Introduction
Public institutions around the world are undergoing a quiet revolution. Artificial Intelligence (AI), once seen as the domain of private tech giants, is now empowering governments to become more responsive, efficient, and transparent. From predictive analytics in urban planning to real-time fraud detection in public welfare programs, the integration of AI is redefining how public services are delivered and experienced. For B2B leaders, CTOs, and innovation-minded executives, understanding these AI use cases in government isn’t just insightful—it’s imperative for anticipating where regulation, collaboration, and opportunity intersect next.
As you explore how AI is transforming public sector operations, it’s important to recognize the value of solutions that move seamlessly from concept to large-scale implementation. For organizations aiming to turn these innovations into real-world impact, our ai-powered software development services offer proven strategies to deliver secure, scalable, and citizen-centric applications.
What is AI and Why Does It Matter in Government?
 Definition and overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in government and public sector applications.
Definition and overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in government and public sector applications.
Definition of AI and Its Core Technologies
Imagine running a city like a complex, ever-evolving organism—millions of moving parts, all needing coordination. That’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in as your smartest ally, simulating human intelligence to manage complexity, drive decisions, and adapt in real time. From analyzing patterns to automating processes, AI becomes the nerve center for modern governance.
At its core, AI is powered by several foundational technologies:
- Machine Learning (ML): Learns from historical and real-time data to refine predictions and optimize outcomes.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables machines to read, understand, and generate human language—making sense of documents, chat logs, and citizen inquiries.
- Computer Vision: Interprets visual data for tasks like traffic analysis, surveillance, and infrastructure monitoring.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Streamlines repetitive, rule-based tasks such as form processing or data entry to free up human bandwidth.
These tools don’t just automate—they evolve. In the context of government, they form the backbone of intelligent systems that address everything from urban planning and public safety to digital citizen services. By embedding AI across departments, public leaders can tackle challenges at scale—with speed, accuracy, and insight. Want to explore how AI can transform your sector? Discover real-world strategies for deploying smart technologies in public systems—visit How to Integrate AI into Your Business in 2025 to get started today and unlock the full potential of AI for your business!
The Growing Role of AI in Transforming Government
Governments are under increasing pressure to do more with less: improve service quality, increase transparency, and reduce costs. AI allows them to automate routine processes, deliver personalized citizen services, and make data-driven policy decisions faster. From chatbots answering tax queries to AI-powered drones inspecting infrastructure, the public sector is evolving rapidly.
According to IBM, 62% of government leaders say that AI and automation will drive innovation across their organizations in the next few years. Countries that integrate AI into their systems today will not only provide better services but also build a foundation for long-term digital sovereignty and citizen trust.
Key Statistics and Trends Highlighting AI Adoption in Government
- According to Deloitte Insights, 80% of public sector leaders believe AI will positively impact their jobs.
- The World Economic Forum reports that over 50 countries have now published national AI strategies.
- A 2023 Gartner survey found that 43% of government organizations are piloting or deploying AI applications.
- European Commission’s 2024 AI Index, nearly 70% of digital government projects involved AI in some capacity.
