Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly reshaping the construction landscape, driving efficiency, safety, and innovation at every stage of the project lifecycle. From automated planning to real-time safety monitoring, AI-powered solutions are transforming how industry leaders build the future. Discover how these cutting-edge technologies can optimize your workflows and deliver measurable results.
Ready to unlock the full potential of AI in your construction projects? Read on to explore real-world use cases and actionable strategies.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Construction?
Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the capability of machines to mimic human intelligence, learning from data, recognizing patterns, making decisions, and understanding language. As defined by IBM, AI includes technologies such as machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, all of which enable systems to sense, analyze, and act intelligently.
In the construction industry, AI is applied to automate and optimize tasks ranging from design and scheduling to equipment operation and safety monitoring. Technologies like AI-powered drones, IoT-enabled sensors, and machine-learning-enhanced Building Information Modeling (BIM) platforms are being integrated to handle complex workflows and improve precision on job sites.
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming Construction
AI is reshaping construction planning by analyzing historical project data, real-time site conditions, and resource availability to produce more accurate and dynamic schedules. Predictive algorithms identify risk points and allow preemptive adjustments, reducing reliance on reactive decision-making.
AI-powered computer vision tools now monitor sites via surveillance cameras and sensors, identifying unsafe practices or code violations as they occur. These systems not only improve compliance but also reduce incident response time, helping firms move toward zero-accident goals.
In design, generative AI allows engineers to simulate hundreds of construction scenarios based on constraints such as budget, environmental impact, and material efficiency. This data-driven approach enables teams to choose the best-performing model with clear trade-offs, rather than relying on intuition or limited CAD iterations.
Key Statistics and Trends Highlighting AI Adoption in Construction
AI adoption in construction is gaining traction. According to McKinsey, AI can increase productivity by up to 20%, reduce costs by up to 15%, and improve project delivery times by up to 30%. As McKinsey noted, “AI-driven project management tools provide the necessary insights to foresee potential risks and optimize resource allocation, leading to substantial gains in project efficiency and cost savings.”
The World Economic Forum estimates that AI integration can reduce project costs by 20% and project durations by 15%. These savings stem largely from material forecasting, sequencing automation, and error prevention.
AI and machine learning has been one of the fastest growing technologies, with 37% of businesses now using this technology, up from 26% of businesses in the first edition of the State of Digital Adoption in the Construction Industry in 2023. The adoption curve is steepening rapidly, suggesting that AI will soon become a competitive baseline, not a differentiator.
Business Benefits of AI in Construction
AI is delivering measurable advantages to construction firms by addressing persistent inefficiencies, managing complexity, and creating better operational visibility. Below are five critical business outcomes from AI adoption, each rooted in practical challenges faced by the industry.

1. Enhanced Productivity
Construction schedules are vulnerable to disruptions caused by supply delays, labor shortages, or weather events. AI-powered planning tools absorb data from multiple streams: delivery timelines, crew capacity, historical delay patterns and dynamically update schedules to reflect changing site conditions.
Real-time progress tracking with AI-integrated drones and cameras replaces time-consuming manual inspections. These systems generate accurate site maps and identify project deviations early, allowing managers to respond based on verified data rather than assumption or anecdotal reporting.
2. Improved Safety and Risk Management
Most construction accidents stem from overlooked hazards or procedural lapses. AI-based computer vision identifies unsafe behaviors such as improper equipment use or missing protective gear by analyzing live video feeds. Automated alerts allow supervisors to intervene in seconds rather than relying on sporadic human oversight.
In parallel, wearable sensors monitor biometric data and environmental conditions such as temperature and air quality. AI analyzes this information to flag early signs of heat stress or fatigue, issues that are often invisible until it’s too late. This adds a layer of preventative care that traditional safety checklists can’t match.
3. Cost Control and Waste Reduction
Material waste and inaccurate forecasting are two of the biggest contributors to budget overruns. AI improves estimation accuracy by using past consumption patterns and real-time progress data to forecast needs more precisely. Overordering and last-minute procurement become exceptions rather than norms.
Equipment breakdowns are another silent budget drain. Predictive maintenance powered by machine learning models can identify mechanical wear patterns before failure occurs. Firms can then plan downtime and service proactively reducing emergency repairs and keeping critical paths intact.
4. Quality Assurance and Defect Detection
Manual inspection processes often fail to detect early-stage defects, especially in large-scale structural work. AI-enabled image recognition scans and compares site visuals to BIM models to identify inconsistencies like cracks, misalignments, or incomplete installations. These issues are flagged well before handover, avoiding costly post-completion remediation.
