In 2023, the world faced a dramatic surge in cyberattacks, with nearly 17 million incidents of cybercrime registered globally. The rise of ransomware alone continues to inflict massive financial damage, with global losses projected to reach $30 billion by the end of the year.
As technology advances, so do the tactics of cybercriminals, pushing businesses and governments into a constant state of defense. This unprecedented scale of digital attacks has led experts to predict that by 2025, cybercrime could cost the world more than $10.5 trillion annually – an economic burden that exceeds even the global drug trade.
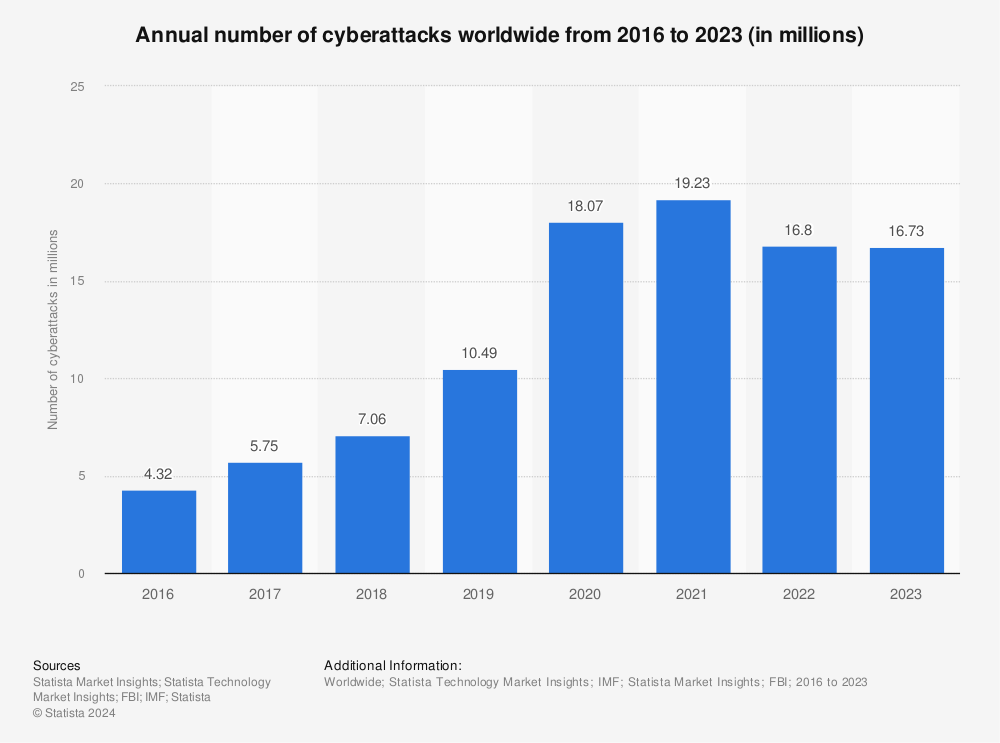
Figure 1: Annual number of cyberattacks worldwide from 2016 to 2023 (in millions)
The Rise of Digital Threats in a Hyper-Connected World
The rapid growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and the shift to remote work have exponentially increased the number of attack surfaces available to cyber criminals. Every new device, data stream, or platform represents a potential vulnerability in this hyper-connected world.
Cybercriminals have not stood still. They are evolving as fast as technology, deploying zero-day exploits, launching sophisticated phishing campaigns, and using increasingly targeted ransomware attacks to breach security systems. As a result, the cybersecurity landscape has become far more complex, and traditional defenses, often designed to respond to known threats, are proving insufficient against these rapidly evolving tactics.
Introducing AI: The Emerging Force in the Battle Against Cyber Threats
This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) is stepping in as a game-changer. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data in real time allows it to identify irregularities and threats before they escalate proactively. Traditional cybersecurity approaches, which often rely on fixed rules and known threat signatures, are no match for the speed and sophistication of today’s cyberattacks.
AI, by contrast, continuously learns from patterns, behaviors, and new data, adapting dynamically to detect and block threats that would otherwise evade human analysts or static security protocols. A 2022 study by Capgemini found that 69% of organizations consider AI essential to responding to cyberattacks, with those adopting AI-driven systems reporting a 60% faster threat detection rate.
