive mechanisms and evade traditional detection tools. This evolution requires BFSI organizations to adopt AI-enabled automated security testing solutions capable of simulating advanced attack paths and detecting abnormal patterns in real time.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Requirements Driving Automation
Compliance obligations significantly shape the BFSI security strategy.
PCI DSS
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard mandates strict controls for handling cardholder data. Organizations must demonstrate continuous vulnerability management, secure coding practices and regular security testing.
ISO 27001
This international standard focuses on information security management systems. It requires risk assessments, documented controls and ongoing monitoring processes to protect sensitive data assets.
SOC 2
SOC 2 emphasizes security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality and privacy. Financial institutions must maintain audit-ready documentation and evidence of control effectiveness.
GDPR and Regional Data Protection Laws
Data protection regulations require organizations to safeguard personal information and report breaches within defined timeframes. Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage.
 Audit Trail and Continuous Monitoring Requirements
Audit Trail and Continuous Monitoring Requirements
Modern regulatory frameworks increasingly demand:
- Real-time monitoring capabilities
- Documented vulnerability remediation processes
- Automated reporting and audit trails
- Continuous risk assessment
Manual reporting methods are insufficient to meet these expectations consistently. Automated security testing platforms generate structured evidence, reduce human error and support compliance alignment.
Understanding these unique challenges, common vulnerabilities and regulatory pressures enables BFSI organizations to design a robust, automation-driven security strategy. By aligning technology, governance and AI-enhanced testing capabilities, financial institutions can reduce risk exposure while maintaining agility in a competitive digital landscape.
Best Practices Automated Security Testing BFSI Organizations Must Follow
1. Shift-Left Security Testing inDevSecOpsPipelines
Shift-left security requires integrating automated testing directly into CI/CD pipelines so vulnerabilities are detected during development rather than after deployment. By embedding SAST, DAST and dependency scans into build workflows, BFSI organizations ensure every code change is automatically validated against security standards.
Early vulnerability detection reduces remediation costs, accelerates release cycles and prevents insecure code from reaching production systems. Secure coding validation tools further enforce encryption standards, access control policies and regulatory requirements consistently across development teams.
2. Implementing Multi-Layered Automated Testing Strategies
A strong automated framework combines multiple testing methods including SAST, DAST, IAST, Software Composition Analysis and API security testing. Each layer addresses different parts of the attack surface, from source code vulnerabilities to runtime misconfigurations and third-party dependency risks.
This multi-layered approach is essential in BFSI environments where applications integrate legacy systems, cloud services and fintech APIs. Comprehensive coverage minimizes blind spots and ensures both internal systems and external interfaces are continuously protected.
3. Risk-Based Test Prioritization
Risk-based prioritization ensures security efforts focus on systems with the highest financial and operational impact. Threat modeling and business impact analysis help identify critical assets such as payment gateways, transaction engines and customer data repositories.
By mapping the attack surface and ranking vulnerabilities based on severity and business risk, BFSI organizations can allocate resources efficiently. This approach improves remediation speed while aligning security initiatives with enterprise risk management strategies.
4. Continuous Security Testing and Monitoring
Security testing must be continuous rather than periodic in fast-moving financial environments. Automated regression tests and ongoing vulnerability scans ensure new releases and infrastructure changes do not introduce additional weaknesses.
Integrating real-time threat intelligence further strengthens monitoring capabilities. Continuous visibility across cloud, on-premise and hybrid systems reduces exposure windows and supports rapid incident response.
5. AI-Driven Security Testing in BFSI
Artificial intelligence enhances automated security testing by enabling anomaly detection, predictive risk analytics and intelligent exploit simulation. Machine learning models analyze transaction behavior and system activity to identify unusual patterns that may signal fraud or intrusion attempts.
AI-driven test case generation and attack path simulation increase coverage while reducing manual workload. This transforms security testing from reactive vulnerability discovery into proactive and predictive risk management.
6. Automation Governance and Reporting
Effective governance ensures automated security testing aligns with compliance frameworks and executive oversight requirements. Tracking key metrics such as mean time to detect and remediate vulnerabilities provides measurable insight into security performance.
Automated dashboards and documentation tools generate audit-ready reports for standards such as PCI DSS and ISO 27001. This reduces administrative effort while maintaining continuous compliance and transparency.
Explore how SmartDev partners with BFSI teams through a focused AI sprint to validate use cases, align stakeholders, and define a clear path forward before AI development begins.
SmartDev helps BFSI organizations clarify AI use cases and assess feasibility, enabling confident decisions and reducing risks before committing to AI development.
Learn how SmartDev accelerates AI initiatives, ensuring rapid deployment and reduced time to market.