Historical defect data also informs AI models that can highlight design elements or phases most likely to produce quality issues. This allows project teams to prioritize quality control efforts where the risk is highest, rather than relying on standard protocols applied uniformly.
5. Smarter Data-Driven Decision-Making
Construction projects generate massive volumes of fragmented data like photos, reports, time logs, sensor feeds, but much of it went unused. AI structures and analyzes this data to deliver contextual, real-time insights to site managers and executives. For example, an AI dashboard might highlight underperforming subcontractor crews or materials at risk of price volatility, informing decisions that would otherwise be delayed or missed.
Scenario modeling using digital twins lets leaders test budget, timeline, or design alternatives virtually before committing resources. Instead of reacting to problems midstream, stakeholders can preemptively select the most resilient course of action based on real data simulations.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Construction
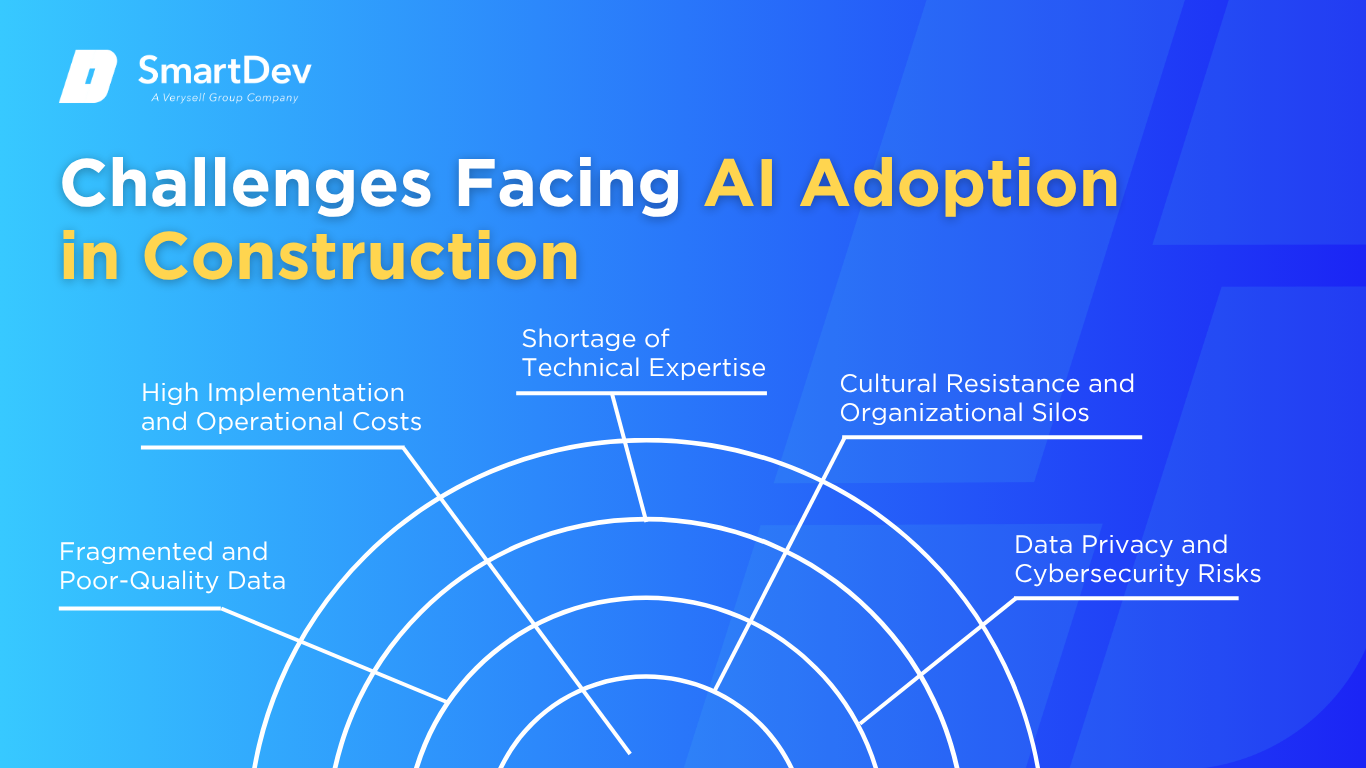
1. Fragmented and Poor-Quality Data
Construction data is notoriously fragmented, spread across disconnected tools like spreadsheets, emails, PDFs, and various subcontractor apps. These datasets often lack consistent formats, contain duplicates or errors, and are rarely centralized, making it extremely difficult for AI systems to ingest and process them accurately.