Thesis Statement: AI’s Role in Transforming Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing cybersecurity by enabling organizations to anticipate and neutralize cyber threats through real-time analysis, advanced pattern recognition, and predictive capabilities.
In an era where cyberattacks are growing in frequency and sophistication, AI is an indispensable tool for staying one step ahead of attackers, allowing organizations to move from a reactive defense to a proactive strategy in safeguarding their digital assets.
1. How AI is Transforming Cybersecurity
1.1 Leveraging Machine Learning to Detect Anomalies
In recent years, financial services companies—long prime targets for cyberattacks—have increasingly turned to AI-driven solutions to safeguard their operations. While specific company stories remain confidential, numerous documented cases exist where AI successfully thwarted potential cyberattacks by detecting subtle anomalies that went unnoticed by human analysts.
In one such case, an AI-powered security system identified unusual access patterns in a global financial firm’s network, flagging login attempts from atypical locations and irregular data transfers. What seemed like routine behavior at first glance was revealed to be part of a larger, coordinated phishing and ransomware attempt. Thanks to AI’s early detection, the company could neutralize the threat before it caused any harm.
This is the power of artificial intelligence. Just as the human brain learns from experience and recognizes patterns, AI mimics this capability but at a scale and speed far beyond human capacity. Traditional cybersecurity systems rely on predefined rules to detect threats, often reacting to known attack vectors.
Conversely, AI continuously learns from vast amounts of data, adjusting to new threats in real-time. This ability to detect anomalies, identify emerging patterns, and respond instantly makes AI an invaluable tool in the cybersecurity arsenal.
1.2 AI Techniques Used in Cybersecurity
Behavioral Analysis: AI-driven systems excel at behavioral analysis by establishing a “normal” activity baseline across networks, devices, and users. These baselines allow AI to detect deviations—no matter how subtle—that could indicate malicious intent.
For example, unusual login times, abnormal data access requests, or deviations in network traffic patterns can trigger alerts. AI flags these behaviors in real-time, providing security teams with crucial early warnings. In financial services, this capability has been instrumental in detecting insider threats where otherwise authorized users might be attempting unauthorized actions. AI’s constant vigilance in monitoring network behavior offers a level of proactive defense that would be impossible for human analysts to match.
Figure 2: AI in Cybersecurity
Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics is another powerful tool in AI’s cybersecurity repertoire. By analyzing historical attack data, AI can forecast where and how future attacks will likely occur. This ability allows organizations to focus their defenses on vulnerable areas before they are targeted.
According to a 2022 study by IBM, companies that used AI for predictive security analytics reduced the average cost of data breaches by nearly 27%, underscoring the value of this capability. AI’s predictive power also helps prioritize patching vulnerabilities, allocating resources efficiently, and preemptively strengthening defenses where risks are highest.
Real-Time Response: One of the most transformative aspects of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to automate real-time responses to threats. AI systems can detect, contain, and mitigate threats as soon as they are identified, often within milliseconds. Whether isolating compromised devices, cutting off malicious network access, or neutralizing malware, AI can act faster than any human-led response.
According to Gartner, by 2025, AI will manage over 75% of all security tasks in real-time, a testament to its growing dominance in this field. This level of automation drastically reduces response times, minimizing potential damage and ensuring that cyberattacks are swiftly neutralized.
By leveraging machine learning, behavioral analysis, predictive analytics, and real-time response, AI transforms how organizations protect their networks. It’s not just a tool for catching threats but a proactive force that continuously learns, evolves, and stays one step ahead of cybercriminals in the ever-changing digital battlefield.
2. Key Advantages of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Defense
Imagine a scenario where a ransomware attack quietly infiltrates an organization’s IT network. Without warning, an AI-powered cybersecurity system detects unusual network behavior: an encrypted file transfer request from a seemingly legitimate source. Rather than waiting for further confirmation, the AI system cross-references this anomaly against vast datasets it has previously analyzed, quickly identifying the behavior as a precursor to a well-known ransomware variant.
Within milliseconds, the system isolates the affected device from the rest of the network, halting the spread of malicious code. The threat is neutralized before it can paralyze the organization’s operations. This proactive defense—where the attack is predicted and stopped before significant damage occurs—illustrates the transformative power of AI in cybersecurity.