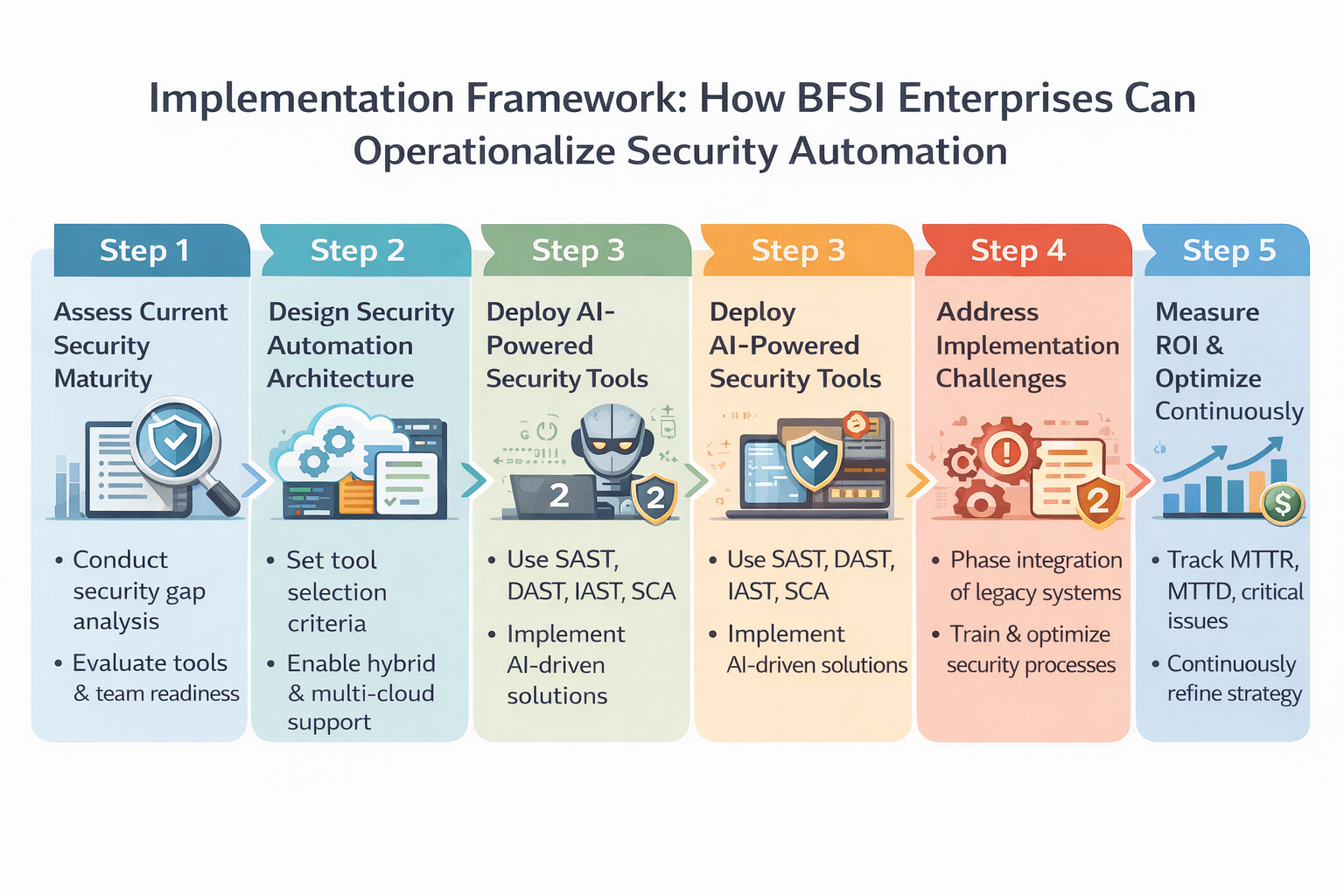
Build Your AI Chatbot With UsImplementation Framework: How BFSI Enterprises Can Operationalize Security Automation
To successfully operationalize automated security testing, BFSI enterprises should follow a structured step-by-step approach. Each step builds on the previous one, ensuring security automation aligns with business risk, regulatory compliance and digital transformation goals.
 Step 1: Assess Current Security Maturity
Step 1: Assess Current Security Maturity
Begin with a comprehensive security gap analysis. Identify vulnerabilities across applications, infrastructure, APIs and cloud environments. Evaluate incident response processes, vulnerability management cycles and compliance alignment to understand where automation can create the greatest impact.
Next, conduct a toolchain and organizational readiness assessment. Review whether existing security tools integrate with DevOps pipelines and whether teams possess the skills required to manage automated platforms. Executive sponsorship and cross-department alignment are essential before moving forward.
Step 2: Design a Scalable Security Automation Architecture
Define clear tool selection criteria based on regulatory requirements, system complexity and integration capability. Choose platforms that support CI/CD integration, API security testing, dependency scanning and AI-driven analytics.
Ensure the architecture supports hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Centralized visibility and unified policy enforcement are critical in BFSI ecosystems that combine legacy systems with modern cloud-native applications.
Step 3: Deploy AI-Powered Security Tools
Implement automated testing platforms such as SAST, DAST, IAST and Software Composition Analysis within development pipelines. This ensures vulnerabilities are continuously detected across the software lifecycle.
Complement these with AI-driven analytics tools, automated penetration testing solutions and orchestration platforms. AI enhances anomaly detection, risk prioritization and attack path simulation, improving overall detection accuracy and operational efficiency.
Step 4: Address Implementation Challenges
Mitigate legacy system constraints through phased integration and API-based connectors. Avoid large-scale disruptions by gradually extending automation coverage across core banking and transaction systems.
Invest in talent development and process optimization. Provide training on AI-driven platforms and implement intelligent filtering mechanisms to reduce false positives and alert fatigue. Align security objectives with measurable business outcomes to justify budget allocation.