Without clean, structured, and unified data, AI models struggle to produce reliable outputs or identify actionable patterns. The challenge also requires cross-functional coordination to standardize data capture processes and maintain data integrity throughout the project lifecycle.
2. High Implementation and Operational Costs
AI deployment requires investment in both hardware like IoT sensors, cameras, and drones and software, including cloud storage, AI platforms, and integration services. For many firms, especially small and mid-sized contractors, these upfront costs are prohibitive without immediate, measurable returns.
Even beyond the initial spend, operationalizing AI demands ongoing funding for system maintenance, upgrades, and user training. This long-term commitment can strain budgets and make it hard to justify continued investment, especially on projects with tight margins or short timelines.
3. Shortage of Technical Expertise
Most construction teams lack in-house talent with expertise in AI, machine learning, or data analytics. As a result, companies often rely heavily on third-party vendors to implement and interpret AI tools, creating knowledge gaps and limiting internal innovation capacity.
This skills deficit also impacts day-to-day operations. Site managers and engineers may be handed AI tools they don’t fully understand or trust, reducing adoption and undermining performance. Building internal capabilities through targeted upskilling or partnerships is crucial for sustainable AI use.
4. Cultural Resistance and Organizational Silos
AI often challenges long-standing workflows and hierarchical decision-making structures. Many experienced construction professionals may view AI as a threat to their roles or a critique of their judgment, especially if it’s introduced without context or training.
Organizational silos further complicate adoption like IT, project management, and site operations may not align on objectives or tool usage. Successful implementation depends on inclusive planning, clear communication, and positioning AI as a support system that complements human expertise, rather than replacing it.
5. Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Risks
AI tools rely on capturing vast amounts of sensitive data such as worker biometrics, video feeds, equipment usage logs, which can be vulnerable to cyberattacks if not properly secured. The construction industry, historically underinvested in cybersecurity, is often unprepared for these digital threats.
Inadequate encryption, shared logins, or unsecured cloud platforms can expose projects to ransomware or data breaches. Addressing this requires robust data governance frameworks, compliance with privacy regulations, and collaboration between IT and operations to build secure-by-design AI systems.
Specific Applications of AI in Construction

1. Generative Design and Optimization
Generative design in construction uses AI to produce diverse design solutions based on material, spatial, and cost constraints. This enables engineers and architects to explore options that balance function and aesthetics while reducing costs. By automating iteration, teams uncover designs that might be missed using traditional methods.
These systems rely on AI models, especially evolutionary algorithms, to simulate structural configurations based on input like CAD data and environmental factors. Each version is scored against performance criteria and refined in real time. Results can be imported directly into BIM systems, streamlining adoption into existing workflows.
Real-World Example:
Engineering firms John Holland and GHD successfully adopted Microsoft’s Copilot to apply generative design in bridge construction. By using AI to generate multiple structural models, they were able to minimize material consumption while maintaining compliance with safety and performance standards. This initiative significantly cut design cycle times and delivered measurable cost savings through optimized resource use.
2. Predictive Maintenance of Equipment
Predictive maintenance leverages AI to anticipate when construction equipment will require servicing, helping to avoid costly breakdowns and project interruptions. The core methodology involves real-time monitoring of operational data via IoT-enabled sensors embedded in machinery. This data is then analyzed using AI models trained to recognize early indicators of mechanical stress or failure.
The AI processes this influx of sensor data using time-series analysis and anomaly detection algorithms, often enhanced by deep learning techniques. The goal is to detect subtle shifts in equipment behavior that precede failure, allowing maintenance teams to schedule repairs during low-impact windows. These insights are typically integrated into centralized equipment management systems to facilitate timely alerts and streamlined maintenance operations.
Real-World Example:
Major construction companies globally have embraced AI-powered predictive maintenance systems for their fleets of excavators, cranes, and earthmovers. Tools such as IBM Maximo and Caterpillar’s CAT Connect have been instrumental in this shift. Implementation has resulted in a 30% decrease in unplanned equipment downtime and over 20% reduction in maintenance-related costs, directly impacting project speed and financial efficiency.