Figure 3: Benefits of using AI in Cybersecurity
2.1 Advantages of AI in Cybersecurity
Speed & Efficiency: AI operates at speeds unimaginable for human analysts or traditional security protocols. Time is often the difference between a minor issue and a full-scale breach in cybersecurity. AI systems can process and analyze vast amounts of data in milliseconds, identifying anomalies and potential threats far quicker than any human could.
For example, an AI system monitoring a large enterprise’s network might simultaneously analyze traffic patterns from thousands of endpoints, identifying even the most minute deviations in behavior that could signal an emerging threat. Traditional security methods rely on predefined rules and signatures to detect threats, which can often lag behind fast-evolving cyberattacks. AI, however, learns from every piece of data it processes, improving its detection capabilities in real-time.
Threat Intelligence: One of AI’s greatest strengths is its ability to aggregate and process threat intelligence from various sources, including dark web activity, network traffic logs, and global cybersecurity incident reports. By continuously learning from new data, AI systems can recognize emerging threats long before they are widely understood or cataloged by traditional methods.
For instance, AI tools can sift through encrypted traffic, analyze unusual patterns, and cross-reference findings with known indicators of compromise (IoCs) from various threat intelligence sources. This kind of real-time aggregation and analysis gives organizations a significant edge, allowing them to preemptively defend against threats that have not yet reached their networks but are known to be circulating elsewhere in the digital landscape.
Adaptability: Unlike signature-based detection systems, which require constant manual updates to stay effective against new threats, AI adapts dynamically to the ever-evolving threat landscape. Thousands of new malware variants are released daily, making it nearly impossible for static systems to keep up.
Conversely, AI can autonomously learn from each interaction, threat, and anomaly, continuously refining its algorithms to detect new patterns that may indicate a potential attack. This adaptability makes AI particularly effective in combating sophisticated attacks like zero-day exploits, which traditional systems often miss due to the absence of pre-existing signatures. AI’s ability to “learn” from every new piece of data allows it to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, evolving in real time as threats become more advanced.
Reduced Human Error: Human analysts, while skilled, are not immune to error, particularly when faced with an overwhelming volume of data. As daily cyber incidents grow, so does the complexity of identifying genuine threats from benign anomalies. AI reduces the reliance on human intervention by automating the detection and analysis process, ensuring that subtle signs of an attack, such as minute changes in network traffic or seemingly innocent file transfers, do not go unnoticed.
Additionally, AI systems can triage alerts by categorizing them by priority so that human teams can focus on the most critical issues. This reduces the potential for oversight and frees up human resources to concentrate on strategic tasks rather than drowning in a sea of alerts.
In conclusion, AI’s speed, intelligence gathering, adaptability, and precision offer a level of cybersecurity that is not only reactive but predictive, allowing organizations to identify and neutralize threats before they escalate.
By analyzing massive datasets in real time, AI systems can catch the threats that traditional methods or human analysts might miss while continuously evolving to address new challenges in the cybersecurity landscape. As the sophistication of cyberattacks continues to grow, so too must the technologies designed to combat them—and AI is proving to be the future of that defense.
3. AI-Powered Tools and Their Role in Cybersecurity
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, organizations increasingly use AI-powered cybersecurity tools to protect themselves from relentless and sophisticated cyberattacks.
Tools like Darktrace, Cylance, and CrowdStrike have become cornerstones in defending corporate networks and sensitive data.
3.1 Automated Threat Detection
AI-powered tools like Cylance, owned by BlackBerry, have revolutionized automated threat detection by leveraging machine learning to scan networks continuously for vulnerabilities. Cylance’s AI-driven detection models boast an impressive 99.1% threat elimination rate, significantly higher than traditional antivirus systems.
These models use predictive algorithms that analyze the environment for signs of known and unknown malware, ensuring early detection before threats can exploit system weaknesses. Unlike traditional antivirus systems, which rely on signature-based detection and require regular updates, AI-powered solutions like Cylance can adapt dynamically to evolving threats, offering far more effective and efficient early threat identification.