Step 5: Measure ROI and Optimize Continuously
Track key performance indicators such as mean time to detect, mean time to remediate and number of critical vulnerabilities per release. These metrics provide clear evidence of security improvements.
Evaluate long-term business impact, including reduced breach probability, faster release cycles and lower compliance costs. Use these insights to continuously refine the automation strategy and strengthen resilience across the BFSI enterprise.
Challenges When Adopting Automated Security Testing in BFSI
Adopting automated security testing in BFSI delivers long-term resilience and efficiency, but implementation is often complex. Financial institutions operate in high-risk, highly regulated and technology-diverse environments. Below are the key challenges organizations must address to successfully implement automation at scale.
 1. Legacy Infrastructure Constraints
1. Legacy Infrastructure Constraints
Many banks and insurance providers still rely on legacy core banking systems built decades ago. These platforms were not designed for API-first architectures or seamless integration with modern DevSecOps and AI-driven security tools. As a result, automated scanners may struggle to connect with outdated databases, monolithic applications or proprietary transaction engines.
Modernizing security without disrupting mission-critical systems is a delicate process. A full system replacement is rarely feasible due to operational risk and cost. Therefore, institutions must adopt phased integration strategies, using middleware, API wrappers or hybrid monitoring solutions to extend automated testing coverage gradually. This increases implementation time and complexity but is necessary for stability.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Sensitivity
BFSI organizations operate under strict regulatory frameworks such as PCI DSS, ISO 27001, SOC 2 and regional data protection laws. Any new security tool or automation workflow must align with compliance requirements and undergo validation before deployment. Even minor configuration changes can trigger audit concerns.
This regulatory pressure often slows decision-making and increases internal review cycles. Security leaders must prove that automation strengthens audit readiness, enhances reporting accuracy and maintains data protection standards. Pilot programs and controlled rollouts are typically required before enterprise-wide adoption is approved.
3. Talent Gaps and Organizational Resistance
Automated security testing requires specialized skills in DevSecOps, cloud security, AI analytics and risk modeling. Many BFSI institutions face talent shortages in these areas. Existing security teams may be experienced in manual penetration testing but lack exposure to automation orchestration and machine learning-based tools.
Beyond technical skills, cultural resistance can also delay adoption. Teams accustomed to manual testing processes may distrust automated findings or fear job displacement. Clear communication, structured training programs and leadership sponsorship are essential to build confidence and ensure collaboration between security, development and operations teams.
4. False Positives and Alert Fatigue
Automated tools can generate high volumes of vulnerability findings, especially in complex BFSI ecosystems with multiple integrations and cloud workloads. Without intelligent prioritization, security teams may become overwhelmed by alerts, leading to slower remediation and missed critical threats.
To address this, organizations must implement contextual risk scoring and AI-based filtering mechanisms. Continuous tuning of detection rules and workflow automation helps reduce noise and focus attention on high-impact vulnerabilities. Managing alert fatigue is critical for sustaining operational efficiency.
5. Budget Constraints and ROI Justification
Security automation initiatives often require significant upfront investment in tools, training and integration. In many financial institutions, security spending is viewed as a cost center rather than a growth driver. This perception can delay approval for automation programs.
To overcome this challenge, organizations must clearly demonstrate measurable business value. Linking automation outcomes to reduced breach probability, faster software release cycles and lower compliance costs strengthens the investment case. When positioned as a strategic enabler of digital transformation, automated security testing becomes a competitive advantage rather than an operational expense.
By proactively addressing these challenges, BFSI enterprises can transition from fragmented manual testing to scalable, AI-enhanced automated security frameworks. Strategic planning, phased implementation and measurable performance tracking are essential to ensure long-term success.
Cybersecurity by the Numbers: Why Automation Is No Longer Optional in BFSI
Cybersecurity incidents are becoming more expensive and harder to manage — and the data proves it. According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, the global average cost of a data breach reached USD 4.44 million, marking the first decline in five years but still representing a substantial financial burden for organizations worldwide.
For highly regulated industries such as BFSI, this cost can be even higher. In the United States, breached organizations faced an average cost of USD 10.22 million, driven by regulatory fines, slower detection and higher operational disruption.
Delayed Detection Keeps Costs High
Time to detect and respond remains a critical factor in total breach cost. On average, it took 168 days to identify and another 51 days to contain a breach in financial organizations, meaning attackers may roam undetected for nearly six months.
Longer breach lifecycles translate directly to higher costs. In some IBM research, breaches that lasted more than 200 days cost 29 % more than those identified and contained quickly.
Automation Dramatically Reduces Breach Costs and Time
Organizations that extensively utilize security automation and AI see measurable benefits. The IBM 2025 report found that companies using AI-driven security tools reduced their breach lifecycle by an average of 80 days and saved approximately USD 1.9 million per breach compared to those without automation.
These improvements stem from automated detection, real-time scanning and faster incident response workflows that continuously monitor systems rather than relying on periodic manual checks. Early identification of threats reduces exposure time, limits data loss and dramatically cuts post-breach recovery costs.
 Manual vs. Automated Security Outcomes
Manual vs. Automated Security Outcomes
Comparative data further supports the ROI of automation:
- Organizations actively deploying AI and automation in security had substantially lower breach costs than those without these tools.