Business Benefits of AI in Government
Let’s cut through the buzzwords—AI isn’t just for tech giants and startups anymore. Governments are putting it to work in real, measurable ways. Whether you’re managing public services or trying to keep pace with growing demands and tighter budgets, AI has something for you. Here’s what it actually delivers when done right:
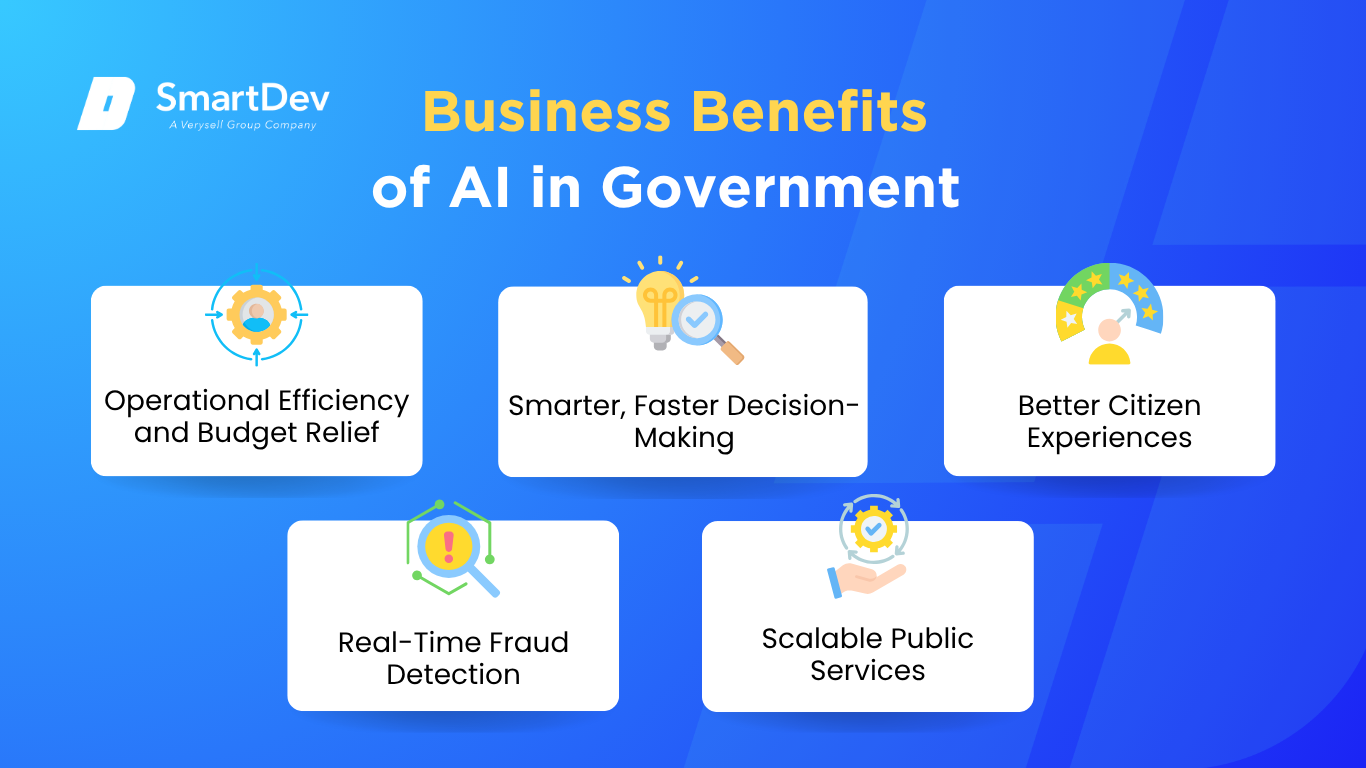 Key business benefits of AI adoption in government, including efficiency, decision-making, citizen experience, fraud detection, and scalable services.
Key business benefits of AI adoption in government, including efficiency, decision-making, citizen experience, fraud detection, and scalable services.
1. Operational Efficiency and Budget Relief
Government operations are famous for paperwork overload. AI flips the script. It takes the grunt work, think form processing, data classification, approval flows—and handles it at machine speed with human-level accuracy (or better). Case management systems can now categorize documents, flag inconsistencies, and route requests automatically, cutting processing times by over half in some cases. That means less backlog, lower costs, and teams finally focusing on the high impact work they were hired to do.
2. Smarter, Faster Decision-Making
Making policy is tough–AI makes it smarter. With predictive analytics, decision–makers get a forward–looking view powered by decades of public data. Want to know how a new housing policy could affect urban sprawl or traffic congestion? AI can simulate that. It’s not about replacing judgment–it’s about giving leaders the data and insights to make decisions that actually work in the real world.
3. Better Citizen Experiences
Let’s face it–navigating government services can be a maze. AI helps clear the path. Digital assistants and chatbots are guiding people through tax filings, permits, benefit applications–you name it. They’re available 24/7, they don’t get tired, and they make services feel more personal. The result? Happier citizens and fewer calls to overloaded service centers.
4. Real-Time Fraud Detection and Compliance
Public funds deserve protection–and AI is proving to be an excellent watchdog. Machine learning models can scan massive datasets in real time, flagging suspicious activity before it becomes a crisis. From tax evasion to procurement anomalies, AI helps compliance teams stay proactive, not reactive. And when you’re managing billions in public spending, that kind of oversight is game–changing.