Figure 4: CylandeMDR
According to a 2020 report by the Ponemon Institute, AI-enhanced security systems can reduce the time it takes to detect and respond to breaches by an average of 12 days – a critical factor when every second can mean the difference between a contained incident and a significant breach.
These systems continuously learn from the data they process, improving their detection capabilities and identifying threats faster than human analysts or signature-based security protocols could.
3.2 AI in Endpoint Protection
AI plays a pivotal role in endpoint protection, which helps safeguard devices from malware infections at entry. CrowdStrike’s Falcon platform is a leading AI-powered tool in this domain, processing over 1 trillion endpoint-related events per day. By analyzing endpoint activities in real-time, including file execution, system calls, and network behaviors, Falcon can detect unusual patterns that indicate a potential threat.
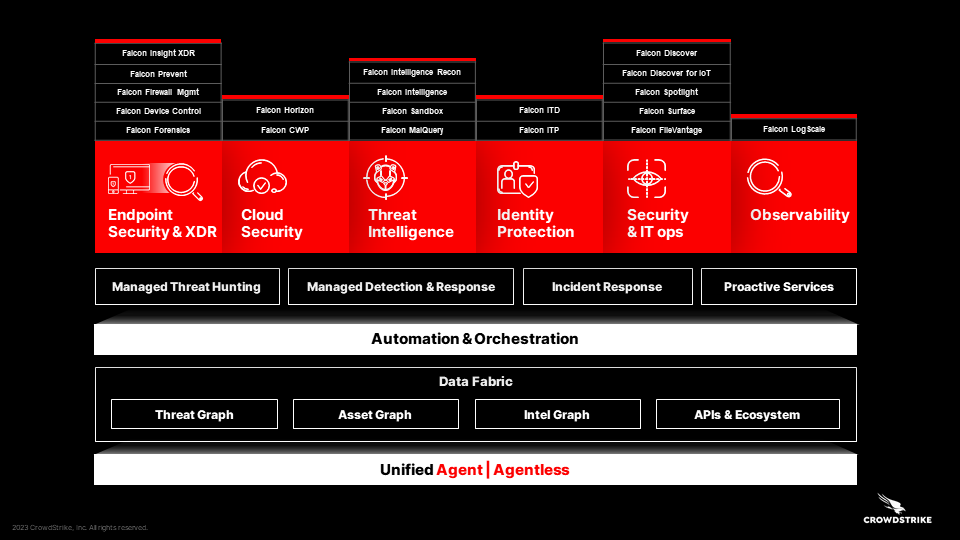
Figure 5: CROWDSTRIKE
In 2021, companies using Falcon experienced a 5x improvement in threat detection speed compared to traditional methods. This boost in speed is due to Falcon’s AI-driven approach, which can autonomously detect and isolate compromised endpoints, preventing malware from spreading across the network.
This level of proactive defense is particularly crucial in large organizations with thousands of endpoints, where even a single breach can lead to significant operational and financial damage. With AI-powered endpoint protection, companies can prevent breaches from escalating and significantly reduce downtime.
3.3. AI in Fraud Detection
AI’s role in fraud detection has become indispensable in the financial sector. AI systems can process and analyze vast amounts of transaction data in real-time, identifying anomalies that indicate potential fraud. These systems excel at detecting unusual behavior, such as deviations from standard spending patterns, irregular transaction locations, or atypical transaction volumes.