- Earlier IBM reports show that organizations integrating AI detected and contained breaches 108 days faster than those relying on manual processes.
Together, these trends confirm that automation not only lowers incident costs but also accelerates remediation timelines — which is crucial for BFSI firms handling real-time transactions and sensitive customer data.
Regulatory Penalties Add to the Financial Burden
Beyond direct breach expenses, regulatory penalties add another layer of risk. While not all BFSI breaches involve financial penalties, frameworks such as GDPR, PCI DSS and regional data protection laws can impose fines based on severity and breach impact. Large fines can push total costs well above breach resolution and recovery expenses, especially when customer data is involved.
Why These Numbers Matter for BFSI Leaders
For BFSI leaders, these figures reveal a strategic truth: manual security testing and reactive approaches are insufficient in a world where breaches cost millions and threat actors act in real time. Continuous, automated security — especially when enhanced with AI — shortens detection times, lowers total breach costs, improves compliance posture and strengthens operational resilience.
Investing in automation isn’t just about technology — it’s about reducing financial risk, protecting customer trust and ensuring regulatory alignment in an era where the cost of inaction can be measured in millions of dollars.
Why BFSI Businesses Should Choose SmartDev for Automated Security Testing
Selecting the right technology partner is as critical as choosing the right security tools. In the BFSI sector, where digital transformation, regulatory pressure and cyber threats converge, organizations need a partner that understands both financial systems and advanced automation. SmartDev positions itself as a strategic technology provider capable of delivering secure, AI-driven and compliance-ready automated security testing solutions tailored specifically for BFSI enterprises.
 1. Deep Expertise in BFSI Digital Transformation
1. Deep Expertise in BFSI Digital Transformation
SmartDev brings hands-on experience across banking, insurance and fintech platforms. BFSI systems are fundamentally different from other industries due to their transaction intensity, regulatory exposure and integration complexity. SmartDev understands the operational realities of core banking systems, payment gateways, digital wallets, insurance claim platforms and open banking APIs.
Beyond development, SmartDev applies a secure-by-design engineering approach. Security is embedded from architecture planning through deployment, ensuring encryption standards, identity controls and secure API structures are implemented from the beginning. This reduces downstream remediation costs and strengthens long-term resilience.
2. AI and Machine Learning Capabilities in BFSI
SmartDev integrates AI and machine learning into automated security testing workflows to enhance detection speed and accuracy. AI-driven test automation allows continuous scanning, anomaly detection and intelligent risk prioritization across large-scale financial environments. This significantly reduces manual analysis and accelerates remediation cycles.
The company also applies AI use cases in cybersecurity, including behavior-based fraud detection and attack path simulation. Generative AI capabilities can support risk modeling and scenario simulation, helping BFSI organizations anticipate emerging threats. In addition, SmartDev understands regional adoption trends in AI across financial markets, allowing clients to align security modernization strategies with global best practices and regulatory developments.
3. End-to-EndDevSecOpsIntegration
Modern financial institutions require security to be seamlessly integrated into DevOps pipelines. SmartDev delivers end-to-end DevSecOps integration, embedding automated testing tools into CI/CD workflows to ensure continuous vulnerability detection throughout the software lifecycle.
The company designs custom automation frameworks tailored to each client’s infrastructure, whether cloud-native, hybrid or legacy-based. Continuous monitoring solutions provide real-time visibility into applications, APIs and infrastructure components. This ensures security is not treated as a periodic activity but as a continuous operational capability.
4. Compliance-Ready Security Engineering
Compliance is non-negotiable in BFSI. SmartDev aligns automated security testing practices with regulatory frameworks such as PCI DSS, ISO 27001 and regional data protection laws. By embedding compliance controls directly into testing workflows, the company helps organizations maintain consistent policy enforcement.
Audit documentation support is another key advantage. Automated reporting dashboards generate structured evidence for audits, reducing manual documentation burdens. Secure architecture design further ensures that systems meet regulatory requirements while remaining scalable and performance-optimized.
5. Proven Methodology and Client Success Outcomes
SmartDev applies a structured implementation methodology that moves from security maturity assessment to AI-enhanced automation deployment and continuous optimization. This phased approach minimizes operational disruption while delivering measurable improvements in vulnerability detection speed.
Clients benefit from faster identification of critical risks, reduced operational exposure and scalable automation frameworks capable of adapting to evolving cyber threats. By combining BFSI domain expertise, AI innovation and compliance-focused engineering, SmartDev enables financial institutions to strengthen resilience while accelerating secure digital transformation.
For BFSI organizations seeking long-term security, regulatory confidence and operational efficiency, partnering with SmartDev provides more than automated testing tools. It delivers a strategic security modernization roadmap aligned with business growth and technological evolution.
Case Studies: Automated Security Testing in Action for BFSI
1. Optimizing Credit Reporting Systems for Enhanced Financial Inclusion and Security
Overview
SmartDev partnered with a financial services organization to modernize its credit reporting system, strengthening data protection while improving scalability and operational efficiency. The platform processed sensitive financial and identity data, requiring high reliability and strict compliance alignment.