3. AI-Enhanced Project Management
AI-enhanced project management tools provide dynamic forecasting and decision-making support throughout the construction lifecycle. These systems ingest a broad range of data from crew schedules and site progress to procurement timelines and weather forecasts and then employ machine learning models to detect risks and optimize project timelines. AI tools can reallocate resources or re-sequence activities to avoid delays and cost overruns.
Under the hood, NLP is often used to parse progress reports and worker feedback, while predictive analytics assesses the probability of various project outcomes. Reinforcement learning models continuously improve scheduling logic by learning from previous project outcomes. This integration enables project managers to adapt to changing site conditions with greater agility and confidence.
Real-World Example:
Autodesk has incorporated AI functionality into its construction management platform to improve visibility and control over project execution. With automated risk identification and real-time progress tracking, managers can preemptively address issues before they escalate. Users have reported up to 20% improvements in project delivery time and significantly enhanced coordination across multidisciplinary teams.
4. Quality Control and Defect Detection
AI-driven quality control systems in construction deploy computer vision technologies to identify defects during the construction process with unmatched speed and accuracy. These systems rely on image recognition models trained on vast datasets of structural imperfections, allowing them to detect anomalies like cracks, material inconsistencies, and dimensional inaccuracies. The analysis is typically conducted on images captured by drones or fixed-site cameras.
AI models, especially convolutional neural networks (CNNs), are used to process visual data and flag deviations from design specifications in near real-time. This enables teams to take corrective actions early, reducing costly rework and ensuring compliance with quality standards. These tools can also maintain a comprehensive record of inspection data, supporting regulatory audits and internal quality assurance.
Real-World Example:
Firms like Sphere have deployed AI-powered drones for autonomous inspection of large construction sites. These drones capture high-resolution images which are then fed into AI systems to identify and classify potential defects. Companies using this technology have reported up to a 50% reduction in inspection time and significant improvements in documentation and quality control consistency.
5. Safety Monitoring and Hazard Prevention
AI systems are now at the forefront of enhancing construction site safety by proactively identifying hazards and preventing accidents. Using computer vision models and edge analytics, AI monitors live video feeds to detect unsafe worker behavior, unauthorized access to danger zones, or equipment malfunctions. The system can instantly alert site supervisors and trigger emergency protocols.
Wearables such as AI-enabled helmets and vests equipped with GPS and biometric sensors further extend safety capabilities. These devices track worker location, fatigue levels, and exposure to hazardous conditions. AI analyzes the data to predict high-risk situations and recommend immediate interventions, significantly reducing the likelihood of accidents.
Real-World Example:
Shawmut Design and Construction has implemented AI-driven safety systems across its projects to analyze site data and detect patterns associated with previous incidents. By combining video analytics with sensor data, they’ve been able to flag risk factors before accidents occur. The result has been a noticeable reduction in workplace injuries and a stronger overall safety culture on their sites.
Examples of AI in Construction
Real-World Case Studies
AI’s integration into construction is not just theoretical; numerous real-world applications demonstrate its transformative impact on the industry.

1. John Holland & GHD: AI-Driven Bridge Design Optimization
John Holland and GHD faced the complex task of designing a bridge for the Parramatta Light Rail Stage 2 in Sydney, aiming to enhance connectivity while managing costs and ensuring structural integrity. Traditional design methods were time-consuming and limited in exploring multiple design alternatives within tight project timelines.
To address this, they adopted Microsoft’s AI Copilot, leveraging generative design algorithms to rapidly produce and evaluate numerous design options based on specified parameters such as materials, load requirements, and environmental factors. This approach enabled the team to identify optimal designs that balanced performance, aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness.
The implementation of AI-driven generative design led to significant time savings and cost reductions. The optimized bridge design not only met all structural and regulatory requirements but also improved efficiency in the design process, demonstrating the value of AI in complex infrastructure projects.
2. Shawmut Design and Construction: Enhancing Job Site Safety with AI
Shawmut Design and Construction aimed to improve safety across its construction sites, addressing the challenge of predicting and preventing potential safety incidents. Traditional safety monitoring methods were reactive and lacked the ability to proactively identify risks.
The company implemented an AI tool developed by a private vendor, which analyzed data from various sources, including weather forecasts and personnel changes, to predict potential safety incidents. The AI system provided real-time risk assessments, enabling proactive measures to mitigate hazards before incidents occurred.
Since adopting the AI-driven safety monitoring system, Shawmut experienced a 53% reduction in OSHA recordable incidents and a 22% increase in safety engagement from 2019 to 2020. This significant improvement underscores the effectiveness of AI in enhancing construction site safety and fostering a proactive safety culture.