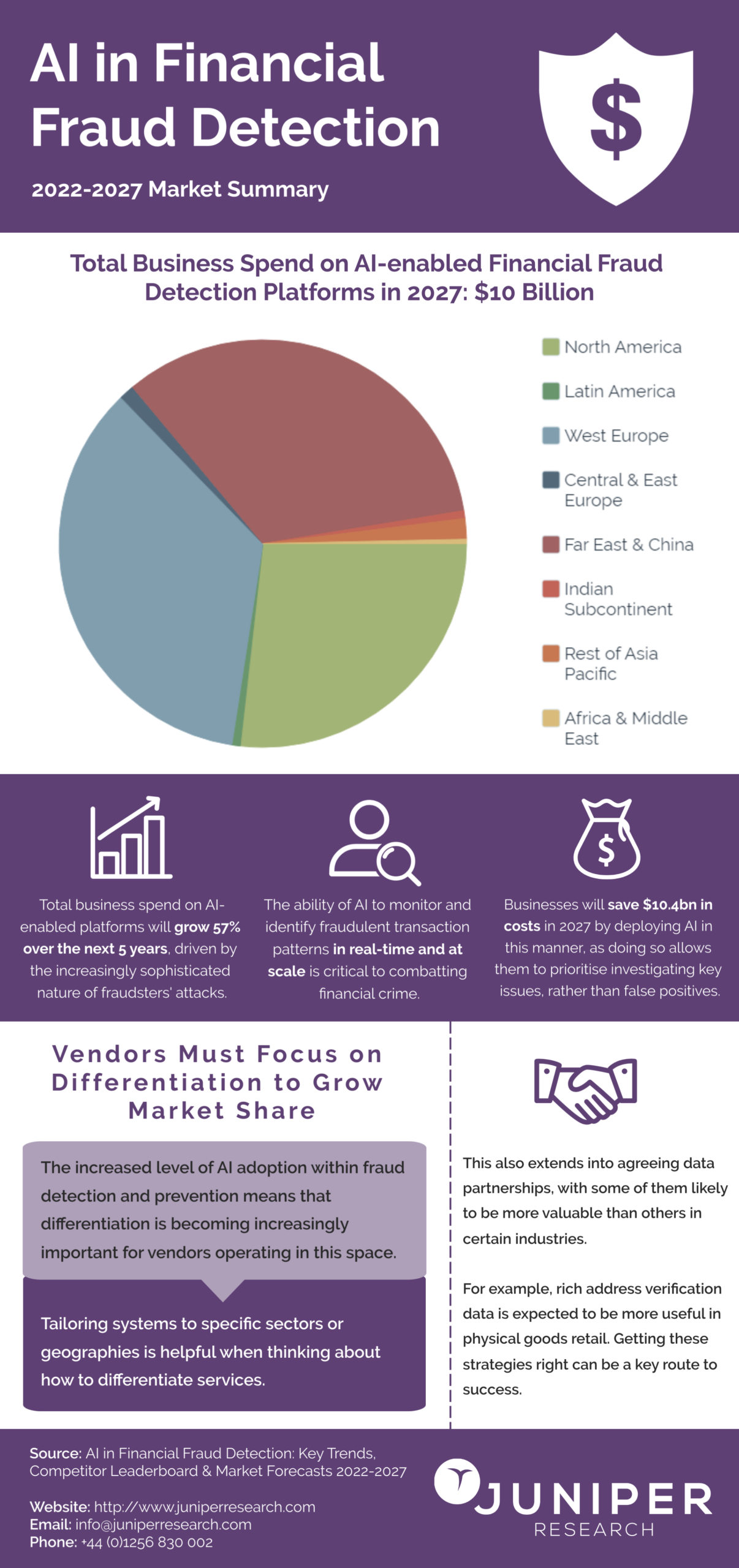
Figure 6: Juniper Reports
A 2021 report by Juniper Research estimated that using AI in fraud detection saved banks and financial institutions over $10 billion in fraud-related losses globally. AI-powered solutions, such as those provided by companies like Darktrace, can detect sophisticated forms of fraud, including insider threats and social engineering attacks, by monitoring user behavior and spotting irregularities that human analysts might miss.
Furthermore, AI’s ability to act in real-time ensures that fraudulent transactions are flagged and blocked before they result in significant losses.
Looking to the future, Gartner predicts that by 2027, AI systems will manage 75% of all digital fraud prevention activities, underscoring their growing importance in safeguarding financial institutions. AI’s ability to instantly recognize and respond to fraudulent transactions minimizes financial losses and reduces false positives, ensuring that legitimate transactions aren’t unnecessarily blocked. AI-powered tools are proving indispensable in various aspects of cybersecurity.
AI is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape from automated threat detection that vastly reduces response times to real-time endpoint protection that prevents malware from spreading and sophisticated fraud detection systems that save billions in losses. By offering unparalleled speed, adaptability, and accuracy, AI enables organizations to stay ahead of cybercriminals in an increasingly complex and dangerous digital world.