Challenges
The legacy system faced performance bottlenecks under increasing transaction volumes. Manual validation processes delayed updates, and growing integration complexity increased exposure to security and compliance risks.
Solutions
- Redesigned architecture using a secure-by-design framework
- Integrated automated security testing into CI/CD pipelines
- Implemented automated API validation and authentication testing
- Deployed continuous vulnerability scanning and performance monitoring
- Strengthened encryption and role-based access control mechanisms
Client’s Achievements
- Reduced critical vulnerability exposure by 45% within the first release cycle
- Improved system processing performance by 30%
- Decreased deployment-related incidents by 40%
- Shortened release validation time by 35%
- Increased audit readiness efficiency by 50% through automated reporting
2. Ultra-Fast Secure BaaS Platform for Next-Gen Digital Banking

3d rendering robot hand holding credit card
Overview
SmartDev delivered a secure, scalable Banking-as-a-Service platform designed to support rapid digital banking expansion and third-party integrations. The system required real-time transaction processing and strong API security controls.
Challenges
The client needed to maintain ultra-fast transaction speeds while securing APIs and managing complex cloud integrations. Frequent feature updates increased the risk of misconfigurations and security gaps.
Solutions
- Integrated automated SAST, DAST and API security testing into CI/CD
- Deployed continuous cloud infrastructure vulnerability scanning
- Implemented AI-driven anomaly detection for transaction monitoring
- Established automated regression testing for high-frequency releases
- Centralized monitoring dashboards for real-time risk visibility
Client’s Achievements
- Reduced API-related security incidents by 50%
- Accelerated release cycles by 38%
- Improved transaction processing stability by 25%
- Lowered manual testing workload by 60%
- Decreased mean time to detect vulnerabilities by 42%
3. Mobile Channel for a Leading European Credit Card Provider

Flat man paying online and receiving cashback to e-wallet. Bonus money or reward back on credit card for purchase. Coins transfer from smartphone to wallet. Cash refund. Financial savings concept.
Overview
SmartDev enhanced the mobile channel of a European credit card provider, focusing on secure authentication, transaction integrity and high-performance delivery for large user volumes.
Challenges
Frequent feature updates and growing customer adoption increased operational pressure. Manual security validation slowed deployment and created potential compliance risks.
Solutions
- Embedded automated security and regression testing into mobile DevOps workflows
- Implemented automated authentication and session management validation
- Deployed continuous monitoring for fraud indicators and anomalies
- Strengthened encryption protocols and mobile API security testing
- Introduced performance benchmarking with automated alerts
Client’s Achievements
- Reduced mobile application vulnerabilities by 47%
- Improved release deployment speed by 40%
- Decreased fraud-related security incidents by 33%
- Enhanced mobile platform uptime to 99.9% availability
- Cut post-release defect rates by 36%
These case studies demonstrate how SmartDev’s automated security testing approach delivers measurable performance improvements, vulnerability reduction and operational efficiency gains. By embedding automation and AI into BFSI environments, SmartDev helps financial institutions reduce risk while accelerating secure digital transformation.
Future Trends in Automated Security Testing for BFSI
1. Autonomous Security Testing Systems
Autonomous security platforms are evolving from simple vulnerability scanners to self-operating systems that detect, prioritize and remediate risks automatically. According to industry predictions, AI-driven security automation can reduce breach lifecycle by up to 80 days compared to manual processes, significantly lowering operational risk and response delays (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023).
For BFSI organizations, autonomous testing enables continuous exposure management instead of periodic assessments. This shift supports real-time risk reduction in high-transaction environments where delays can lead to direct financial losses.
2. AI-Augmented Penetration Testing
Traditional penetration testing is periodic and heavily manual. AI-augmented penetration testing enhances this model by simulating attack paths continuously and learning from previous exploit attempts. Organizations using AI and automation in security have reported saving approximately USD 1.76 million per breach compared to those without automation (IBM 2023).
In BFSI ecosystems, AI-driven offensive testing allows institutions to proactively identify vulnerabilities across APIs, cloud workloads and transaction systems before attackers exploit them.
3. Zero Trust Architecture Integration
Zero Trust security models are becoming foundational in financial services. Instead of trusting internal networks, Zero Trust enforces continuous identity verification and least-privilege access. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 60% of organizations will embrace Zero Trust as a starting point for security, up from less than 10% in 2020.
Automated security testing in Zero Trust environments focuses on validating access controls, authentication logic and micro-segmentation policies continuously. This reduces lateral movement risks and strengthens breach containment.
4. API-First Security Models
APIs are now core to open banking and fintech integration. However, APIs remain a major attack vector. Industry research shows that API attacks increased significantly in recent years, with API abuse becoming one of the fastest-growing attack methods.
Automated API security testing embedded in DevSecOps pipelines ensures continuous validation of authentication, rate limiting and data exposure. For BFSI institutions, API-first security is no longer optional due to growing third-party integration complexity.
5. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography Testing
As quantum computing advances, current encryption methods such as RSA and ECC may become vulnerable. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology is actively standardizing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms to prepare for future threats.
Forward-looking BFSI organizations are beginning to test quantum-resistant cryptography within automated validation frameworks. Early adoption ensures long-term data protection, particularly for financial records that must remain secure for decades.