3. Autodesk: Streamlining Construction Project Management with AI
Construction projects often involve complex coordination among various stakeholders, leading to challenges in project management, including delays and cost overruns. Autodesk recognized the need for a solution to enhance efficiency and decision-making in construction project management.
Autodesk integrated AI capabilities into its construction management software, enabling real-time analysis of project data. The AI tools assist project managers in identifying risks early, optimizing workflows, and making informed decisions to keep projects on track.
The integration of AI into Autodesk’s construction management platform has led to improved project delivery times and enhanced coordination across multidisciplinary teams. Users have reported up to a 20% improvement in project delivery time, highlighting the impact of AI on construction project efficiency.
4. Sphere Drones: Revolutionizing Construction Site Inspections with AI-Powered Drones
Traditional construction site inspections are labor-intensive and time-consuming, often leading to delays in identifying and addressing structural issues. Sphere Drones sought to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of construction site inspections.
The company deployed AI-powered drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and 3D scanning capabilities to capture detailed images and scans of construction sites. These images are analyzed in real-time using AI algorithms to detect misalignments, structural deviations, or incomplete tasks by comparing them with Building Information Modeling (BIM) data.
The implementation of AI-powered drone inspections has significantly reduced inspection times and improved the accuracy of defect detection. This innovative approach has streamlined the inspection process, allowing for prompt corrective actions and enhancing overall construction quality.
Innovative AI Solutions
The construction industry is embracing a new wave of AI innovations that are reshaping how projects are executed. These emerging technologies address complex challenges related to labor shortages, cost overruns, and project delays. By integrating AI into robotics, printing, and visualization, firms can significantly boost productivity and efficiency.
One of the most impactful innovations is the use of AI-powered autonomous equipment. Startups like Built Robotics have developed self-operating excavators and bulldozers that rely on computer vision, GPS, and deep learning to perform site preparation tasks without human operators. This reduces reliance on manual labor, shortens timelines, and minimizes human error in repetitive tasks. Another example is the use of AI-driven 3D printing systems, which enable rapid, cost-effective construction of building shells using concrete layering.
In parallel, AR enhanced by AI is improving planning and communication across construction teams. AI algorithms help translate 3D models into immersive visualizations that project managers can use onsite for layout verification and clash detection. This improves collaboration between stakeholders, reduces miscommunication, and leads to fewer design-related errors during construction.
AI-Driven Innovations Transforming Construction
Emerging Technologies in AI for Construction
The construction industry is undergoing a significant transformation, with artificial intelligence (AI) at the forefront. AI technologies are revolutionizing traditional construction practices, enhancing efficiency, safety, and decision-making processes. For instance, Autodesk, known for its AutoCAD software, is now integrating AI into construction sites to boost efficiency and precision.
Generative AI applications are also making their mark in construction. These tools can automate design processes, generate multiple design options, and optimize building layouts for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This not only accelerates the design phase but also ensures more sustainable and innovative building solutions.
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
AI plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability within the construction industry. By leveraging predictive analytics, construction companies can reduce waste by accurately forecasting material requirements and minimizing overordering. This not only cuts costs but also lessens the environmental impact of construction projects.
Moreover, AI-powered smart systems optimize energy consumption in buildings. By analyzing data on occupancy patterns and energy usage, these systems can adjust heating, cooling, and lighting in real-time, leading to significant energy savings. Such innovations are essential in the industry’s move towards greener and more sustainable practices.