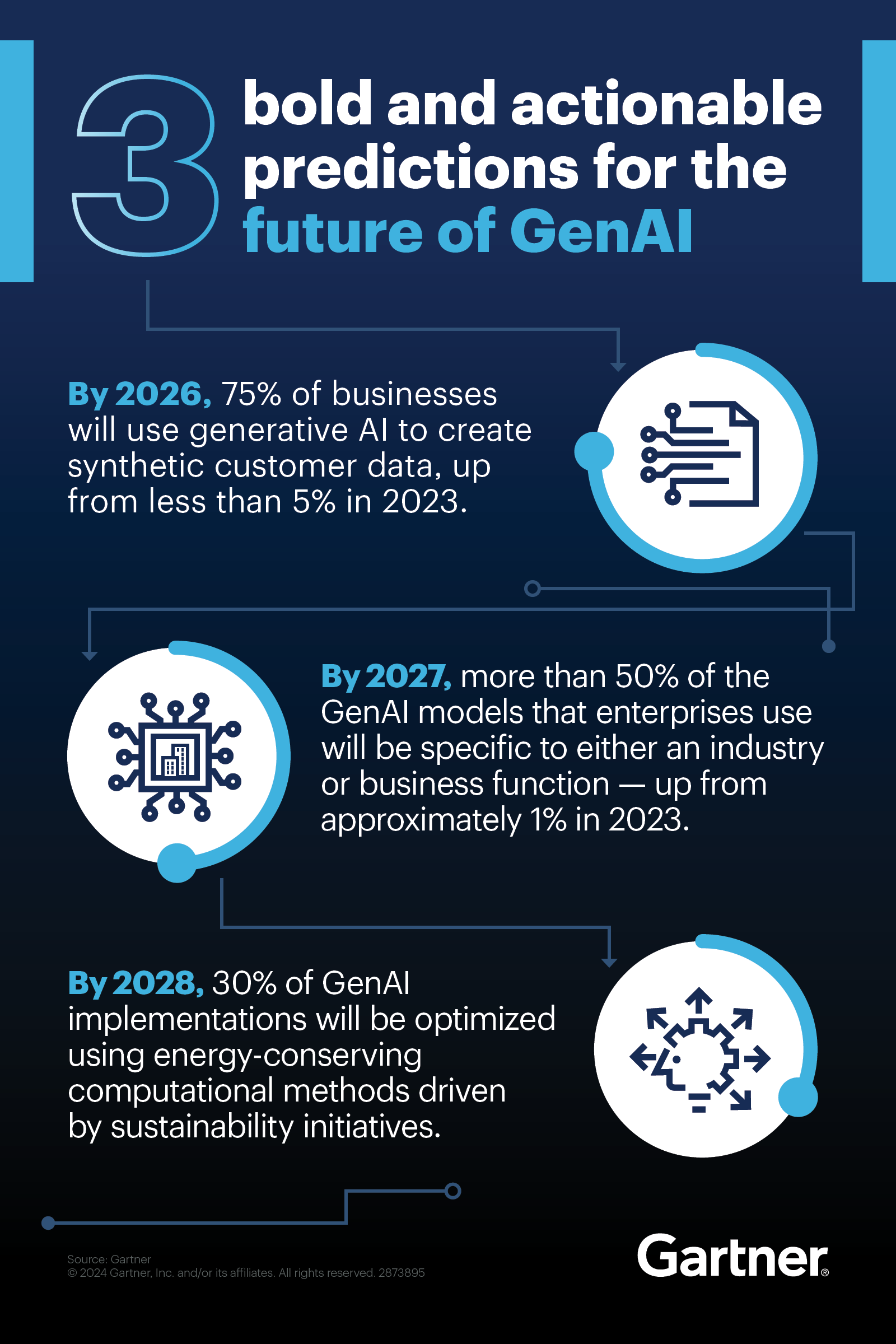
Figure 7: The future of GenAI
4. Challenges and Ethical Concerns in AI-Driven Cybersecurity
4.1. False Positives/Negatives
One of the most significant challenges in AI-driven cybersecurity is the issue of false positives and negatives. AI systems often rely on machine learning models to detect patterns and behaviors that could indicate malicious activity. However, these models are only sometimes perfect. In some cases, they may misidentify legitimate traffic as a threat—resulting in false positives that can disrupt operations, as seen in the healthcare example.