Conclusion
Automated security testing is no longer a technical enhancement for BFSI institutions. It is a strategic necessity in an environment defined by rising breach costs, strict regulatory enforcement and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
For BFSI leaders looking to future-proof their digital infrastructure, the time to act is now. Partnering with an experienced technology provider that understands financial systems, regulatory complexity and AI-powered security innovation can significantly accelerate transformation.
If your organization is ready to strengthen its cybersecurity posture, reduce risk and scale securely, connect with SmartDev to build a tailored automated security testing roadmap designed specifically for the BFSI sector.


 2. Common Vulnerabilities in BFSI Applications
2. Common Vulnerabilities in BFSI Applications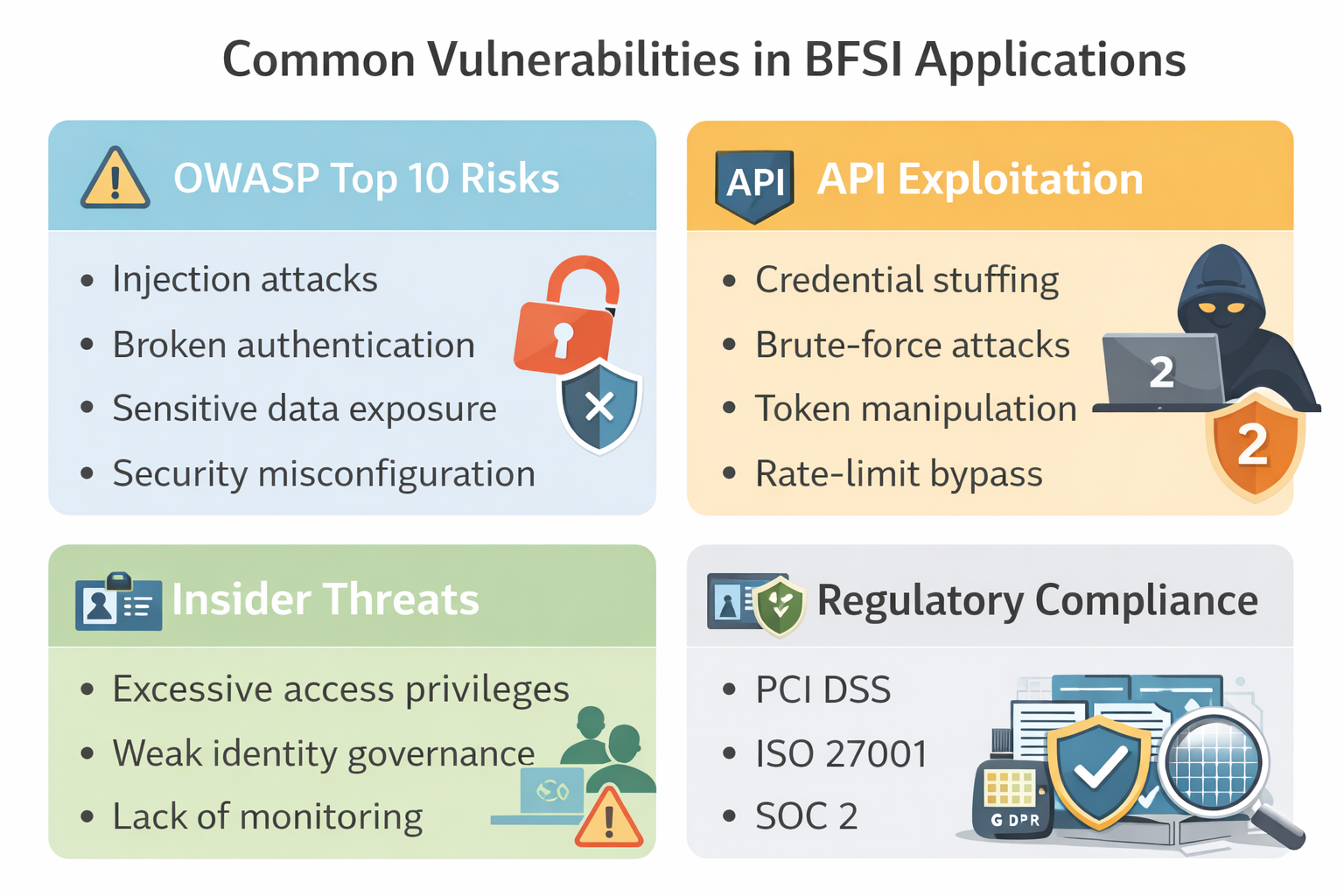 Audit Trail and Continuous Monitoring Requirements