How to Implement AI in Construction
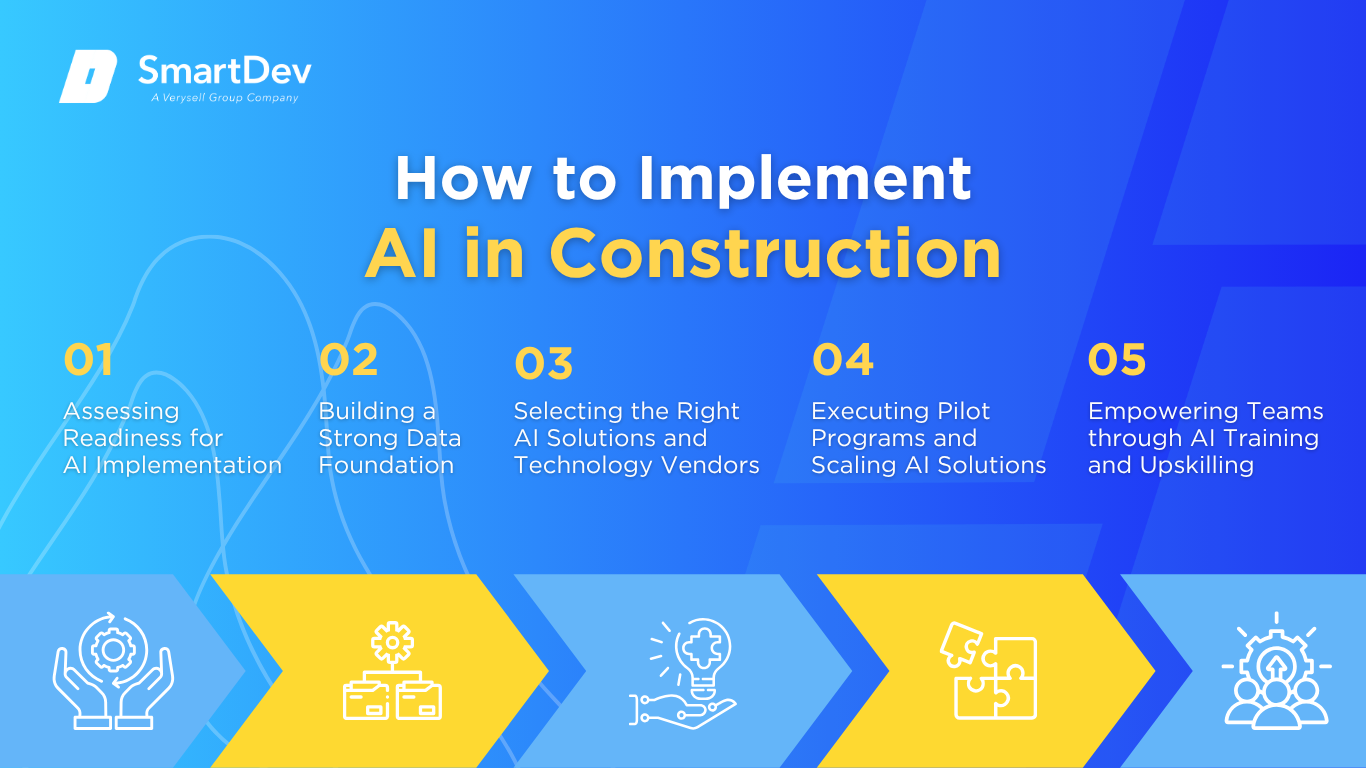
Step 1: Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Before diving into AI implementation, construction firms must critically evaluate where AI can bring the most value, be it project scheduling, safety analytics, or machinery maintenance. This assessment should align with business objectives and consider technical infrastructure, cultural readiness, and stakeholder support. Without this strategic alignment, AI risks becoming an underutilized investment rather than a transformative tool.
Step 2: Building a Strong Data Foundation
AI thrives on quality data, making disciplined data governance a non-negotiable starting point. Construction firms must ensure their datasets are clean, standardized, and continuously updated to reflect real-time conditions. This foundational integrity empowers AI algorithms to generate insights that are both actionable and trustworthy.
Step 3: Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Selecting AI tools is not just about flashy features, it’s about compatibility, scalability, and proven industry relevance. Companies should prioritize vendors with deep construction domain expertise and strong support ecosystems. This ensures the solutions are not only technically sound but also aligned with the nuances of construction workflows.
Step 4: Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Starting small with pilot projects enables firms to validate AI use cases under controlled conditions, identify bottlenecks, and fine-tune deployment strategies. Measured scaling allows gradual integration into broader operations, reducing disruption and improving user adoption. Success in pilots also helps build internal confidence and executive buy-in for larger investments.