Conversely, AI systems may fail to recognize an actual attack, especially if the attack is highly sophisticated or designed to evade detection, leading to a false negative. According to a 2020 report by Accenture, around 23% of organizations faced challenges due to false positives in their AI-based security systems, which resulted in wasted resources and operational downtime.
4.2 AI Hacking
As cybercriminals become more adept at using technology to advance their attacks, they have also started leveraging AI for malicious purposes. AI hacking is a growing concern, where attackers use AI to automate their cyberattacks, making them more efficient and difficult to detect. These AI-powered attacks can adapt in real-time, learning from failed attempts and continuously evolving.
For instance, attackers might deploy AI to bypass security measures by mimicking legitimate behavior or launching coordinated attacks that overwhelm defense systems. The ability to automate these processes increases the scale and sophistication of attacks, raising the stakes for AI-powered cybersecurity systems.
4.3 Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of AI in cybersecurity go beyond technical challenges and extend into the realm of privacy and data usage. AI systems require vast amounts of data to train their models, and this data often includes sensitive information about users and organizations. The potential misuse of such data through unauthorized access or surveillance raises critical ethical concerns. Who owns the data, and how is it being used?
Additionally, the moral implications of removing human oversight must be considered as organizations move toward fully automating cybersecurity. Full automation risks dehumanizing security processes and potentially making decisions that have wide-ranging impacts—decisions that might not always account for context or nuance that a human operator could provide.

Moreover, there is a growing concern about algorithmic bias in AI systems. If an AI-driven cybersecurity system is trained on biased data, it may inadvertently prioritize certain types of threats over others, leading to unequal protection or gaps in security. The reliance on automated systems without proper transparency or accountability could lead to unjust outcomes or exacerbate existing vulnerabilities, particularly for marginalized communities.
While AI is undeniably a powerful tool in the fight against cybercrime, it is not a silver bullet. The risk of false positives, the threat of AI-powered attacks, and the ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and full automation all point to the need for a balanced approach.
Organizations must recognize AI’s potential pitfalls and ensure that human oversight remains a critical part of the cybersecurity process. Rather than entirely relying on AI, companies should consider hybrid approaches, where AI works alongside human experts, enhancing their capabilities without removing their judgment from critical security decisions. In the rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, a cautious yet innovative approach will be key to harnessing the full potential of AI while mitigating its risks.
4.4. Financial Considerations in AI-Driven Cybersecurity
Implementing AI-driven cybersecurity solutions involves not only technical and ethical challenges but also significant financial investments. From developing customized AI algorithms to deploying scalable infrastructure, the costs can vary widely depending on your organization’s needs.
To understand these expenses better and ensure your strategy is financially viable, explore our detailed guide on the cost of AI development.
5. The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Defense
Imagine a future where AI-driven cybersecurity systems are no longer just cutting-edge tools but integral to the very fabric of cyber defense. In this vision, AI operates at every level of network security, continuously monitoring, analyzing, and adapting in real time to keep malicious actors at bay.
However, this future is not complete automation but a collaboration between AI systems and human analysts. Picture an advanced cybersecurity control center where AI scans trillions of data points per second, flagging suspicious activity, while human analysts, empowered by AI’s insights, make critical decisions on responding. This seamless integration of machine precision and human intuition will represent the pinnacle of cyber defense.
AI’s role in cybersecurity will evolve in ways that extend beyond today’s capabilities. This future promises enhanced protection against threats and new challenges as AI becomes a more active player in defense and offense in the cyber world.
5.1 Predictions for AI’s Future Role
AI Collaboration with Humans:In the future, AI will not replace human cybersecurity experts but rather augment their capabilities, creating a powerful partnership between human intuition and machine efficiency. AI will handle the heavy lifting—scanning vast amounts of network traffic, identifying patterns in real-time, and predicting where the next attack might come from—while human analysts will focus on higher-level strategic decisions and nuanced judgments.
This collaborative model is already emerging. In the future, AI will enhance human capacity by reducing false positives, analyzing increasingly complex threats, and recommending how best to neutralize them. Human analysts will retain control over critical decisions, ensuring that ethical considerations, risk assessments, and contextual understanding remain part of the defense process.