Audit Trail and Continuous Monitoring Requirements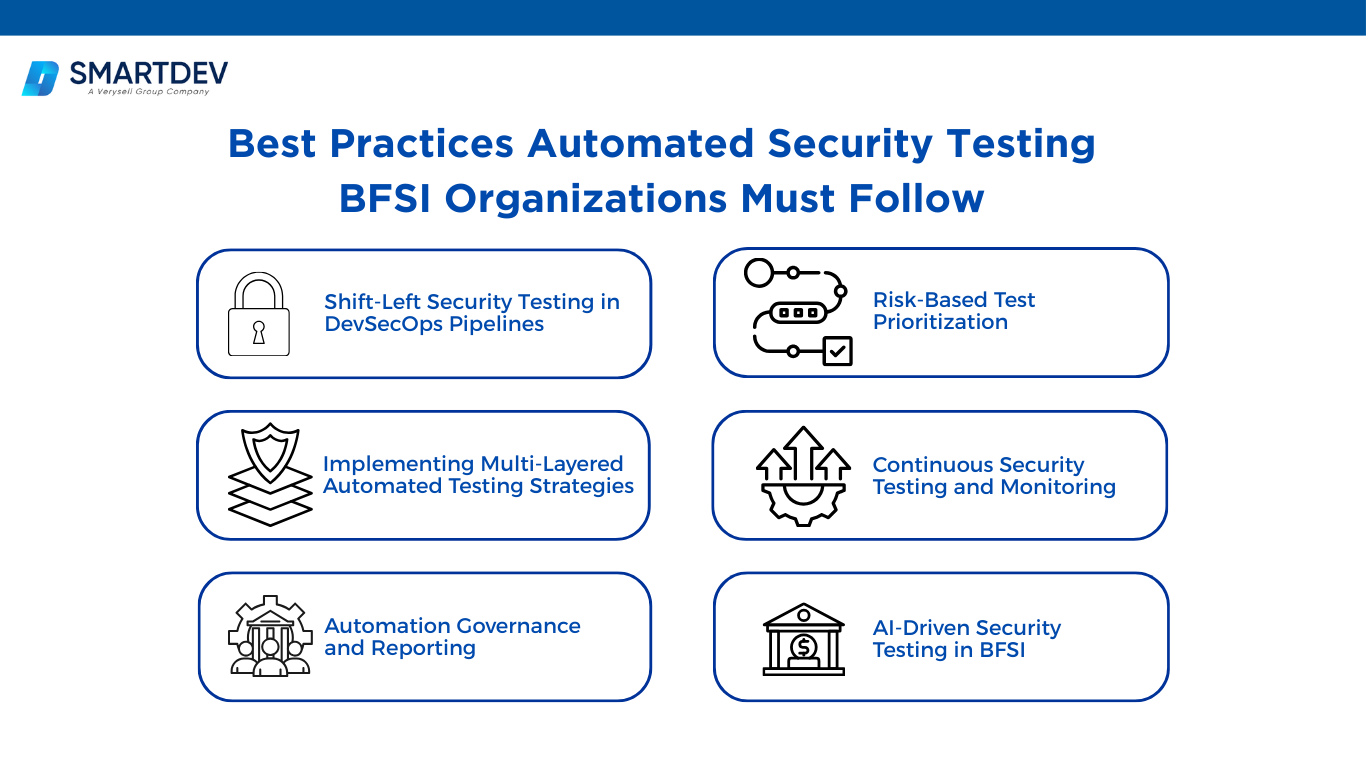
 Step 1: Assess Current Security Maturity
Step 1: Assess Current Security Maturity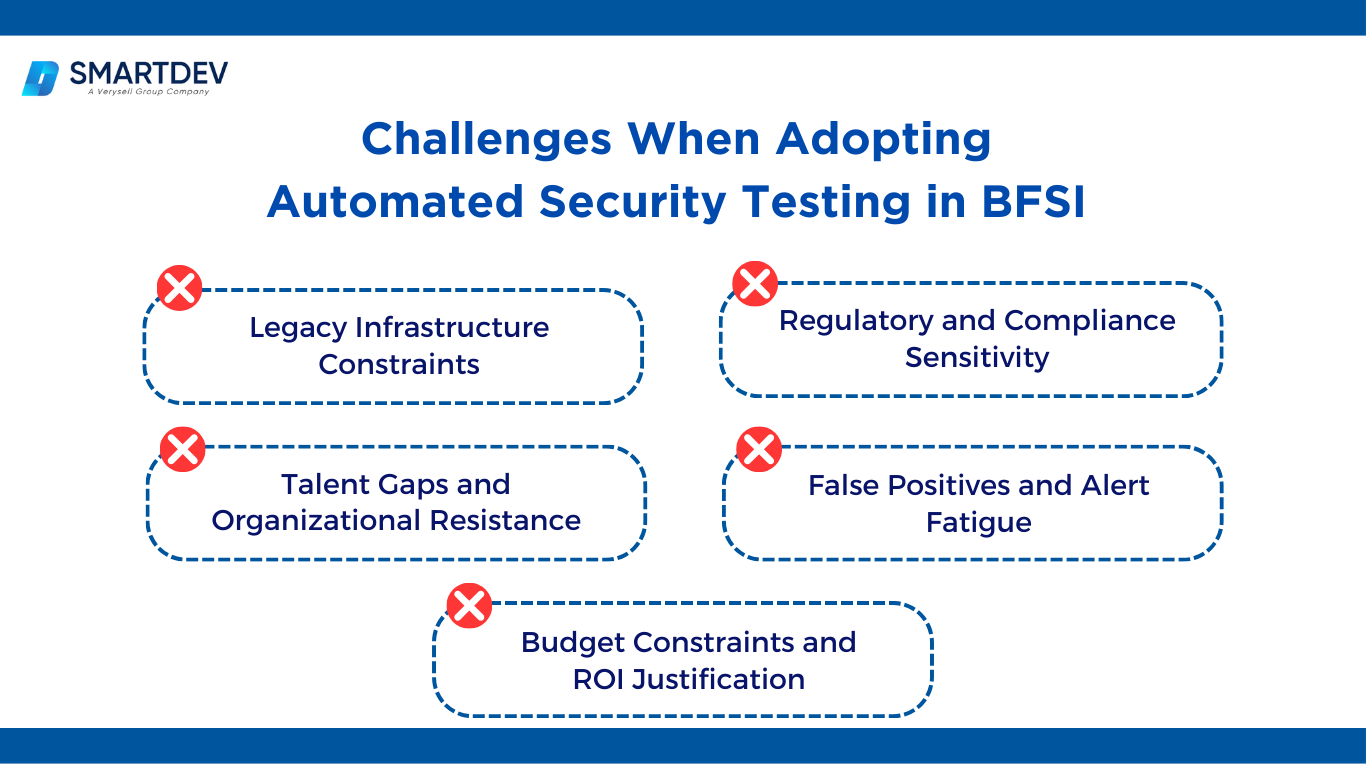 1. Legacy Infrastructure Constraints
1. Legacy Infrastructure Constraints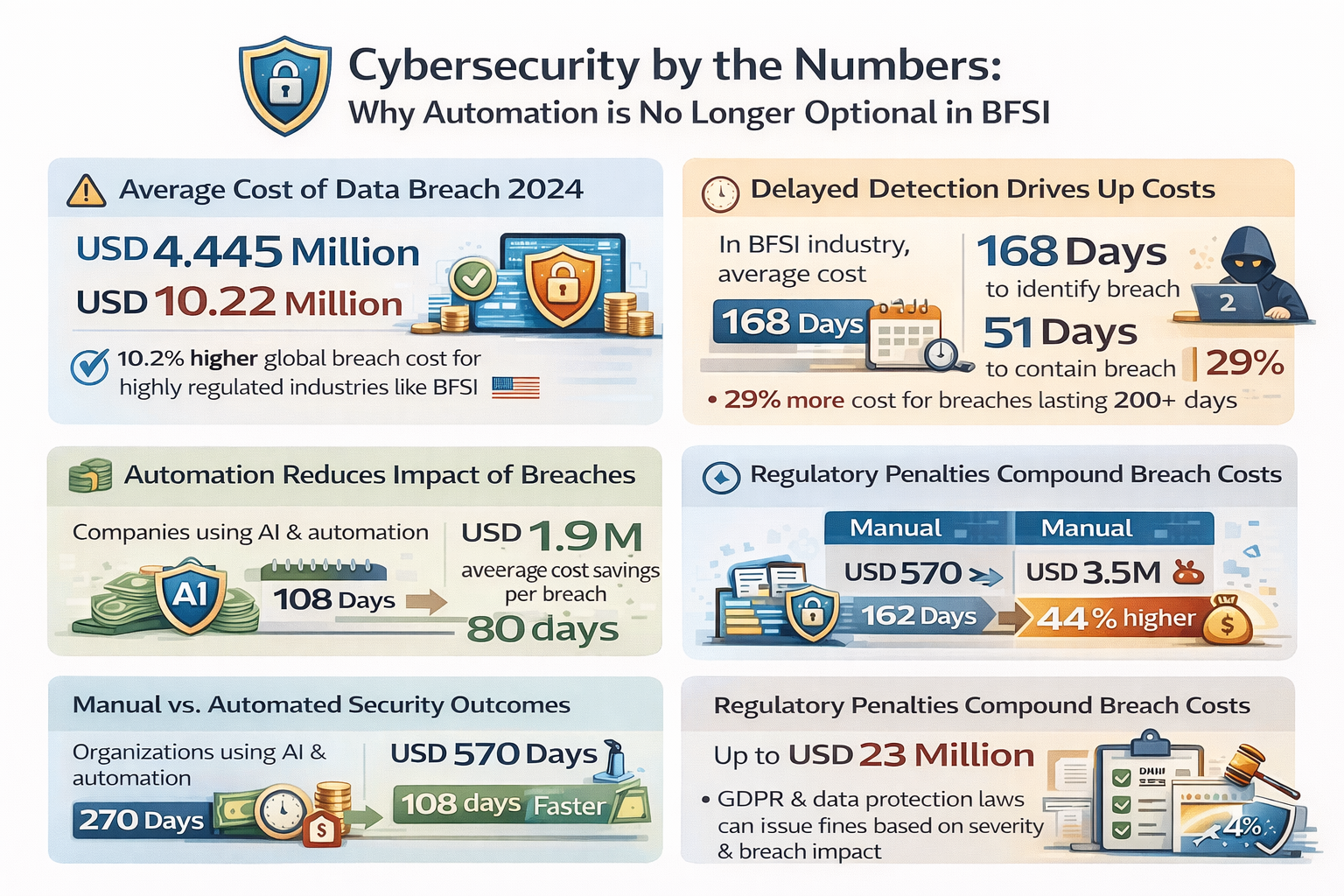 Manual vs. Automated Security Outcomes
Manual vs. Automated Security Outcomes 1. Deep Expertise in BFSI Digital Transformation
1. Deep Expertise in BFSI Digital Transformation