Step 5: Training Teams for Successful Implementation
AI implementation is as much a people challenge as a technical one; upskilling your workforce ensures adoption doesn’t stall at the tool level. Teams must learn to interpret AI-generated insights and apply them to on-site decision-making. Ongoing training and change management are critical to transforming AI from a novelty into a core operational capability.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Construction
Key Metrics to Track Success
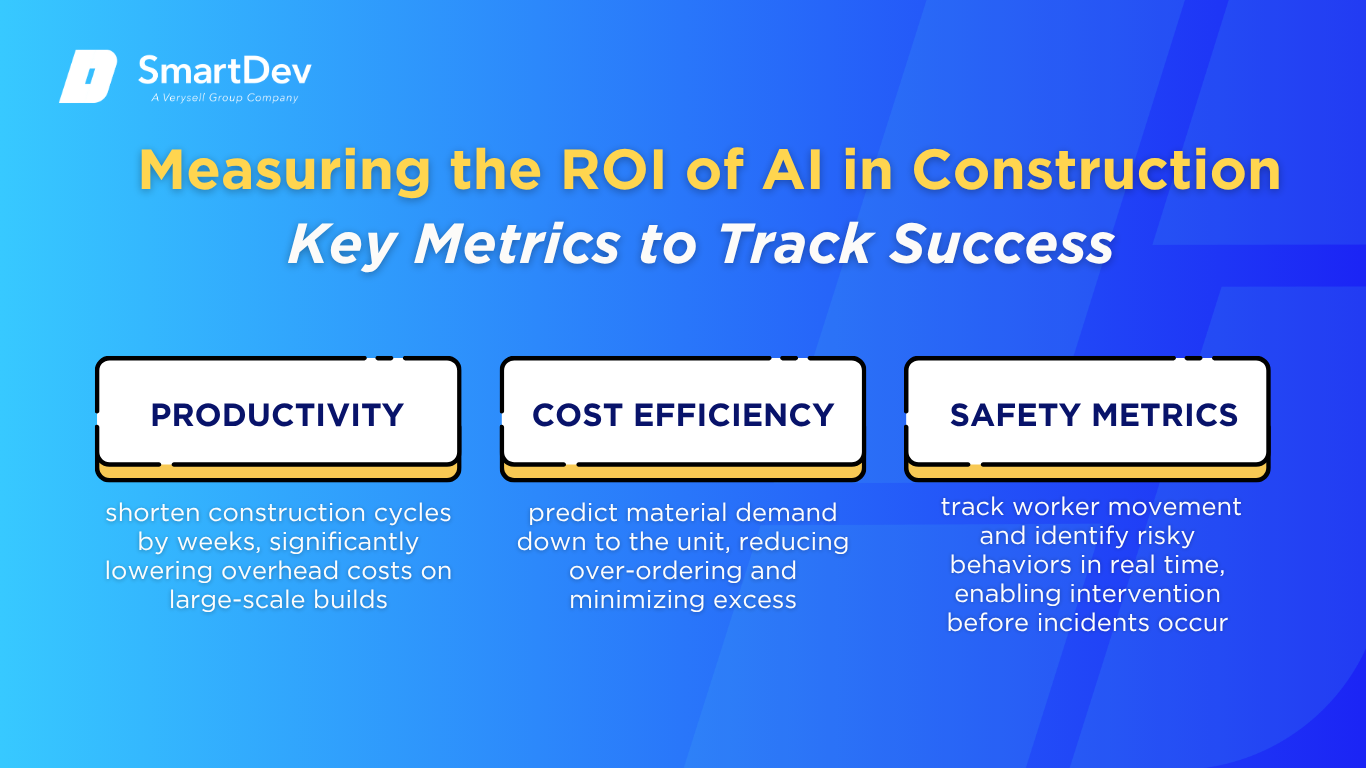
In construction, the most immediate ROI indicator is productivity on the job site, specifically, whether AI tools can help crews do more in less time without sacrificing quality. With technologies like AI-powered scheduling, drone site surveys, and automated progress tracking, project managers can reduce delays and better coordinate subcontractors. These productivity gains can shorten construction cycles by weeks, significantly lowering overhead costs on large-scale builds.
Cost efficiency is another cornerstone of AI’s return in construction. AI algorithms are now used to predict material demand down to the unit, reducing over-ordering and minimizing excess that often ends up as waste. Additionally, predictive maintenance powered by AI for heavy machinery prevents unplanned breakdowns that can stall entire operations, deliver major savings on both repair costs and rental equipment.
Safety metrics are also central to ROI, especially in an industry where workplace accidents are both common and costly. AI-enabled vision systems and wearables track worker movement and identify risky behaviors in real time, enabling intervention before incidents occur. This proactive approach not only reduces injury claims but also protects timelines, reputations, and human lives – a profound yet quantifiable return.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Buildots partnered with top-tier general contractors to implement AI for real-time progress verification using helmet-mounted 360-degree cameras. On a multi-million-dollar office tower project, one firm reported up to 25% faster completion times by identifying discrepancies between construction progress and BIM plans early. The use of Buildots also slashed the need for manual progress reporting, freeing up engineers and supervisors to focus on higher-impact tasks.