5. Scalable Public Services
Here’s the reality: populations grow, crises happen, and expectations keep rising. But budgets? Not so much. AI helps governments scale services without scaling costs. Think of it as your invisible team–ready to ramp up during disaster relief, pandemic surges, or election season. It flexes when you need it, ensuring continuity without burning out your workforce. While this model is transforming government, AI’s transformative role in asset management offers additional insight into how intelligent technologies can optimize infrastructure, public utilities, and large-scale logistics in the public domain.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Government
Let’s be real–bringing AI into government isn’t plug–and–play. The potential is massive, but so are the hurdles. From outdated systems to public skepticism, there are a few key challenges that can stall even the most promising AI initiatives. Here’s what you need to watch out for–and how smart governments are tackling them.
 Key challenges governments face when adopting AI, including data privacy, legacy systems, bias, talent gaps, and public trust.
Key challenges governments face when adopting AI, including data privacy, legacy systems, bias, talent gaps, and public trust.
1. Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
When you’re dealing with healthcare records, tax filings, and social services data, there’s zero room for error. AI systems in government need airtight security and full compliance with regulations like GDPR and NIST standards. It’s not just about ticking boxes–it’s about earning public trust. Citizens want transparency around how their data is used, and rightly so. Without it, even the best AI tools won’t get off the ground.
2. Legacy Tech That Just Won’t Cooperate
You can’t build tomorrow’s government services on yesterday’s infrastructure. But that’s the reality many agencies face. Legacy systems were never designed to integrate with AI, and trying to bolt new tech onto outdated platforms? That’s a recipe for bottlenecks. The fix isn’t always a full system overhaul–it’s often about finding smart, hybrid solutions that bridge old and new without breaking the budget.
3. Bias and Ethics Aren’t Optional
Here’s the hard truth: if AI is trained on biased data, it’ll make biased decisions. That’s a big problem when you’re dealing with public benefits, law enforcement, or housing. Governments have a responsibility to ensure fairness, accountability, and transparency. That means explainable AI models, diverse datasets, and real oversight–not just trusting the algorithm and hoping for the best. For those navigating these complex waters, a business-oriented guide to responsible AI and ethics offers practical insights on deploying AI responsibly and transparently, especially when public trust is at stake.
4. The Talent Gap Is Real
AI expertise is in short supply–and the public sector often can’t match private–sector salaries. But that doesn’t mean you’re stuck. Smart agencies are investing in internal training, partnering with universities, and co–building solutions with tech companies. The key is to build cross–functional teams that bring together tech, policy, and operational know–how. AI success isn’t just about tools–it’s about people.
5. Earning Public Trust Takes Work
If citizens don’t understand how an AI system works-or why it made a decision-they’ll question it. And they should. Governments need to communicate clearly about where AI is used, what it does, and how it’s kept in check. That means no black boxes. Think explainability, oversight, and open dialogue. When people feel informed, they’re far more likely to support (and use) AI-powered services.
Facing these challenges doesn’t mean abandoning AI. It means approaching it with intention, transparency, and a clear roadmap. The good news? The path forward is already being paved by governments who are doing it right.
Specific Applications of AI in Government
AI isn’t just a buzzword in the public sector—it’s a tool that’s reshaping how governments operate, engage with citizens, and tackle long-standing challenges. From safety and sustainability to tax efficiency, here’s how AI is being applied across different areas of governance—with real-world results to back it up.
 Key AI applications in government including predictive policing, smart city planning, and tax administration with real-world examples.
Key AI applications in government including predictive policing, smart city planning, and tax administration with real-world examples.
-
AI for Predictive Policing
Traditional policing relies heavily on reactive approaches-responding after incidents occur. Predictive policing flips that model on its head. By analyzing years of crime data, time-stamped locations, weather patterns, and even local event schedules, AI systems can forecast where and when crimes are more likely to happen. This allows law enforcement agencies to deploy officers more effectively, increase presence in high-risk areas, and potentially stop crime before it starts.
It’s not about replacing judgment-it’s about augmenting it with insights that a human simply can’t process at scale.
Real-world examples
Los Angeles Police Department implemented PredPol, a predictive policing software that ingests historical crime data and suggests specific areas where patrols could prevent crime. Officers receive daily recommendations, helping them focus their efforts where they’re needed most.
In Chicago, Strategic Decision Support Centers (SDSCs) integrate real-time surveillance feeds, sensor data, and AI-driven analytics to help officers respond to incidents faster and spot patterns that point to emerging threats. SDSCs have been credited with reducing crime in key neighborhoods.