Next-Generation Tools: The future of AI in cybersecurity isn’t limited to today’s machine learning algorithms or automated response systems. Quantum computing, for instance, is poised to revolutionize both encryption and decryption processes, and AI will be at the forefront of this evolution. In a world powered by quantum technologies, current encryption methods may become obsolete, and AI-driven tools will be essential in developing quantum-resistant security protocols to safeguard sensitive data.
Blockchain technology is another area where AI could play a transformative role. As more industries adopt blockchain for decentralized, secure data storage and transactions, AI could enhance blockchain security by monitoring blockchain nodes, detecting vulnerabilities in smart contracts, and predicting potential attacks on blockchain-based systems.
Additionally, AI-driven self-healing systems may become a reality. These systems would detect and neutralize threats in real-time and autonomously repair and reinforce network infrastructures. For example, if a breach occurs, AI could automatically reroute network traffic, patch vulnerabilities, and even rebuild compromised systems without human intervention. This could drastically reduce downtime and improve resilience to cyberattacks.
6. Overview: Embracing AI as a Cybersecurity Ally
The rise of AI in cybersecurity marks a fundamental shift in how organizations protect themselves from digital threats. From its ability to proactively identify vulnerabilities to its near-instantaneous response to evolving attacks, AI is transforming cybersecurity into a predictive and dynamic defense mechanism. Gone are the days of solely reactive strategies, where security teams were forced to chase down threats after the damage was done.
Today, AI-driven systems continuously learn, adapt, and evolve, detecting subtle anomalies that might go unnoticed by traditional tools or human analysts. Whether through automated threat detection, real-time incident response, or advanced endpoint protection, AI is already proving its unmatched capability in neutralizing cyberattacks before they can escalate.
However, this transformation is just the beginning. As cyber criminals adopt more sophisticated tactics, the need for AI-enhanced defenses will only grow. The future belongs to organizations prepared to face these challenges with AI as their ally.
Now is the time to invest in AI-powered solutions, not just as a tool but as an essential part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. In an era where every second counts, AI provides the speed, intelligence, and adaptability companies need to stay ahead of threats and protect their most valuable assets.
AI is more than a technological advancement—it is a strategic partner in the evolving battle against cybercrime. By embracing AI’s potential, organizations can move beyond mere survival in the digital age toward a future where cybersecurity is stronger, smarter, and more resilient than ever. The key to maintaining a secure digital landscape lies in defending against today’s threats and anticipating tomorrow’s, and AI is the force that will make that possible.
7. About SmartDev and Applied AI Lab
As AI continues to reshape industries, businesses embracing these cutting-edge technologies will be best positioned to lead in the rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape. Companies that fail to integrate AI into their cybersecurity strategies risk exposing themselves to increasingly sophisticated threats. Now is the time to explore how AI-driven security solutions can help proactively identify threats, improve response times, and fortify network defenses.
At SmartDev and Applied AI Lab, we specialize in designing tailored AI solutions that address your unique cybersecurity needs. Whether your goal is to enhance operational security, prevent future breaches, or gain a deeper understanding of potential vulnerabilities, we have the tools and expertise to guide your organization through its AI-driven cybersecurity journey.
Our AI Readiness Assessment helps identify your company’s most critical areas for AI integration, ensuring a smooth and effective implementation that aligns with your security objectives.
Transform your cybersecurity strategy with our bespoke AI solutions. Speak with our AI experts today to receive a customized roadmap designed to maximize the impact of AI in protecting your organization from evolving digital threats. CONTACT US HERE to get started.
Future Outlook
As we look to the future, AI will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping cybersecurity. The rise of predictive threat analytics, the integration of AI into automated incident response systems, and emerging technologies like quantum-resistant encryption and self-healing networks will drive the evolution of cybersecurity strategies.
Organizations that invest in AI-powered security now will bolster their defenses against today’s threats and position themselves at the forefront of innovation, prepared to tackle the challenges of tomorrow’s digital world.
At Applied AI Lab, we believe that AI powers the future of cybersecurity, and the future is already here. Let us help you navigate the complexities of AI adoption and unlock new possibilities for resilience, efficiency, and security in your organization.