Balfour Beatty, a major UK infrastructure firm, used predictive analytics to forecast project resource needs more accurately across civil and rail projects. The AI insights led to a 20% drop in material waste and helped the company hit budget targets with 94% accuracy. Their success proved that integrating AI into pre-construction planning and supply chain logistics can drive results well beyond operational sites—making AI a strategic asset from bid to build.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
A frequent challenge in construction AI initiatives is underestimating the complexity of data environments across jobsites. Construction data often comes from disparate sources like project management software, IoT sensors, drones, and manual logs, which can lead to fragmentation. Firms that fail to unify these streams risk feeding AI models poor inputs, so the focus must begin with strong data integration and cleansing practices.
Another pitfall is choosing AI tools without clearly defined construction-specific use cases. Some firms are drawn to generalized AI platforms that don’t account for the intricacies of construction workflows, such as sequencing trades or accounting for unpredictable site conditions. The solution lies in selecting industry-focused solutions co-developed with construction professionals, ensuring AI augments how teams work on-site.
Future Trends of AI in Construction

Predictions for the Next Decade
AI is set to redefine the construction industry over the next ten years, becoming as fundamental to building sites as cranes and CAD software. As machine learning evolves, we’ll see AI take the lead in predicting project outcomes, flagging risks before they manifest, and optimizing resource deployment with unprecedented precision. These predictive insights will dramatically improve how contractors manage budgets, timelines, and regulatory compliance, especially on large-scale infrastructure projects where delays often spiral into multi-million-dollar losses.
Emerging tech convergence will further accelerate change. Drones combined with AI are already enabling real-time 3D site mapping, while IoT-connected machinery feeds operational data to AI platforms that forecast maintenance and prevent downtime. As automation becomes more sophisticated, AI will take on more of the repetitive, high-risk tasks, helping the industry address persistent labor shortages while elevating the strategic role of human workers on-site.
How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
To remain competitive, construction companies must proactively embrace AI technologies. This involves staying informed about emerging AI trends, investing in continuous learning for staff, and fostering a culture that encourages innovation. Collaborating with tech providers and participating in industry forums can also provide valuable insights and opportunities for growth.
To accelerate progress, firms should partner with proven AI specialists who bring tailored expertise to the construction space. SmartDev helps forward-thinking construction companies deploy AI that fits their exact workflows, from predictive maintenance systems to digital twins and generative design platforms. With the right support and mindset, construction firms can future-proof their operations, improve margins, and deliver projects faster, safer, and smarter than ever before.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI is becoming essential for firms that want to stay competitive. From generative design tools that accelerate planning to predictive analytics that anticipate site delays, AI empowers teams to move faster and more precisely. It’s enabling contractors to shift from reactive to proactive project management, which is critical in an industry where margins are tight and deadlines unforgiving.
Safety and sustainability are two other areas where AI is making a real impact. AI-driven vision systems and wearables are reducing incidents on job sites by flagging hazards in real-time, while smart resource tracking is cutting down material waste. These improvements not only reduce costs but also support stricter environmental and safety regulations that are shaping the future of construction.
The key to unlocking these benefits lies in strategic planning and execution. Construction companies must ensure they have the right data infrastructure, choose tools that fit their operations, and train their teams to work effectively with AI. When those elements align, AI delivers a clear and measurable ROI, turning digital innovation into practical, on-the-ground results.
Moving Forward: A Path to Progress
AI is rapidly becoming a strategic pillar in modern construction, helping companies respond to tighter timelines, labor challenges, and growing demands for efficiency. Forward-thinking firms are using AI to drive better decisions, streamline operations, and enhance site safety, transforming how buildings are designed, managed, and delivered.
At SmartDev, we develop AI solutions built for the realities of construction. From predictive scheduling and risk detection to resource optimization and digital site monitoring, our tools are designed to generate real results on real projects.
Get in touch with SmartDev to explore how AI can elevate your construction operations. Let’s build faster, safer, and smarter today!
—
References:
- State of Digital Adoption in the Construction Industry | Deloitte
- Copiloting Construction: John Holland Embraces Generative AI | Microsoft News Australia
- AI for Worker Site Safety in Construction | Business Insider
- Construction Project Management Workflows | Autodesk Construction Cloud
- AI in Construction | Construction Management Association of America (CMAA)
- IBM Maximo for Asset Management and AI Integration | IBM Documentation
- CAT Connect: Product Support for Electric Power | Caterpillar
- Sphere Drones Partners with Skydio for Autonomous Drone Distribution | Sphere Drones