-
AI in Smart City Planning
Managing a city is like juggling 100 things at once-traffic congestion, waste collection, energy demands, population growth, and climate impact. AI makes this complexity manageable by converting citywide data into actionable intelligence.
AI-powered platforms collect data from sensors, drones, satellites, and public feedback systems to track everything from vehicle movement and air quality to utility usage. City planners and infrastructure managers can then make more informed decisions-whether it’s rerouting traffic in real-time, optimizing public transportation schedules, or prioritizing green construction initiatives.
Real-world examples
Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative uses AI at the heart of its urban operations. Through its Intelligent Transport System, traffic flow is optimized using live camera feeds and predictive modeling, easing congestion during peak hours. Its Urban Redevelopment Authority also uses AI to simulate population and resource scenarios for long-term planning.
Barcelona is using AI to optimize energy usage in municipal buildings, manage waste collection routes dynamically based on fill levels, and monitor water usage to detect leaks-saving both money and natural resources.
-
AI in Tax Administration
Government tax departments process millions of filings annually-many of which include inconsistencies, errors, or deliberate fraud. AI helps tax authorities move from labor-intensive audits to intelligent, data-driven compliance checks.
By cross-referencing income declarations with third-party data-like banking records, investment activity, or property ownership-AI can quickly spot discrepancies and flag high-risk filings for human review. NLP tools also make tax systems more accessible, simplifying complex codes for taxpayers and enabling chatbots to answer inquiries 24/7.
Real-world examples
HM Revenue & Customs (UK) uses AI to spot patterns in tax return data, identify unusual claims, and recommend cases for audit-resulting in millions of pounds recovered. AI also powers their digital assistants, helping the public get answers without needing to call an agent.
India’s Central Board of Direct Taxes has developed AI systems that match income filings with external data from financial institutions, catching discrepancies in near real-time. This approach has not only improved compliance rates but also reduced the manual burden on tax officers.
Examples of AI in Government
Real-World Case Studies
Artificial Intelligence is no longer confined to experimental labs—it is actively transforming how governments operate. From digital courts to immigration reform, the following case studies showcase how forward-thinking public agencies are leveraging AI to solve long-standing challenges and deliver more efficient, transparent, and citizen-centric services.
 AI case studies from Estonia, Canada, and the United States demonstrating real-world government applications.
AI case studies from Estonia, Canada, and the United States demonstrating real-world government applications.
1. AI-Powered Judiciary and Digital Public Services
Estonia has long been recognized as a pioneer in digital governance, and its use of AI in the public sector exemplifies this leadership. One of the country’s standout innovations is an AI-based judge assistant, designed to expedite the resolution of small claims cases.
The system reviews documentation, evaluates precedents, and provides initial assessments for claims under €7,000, helping reduce court backlogs and allowing human judges to focus on more complex legal matters. In parallel, Estonia deployed AI-driven chatbots across its digital government portals to assist citizens with filing taxes, renewing licenses, and navigating social service applications. These bots provide 24/7 multilingual support and are continually trained using real user feedback to improve accuracy and responsiveness.
The combined use of AI in both legal and service-delivery contexts has significantly enhanced the efficiency, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness of Estonia’s public sector-demonstrating a scalable model for small, resource-conscious governments seeking digital transformation.
2. Optimizing Immigration Processing with AI Triage Systems
Canada’s immigration system processes hundreds of thousands of applications annually, creating significant administrative pressure and long wait times. To address these challenges, Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) piloted an AI-based triage system aimed at streamlining the initial review phase.
The system was trained on historical application data to identify patterns and determine the likelihood of approval based on predefined eligibility criteria. Applications that scored high were fast-tracked for processing, while those requiring deeper assessment were forwarded to human case officers. This risk-based segmentation approach not only helped reduce processing time but also improved the consistency and transparency of decision-making. Importantly, all AI-generated recommendations were subject to human oversight to ensure fairness and compliance with anti-discrimination policies.
Following the pilot, IRCC reported measurable reductions in backlogs and improved client satisfaction. The initiative is now informing broader efforts to embed ethical, accountable AI into public administration while enhancing service delivery at scale.
3. Enhancing Compliance and Security Through AI Automation
In the U.S., federal agencies such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) have integrated AI to improve fraud detection and operational efficiency. The IRS implemented machine learning algorithms to analyze millions of tax returns, detecting anomalies indicative of identity theft or fraudulent claims.
By automating this process, the agency increased its capacity to identify high-risk filings in real time, prioritizing them for manual review and intervention. Meanwhile, USCIS faced growing delays in reviewing complex immigration documentation. To address this, it adopted natural language processing (NLP) tools capable of scanning legal texts and flagging inconsistencies or potential misrepresentations. These AI solutions not only accelerated document review times but also reduced errors and improved overall case management.
Together, these deployments have strengthened fraud prevention, optimized resource allocation, and improved the public’s confidence in the integrity of federal systems-demonstrating how AI can enhance security without compromising due process or human oversight.
These examples reflect the value of working with technology partners who understand both the technical and policy implications. If you’re considering a similar digital transformation, don’t hesitate to connect with AI implementation experts to explore what’s possible in your context.
Innovative AI Solutions
Beyond traditional automation, a new generation of AI technologies is transforming how governments anticipate needs, deliver services, and manage complexity. These innovations offer scalable, intelligent tools to enhance decision-making, operational resilience, and citizen engagement across diverse domains.
Generative AI is rapidly gaining traction in the public sector for its ability to produce human-like content at scale. Governments are leveraging this technology to automate routine communications, such as drafting policy summaries, response letters, and public-facing FAQs.
For instance, when processing high volumes of citizen inquiries-whether about tax deadlines or healthcare benefits-generative AI systems can generate consistent, policy-aligned responses instantly. These tools also assist internal departments by summarizing lengthy legislation, converting dense legal language into digestible formats for both officials and the general public. As large language models improve, agencies are exploring their use in collaborative drafting of white papers, departmental memos, and even preliminary policy proposals.
When properly governed and human-reviewed, generative AI reduces administrative workloads, enhances clarity in public messaging, and enables faster, more responsive communication between government and citizens.
Computer vision-the ability of machines to interpret visual information-has become a cornerstone of AI-driven infrastructure and environmental management. In public works, governments use computer vision to inspect roads, bridges, and railways for wear and structural damage, often via drones or mobile-mounted cameras.
These systems can detect cracks, corrosion, or obstructions with greater accuracy and frequency than manual inspections, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing safety risks. In disaster response, satellite and aerial imagery interpreted by AI helps assess post-event damage, prioritize rescue operations, and allocate relief resources more efficiently. Environmental agencies also use computer vision to track illegal dumping, deforestation, or air quality changes through real-time video feeds and sensor-integrated systems.
By automating what once required large field teams, computer vision extends the reach of public institutions and enhances oversight across urban and rural areas alike-without increasing costs proportionally.
Speech recognition and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are revolutionizing how governments interact with their constituents and analyze public discourse. At public hearings, council meetings, or town halls, speech recognition tools can transcribe spoken input in real time, while NLP models analyze the content to extract key topics, sentiment, and citizen concerns.
This transforms raw discussion into structured insights that policymakers can act on-improving responsiveness and data-informed governance. Additionally, multilingual NLP engines support inclusive service delivery by enabling real-time translation and comprehension of citizen requests in various languages, thereby expanding access for immigrant and minority communities. In back-end applications, NLP is used to process unstructured data such as feedback forms, social media posts, and complaint logs-surfacing trends and identifying areas for improvement.
These technologies bridge communication gaps, ensure more equitable service provision, and allow governments to better understand the evolving needs and expectations of their populations.
Governments looking to deploy these next-gen technologies can benefit from custom AI solutions for government operations tailored to meet their unique regulatory and infrastructure challenges.
How These Solutions Are Transforming Business Operations
AI enables governments to make faster, evidence–based decisions. AI–generated insights can predict healthcare demands, optimize resource distribution during crises, and even simulate economic scenarios for fiscal planning. By automating repetitive yet critical tasks, governments are reshaping how services are conceptualized and delivered.
AI-Driven Innovations Transforming Government
Beyond traditional automation, a new generation of AI technologies is transforming how governments anticipate needs, deliver services, and manage complexity. These innovations offer scalable, intelligent tools to enhance decision-making, operational resilience, and citizen engagement across diverse domains.
-
Emerging Technologies in AI for Government
Generative AI: Drafts policy briefs, automates document processing, and simulates public policy outcomes. It’s increasingly used in legal document analysis and automating responses to citizen requests.
Computer Vision: Analyzes video feeds for urban traffic control, identifies safety risks in public spaces, and manages environmental data from drones and satellites.
-
AI’s Role in Sustainability Efforts
- Reducing Waste: Smart waste bins embedded with AI sensors notify collection crews when full, optimizing pickup schedules and minimizing fuel use.
- Optimizing Energy Consumption: AI-driven energy grids predict peak loads, adjust distribution dynamically, and identify infrastructure inefficiencies. In Stockholm, AI helped reduce energy use by 15% across public buildings.
- Environmental Monitoring: AI processes satellite data to detect illegal deforestation, track pollution patterns, and forecast natural disasters more accurately.
How to Implement AI in Government
Successfully implementing AI in the public sector requires more than simply deploying new technologies—it involves a holistic transformation across people, processes, and infrastructure. Below are key stages to guide a thoughtful and sustainable AI adoption strategy.
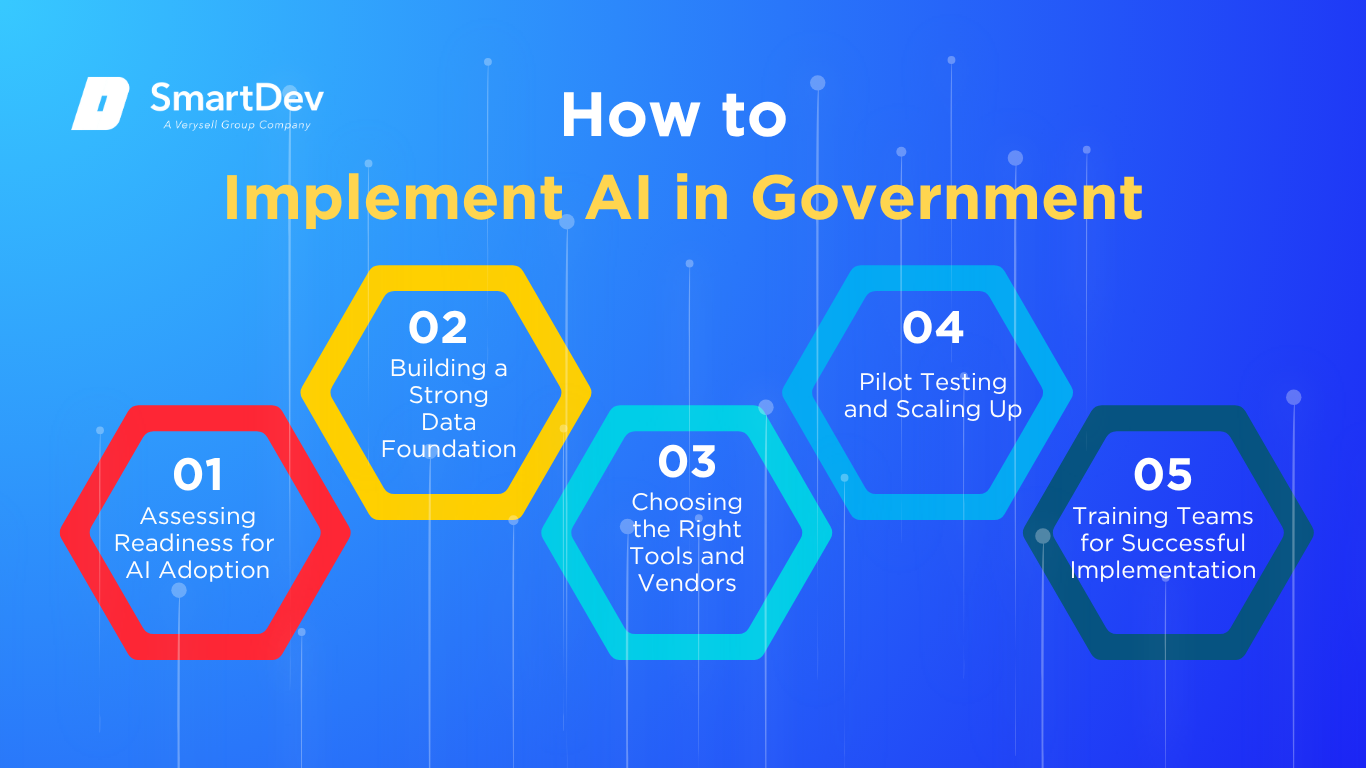 Step-by-step guide to implementing AI in government, covering readiness, data, tools, pilots, and training.
Step-by-step guide to implementing AI in government, covering readiness, data, tools, pilots, and training.
-
Assessing Readiness for AI Adoption
Begin by evaluating your agency’s digital maturity, infrastructure, and workforce capacity. Identify AI use cases that offer quick wins-such as reducing delays or improving service delivery-and align them with strategic objectives. Develop a clear roadmap that accounts for regulatory requirements and long-term goals.
-
Building a Strong Data Foundation
AI success depends on high-quality, accessible data. Ensure data interoperability across departments and implement governance policies focused on quality, security, and privacy. Where centralization isn’t possible, adopt federated models that allow collaboration without compromising data ownership.
-
Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Select vendors with proven public sector experience and strong security credentials. Involve legal, procurement, and IT teams in the evaluation process. Favor long-term partnerships that include support, training, and system updates to ensure scalability and sustainability.
-
Pilot Testing and Scaling Up
Start small with pilots in departments like tax or licensing. Track KPIs such as cost savings and user satisfaction. Use the results to refine strategies and scale gradually, minimizing risk and maximizing learning across teams.
-
Training Teams for Successful Implementation
Provide staff with practical training in AI tools, ethics, and data literacy. Partner with educational institutions for certification programs. Appoint AI ethics officers to guide responsible deployment and foster accountability throughout your implementation journey.
Whether you’re exploring your first pilot or scaling an enterprise-wide solution, our team is here to help. Get in touch with SmartDev and let’s turn your supply chain challenges into opportunities.
Measuring the ROI of AI in Government
For governments investing in AI, return on investment (ROI) isn’t just about cost savings—it’s about delivering better outcomes for citizens, enhancing public trust, and increasing institutional agility. To evaluate AI’s true impact, agencies must look beyond surface-level metrics and build a framework that captures both quantitative and qualitative returns.
-
Key Metrics to Track Success
To effectively measure AI performance in the public sector, agencies must track metrics that align with service delivery goals and fiscal responsibility.
One of the most telling indicators is service efficiency, measured by the reduction in turnaround times for citizen services. Whether it’s processing applications or responding to queries, faster service enhances both public satisfaction and operational capacity.
Operational cost savings also play a critical role in ROI. AI solutions that automate manual workflows-such as document classification, fraud detection, or call center operations-can reduce the need for overtime, third-party contractors, or paper-based processes.
Additionally, tracking citizen engagement metrics, such as satisfaction scores, channel usage rates, and feedback sentiment, provides insight into how well digital services are resonating with users.
Lastly, accuracy improvements-fewer manual errors, better compliance rates, and reduced audit discrepancies-can prevent reputational damage and costly rework. Together, these KPIs offer a well-rounded view of performance that supports evidence-based decision-making.
Understanding ROI is possibly a challenge to many businesses and institutions as different in background, cost. So, if you need to dig deep about this problem, you can read AI Return on Investment (ROI): Unlocking the True Value of Artificial Intelligence for Your Business
-
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Real-world examples illustrate how targeted AI implementation can generate substantial returns for public agencies.
The New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) introduced “MyNYCHA,” an AI-powered chatbot designed to answer tenant inquiries and service requests. By automating over 400,000 conversations annually, the tool significantly reduced call center volume and improved response times-leading to an estimated annual savings of $2.7 million. More importantly, it allowed human agents to focus on complex or high-priority cases, elevating the quality of tenant support.
In France, the Ministry of Economy deployed AI to enhance its tax audit programs. By analyzing large datasets and identifying hidden patterns of tax evasion, the system helped auditors pinpoint high-risk profiles with greater precision. The result was the recovery of over €1.2 billion in lost revenue-a strong financial return that underscored the value of intelligent automation in complex, data-heavy departments. These examples demonstrate that when AI is strategically aligned with specific operational challenges, measurable ROI can be both rapid and transformative.
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Despite its potential, AI implementation often stumbles when strategic planning and change management are overlooked.
One of the most common pitfalls is underestimating the cultural shift required to embed AI within government workflows. Resistance from staff-fueled by uncertainty about job security or unfamiliarity with new tools-can delay or derail adoption. Agencies must address these concerns early through transparent communication, hands-on training, and clear articulation of how AI will enhance, not replace, human roles.
Another frequent issue is the lack of clearly defined objectives. Without SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals, AI projects risk drifting off course or under-delivering. Every initiative should start with a clear problem statement, expected outcomes, and a structured evaluation plan.
Finally, overreliance on external vendors can create long-term dependency and limit flexibility. While third-party expertise is often essential for initial deployment, governments should simultaneously invest in building internal AI capabilities-ensuring control over data, technology adaptation, and long-term sustainability.
By learning from these common missteps, public agencies can de-risk AI adoption and maximize long-term value.
Future Trends of AI in Government
As governments increasingly embrace digital transformation, the next decade will bring profound changes in how AI is used to govern, regulate, and serve. Future trends point not only to technological advancements, but also to deeper integration of ethical standards, security frameworks, and cross-sector collaboration.

Key future trends shaping AI adoption and governance in the public sector.
1. Predictions for the Next Decade
AI in government will move toward hyper-personalization, delivering services tailored to individual needs. In healthcare, for example, predictive models may anticipate patient risks based on lifestyle and genetic data-guiding proactive care interventions. In education, AI tutors could adapt to student learning styles in real-time, while social programs could be customized for financial behaviors and regional challenges. This shift will significantly improve service outcomes, but will require robust consent mechanisms and privacy safeguards.
Meanwhile, AI ethics and regulatory frameworks are expected to mature. Over the next decade, standardized practices will likely guide how governments procure, audit, and deploy AI-ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability. These standards will influence everything from dataset curation to how outcomes are explained to citizens. Governments may also increasingly adopt AI-blockchain integration to strengthen trust. Blockchain’s immutability and transparency can secure digital identities and ensure that AI decisions-especially in justice, licensing, or voting systems-are traceable and verifiable.
Another critical trend will be the use of federated learning-a method that enables AI models to be trained across multiple institutions without sharing sensitive raw data. This is particularly relevant in multinational governance or inter-agency cooperation, where data privacy laws vary. Federated AI enables collaborative learning from diverse datasets while respecting jurisdictional data boundaries-paving the way for global policy alignment and more equitable algorithm performance across demographics.
2. How Businesses Can Stay Ahead of the Curve
As governments adapt to this evolving AI landscape, there is significant opportunity for the private sector to contribute meaningfully. One emerging field is RegTech (Regulatory Technology)-solutions that help public agencies maintain compliance with AI laws, monitor algorithmic fairness, and conduct transparent audits. Companies offering tools for bias detection, model explainability, and documentation will be critical in supporting ethical AI implementation in government workflows.
Businesses can also gain a competitive edge by specializing in GovTech verticals-AI applications built specifically for public needs. This includes solutions designed for rural access to services, automated accessibility support for persons with disabilities, and AI-driven infrastructure planning for underserved areas. Government clients often require technologies that are explainable, interoperable, and compliant by design, so tailoring offerings with these principles in mind can increase adoption and partnership opportunities.
Finally, the most forward-looking businesses will actively participate in AI governance and policy development. This means contributing to public consultations, joining advisory panels, or collaborating with regulatory bodies. By engaging early, businesses can help shape policies that are realistic, innovation-friendly, and aligned with industry capabilities-while also staying ahead of compliance requirements. In a future where trust and accountability are paramount, being part of the conversation will be just as valuable as the technology itself.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI is transforming public sector operations across the board—from predictive policing and smart cities to fraud prevention and environmental protection. With real-world deployments delivering measurable ROI, the future of governance will be digital, data-driven, and deeply infused with AI.
Moving Forward: A Path to Progress
Now is the time to align your solutions with the needs of public institutions. Whether you’re a tech innovator or a service provider, embedding AI in the government landscape means solving big problems with long-term impact. Reach out today to explore how your business can partner in this transformation.
At SmartDev, we specialize in helping organizations unlock the full potential of AI in supply chain operations. Ready to bring AI into your supply chain? Let SmartDev help. Start with a tailored pilot today.
—
References:
- AI in government: Top use cases
- AI for the People: Use Cases for Government
- The Government and Public Services AI Dossier
- AI in government: top use cases in the public sector
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Government
- Artificial Intelligence in the Public Sector
- Unlocking the potential of generative AI: Three key questions for government agencies






